Application of Gray Metabolism GM (1,1) Model on Prediction of Minimum Wage Standard in Shanghai
-
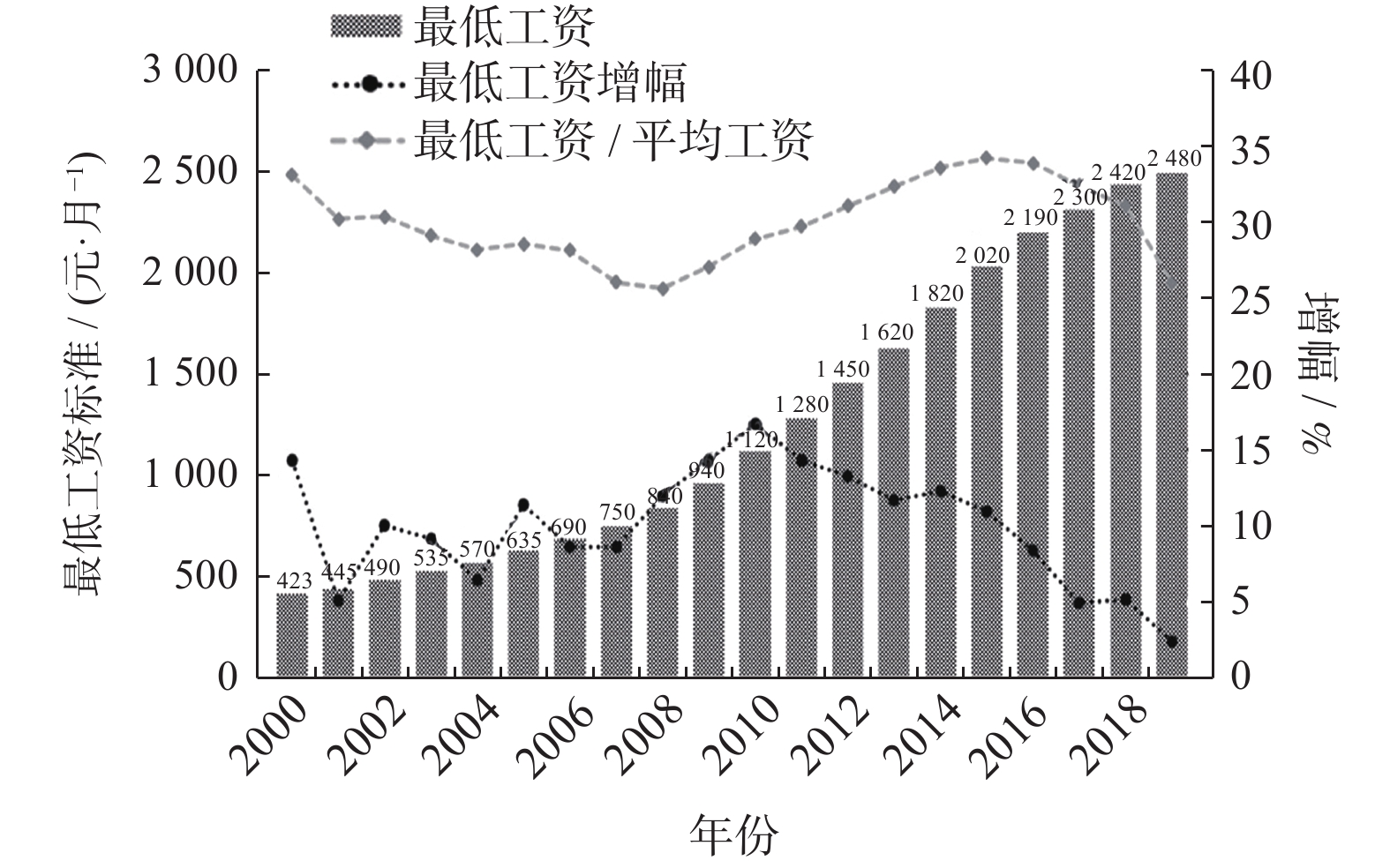
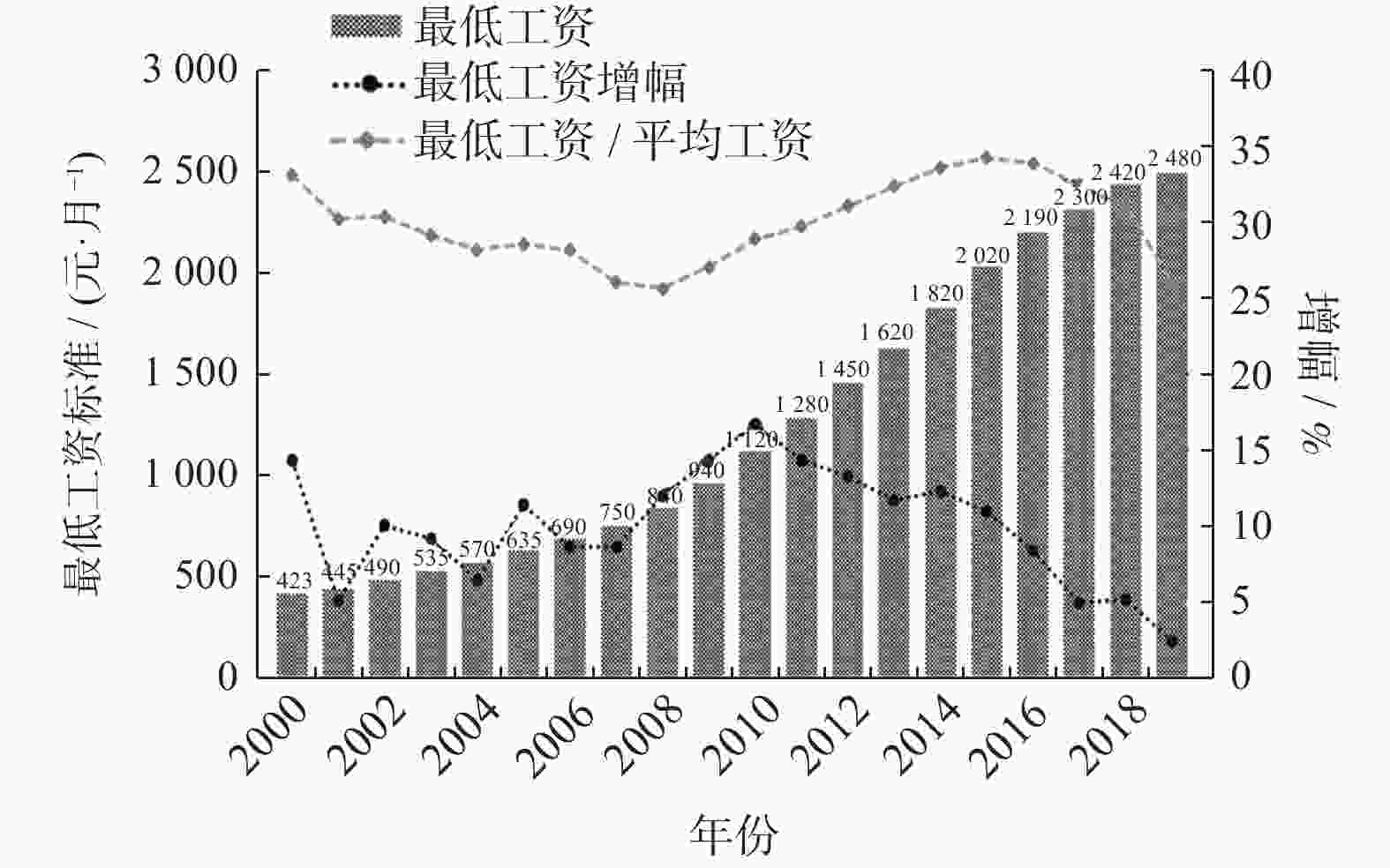
摘要: 最低工资制度的建立是我国构建和谐劳动关系的一个重要制度,开展最低工资预测具有重要意义. 以上海市为例,基于灰色系统理论和方法,构建最低工资标准的常规GM(1,1)模型和灰色新陈代谢GM(1,1)模型,对未来短期内上海市最低工资标准进行预测研究,预测结果符合上海市政府提出的平稳调整最低工资标准目标. 通过对上海市最低工资标准的拟合和预测,为政府和企业制定相关决策提供科学合理的依据,具有一定的理论意义和现实意义.
-
关键词:
- 最低工资标准 /
- 灰色系统 /
- 灰色新陈代谢GM(1,1)模型 /
- 拟合与预测
Abstract: The establishment of the minimum wage system is an important social institution for building harmonious labor relations in China. It is of great significance to carry out minimum wage prediction. Taking Shanghai as an example, the conventional GM(1,1) model and gray metabolism GM(1,1) model were established to predict the minimum wage standard of Shanghai in the short term based on the gray system theory and method. The prediction result is in line with the Shanghai government’s goal of smoothly adjusting the minimum wage standard. Through the fitting and forecasting of the minimum wage standard in Shanghai, it can provide a scientific and reasonable basis for the government and enterprises to make relevant decisions, which has great theoretical and practical significance. -
表 1 灰色模型预测精度检验等级参照
Table 1. Reference of prediction accuracy test of gray model
模型等级 平均相对误差 平均相对精度p C值 一级(优) ≤1% ≥95% ≤0.35 二级(合格) ≤5% 80%≤p<95% 0.35<C≤0.5 三级(勉强合格) ≤10% 70%≤p<80% 0.5<C≤0.65 四级(不合格) ≤20% <70% >0.65 表 2 常规GM(1,1)模型的预测结果及预测精度
Table 2. Prediction result and prediction accuracy of conventional GM(1,1) model
年份 实际值 /
(元·月−1)预测值 /
(元·月−1)残差 /
(元·月−1)相对误差 /
%预测精度 /
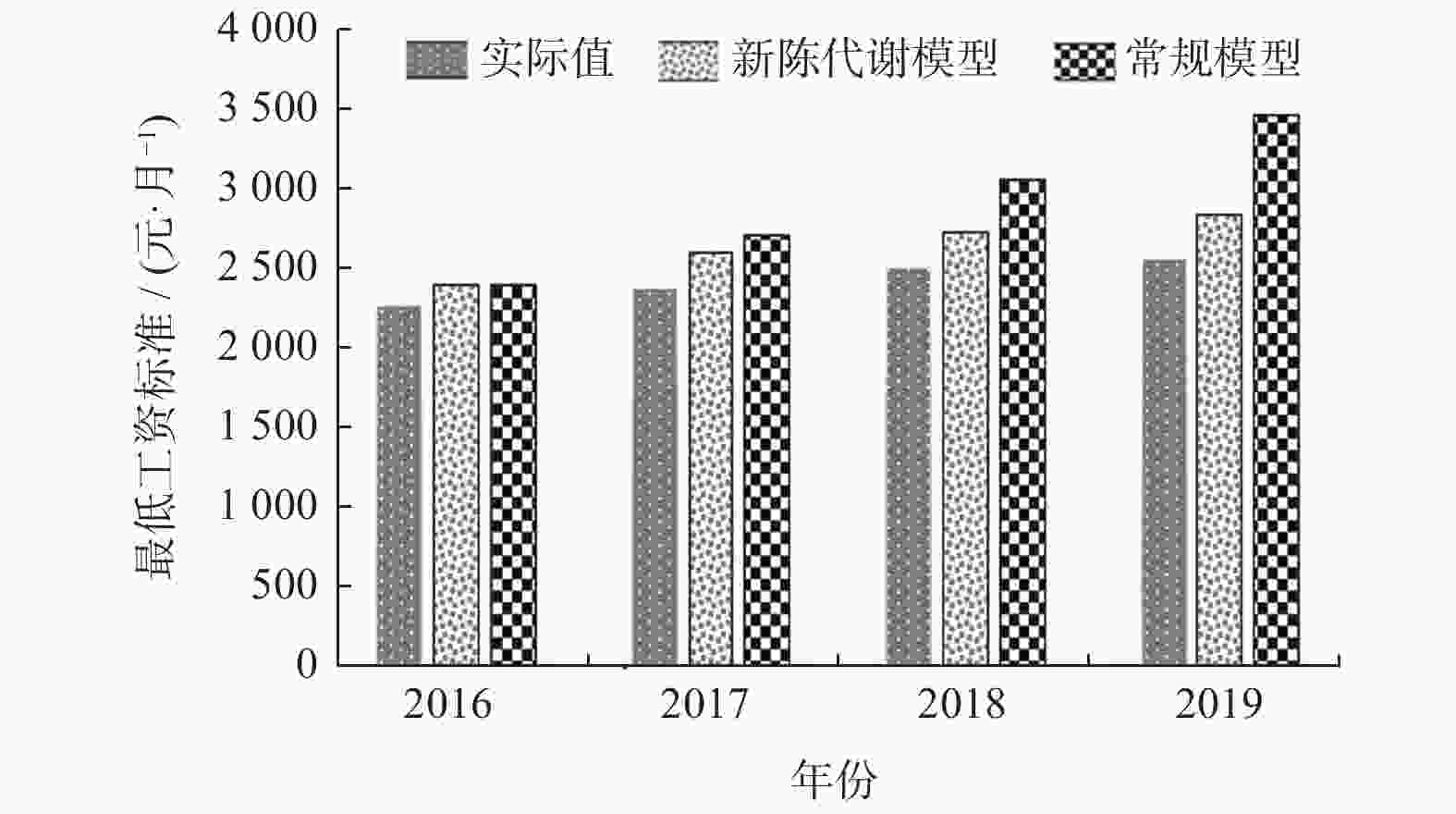
%2016 2 190 2 313 123 5.62 94.38 2017 2 300 2 614 314 13.65 86.35 2018 2 420 2 953 533 22.02 77.98 2019 2 480 3 337 857 34.56 65.44 表 3 灰色新陈代谢GM(1,1)模型的预测结果及预测精度
Table 3. Prediction result and prediction accuracy of gray metabolism GM(1,1) model
灰色新陈代谢GM(1,1)模型 年份 实际值 / (元·月−1) 预测值 / (元·月−1) 残差 / (元·月−1) 相对误差 / % 预测精度 / % 模型1 2017 2300 2509 209 9.09 90.91 2018 2420 2810 390 16.12 83.88 2019 2480 3147 667 26.90 73.10 模型2 2018 2420 2639 219 9.05 90.95 2019 2480 2917 437 17.62 82.38 模型3 2019 2480 2743 263 10.60 89.40 表 4 不同维度基础GM(1,1)模型精度比较
Table 4. Comparison of prediction accuracy of different dimensional GM(1,1) models
基础模型 维度 平均相对误差 / % 平均相对精度 / % C值 模型等级 模型1 5 0.61 99.39 0.0620 优 模型2 7 2.10 97.90 0.0945 合格 模型3 9 3.51 96.49 0.1090 合格 模型4 11 4.70 95.30 0.1109 合格 模型5 13 6.42 93.58 0.1097 合格 模型6 15 7.37 92.63 0.1048 合格 模型7 17 7.67 92.33 0.1012 合格 表 5 5维灰色新陈代谢GM(1,1)模型最低工资标准模拟结果
Table 5. Simulation result of minimum wage standard using 5-dimensional gray metabolism GM(1,1) model
年份 实际值 /
(元·月−1)预测值 /
(元·月−1)绝对误差 /
(元·月−1)相对误差 /
%2015 2020 2020 0 0.00 2016 2190 2201 11 0.50 2017 2300 2295 −5 −0.22 2018 2420 2394 −26 −1.07 2019 2480 2497 17 0.69 表 6 灰色新陈代谢GM(1,1)模型最低工资标准预测结果
Table 6. Prediction result of minimum wage standard using gray metabolism GM(1,1)
未来调整年次 预测值 /
(元·月−1)取整数值 /
(元·月−1)调整数值 /
(元·月−1)调整幅度 /
%1 2604 2600 120 4.84 2 2716 2710 110 4.23 3 2832 2830 120 4.43 -
[1] 杨灿, 叶林祥, 詹鹏. 我国最低工资标准制定中的“跟风行为”: 基于2004—2017年省级面板数据的实证研究[J] . 经济社会体制比较,2020(5):79 − 89. [2] JONATHAN M, JEREMY W. Effects of the minimum wage on employment dynamics[J] . The Journal of Human Resources,2016,51(2):500 − 522. doi: 10.3368/jhr.51.2.0414-6298R1 [3] 王蓓. 最低工资标准的科学测算与制度完善[J] . 山东大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2017(4):54 − 64. [4] 权衡, 李凌. 上海提高最低工资标准的收入分配效应: 实证与模拟[J] . 上海经济研究,2011(4):96 − 109. [5] FANG T, LIN C. Minimum wages and employment in China[J] . IZA Journal of Labor Policy,2015,4(1):1 − 30. doi: 10.1186/s40173-014-0027-0 [6] 张学鹏, 宋蕾. 我国最低工资标准及其变动的决定因素实证分析[J] . 当代经济科学,2018,40(5):117 − 123, 128. [7] 杨莲秀. 最低工资标准影响因素实证分析: 以上海为例[J] . 上海大学学报(社会科学版),2014,31(5):91 − 102. [8] 杨莲秀. 上海市最低工资标准的影响因子研究[J] . 复旦学报(自然科学版),2014,53(2):284 − 296. [9] 汪泓. 用神经网络模型对上海最低工资标准的分析和研究[J] . 东华大学学报(自然科学版),2001,27(6):79 − 86. [10] 韩兆洲, 魏章进. 基于灰色系统模型的最低工资研究[J] . 数学的实践与认识,2005,35(9):99 − 104. [11] 范君晖, 吴忠, 李旭芳. 基于粗糙集和神经网络的上海最低工资标准研究[J] . 计算机工程与设计,2007,28(12):2918 − 2921. [12] 关娇. 上海市最低工资标准现状研究[J] . 经济研究导刊,2018(17):100 − 101. [13] 刘思峰, 杨英杰. 灰色系统研究进展(2004—2014)[J] . 南京航空航天大学学报,2015,47(1):1 − 18. [14] 孟伟, 刘思峰, 曾波, 等. 分数阶灰色累加生成算子与累减生成算子及互逆性[J] . 应用泛函分析学报,2016,18(3):274 − 283. [15] 张朝飞, 罗建军, 徐兵华, 等. 基于灰色理论的新陈代谢自适应多参数预测方法[J] . 上海交通大学学报,2017,51(8):970 − 976. [16] 易梅, 高雅萍, 郭瑞雪, 等. 动态残差修正的新陈代谢灰色模型在沉降预测中的应用[J] . 工程勘察,2018,46(4):44 − 48. [17] 黄任宏, 李程程. 灰色系统理论在工程实践中应用研究[J] . 科学技术创新,2019(13):4 − 6. -





 下载:
下载: