Research on mechanism and capability of new type of wall-climbing robot overconming obstacles
-
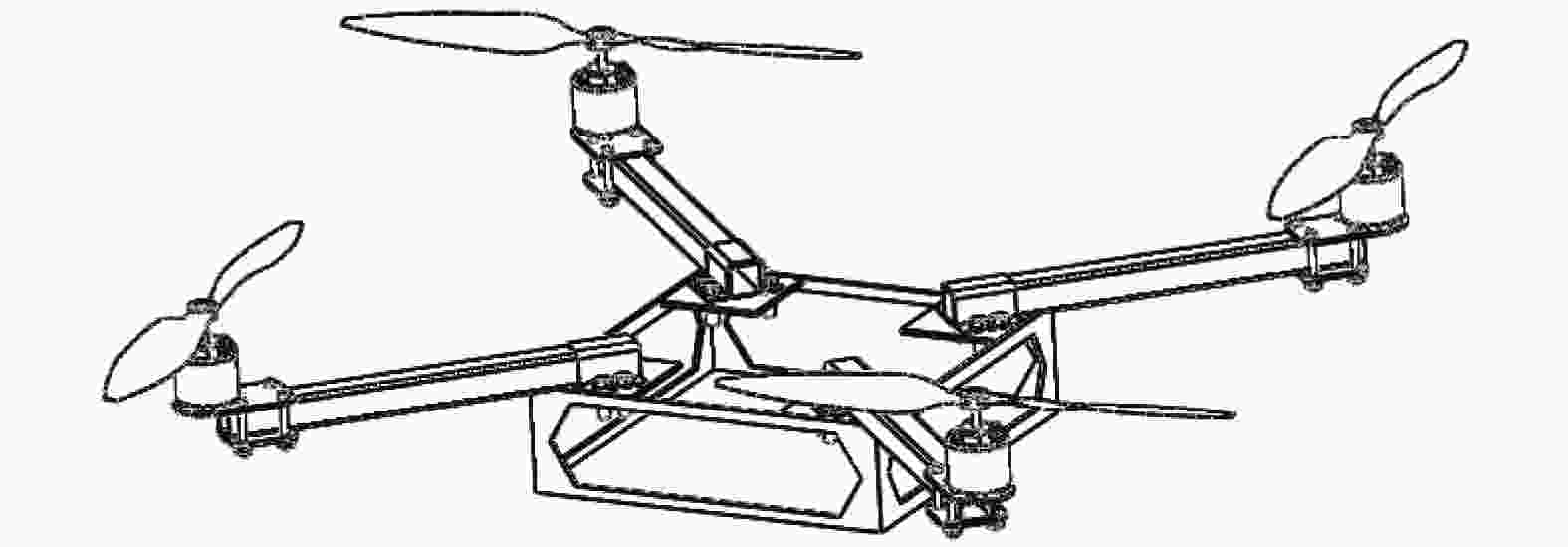
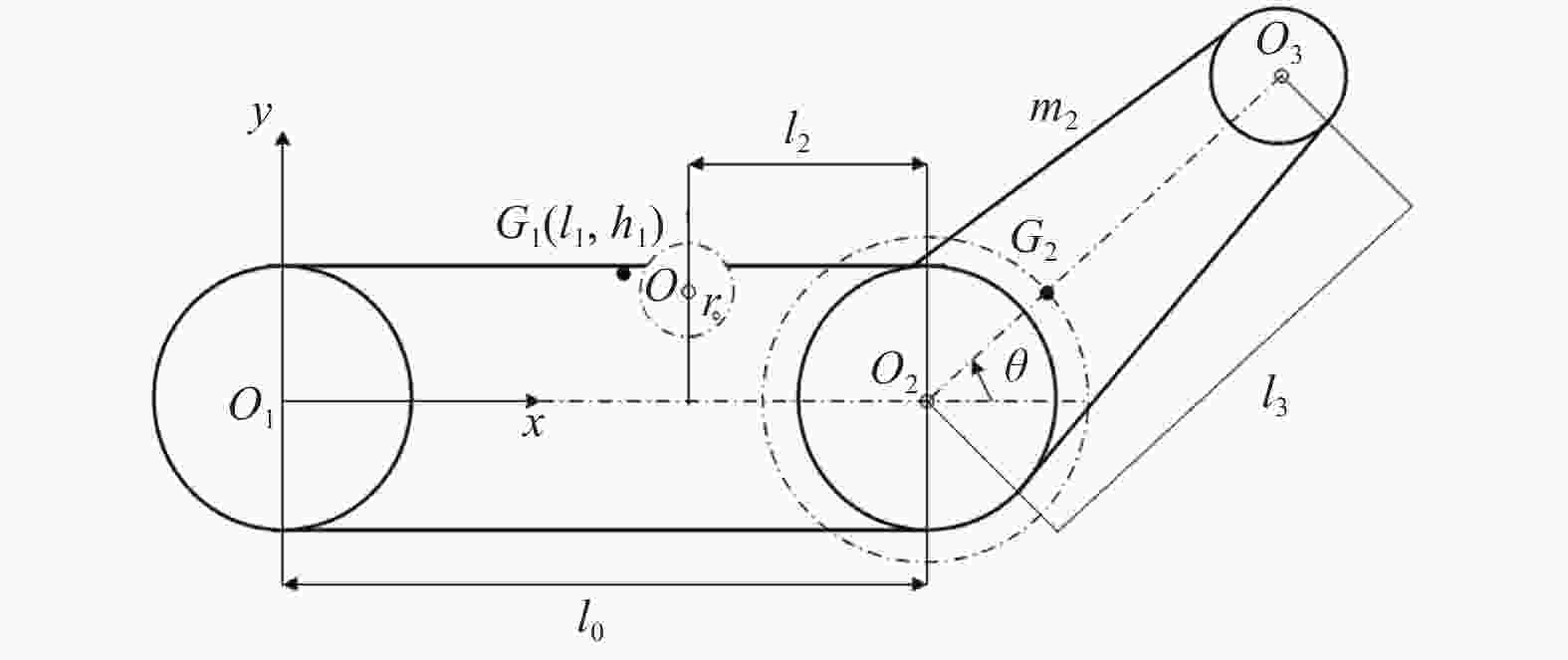
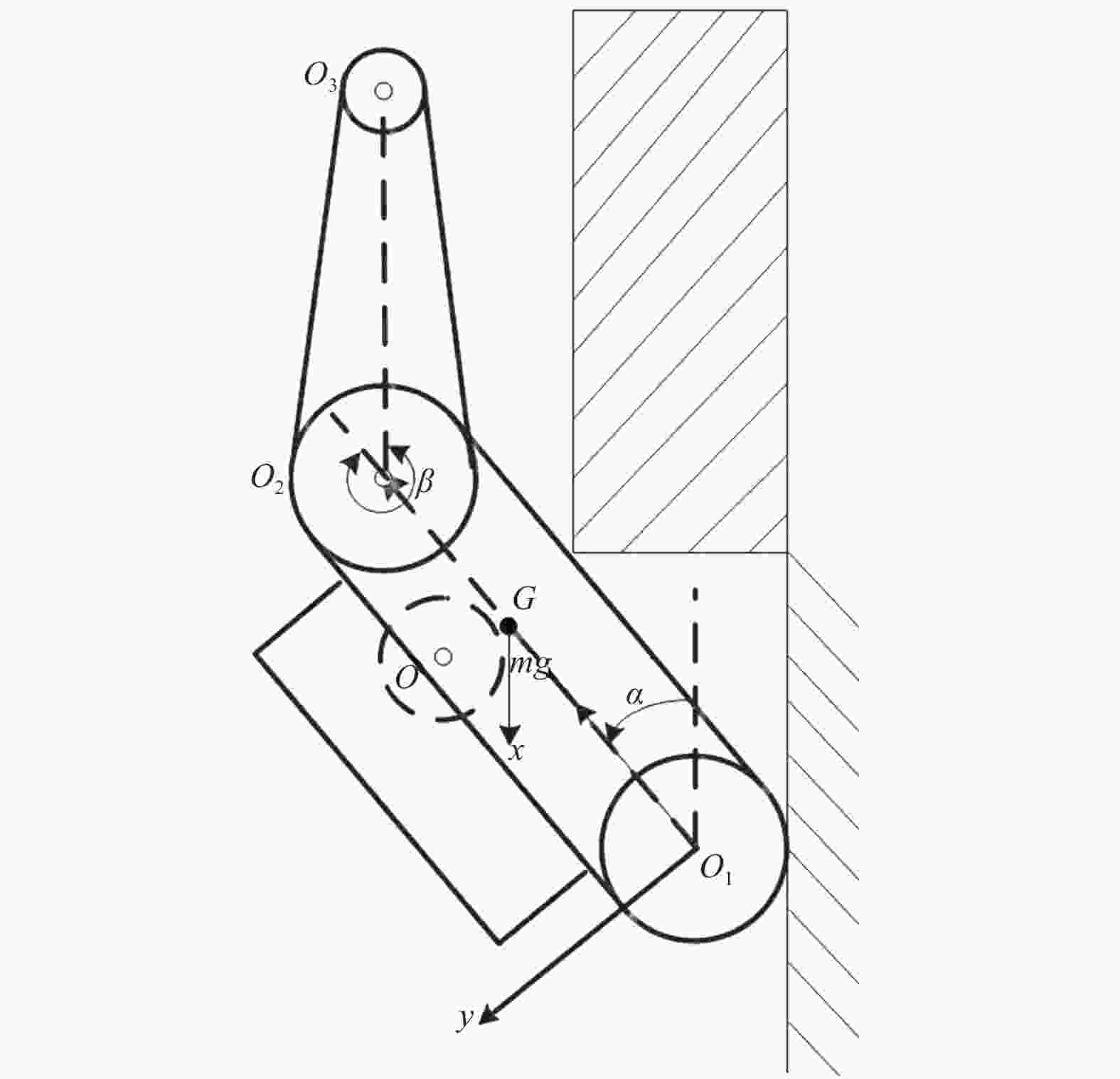
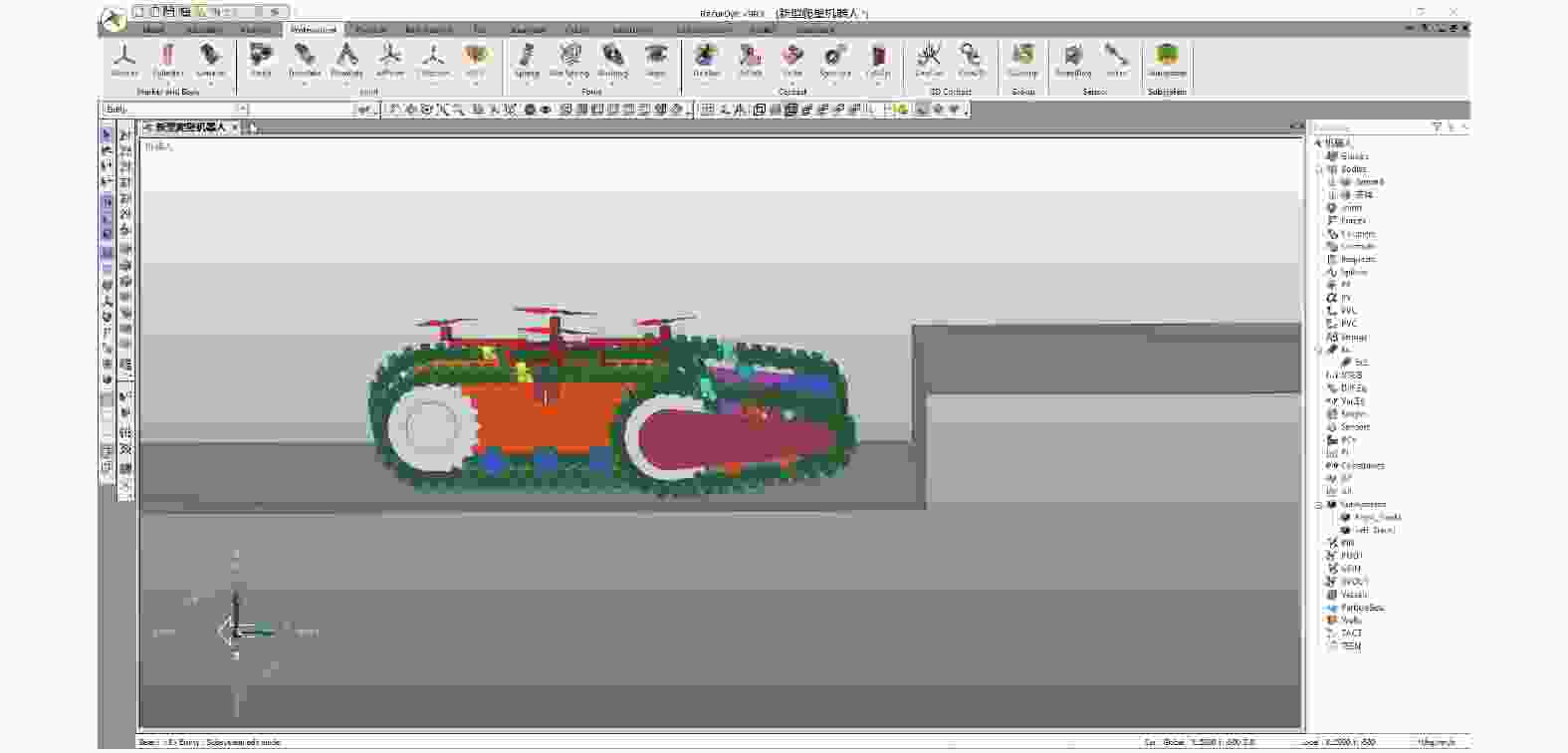
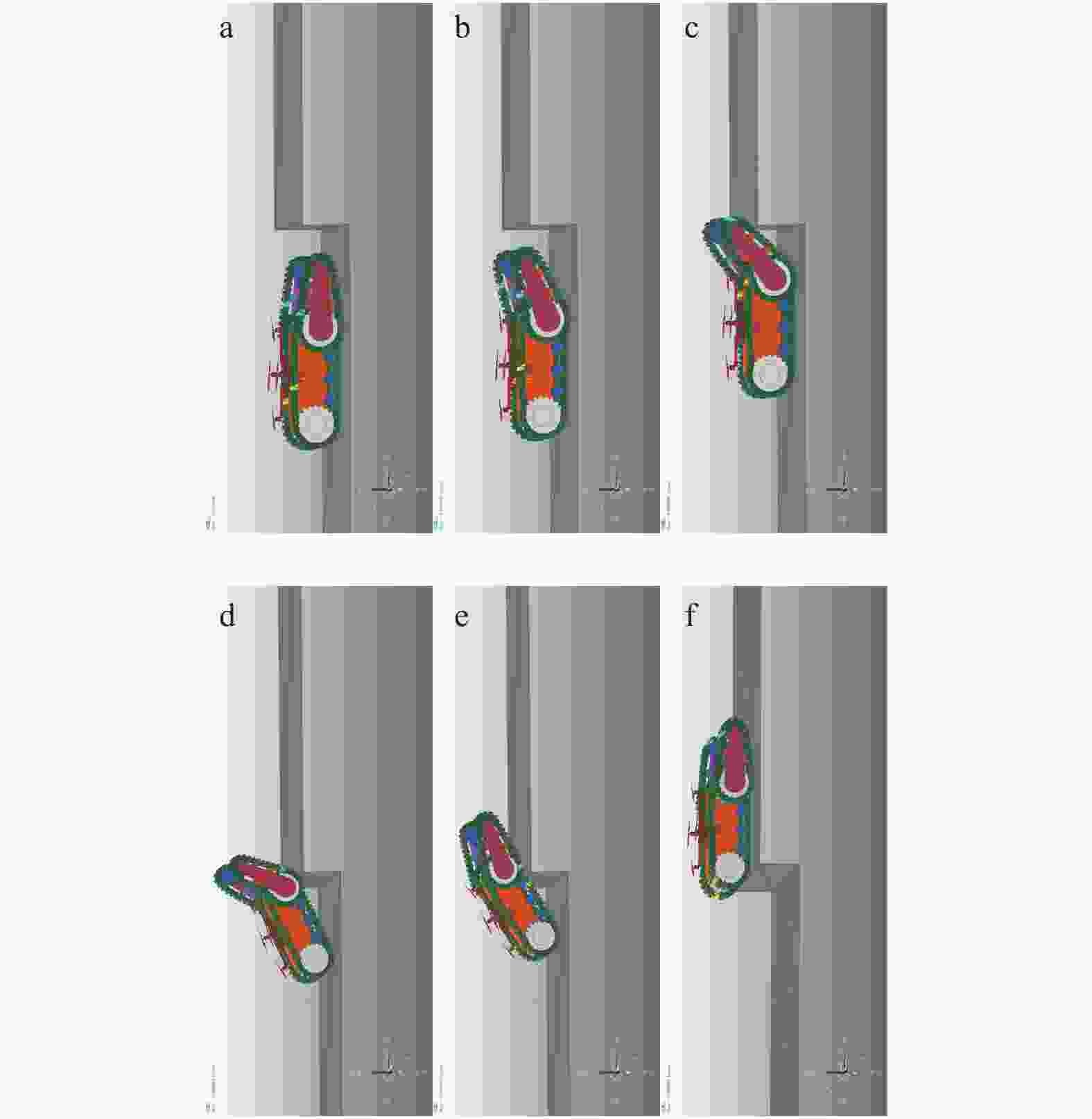
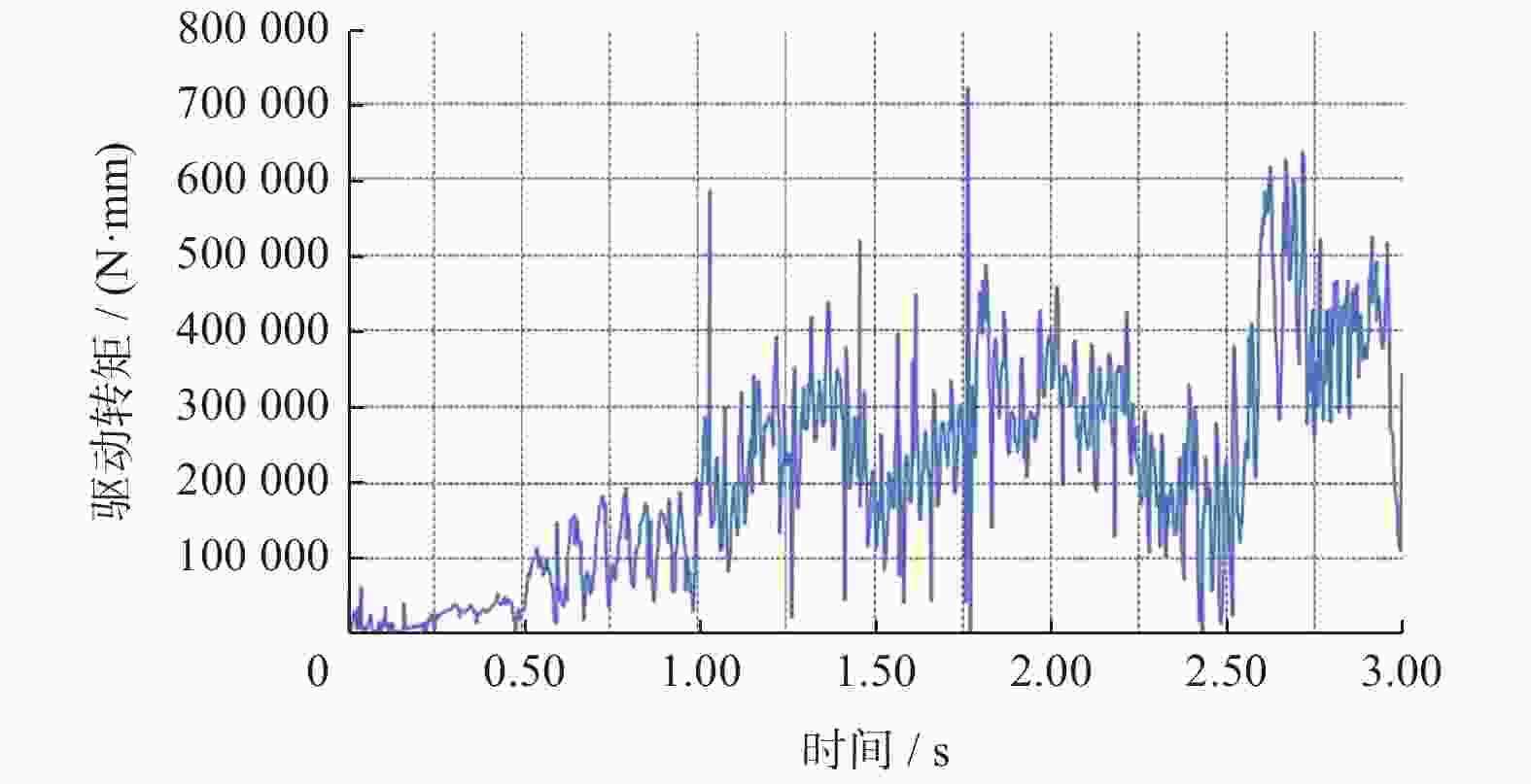
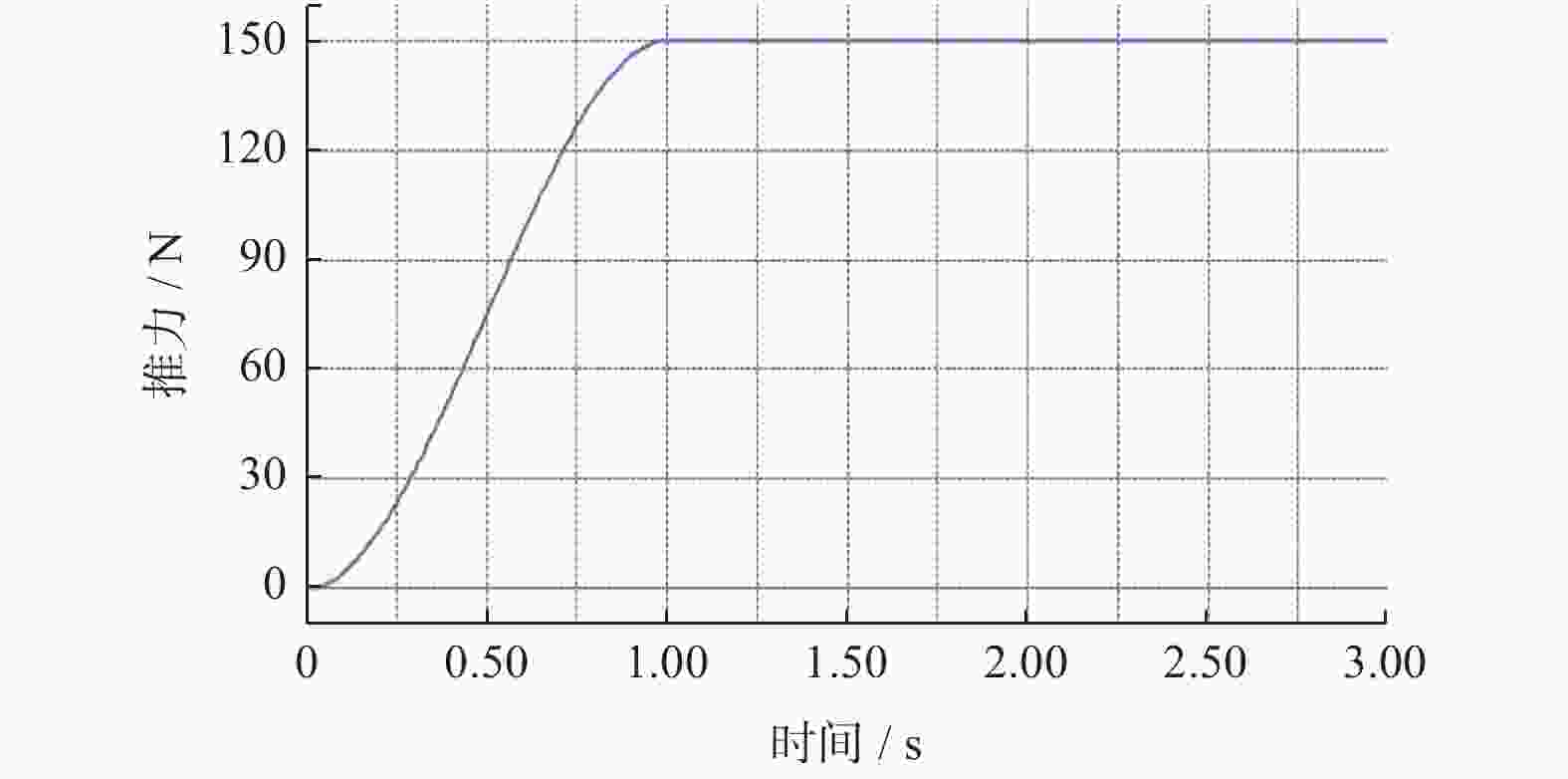
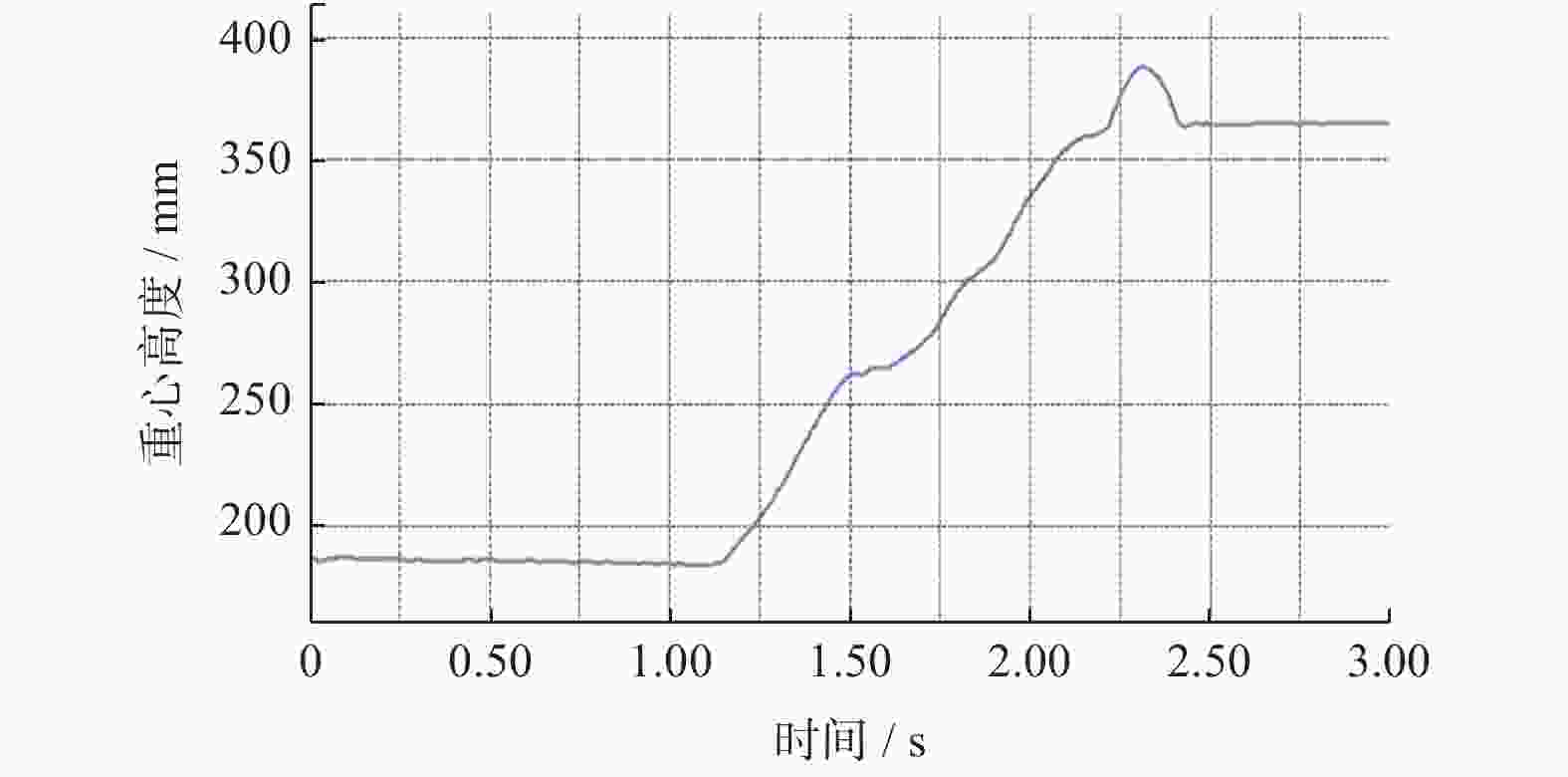
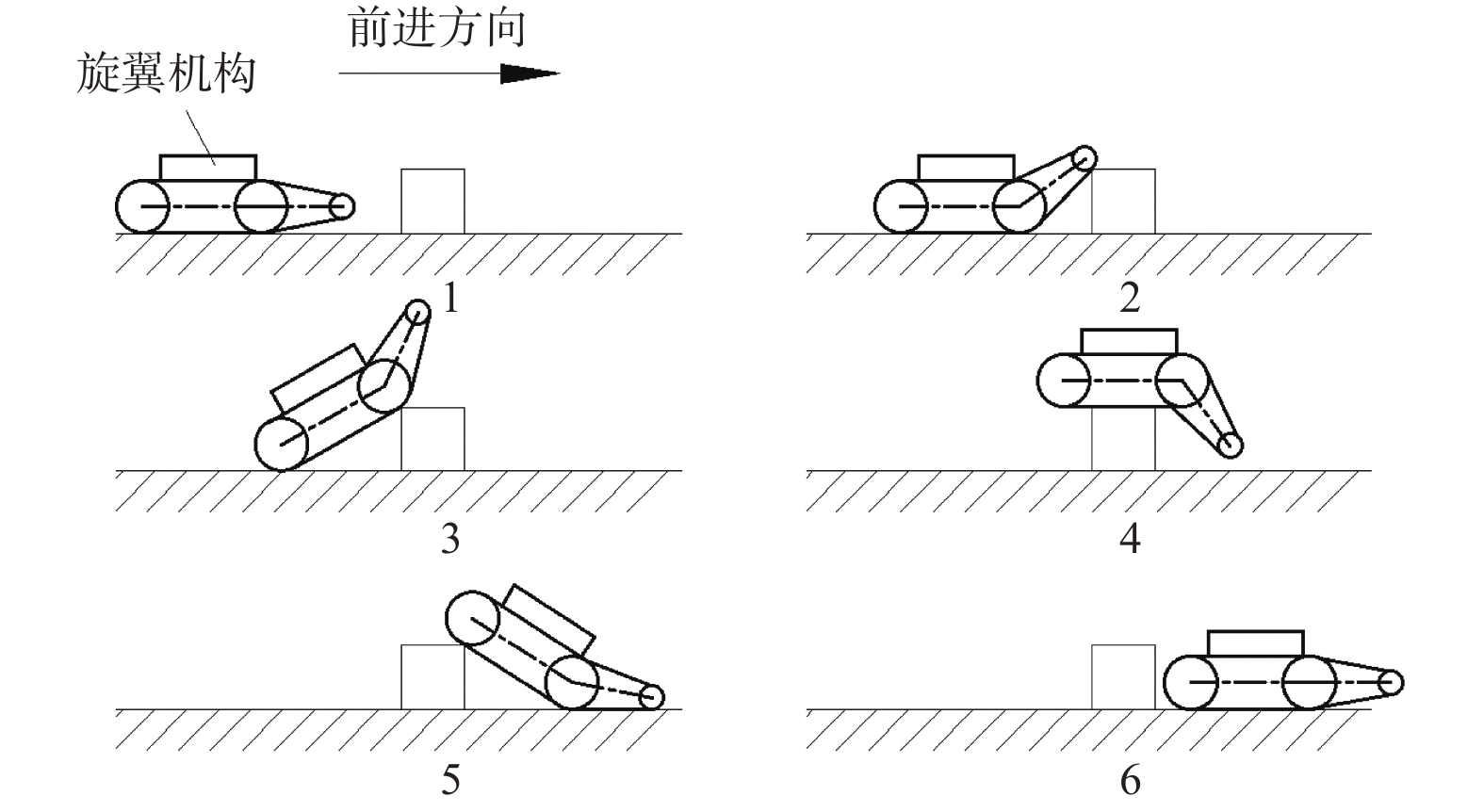
摘要: 爬壁清洗机器人是在危险的高层建筑环境下替代人进行清洗工作的机械,其可靠性和稳定性尤为重要. 在分析传统爬壁清洗机器人弊端的基础上,针对玻璃存在的窗框障碍物,设计一种四旋翼摆臂式爬壁清洗机器人.机器人基于履带式底盘结构,通过旋翼旋转产生推力提供壁面行走所需的吸附力,并设计相应的机器人摆臂变形机构,增加机器人的壁面越障能力. 从运动学角度分析机器人越障时的运动机理,建立机器人壁面攀爬的运动学模型. 在RecurDyn的Track LM模块环境下,对机器人越障过程进行运动学仿真,得到驱动轮的驱动转矩、旋翼推力随时间变化曲线;对Y轴重心位置和加速度变化曲线分析,机器人在越障过程中能够保持良好的平稳性,论证了四旋翼摆臂式爬壁清洗机器人的越障能力和越障过程中的平稳性.
-
关键词:
- 爬壁清洗机器人 /
- 履带式 /
- RecurDyn仿真软件 /
- 旋翼
Abstract: The wall-climbing cleaning robot is a cleaning machine and assigned to replace human to work in the dangerous high-rise building environment, so its reliability and stability are particularly important. On the basis of analyzing the disadvantages of traditional wall-climbing cleaning robot, aiming at the obstacles of glass window frame, a four-rotor swinging arm wall-climbing cleaning robot was designed. Based on crawler chassis structure, rotary wing was designed to generate thrust to provide the adsorptive force required for wall walking, and the corresponding robot swinging arm deformation mechanism was designed to increase the obstacle surmounting ability of the robot on the wall. The kinematic mechanism of the robot over the obstacle was analyzed, and the kinematic model of the robot wall-climbing was established. Under the RecurDyn Track LM module, kinematic simulation was carried out for the obstacle crossing process of the robot, and the curve of driving torque and rotor thrust changing with time was obtained. By analyzing the curve of Y-axis center position and acceleration change, the robot can maintain good stability in the process of obstacle surmounting, demonstrating the ability of the new four-rotor swinging arm wall-climbing robot to surmount obstacles and the stability in the process of obstacle surmounting.-
Key words:
- wall-climbing cleaning robot /
- caterpillar /
- RecurDyn simulation software /
- rotor
-
表 1 爬壁机器人初步设计参数
Table 1. Preliminary design parameters of wall-climbing robot
参数 数值 车体尺寸/${(\rm{mm}\times\rm{mm}\times\rm{mm}) }$ 400×335×210 摆臂长度
${l_2}/{\rm{mm}}$195 主车质量
${m_1}/{\rm{kg}}$12 双摆臂质量
${m_2}/{\rm{kg}}$3 主动轮直径
$d/{\rm{mm}}$100 主惰轮直径
${d_{\rm{1} } }/{\rm{mm}}$100 副惰轮直径
${d_{\rm{2} } }/{\rm{mm}}$100 小惰轮直径
${d_{\rm{3} } }/{\rm{mm}}$20 表 2 单侧履带约束副对应关系
Table 2. Correspondence of constraint pair of unilateral crawler
约束 基体 操作体 旋转副 母体 主动轮 旋转副 张紧器 主惰轮 旋转副 连接板1 负重轮1 旋转副 连接板1 负重轮2 旋转副 连接板1 负重轮3 旋转副 连接板1 托轮 旋转副 连接板2 负重轮4 旋转副 连接板2 负重轮5 旋转副 连接板2 负重轮6 旋转副 连接板2 小惰轮 旋转副 母体 连接板2 固定副 母体 连接板1 表 3 主要仿真参数
Table 3. Main simulation parameters
零部件 材质 摩擦因数 弹性模量/GPa 履带 Rubber 0.65 0.0078 主动(惰)轮 Steel 0.15 206 副(小)惰轮 Steel 0.15 206 表 4 各部件驱动函数
Table 4. Driver functions of each component
驱动部件 驱动函数 主动轮 [STEP(TIME, 0.1,0,1,360D)+
STEP(TIME,1.5,0,2,−90D)+
STEP(TIME,2.5,0,3,−270D)]摆臂 [STEP(TIME,0.1,0,1,−40D)+
STEP(TIME,1.5,0,2,80D)+
STEP(TIME,2,0,2.5,−40D)]旋翼 [STEP(TIME,0,0,1,−18 000D)] -
[1] MANUEL A,PABLO GONZALEZ D S,MARIA A, et al. Application of CLAWAR machines[J] . The International Journal of Robotics Research,2003,22(3−4):251 − 264. [2] SORIOKA Y, YAMAGUCHI T, HASHIMOTO S. 1302 Title development of a telescopic- arm type, climbing support robot[J] . 2008,2008:79 − 83. [3] 刘淑霞, 王炎, 徐殿国, 等. 爬壁机器人技术的应用[J] . 机器人,1999(2):148 − 155. [4] 汪家斌, 李丽荣, 陈咏华, 等. 壁面移动机器人吸附方式的研究现状与发展[J] . 机械,2012(1):1 − 5. [5] 刘京诚. 微小步行爬壁机器人驱动与位置检测技术及系统[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2003. [6] 刘彦伟, 黄响, 王李梦, 等. 仿生爪刺式双足爬壁机器人设计与分析[J] . 机械科学与技术,2019,38(8):1185 − 1190. [7] 董寒, 崔登祺, 李方兴, 等. 多吸盘框架式爬壁机器人系统的设计与分析[J] . 制造业自动化,2016,38(6):59 − 63,69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0134.2016.06.015 [8] 付宜利, 李志海. 爬壁机器人的研究进展[J] . 机械设计,2008(4):1 − 5. [9] 刘松国. 六自由度串联机器人运动优化与轨迹跟踪控制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2009. [10] 孟广耀, 王振华, 黄居鑫, 等. 双摆臂履带可变形机器人结构设计与越障性能研究[J] . 机械传动,2019,43(8):144 − 149. [11] 徐正飞, 杨汝清, 王韬. 关节式移动机器人的越障运动[J] . 中国机械工程,2003,14(12):69 − 72,6. [12] 杨春, 罗天洪. 一种新型爬壁机器人越障过程的运动及动力学分析[J] . 机械传动,2019,43(9):87 − 92,95. -






 下载:
下载: