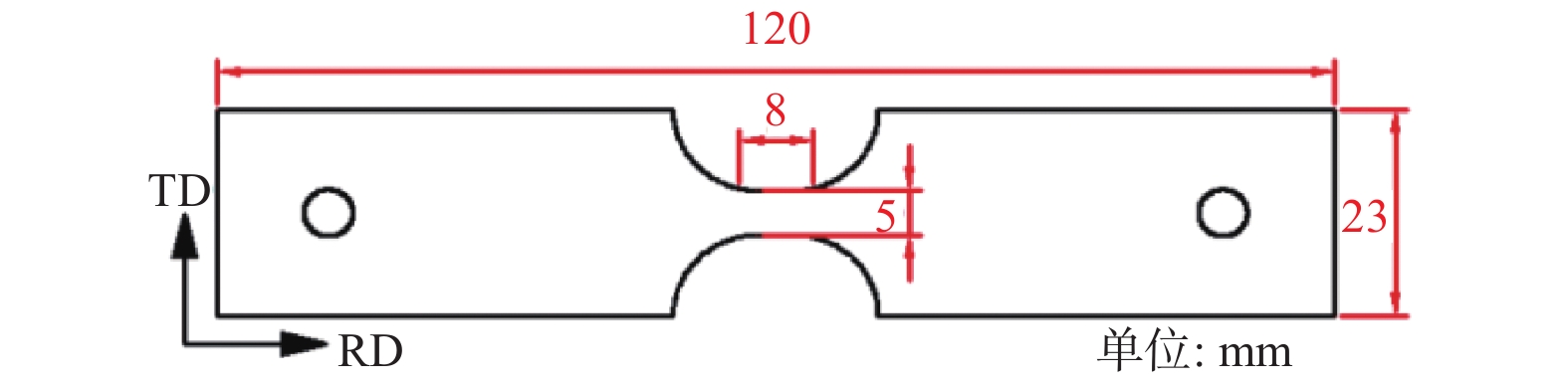
Effect of quenching and partitioning process on texture and properties of high strength Q&P steel
-
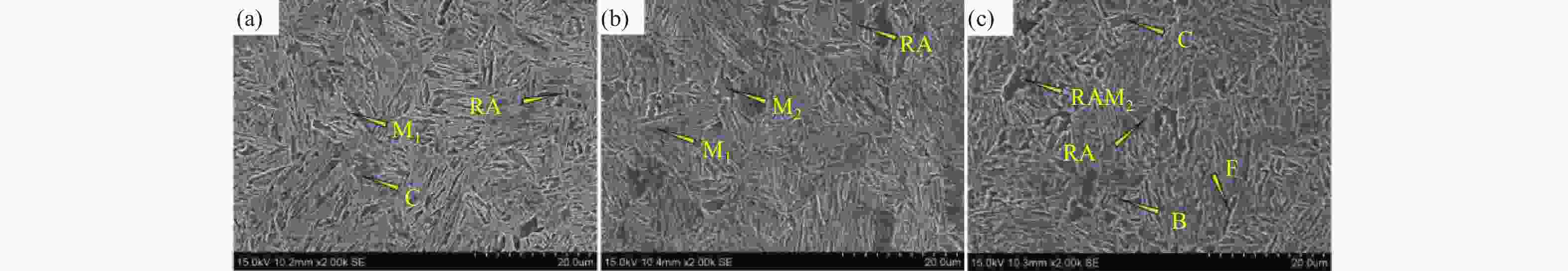
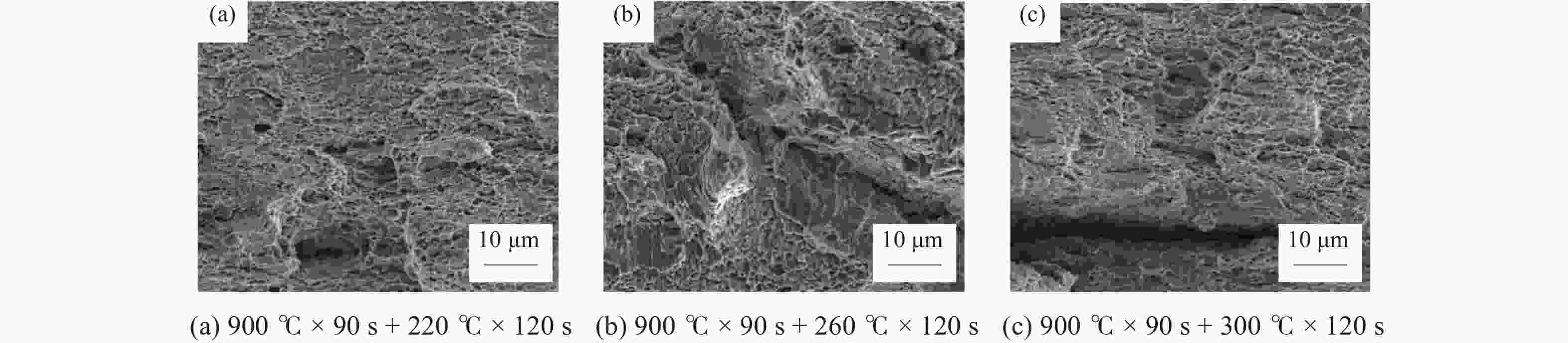
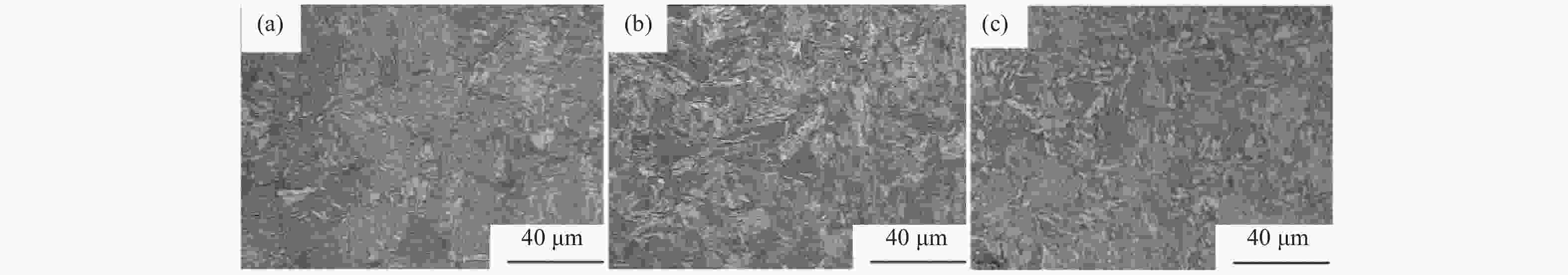
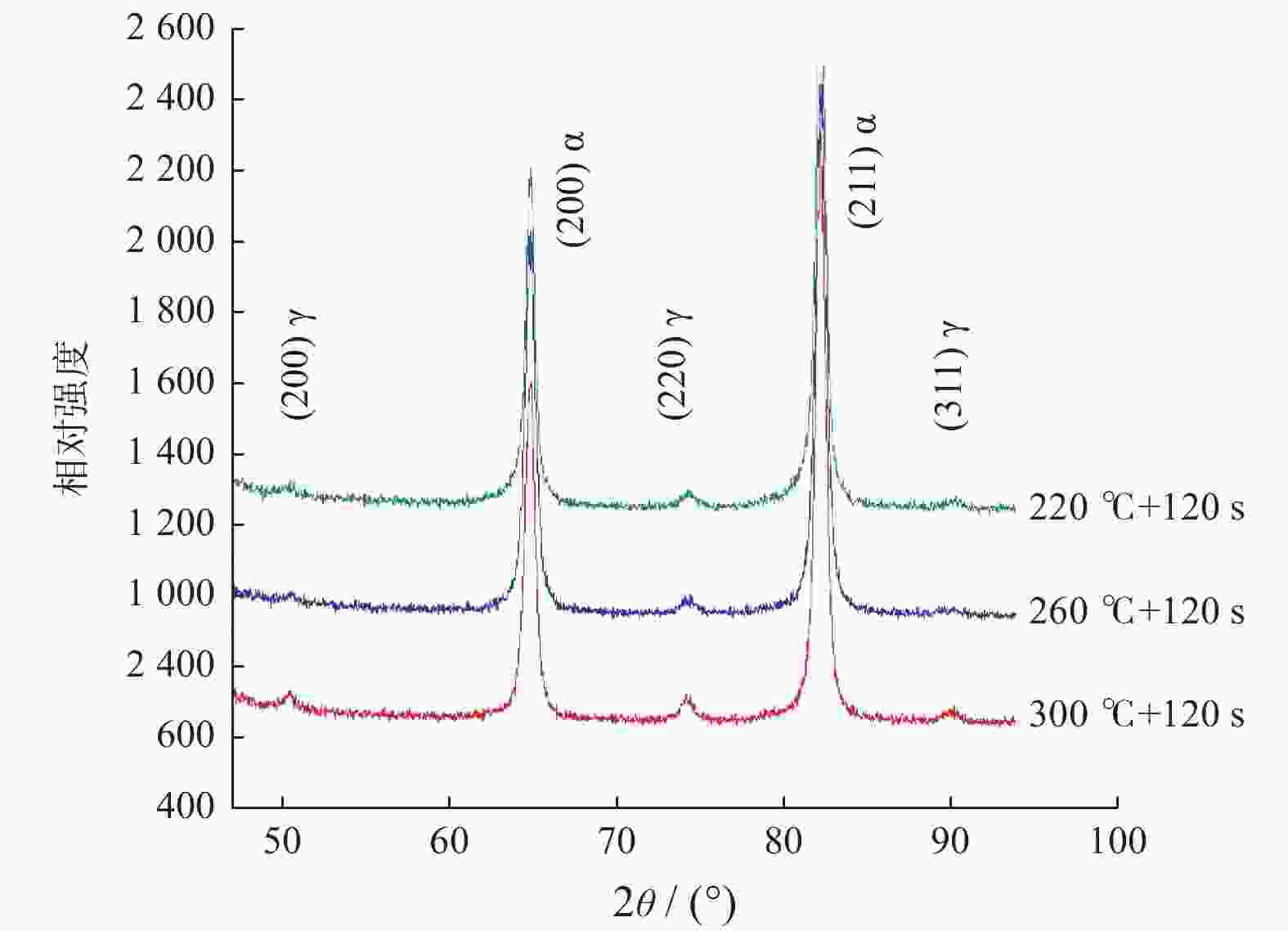
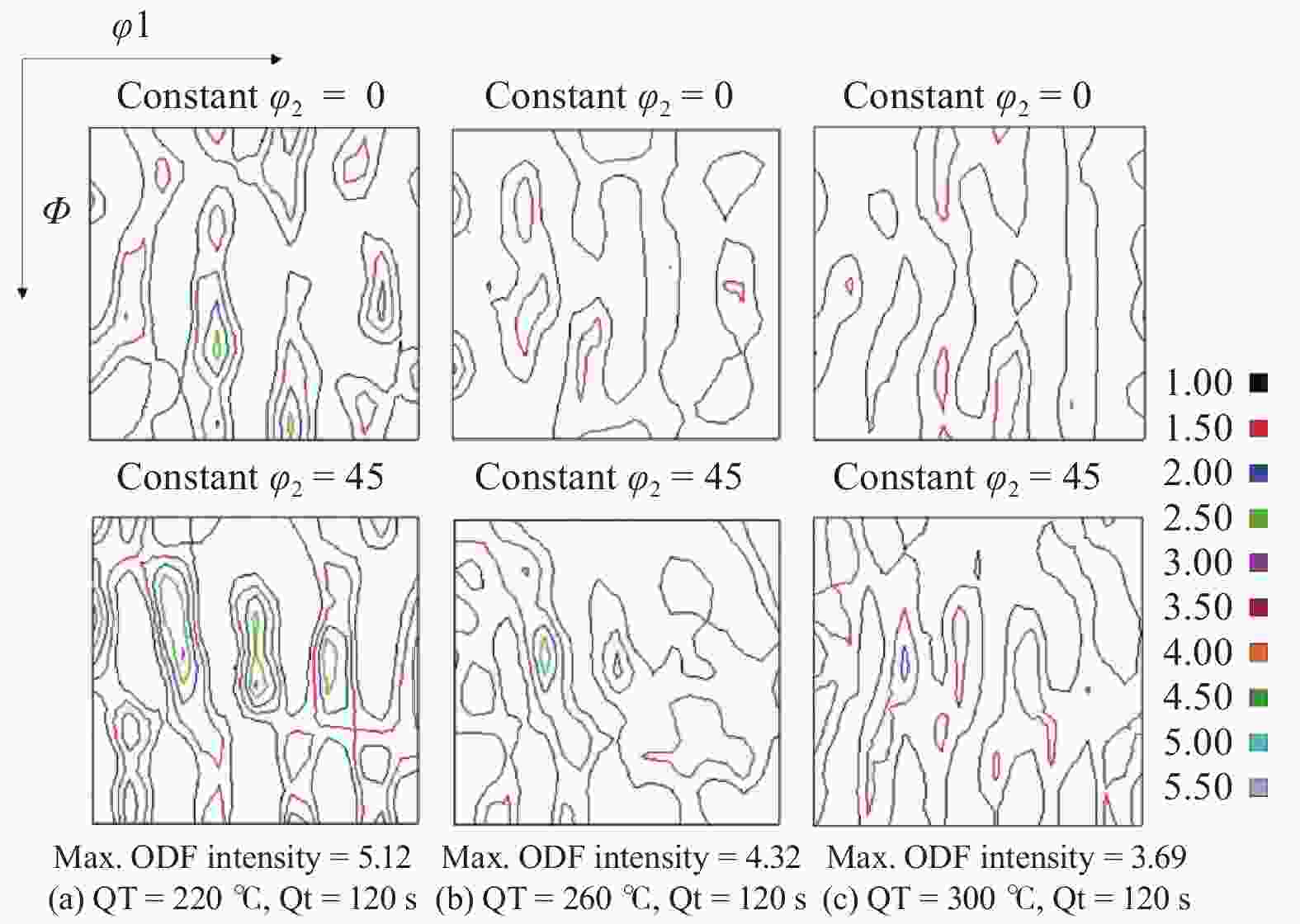
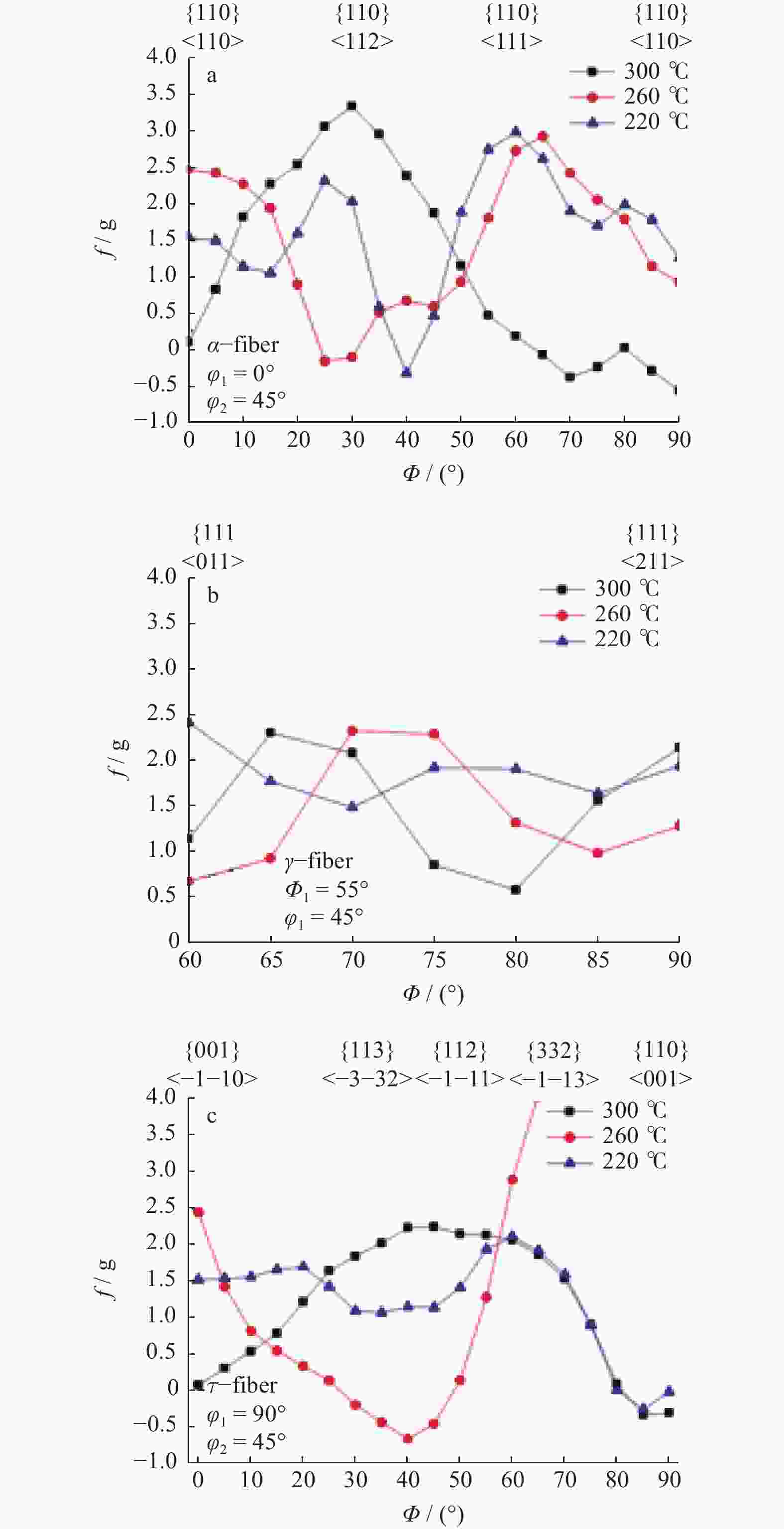
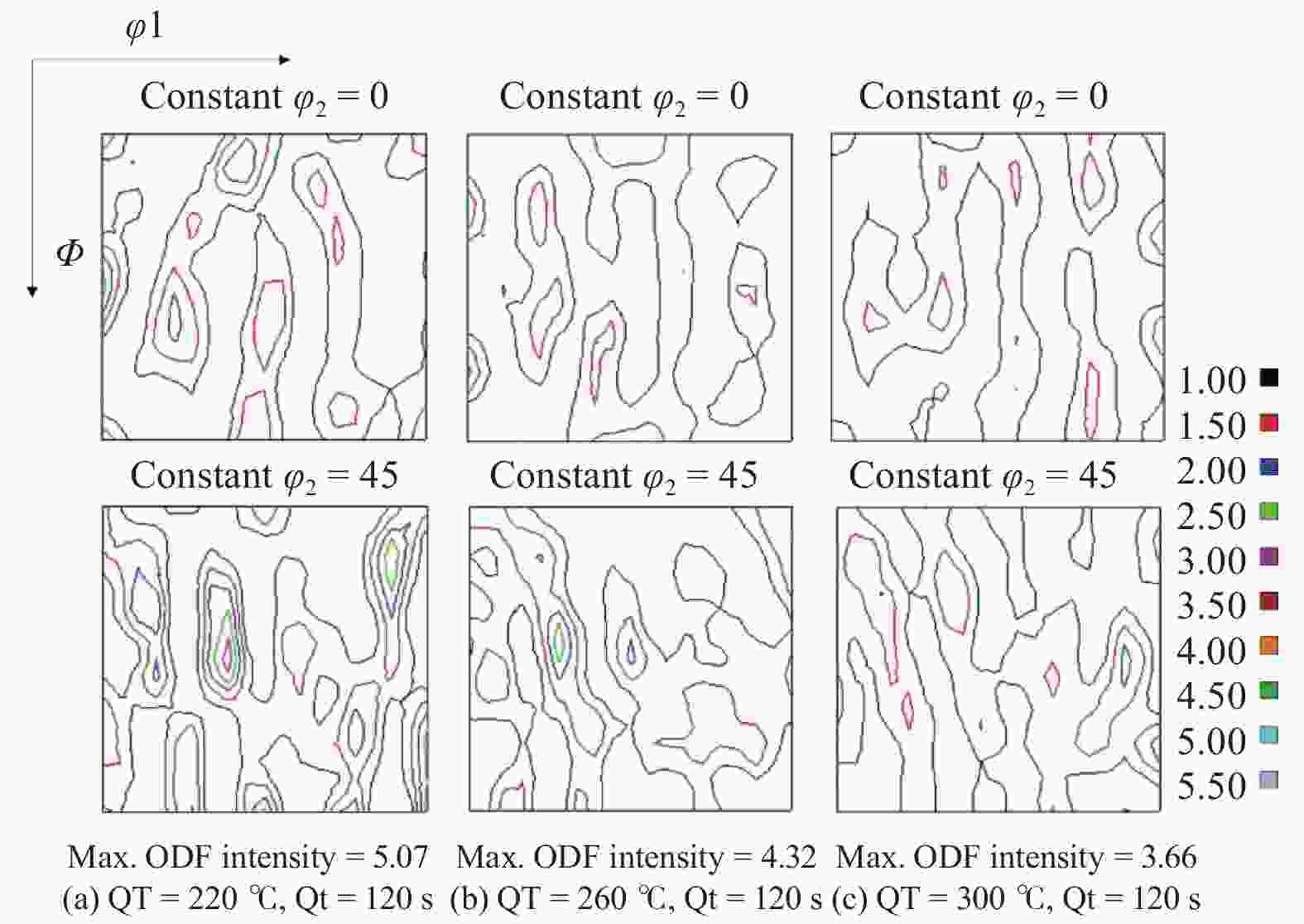
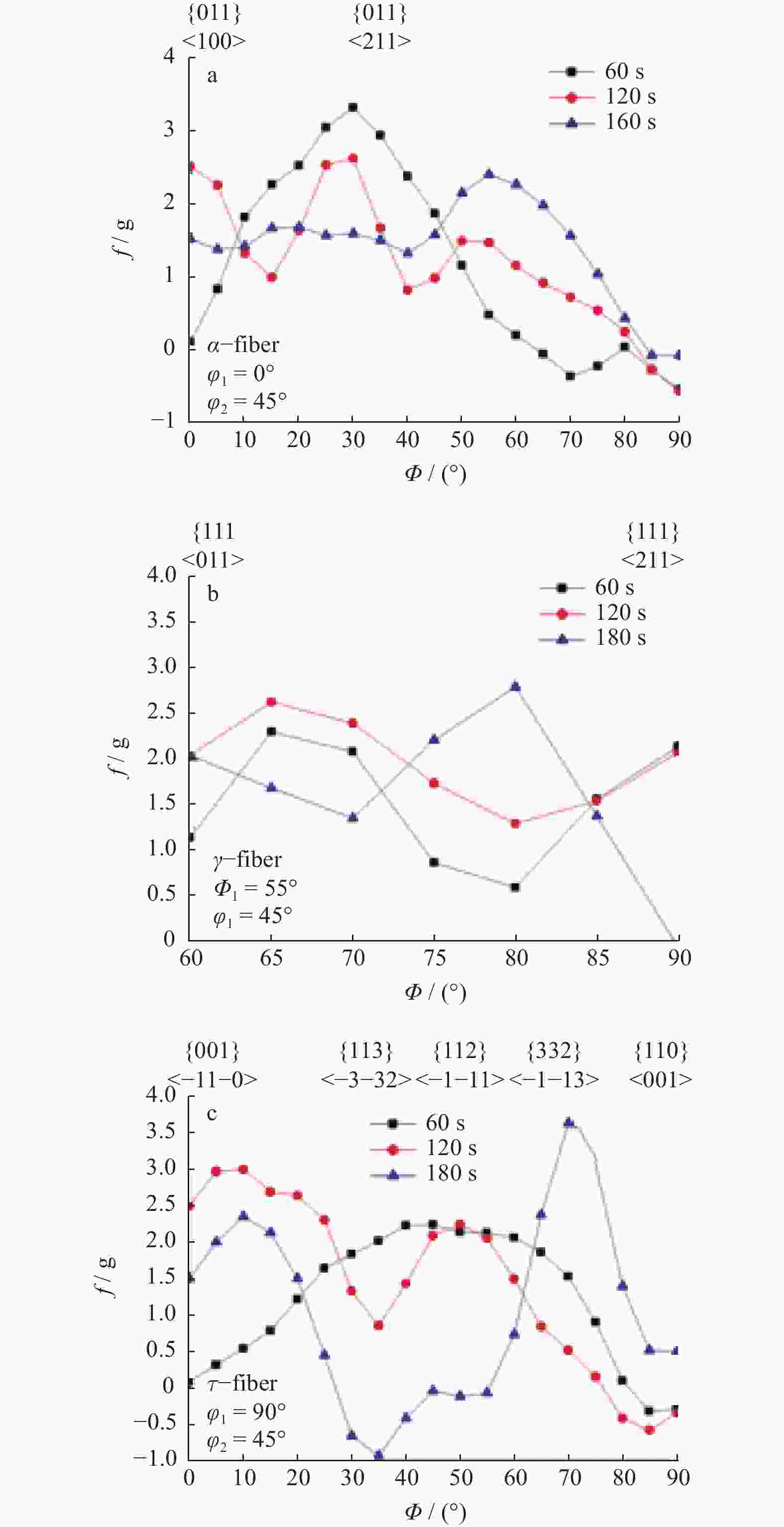
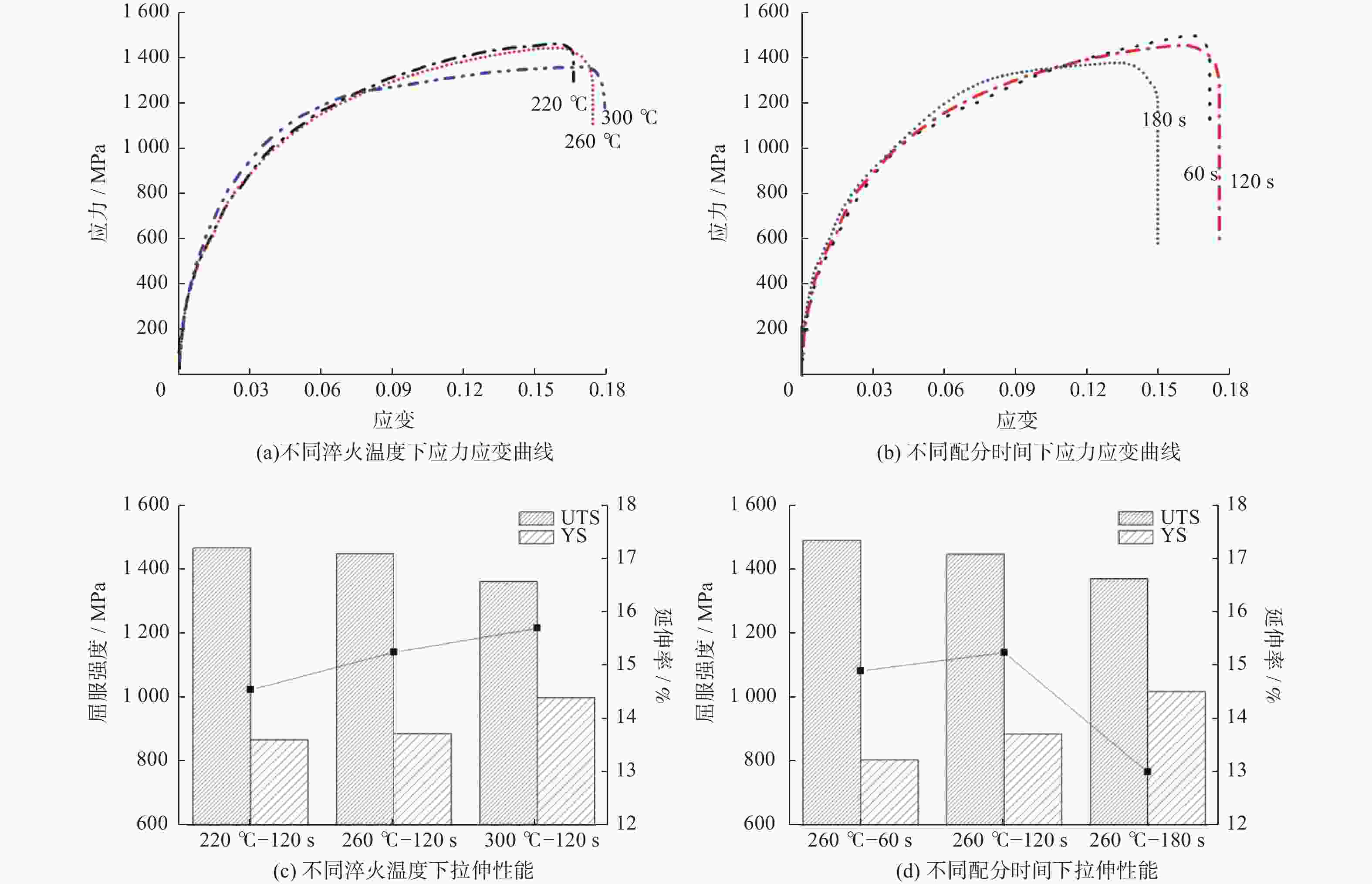
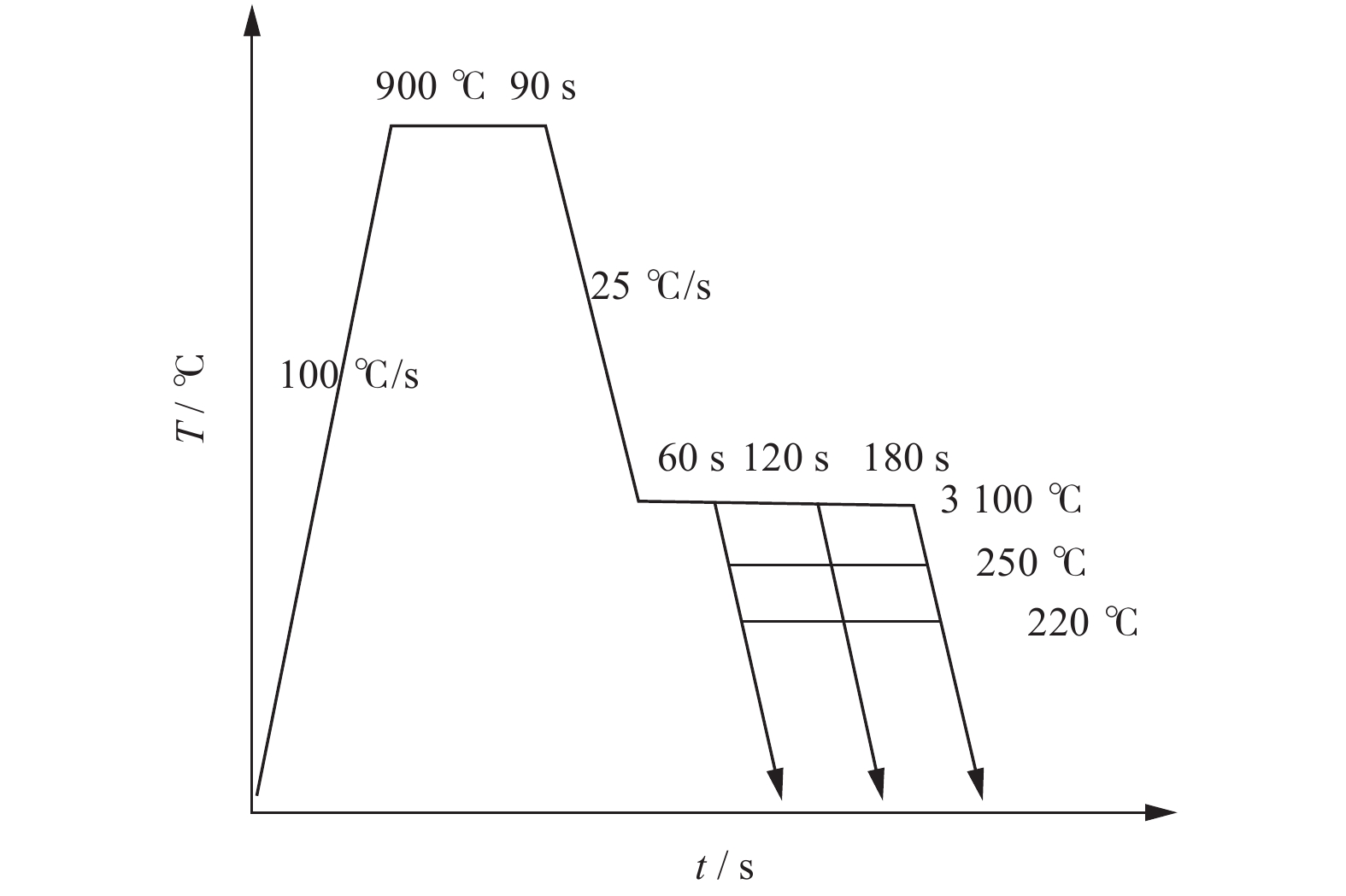
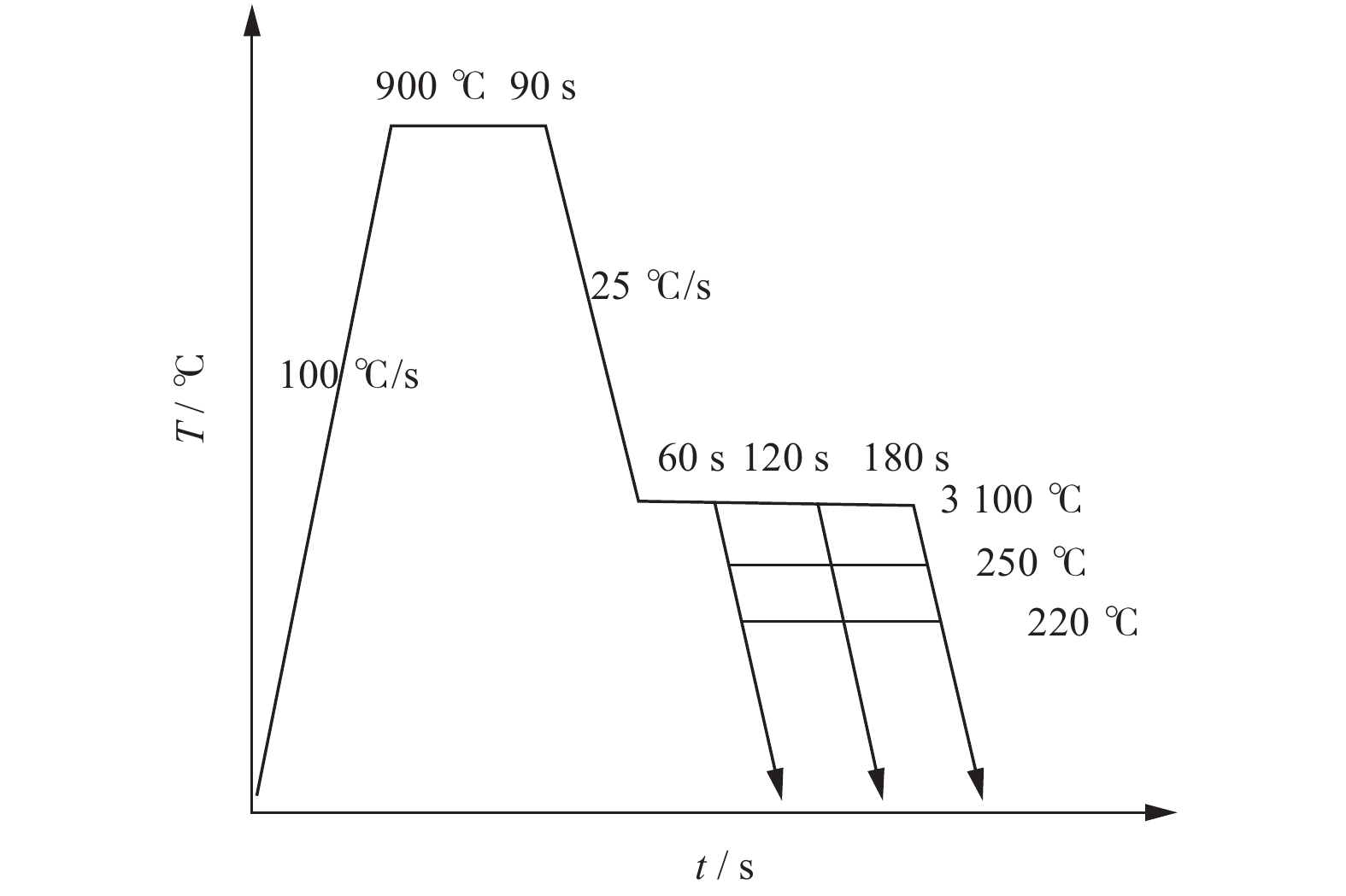
摘要: 对试验用淬火配分(Quenching and Partitioning,Q&P)钢在一步淬火配分工艺中不同淬火温度(220 、260 、300 ℃)和淬火时间(60 、120 、180 s)下组织、织构、力学性能及拉伸断口特征进行研究. 结果表明:试验用Q&P钢在一步淬火配分中获得的最大残余奥氏体体积分数为7.12%;随着淬火温度升高,板条马氏体的宽度增大;随着淬火温度和配分时间升高,织构的最大强度逐渐降低,抗拉强度逐渐减少;屈服强度和延伸率呈相反的变化趋势.Abstract: The microstructure, texture, mechanical properties and tensile fracture characteristics of quenching and partitioning (Q&P) steel were studied at different quenching temperatures (220, 260, 300 ℃) and quenching times (60 , 120 , 180 s) in one-step Q&P process. The results show that the maximum volume fraction of residual austenite(RA)obtained in one-step Q&P was 7.12%. With the increase of quenching temperature, the width of lath martensite increased. With the increase of quenching temperature and partition time, the maximum strength of the texture decreased, so did the tensile strength, while the yield strength and elongation showed opposite trends.
-
表 1 试验用Q&P钢的主要成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of test Q&P steel
元素 C Si Mn Al Fe 质量分数/% 0.23 1.55 1.92 0.04 余量 表 2 试样中残余奥氏体体积含量及其含碳量
Table 2. Volume content and carbon content of retained austenite in samples
试样 RA/% RA中C含量/% 300 ℃/s + 120 s 6.82 1.20 260 ℃/s + 120 s 7.12 1.26 220 ℃/s + 120 s 4.28 1.29 -
[1] LEE S J, LEE S, DE COOMAN B C. Mn partitioning during the intercritical annealing of ultrafine-grained 6% Mn transformation-induced plasticity steel[J] . Scripta Materialia,2011,64(7):649 − 652. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.12.012 [2] ISHIDA K. Effect of alloying elements on the critical driving force of martensitic transformation in iron alloys[J] . Scripta Metallurgica,1977,11(3):237 − 242. [3] JIMENEZ-MELERO E, VAN DIJK N H, ZHAO L, et al. D9 in situ observation of the martensitic transformation of individual grains using a high-energy X-ray microbeam[J] . Powder Diffraction,2007,22(2):180. [4] YANG Y G, MI Z L, XU M, et al. Impact of intercritical annealing temperature and strain state on mechanical stability of retained austenite in medium Mn steel[J] . Materials Science and Engineering:A,2018,725(14):389 − 397. [5] SPEER J, MATLOCK D K, DE COOMAN B C, et al. Carbon partitioning into austenite after martensite transformation[J] . Acta Materialia,2003,51(9):2611 − 2622. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(03)00059-4 [6] SANTOFIMIA M J, ZHAO L, SIETSMA J. Microstructural evolution of a low-carbon steel during application of quenching and partitioning heat treatments after partial austenitization[J] . Metallurgical & Materials Transactions A,2009,40(1):46 − 57. [7] ZAEFFERER S, OHLERT J, BLECK W. A study of microstructure, transformation mechanisms and correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties of a low alloyed TRIP steel[J] . Acta-Materialia,2004,52(9):2765 − 2778. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.02.044 [8] PENG F, XU Y B, G X L, et al. Microstructure characterization and mechanical behavior analysis in a high strength steel with different proportions of constituent phases[J] . Materials Science and Engineering:A,2018,734:398 − 407. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.08.018 [9] CLARKE A J, SPEER J G, MATLOCK D K, et al. Influence of carbon partitioning kinetics on final austenite fraction during quenching and partitioning[J] . Scripta Materialia,2010,61(2):149 − 152. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2009.03.021 [10] DE MOOR E, LACROIX S, CLARKE A J, et al. Effect of retained austenite stabilized via quench and partitioning on the strain hardening of martensitic steels[J] . Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A:Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science,2008,39(11):2586 − 2595. [11] ZHAO Q, LIU Z Y, HUANG T T, et al. Enhanced fracture toughness in an annealed Al-Cu-Mg alloy by increasing Goss/Brass texture ratio[J] . Materials Characterization,2016,119(7):47 − 54. [12] DE KNIJF D, NGUYEN-MINH T, PETROV R H, et al. Orientation dependence of the martensite transformation in a quenched and partitioned steel subjected to uniaxial tension[J] . Journal of Applied Crystallography,2014,47(4):1261 − 1266. doi: 10.1107/S1600576714011959 [13] TAN X D, XU Y B, YANG X L, et al. Microstructure-properties relationship in a one-step quenched and partitioned steel[J] . Materials Science & Engineering A,2014,589(34):101 − 111. [14] LIU B G, LI W, LU X W, et al. The effect of retained austenite stability on impact-abrasion wear resistance in carbide-free bainitic steels[J] . Wear,2019,428-429(8):127 − 136. [15] DAN W J, LIN Z Q, LI S H, et al. Study on the mixture strain hardening of multi-phase steels[J] . Materials Science & Engineering A,2012,552(34):1 − 8. [16] YANG J L, HUANG F, GUO Z H, et al. Effect of retained austenite on the hydrogen embrittlement of a medium carbon quenching and partitioning steel with refined microstructure[J] . Materials Science & Engineering A,2016,665(4):76 − 85. -





 下载:
下载: