An empirical research on regional development of higher vocational education based on factor analysis
-
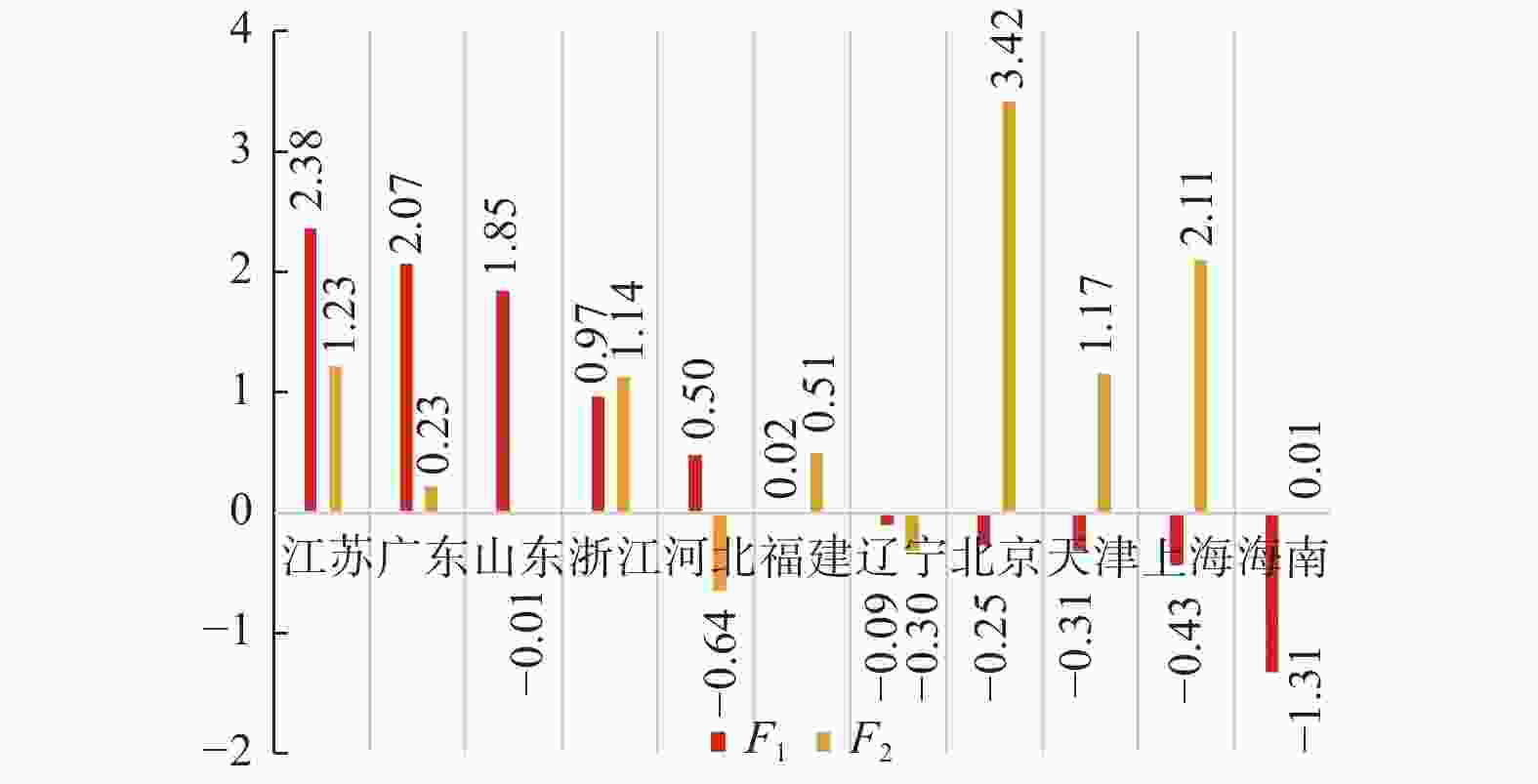
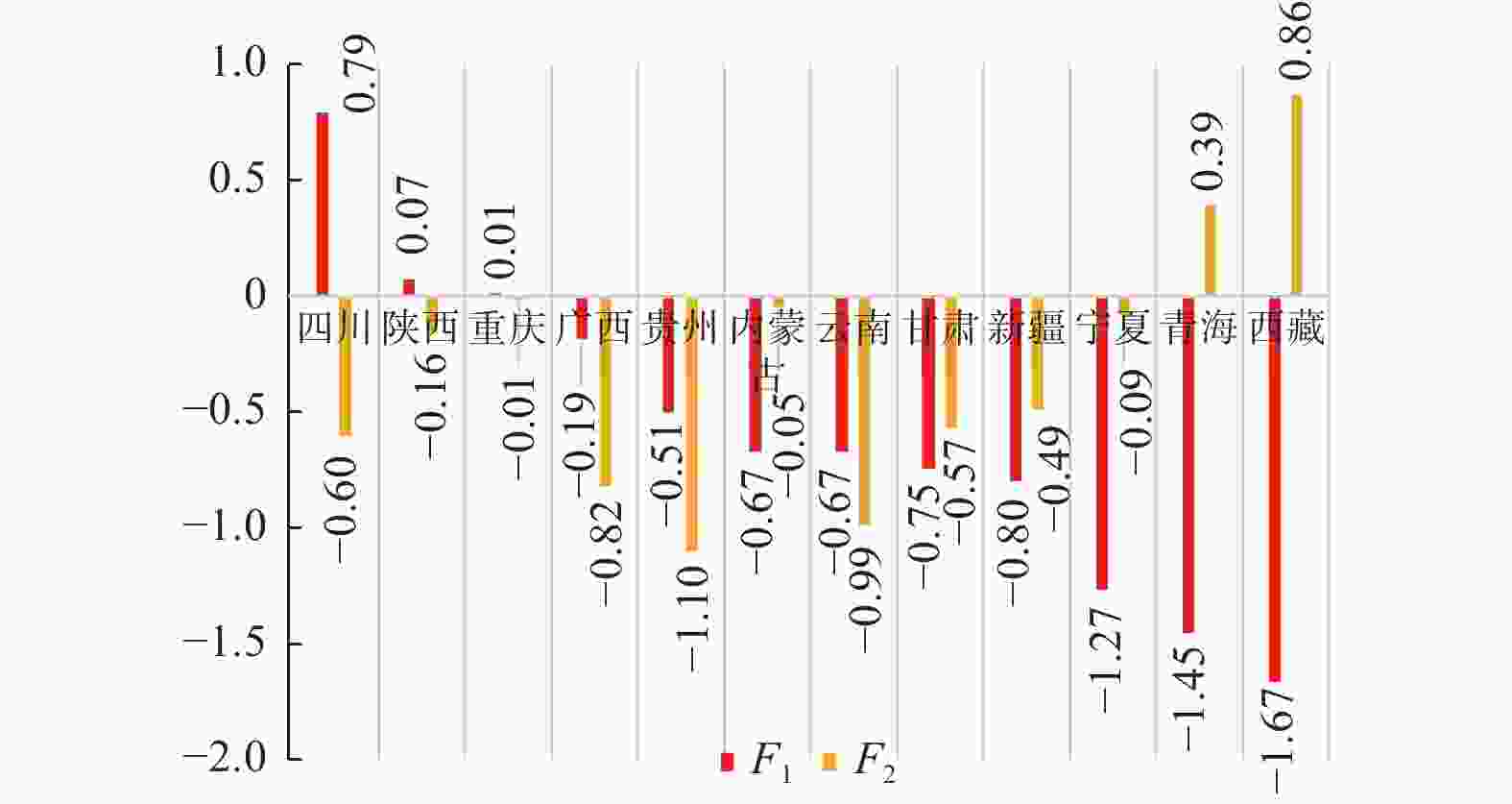
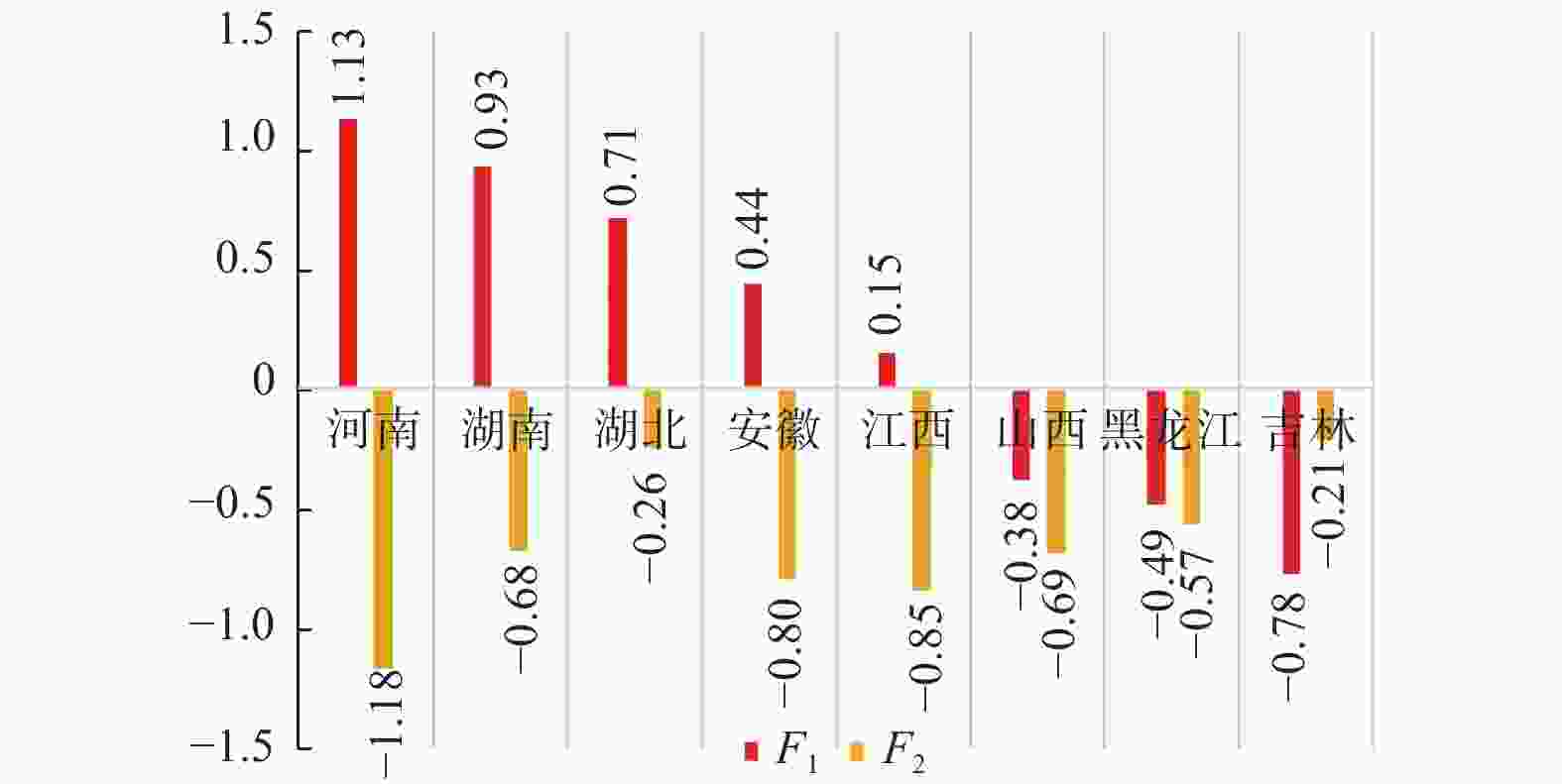
摘要: 着眼高等职业教育“扩容提质”的分类实施,运用因子分析法,采用省级截面数据,从办学规模、办学质量和经费投入3个维度对我国高等职业教育区域发展状况进行实证研究. 从全国层面看,江苏、广东和山东总体领先;从地区发展状况看,东中部总体优于西部. 然细分显示,西部要侧重夯实高职教育办学基本要素建设,东中部则要进一步强化办学绩效. 结合不同区域产业特点和我国的制度优势,从政策与策源、产教融合、区域统筹3个层面提出相应对策建议.Abstract: Focusing on “expansion and quality improvement” of higher vocational education, factor analysis method and provincial cross-section data were used to conduct empirical research on the regional development of China’s higher vocational education from three dimensions of school scale, school quality and funding input. At the national level, Jiangsu, Guangdong and Shandong are the leading provinces. At the regional level, the east and central are generally superior to the west. However, subdivision results show that the western needs to consolidate basic elements, as while as the eastern and central should further improve education performance. Based on the industrial characteristics of different regions and the institutional advantages of China, some suggestions were put forward from three aspects of government policy and financing, integration of industry and education and regional coordination.
-
Key words:
- factor analysis /
- higher vocational education /
- regional development /
- empirical research
-
表 1 评价高等职业教育发展状况的指标
Table 1. Indicators for evaluating development of higher vocational education
维度 指标 办学规模 高职院校数$ {X}_{1} $/所 招生数$ {X}_{2} $/人 在校生数$ {X}_{3} $/人 办学质量 “双高计划”建设院校数$ {X}_{4} $/所 国家示范性(骨干)高职院校数$ {X}_{5} $/所 全国职业教育技能大赛获奖数$ {X}_{6} $/个 经费投入 高职院校国家财政性教育经费投入$ {X}_{7} $/千元 生均教育经费支出$ {X}_{8} $/元 国内生产总值$ {X}_{9} $/亿元 人均国内生产总值$ {X}_{10} $/元 表 2 因子旋转矩阵
Table 2. Factor rotation matrix
指标 ${{ {F} } }_{1}$ ${{ {F} } }_{2}$ $ {X}_{1} $ 0.918 − 0.299 $ {X}_{2} $ 0.916 − 0.297 $ {X}_{3} $ 0.944 − 0.258 $ {X}_{4} $ 0.903 0.151 $ {X}_{5} $ 0.925 0.164 $ {X}_{6} $ 0.846 0.028 $ {X}_{7} $ 0.957 − 0.079 $ {X}_{8} $ − 0.369 0.779 $ {X}_{9} $ 0.946 0.188 $ {X}_{10} $ 0.323 0.879 -
[1] 中华人民共和国中央人民政府. 中共中央关于制定国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和二〇三五年远景目标的建议[EB/OL]. (2020-11-03)[2021-05-24]. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2020-11/03/content_5556991.htm. [2] 王兵, 赵惠莉. 省域统筹视角下江苏高等职业教育发展研究[J] . 江苏高教,2016(3):22 − 26. [3] 宋韬. 山西高等职业教育发展: 地区差异与分析[J] . 职业技术教育,2014(15):52 − 54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3219.2014.15.026 [4] 郑雁. 浙江省高等职业教育区域均衡发展实证研究[J] . 职业技术教育,2015(12):67 − 72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3219.2015.12.026 [5] 王辉晖, 田雪莹. 高等职业教育经费投入的地区差异现状及成因研究[J] . 职业技术教育,2017, 38(33):52 − 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3219.2017.33.016 [6] 濮筠, 崔玉平. 我国高职教育经费投入的空间关联性和空间影响因素[J] . 现代教育管理,2017(2):85 − 90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5485.2017.02.014 [7] 万伟平, 聂劲松, 樊孝凯. 省域内高等职业教育生均经费基尼系数研究: 基于广东省公办高职院校的统计数据[J] . 当代教育论坛,2021(5):116 − 124. [8] 房巍, 陈衍. 我国省域高等职业教育存量规模竞争力比较分析[J] . 江苏高教,2015(1):142 − 143. [9] 王丹, 邵汝军. 江苏省高等职业教育发展区域差异及成因分析[J] . 职业技术教育,2013(7):47 − 54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3219.2013.07.010 [10] 河南省教育厅. 河南省教育厅关于2021年申报设置高等职业学校的公示[EB/OL]. (2021-01-15) [2021-05-24]. http://jyt.henan.gov.cn/2021/01-15/2079941.html. [11] 河南省教育厅. 2021年河南省高考人数统计[EB/OL]. (2021-06-01)[2021-07-01]. http://jyt.henan.gov.cn/. [12] 中华人民共和国教育部. 全国高等学校名单[EB/OL]. (2020-07-09)[2021-05-24]. http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_xxgk/s5743/s5744/202007/t20200709_470937.html. [13] 蔡群青, 袁振国, 贺文凯. 西部高等教育全面振兴的现实困境、逻辑要义与破解理路[J] . 大学教育科学,2021(1):26 − 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0717.2021.01.03 [14] 中华人民共和国教育部. 教育部、国家统计局、财政部关于2019年全国教育经费执行情况统计公告[EB/OL]. (2020-10-28)[2021-05-24]. http://www.moe.gov.cn/srcsite/A05/s3040/202011/t20201103_497961.html. [15] 中华人民共和国教育部. 教育部: 到“十四五”末, 高等教育毛入学率力争提升到60% [EB/OL]. (2021-03-31)[2021-05-24]. http://www.moe.gov.cn/jyb_xwfb/moe_2082/2021/2021_zl25/bd/202104/t20210401_523936.html. -






 下载:
下载: