Influence of Process Parameters on Microstructure and Microhardness of TC4 Joints
-
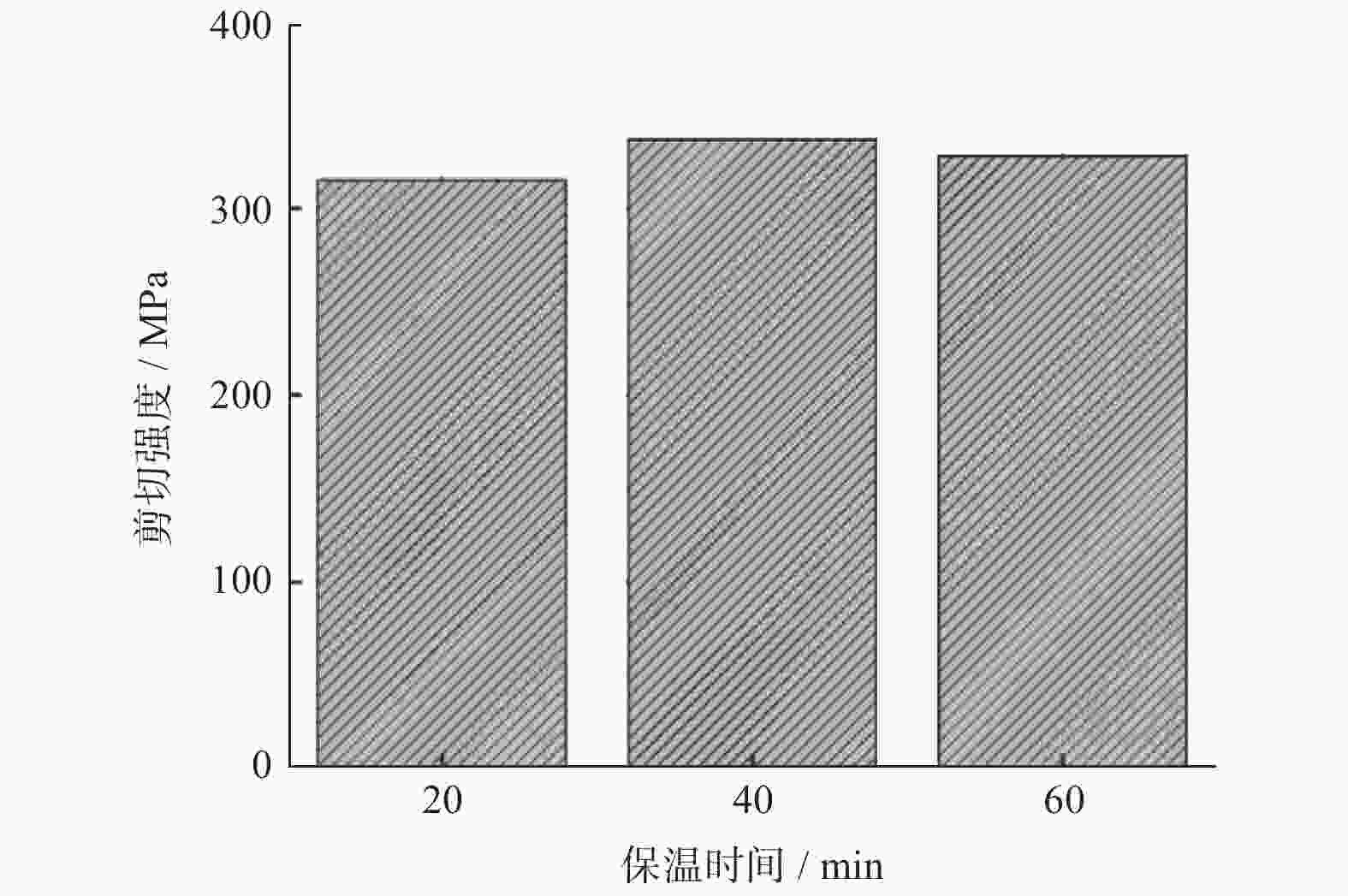
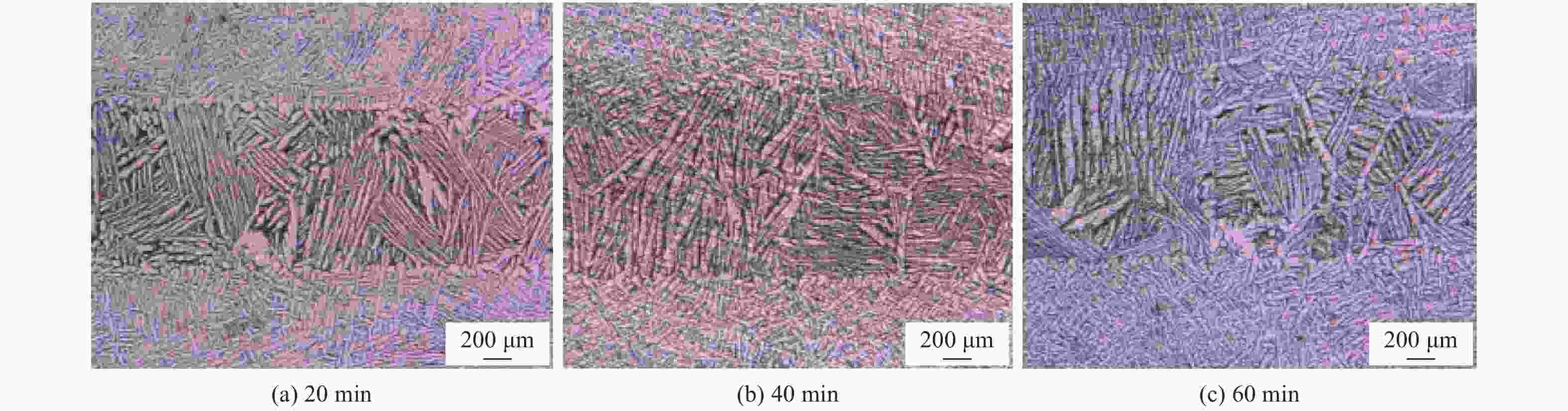
摘要: 采用Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni非晶钎料真空钎焊TC4钛合金,研究不同保温时间对钎焊接头的影响. 采用光学显微镜(OM),扫描电子显微镜(SEM),能谱仪(EDS)和显微硬度计对接头的显微组织和力学性能进行分析. 结果表明,焊缝主要组织为α-Ti与β-Ti,且随着保温时间的增加,焊缝区逐渐增厚,组织逐渐粗大. 当保温时间为40 min时,焊缝显微硬度最大,平均硬度(HV)为328,最大硬度为335.Abstract: TC4 titanium alloy was vacuum brazed with Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni amorphous brazing alloy, and the effects of different holding times on brazed joints were investigated. The optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), energy data spectrometer (EDS) and micro-hardness tester were used to analyze the microstructure and mechanical properties of the joints. The results show that the main microstructure of the weld was α-Ti and β-Ti, and with the increase of holding time, the weld zone is gradually thickened and the microstructure is gradually coarse. When the holding time was 40 min, the micro-hardness of the weld was the largest, the average hardness (HV) was 328, and the maximum hardness was 335.
-
Key words:
- TC4 titanium alloy /
- amorphous brazing alloy /
- microstructure /
- mechanical property
-
表 1 TC4钛合金元素含量
Table 1. Elemental composition of TC4 titanium alloy
% 试样 Al V Ti Fe Si C N H O 其他 TC4钛合金 5.50~6.80 3.50~4.50 余量 ≤0.30 ≤0.15 ≤0.10 ≤0.05 ≤0.01 ≤0.20 <0.50 表 2 Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni非晶钎料元素含量
Table 2. Elemental composition of Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni amorphous brazing material
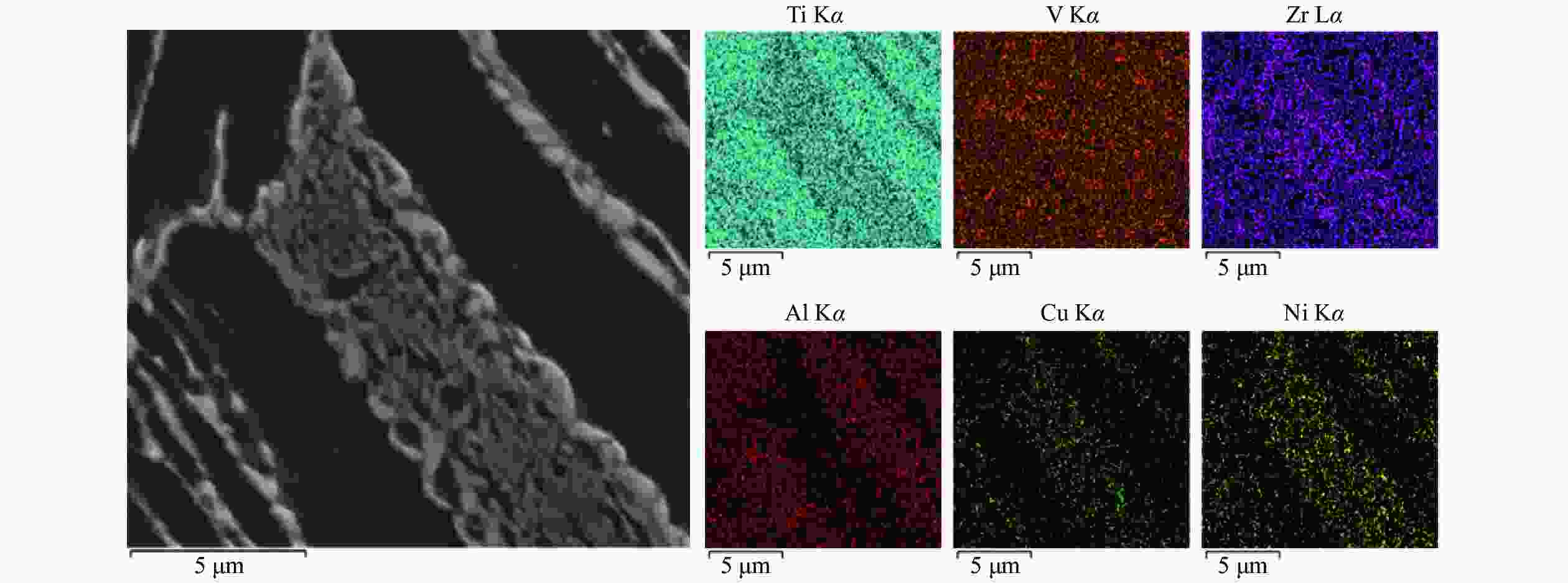
% 试样 Ti Zr Cu Ni 杂质 Ti-Zr-Cu-Ni非晶钎料 36.5 33.0 16.2 13.3 < 1.0 表 3 保温时间20 min时接头EDS测试结果
Table 3. EDS test results of joints with holding time of 20 min
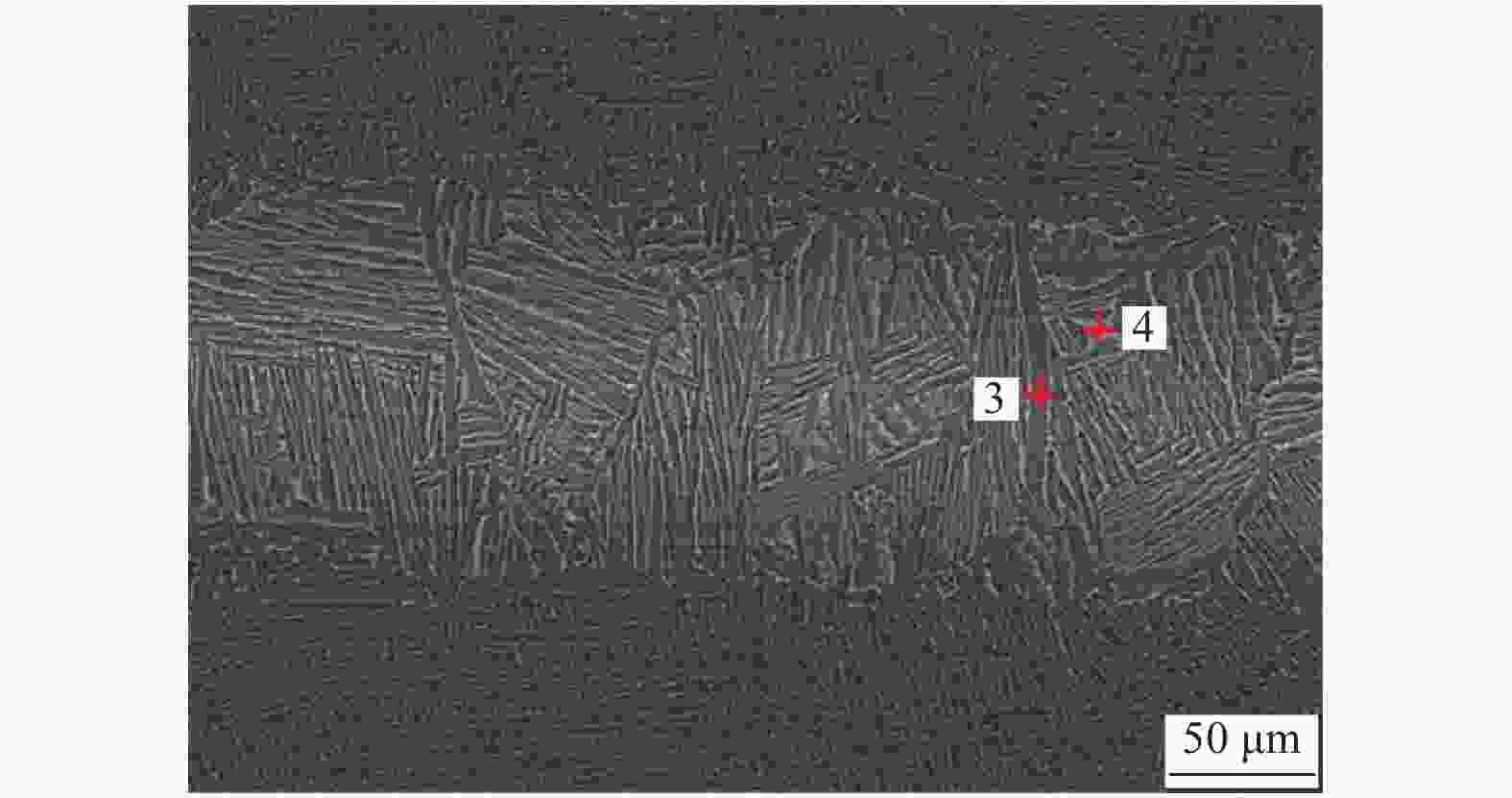
% 项目 Al Cu Ti Zr V Ni 点1 10.08 1.07 83.06 3.13 2.08 0.59 点2 6.27 3.99 76.06 7.32 3.26 3.10 表 4 保温时间40 min时接头EDS测试结果
Table 4. EDS test results of joints with holding time of 40 min
% 项目 Al Cu Ti Zr V Ni 点3 9.90 0.69 85.24 2.75 1.42 — 点 4 5.83 4.82 74.90 7.43 4.45 2.47 表 5 保温时间60 min时接头EDS测试结果
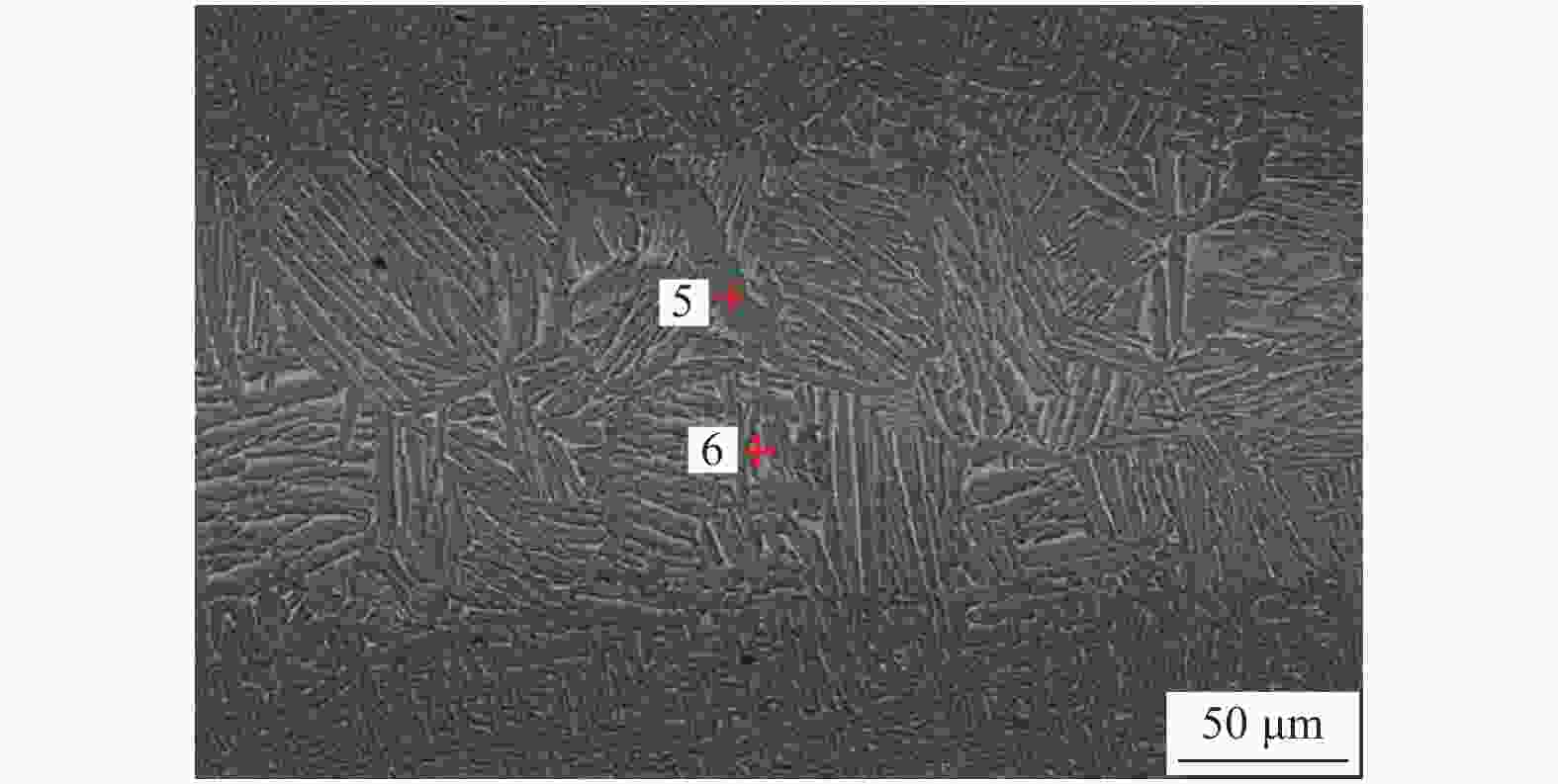
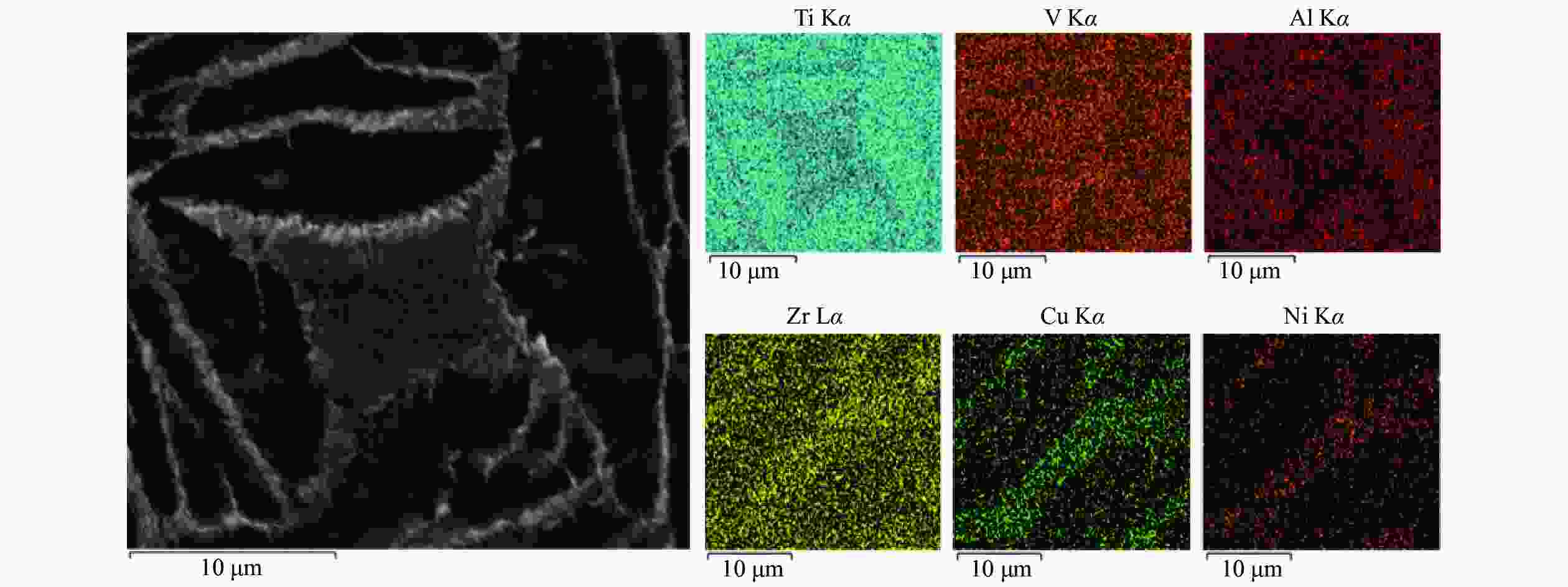
Table 5. EDS test results of joints with holding time of 60 min
% 项目 Al Cu Ti Zr V Ni 点 5 9.84 — 86.62 3.54 — — 点 6 7.14 6.71 67.27 5.00 5.48 8.40 -
[1] 原国森, 兖利鹏, 韩艳艳. 钛合金的应用进展[J] . 热加工工艺,2019,46(4):13 − 16. [2] 刘捷, 尚青亮, 张炜, 等. 氢化钛粉制备钛及钛合金材料研究进展[J] . 材料导报,2013,27(13):99 − 102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2013.13.021 [3] SONG X G, CAO J, CHEN H Y, et al. Contact reactive brazing of Ti53311S alloy using Cu foil as interlayer: Interfacial microstructure and joining properties[J] . Materials and Design,2013,46:895 − 901. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2012.11.044 [4] 余春, 吴铭方, 于治水, 等. Ti/Cu/Ti接触反应钎焊微观组织分析[J] . 华东船舶工业学院学报(自然科学版),2004,18(2):56 − 60. [5] TASHI R S, MOUSAVI S A A A, ATABAKI M M. Diffusion brazing of Ti-6Al-4V and austenitic stainless steel using silver-based interlayer[J] . Materials and Design,2014,54:161 − 167. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.103 [6] SHIUE R K, CHEN C P, WU S K. Infrared brazing of Ti50Ni50 shape memory alloy and 316L stainless steel with two sliver-based fillers[J] . Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A,2015,46:2364 − 2371. doi: 10.1007/s11661-015-2830-7 [7] JUNG G L, MIN-KU L. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of a titanium-to-stainless steel dissimilar joint brazed with Ag-Cu alloy filler and an ag interlayer[J] . Materials Characterization,2017,129:98 − 103. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.04.032 [8] JING Y J, YUE X S, GAO X Q, et al. The influence of Zr content on the performance of TiZrCuNi brazing filler[J] . Materials Science and Engineering A,2016,678:190 − 196. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.115 -





 下载:
下载: