Finite Element Analysis of Dynamic Behavior of Microbubble with Different Wall Shapes
-
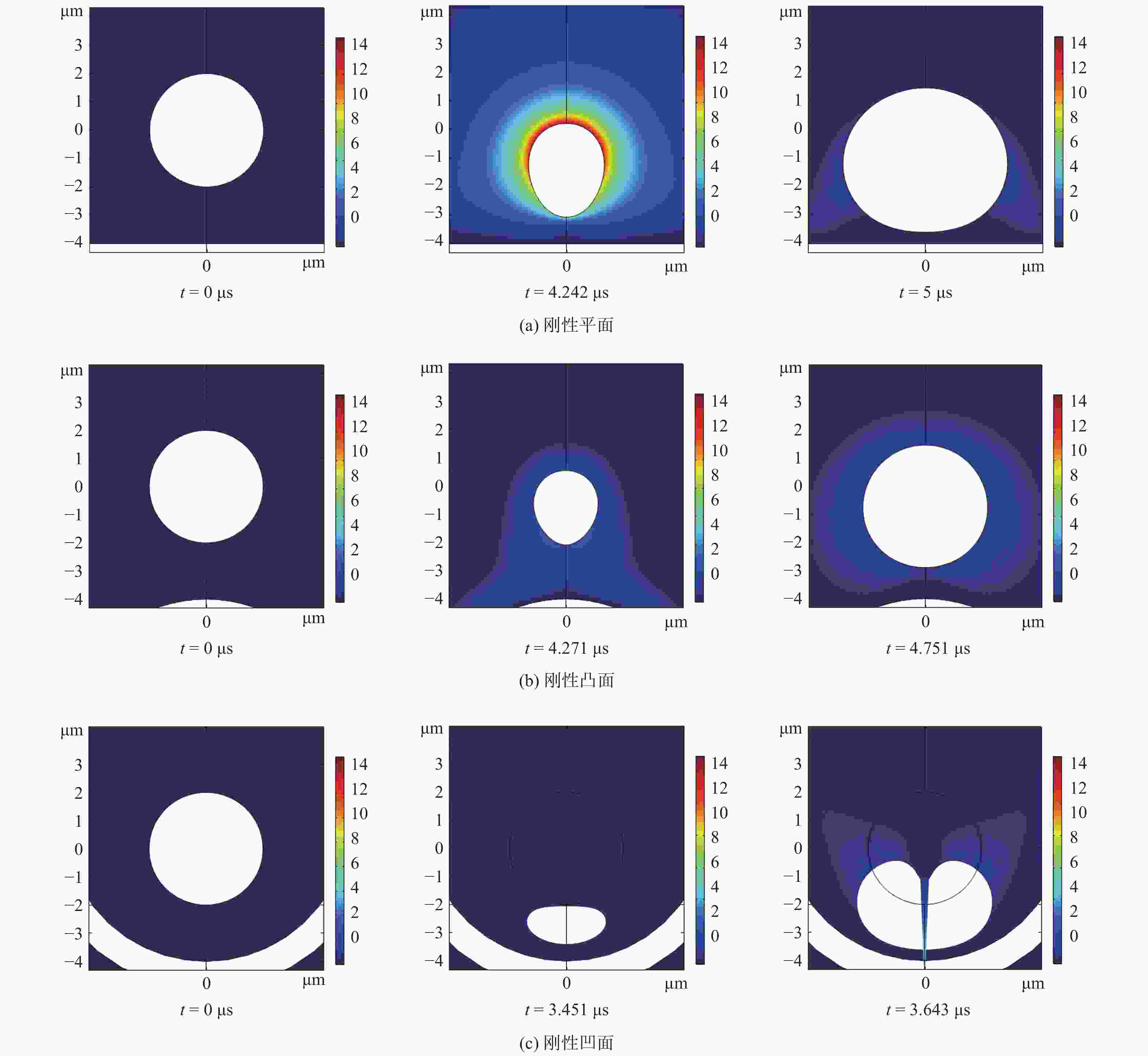
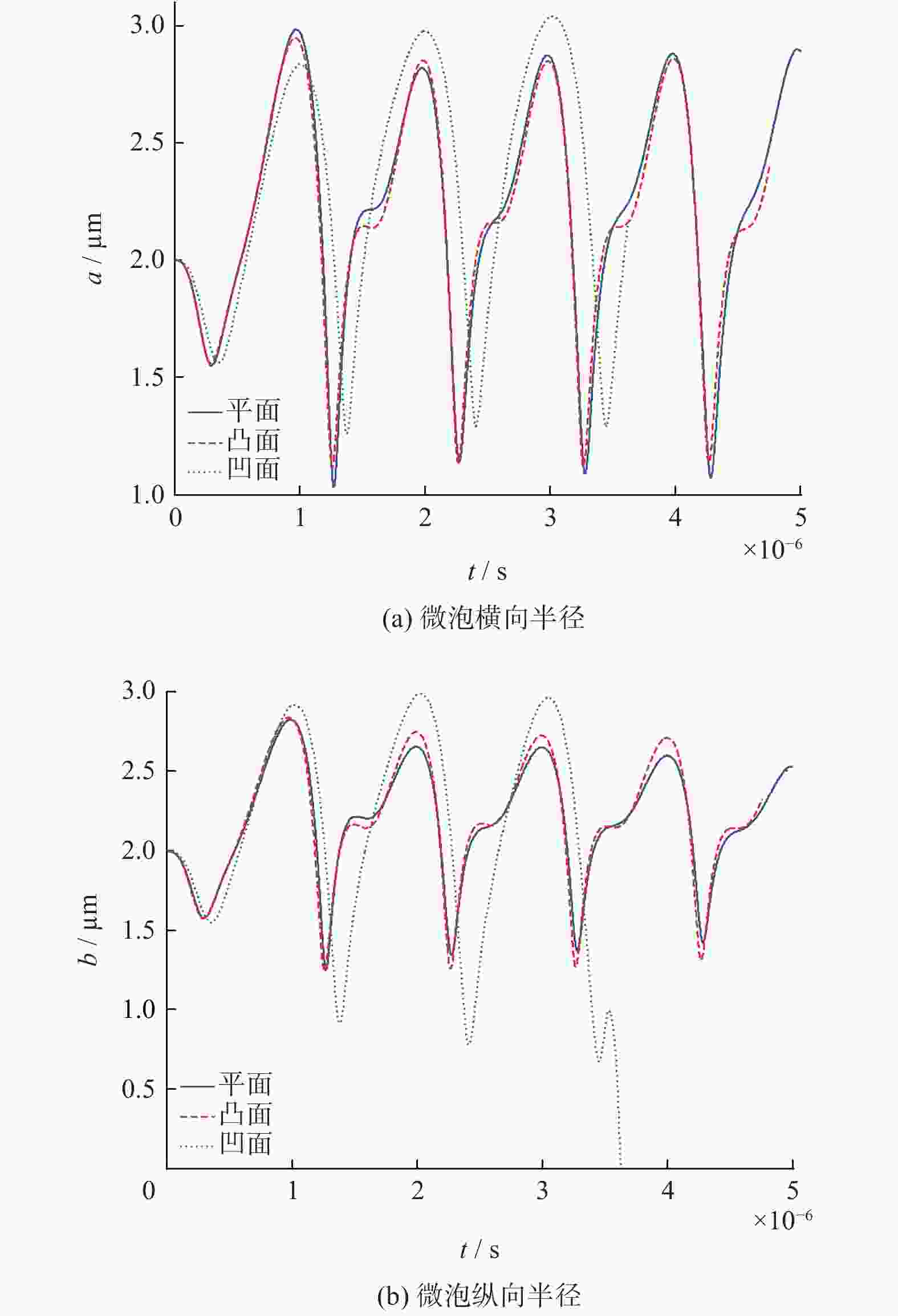
摘要: 为研究刚性平面、凸面和凹面附近的微泡动力学行为的差异,建立超声激励下3种刚性壁面附近微泡的有限元模型. 结果显示,刚性凹面附近的微泡形变较明显,易产生瞬态空化导致破裂. 同时,微泡具有偏离初始位置向壁面振荡靠近的动力学行为. 在声学参数以及距离壁面底部距离相等的情况下,近刚性凹面下的微泡重心振荡更剧烈,偏离初始位置距离最大,且凹面受到的压力较大,凸面受到的压力相对较小,壁面受到的压力与入射声压呈正相关,平面所受压力和附近微泡重心偏离程度介于凸面和凹面之间. 本模型可为靶向药物治疗等研究提供理论参考.Abstract: In order to study the difference in dynamic behavior of microbubble near rigid plane, convex and concave surfaces, a finite element model of three kinds of microbubble near rigid walls under ultrasonic excitation was established. Results show that the microbubble deformation near the rigid concave surface is more obvious, and it is easy to cause transient cavitation and rupture. At the same time, the microbubble has a dynamic behavior that was deviating from the initial position and oscillating toward the wall. When the acoustic parameters and the distance from the bottom of the wall are equal, the center of gravity of the microbubble under the nearly rigid concave surface oscillates more violently, and the deviation from the initial position is the largest. The pressure on the concave surface is relatively large, the pressure on the convex surface is relatively small, and the pressure on the wall surface is positively correlated with the incident sound pressure, and the deviation between the pressure on the plane and the center of gravity of the nearby microbubble is between the convex and concave surfaces. The proposed model can provide a theoretical reference for targeted drug therapy and other aspects.
-
Key words:
- ultrasound /
- microbubble /
- rigid wall /
- finite element
-
表 1 模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of geometry model
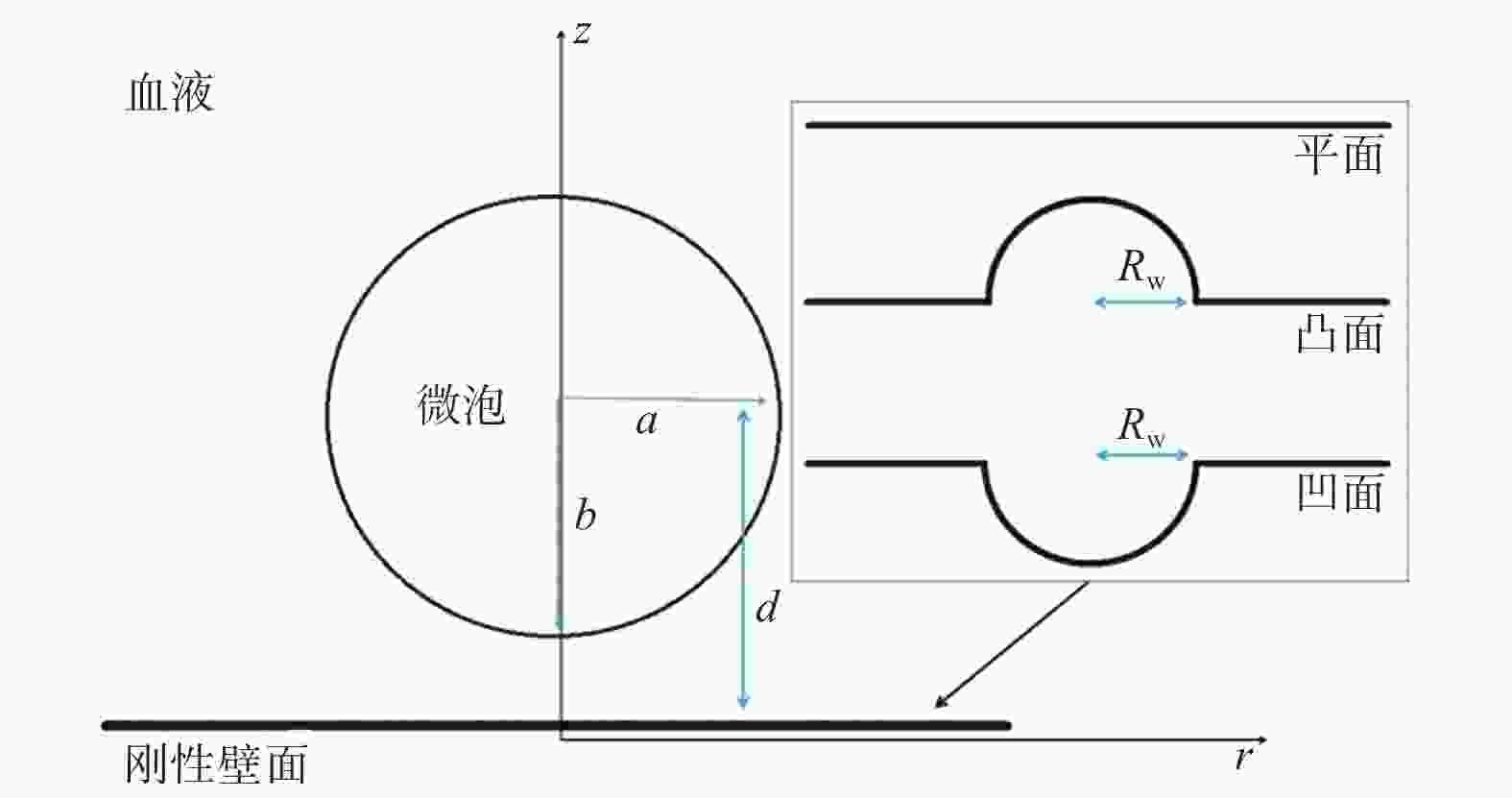
名称 参数 数值 气体多方指数 $\gamma $ 1.070 0 饱和蒸汽压 ${P_{\rm{v}}}$ / Pa 2 330 0 初始半径 ${R_0}$ / μm 2.000 0 气液表面张力系数 $\sigma $ / (N·m−1) 0.056 0 血液密度 $\rho $ / (kg·m−3) 1.059 0 血液动力黏度 $\mu $ / (Pa·s) 0.003 5 超声声压 ${P_{{\rm{in}}} }$ / MPa 0.100 0 超声频率 $f$ / MHz 1.000 0 初始血液压力 ${ {{p} }_0}$ / MPa 0.101 3 -
[1] 刘晓晖, 任艳, 韩婷婷, 等. 超声空化联合微泡造影剂增强肿瘤化疗的初步应用[J] . 临床医药文献电子杂志,2020,7(37):54. [2] MOVAHED P, KREIDER W, MAXWELL A D, et al. Cavitation-induced damage of soft materials by focused ultrasound bursts: A fracture-based bubble dynamics model[J] . Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,2016,140(2):1374 − 1386. doi: 10.1121/1.4961364 [3] 江行军, 牛传筱, 吴宇鹏, 等. 低频超声场中微血管内微泡动力学仿真研究[J] . 中国医学物理学杂志,2017,34(2):182 − 187. [4] ZUDIN Y B. Analog of the Rayleigh equation for the problem of bubble dynamics in a tube[J] . Journal of Engineering Physics and Thermophysics,1992,63:672 − 675. doi: 10.1007/BF00853959 [5] 姜学平, 程茜, 钱梦騄. 刚性边界附近微泡运动特性的计算及数值模拟[C]//2008年全国声学学术会议论文集, 上海: 中国声学学会, 2008. [6] 邱晓晖, 沈圆圆, 钱建庭, 等. 刚性微管内微泡动力学行为的有限元数值分析[J] . 生物医学工程学杂志,2011,28(5):911 − 915. [7] JEREMY E, PÁLFI KATALIN, LUISE D F, et al. 3D imaging and quantitative analysis of vascular networks: A comparison of ultramicroscopy and micro-computed tomography[J] . Theranostics,2018,8(8):2117 − 2133. doi: 10.7150/thno.22610 [8] JOHNSEN E, COLONIUS T. Shock-induced collapse of a gas bubble in shockwave lithotripsy[J] . Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,2008,124(4):2011 − 2020. doi: 10.1121/1.2973229 [9] 盛常睿, 陈赛君, 严利明, 等. 注射用六氟化硫微泡造影剂剂量与机械指数对孕鼠胎盘超声造影成像的影响[J] . 中华妇幼临床医学杂志(电子版),2020,16(3):329 − 334. [10] QIN S P, FERRARA K W. Acoustic response of compliable microvessels containing ultrasound contrast agents[J] . Physics in Medicine & Biology,2006,51(20):5065 − 5088. [11] WEISS H L. Mechanical damage from cavitation in high intensity focused ultrasound accelerated thrombolysis[D]. Berkeley: University of California, 2012. [12] 姚文瑛, 许松林, 吴云, 等. 基于计算流体力学的血液和血栓通过静脉瓣时流动分析[J] . 大连理工大学学报,2020,60(4):339 − 348. [13] 蔡晨亮, 屠娟, 郭霞生, 等. 包膜黏弹特性及声驱动参数对相互作用微泡动力学行为的影响[J] . 声学学报,2019,44(4):772 − 779. -





 下载:
下载: