First-principles study on adsorption of toxic gases by two-dimensional AlC nanosheets
-
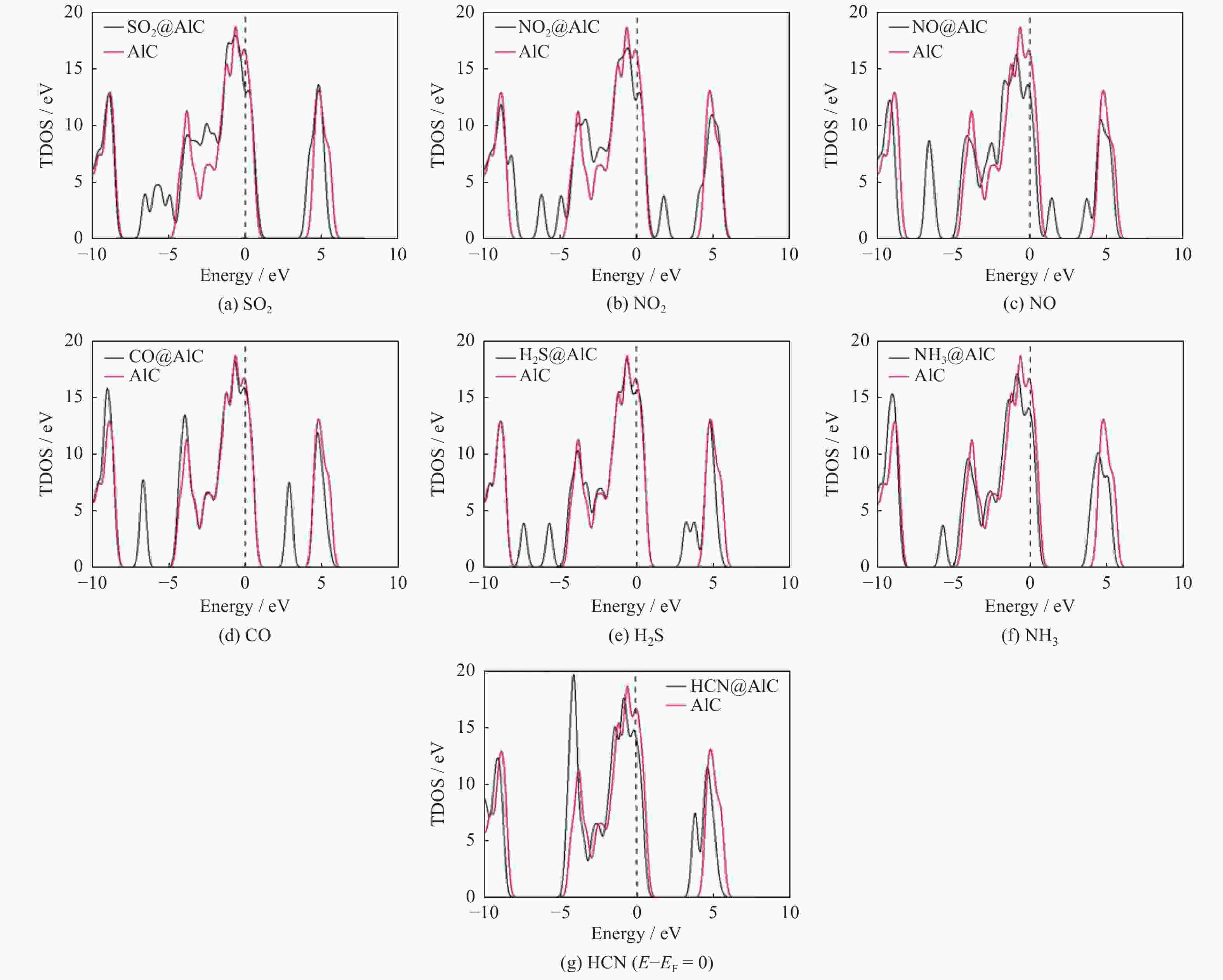
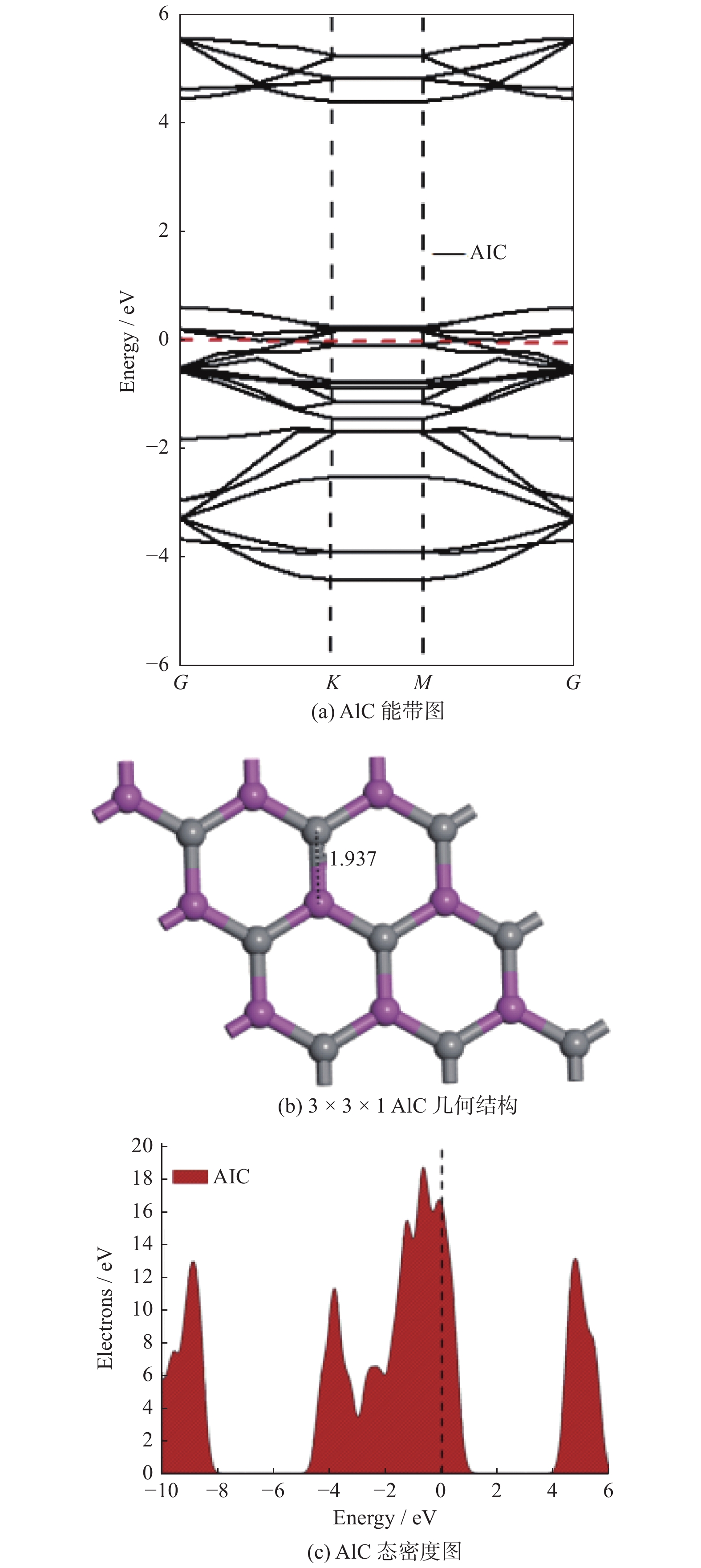
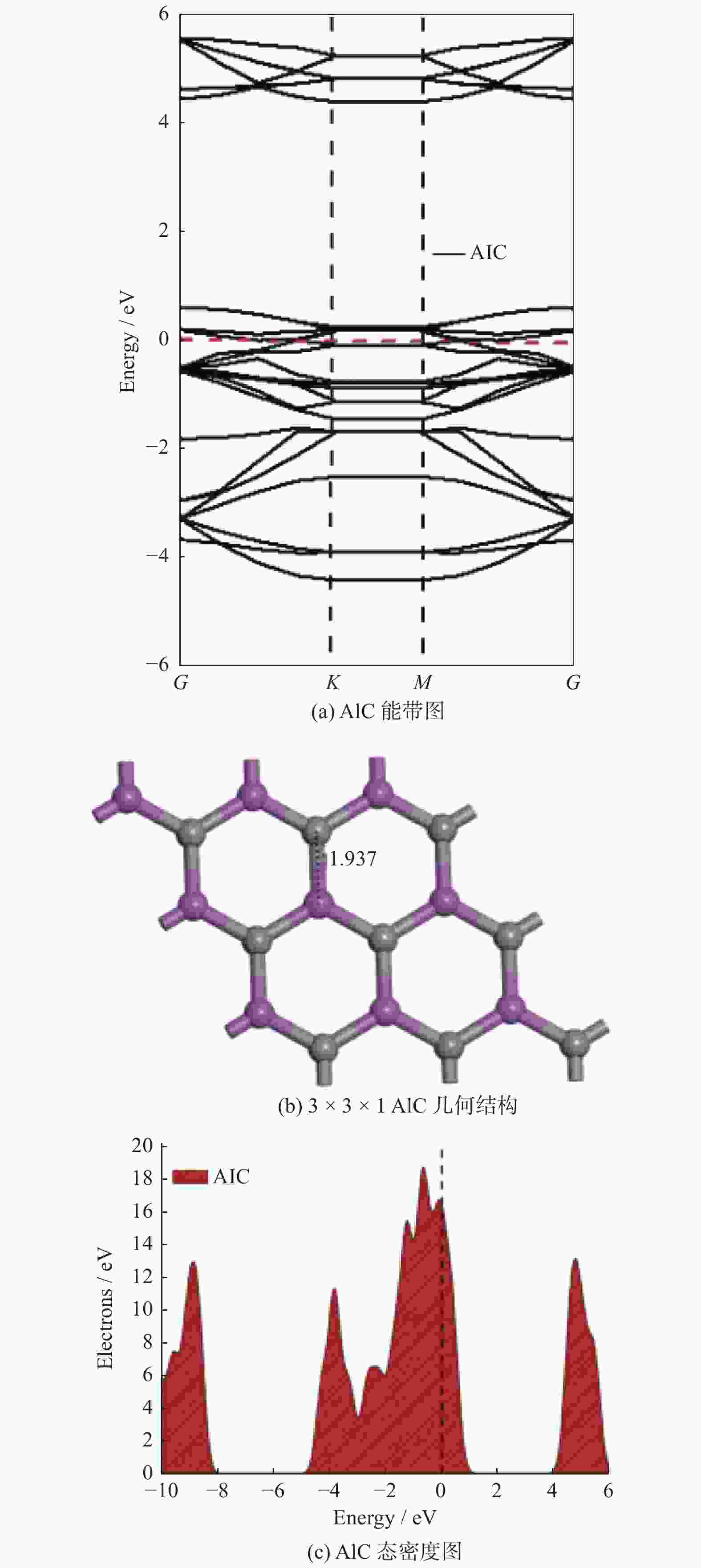
摘要: 基于密度泛函理论研究有毒气体(SO2、NO2、NO、CO、H2S、NH3和HCN)在二维碳化铝(AlC)纳米片上的吸附性能,并进一步计算各种吸附体系的电子性质以及功函数. 计算结果表明:吸附气体后AlC单层并未改变其金属性,吸附能的变化区间为[−3.11,−0.09] eV,除CO和HCN外,其他气体均可以通过化学吸附被稳定地吸附在AlC单层上;电荷分析表明,被吸附后,NO2、NO和SO2分别从AlC单层上得到0.473|e|,0.317|e|和0.249|e|;电荷密度差分图也进一步说明AlC单层与NO2、NO和SO2这3种有毒气体间存在较强的相互作用,并且SO2、NO2和NO在吸附后,体系的功函数明显增加. 基于AlC单层吸附有毒气体后能量、电子性质和功函数的响应,AlC单层有望成为SO2、NO2和NO等有毒气体的检测材料或传感材料.Abstract: Based on density functional theory, the adsorption performances of toxic gases (SO2, NO2, NO, CO, H2S, NH3, HCN) on two-dimensional AlC nanosheets were studied, and the electronic properties and work functions of various adsorption systems were further calculated. The calculated results show that the metallic properties of the AlC monolayer does not change after gas adsorption , and the variation range of adsorption energy was [−3.11, −0.09] eV. All gases except CO and HCN can be stably adsorbed on the AlC monolayer by chemical adsorption. Charge analysis shows that after adsorption, NO2, NO and SO2 can obtain 0.473|e|, 0.317|e| and 0.249|e| from the AlC monolayer, respectively. The charge density difference diagram also shows that there are strong interaction of electrons from the AlC monolayer with the three toxic gases of NO2, NO and SO2, and the work function of the system increase significantly after NO2, NO and SO2 are adsorbed. Based on the energy, electronic properties and work function response of the AlC monolayer after adsorbing toxic gases, the AlC monolayer will be expected to become a detection material or sensing material for toxic gases such as SO2, NO2, and NO.
-
Key words:
- AlC monolayer /
- toxic gases /
- sensor /
- work function /
- first-principles calculation
-
表 1 吸附有毒气体的能带结构参数、吸附能、转移电子数、费米能量和功函数
Table 1. Band structure parameters, adsorption energy, number of transferred electrons, Fermi energy and work function for adsorbing toxic gases
体系 导电性 距离/Å 吸附能Ead /eV 转移电子数Q /e− 费米能量EF /eV 功函数Φ/eV 功函数偏差ΔΦ AlC − 4.96 4.76 0 NO2 Metallic 1.413 − 3.11 − 0.473 − 5.25 5.17 0.41 NO Metallic 1.344 − 2.92 − 0.317 − 5.11 5.03 0.27 SO2 Metallic 1.753 − 2.81 − 0.249 − 5.09 5.00 0.24 CO Metallic 3.431 − 0.13 − 0.003 − 4.96 4.79 0.03 H2S Metallic 2.607 − 0.50 0.085 − 4.64 4.46 − 0.30 NH3 Metallic 2.128 − 0.99 0.117 − 4.46 4.25 − 0.51 HCN Metallic 3.489 − 0.09 0.004 − 4.92 4.76 0 -
[1] KAMPA M, CASTANAS E. Human health effects of air pollution[J] . Environmental Pollution,2008,151(2):362 − 367. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2007.06.012 [2] JIA X T, ZHANG H, ZHANG Z M. First-principles investigation of vacancy-defected graphene and Mn-doped graphene towards adsorption of H2S[J] . Superlattices and Microstructures,2019,134:9. [3] MA S X, SU L C, JIN L, et al. A first-principles insight into Pd-doped MoSe2 monolayer: A toxic gas scavenger[J] . Physics Letters A,2019,383(30):9. [4] QIN Y X, ZHANG Z. Co-modulation of graphene by N hetero-doping & vacancy defects and the effect on NO2 adsorption and sensing: First-principles study[J] . Physica E-Low-Dimensional Systems & Nanostructures,2020,116:7. [5] BASHARNAVAZ H, HABIBI-YANGJEH A, KAMALI S H. A first-principle investigation of NO2 adsorption behavior on Co, Rh, and Ir-embedded graphitic carbon nitride: Looking for highly sensitive gas sensor[J] . Physics Letters A,2020,384(2):8. [6] YANG L M, TANG Y H, YAN D F, et al. Polyaniline-reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanosheets with nearly vertical orientation anchoring palladium nanoparticles for highly active and stable electrocatalysis[J] . Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(1):169 − 176. [7] ALI M, TIT N. Adsorption of NO and NO2 molecules on defected-graphene and ozone-treated graphene: First-principles analysis[J] . Surface Science,2019,684:28 − 36. doi: 10.1016/j.susc.2019.01.012 [8] BASHARNAVAZ H, HABIBI-YANGJEH A, KAMALI SH. Fe, Ru, and Os-embedded graphitic carbon nitride as a promising candidate for NO gas sensor: A first-principles investigation[J] . Materials Chemistry and Physics,2019,231:264 − 271. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.04.003 [9] CUI H P, ZHENG K, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Superior selectivity and sensitivity of C3N sensor in probing toxic gases NO2 and SO2[J] . IEEE Electron Device Letters,2018,39(2):284 − 287. doi: 10.1109/LED.2017.2787788 [10] NIU F F, YANG D G, CAI M, et al. A first principles study of blue phosphorene as a superior media for gas sensor[C]//19th International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology,New York, 2018: 1149−1152. [11] MAO Y L, LONG L B, YUAN J M, et al. Toxic gases molecules (NH3, SO2 and NO2) adsorption on GeSe monolayer with point defects engineering[J] . Chemical Physics Letters,2018,706(1):501 − 508. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2018.06.061 [12] RAD A S, ESFAHANIAN M, MALEKI S, et al. Application of carbon nanostructures toward SO2 and SO3 adsorption: a comparison between pristine graphene and N-doped graphene by DFT calculations[J] . Journal of Sulfur Chemistry,2016,37(2):176 − 188. doi: 10.1080/17415993.2015.1116536 [13] ROONDHE B, PATEL K, JHA P K. Two-dimensional metal carbide comrade for tracing CO and CO2[J] . Applied Surface Science,2019,496:14. [14] KRESSE G, FURTHMÜLLER J. Efficient iterative schemes for Ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set[J] . Physical Review. B, Condensed Matter,1996,54:11169 − 11186. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11169 [15] KRESSE G, JOUBERT D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method[J] . Physical Review,1999,59(3):1758 − 1775. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.59.1758 [16] GRIMME S. Semiempirical GGA-type density functional constructed with a long-range dispersion correction[J] . Journal of computational chemistry,2006,27(15):1787 − 1799. [17] GRIMME S, ANTONY J, EHRLICH S, et al. A consistent and accurate ab initio parametrization of density functional dispersion correction (DFT-D) for the 94 elements H-Pu[J] . Journal of Chemical Physics,2010,132(15):154104. doi: 10.1063/1.3382344 [18] PATEL K, BARAIYA B A, SOM N N, et al. Investigating hydrogen evolution reaction properties of a new honeycomb 2D AlC[J] . International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2020,45(37):18602 − 18611. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.10.131 [19] POHLE R, TAWIL A, DAVYDOVSKAYA P, et al. Metal organic frameworks as promising high surface area material for work function gas sensors[J] . Procedia Engineering,2011,25:108 − 111. [20] OUYANG T H, QIAN Z, HAO X P, et al. Effect of defects on adsorption characteristics of AlN monolayer towards SO2 and NO2: Ab initio exposure[J] . Applied Surface Science,2018,462:615 − 622. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.08.073 -





 下载:
下载: