Influence of weld width on fatigue strength of butt joint
-
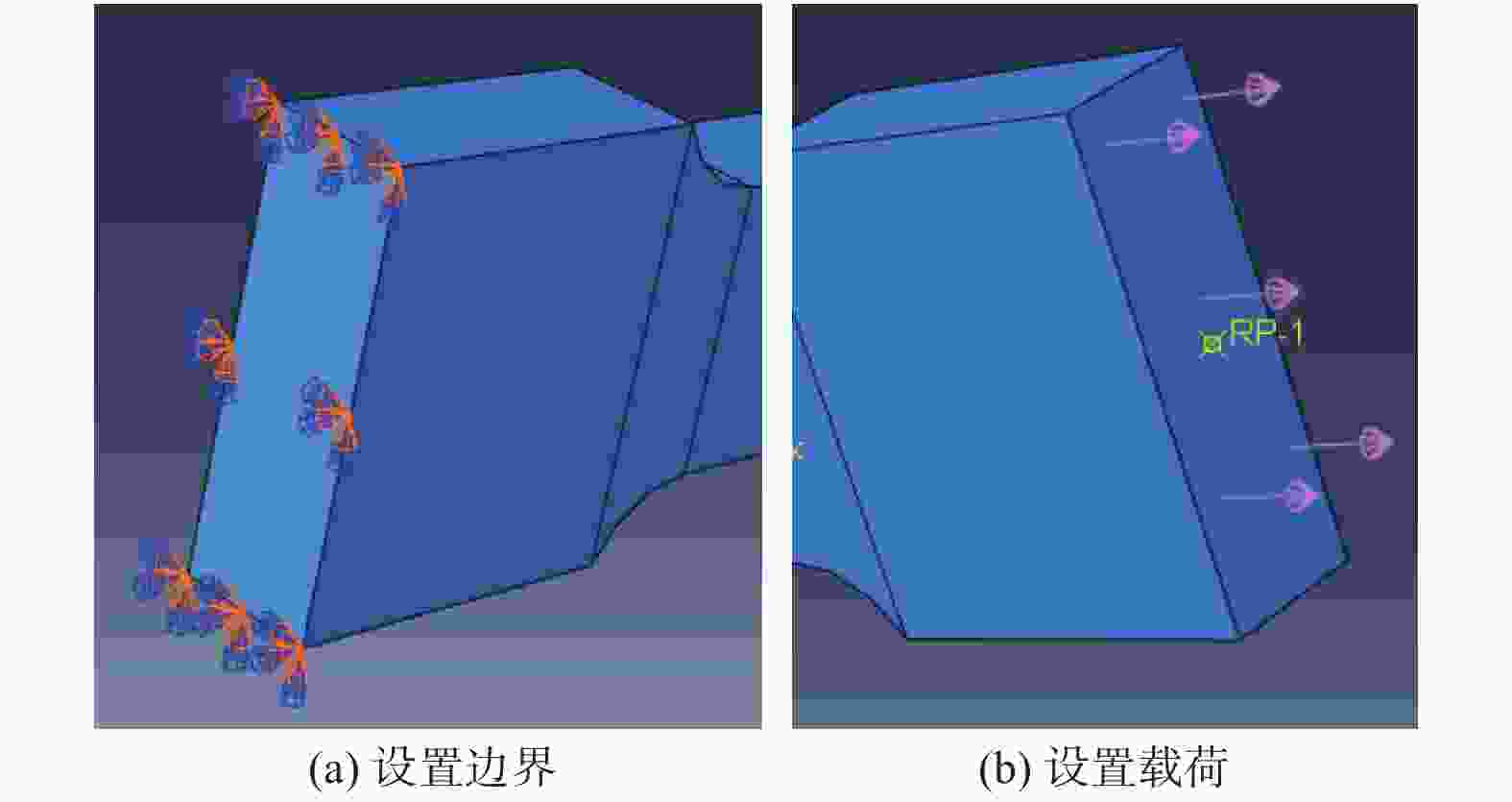
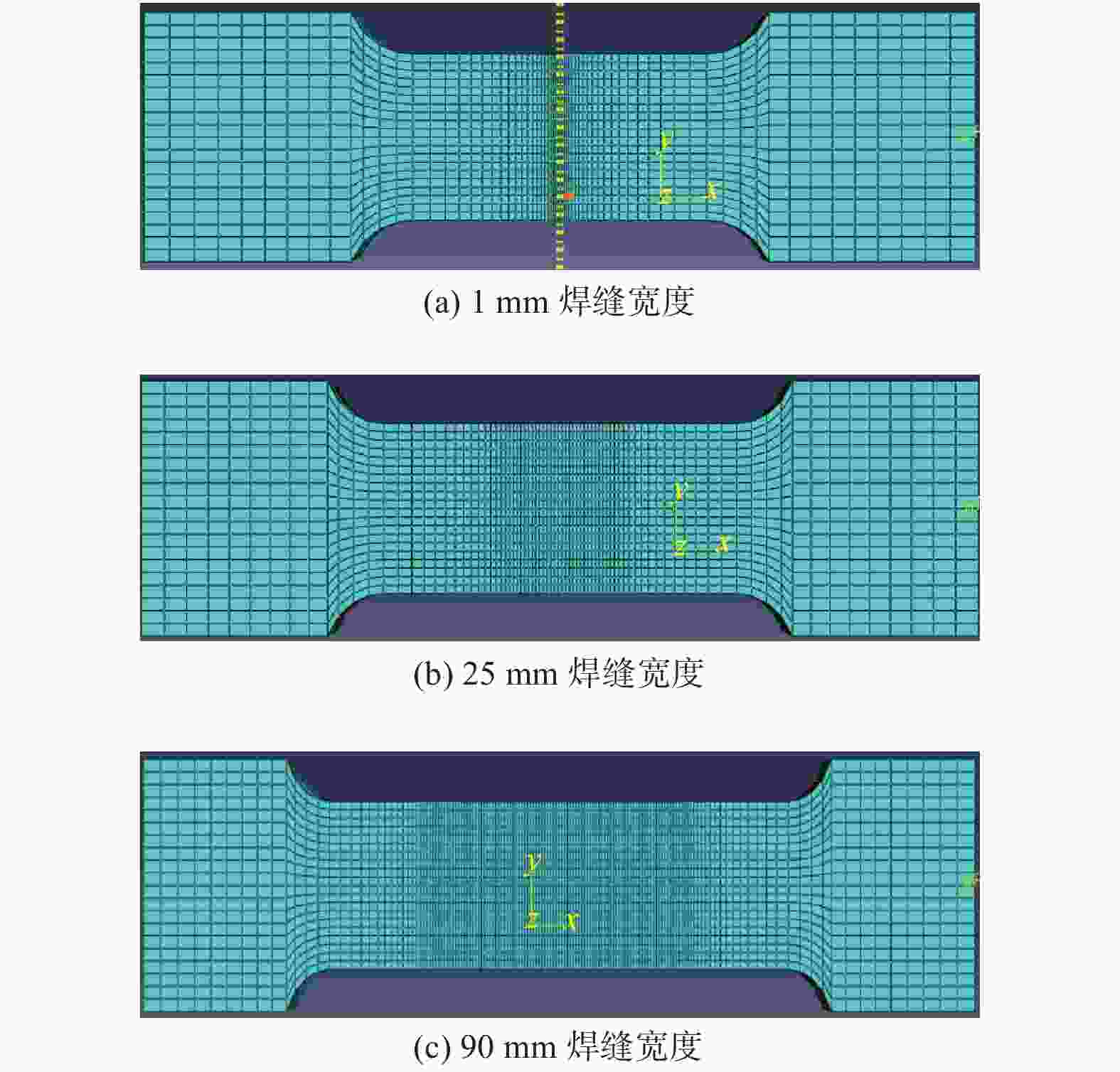
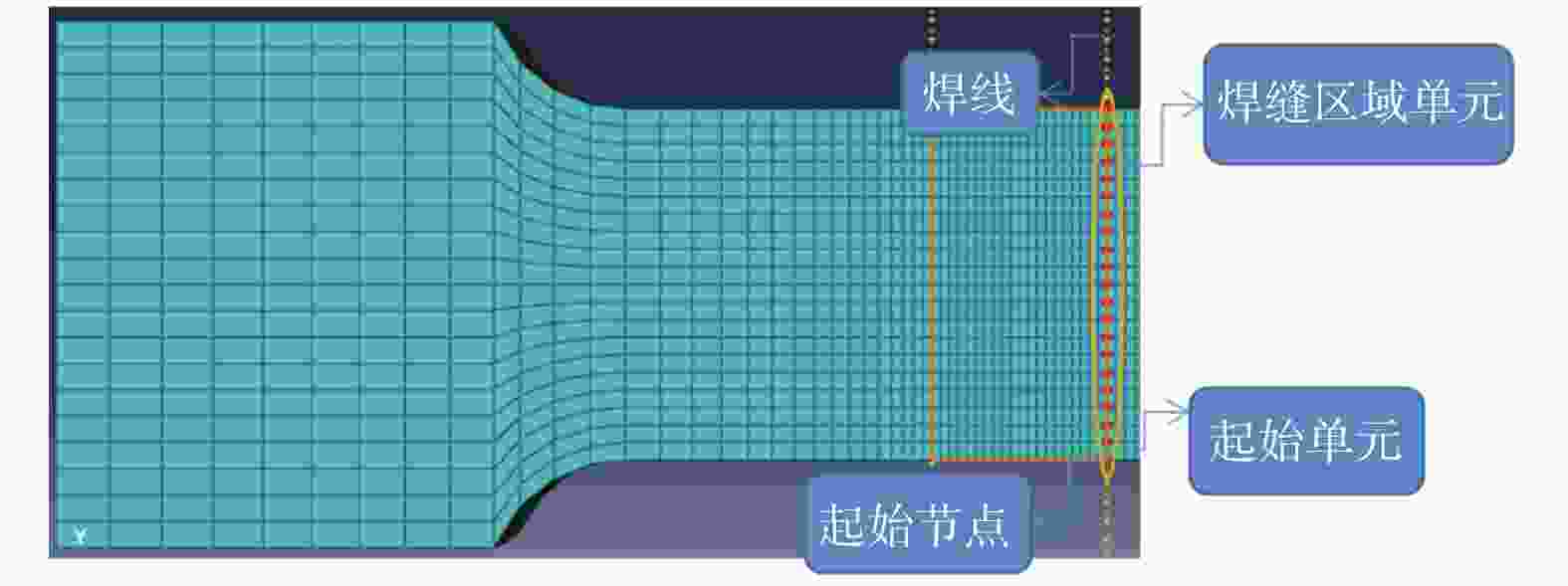
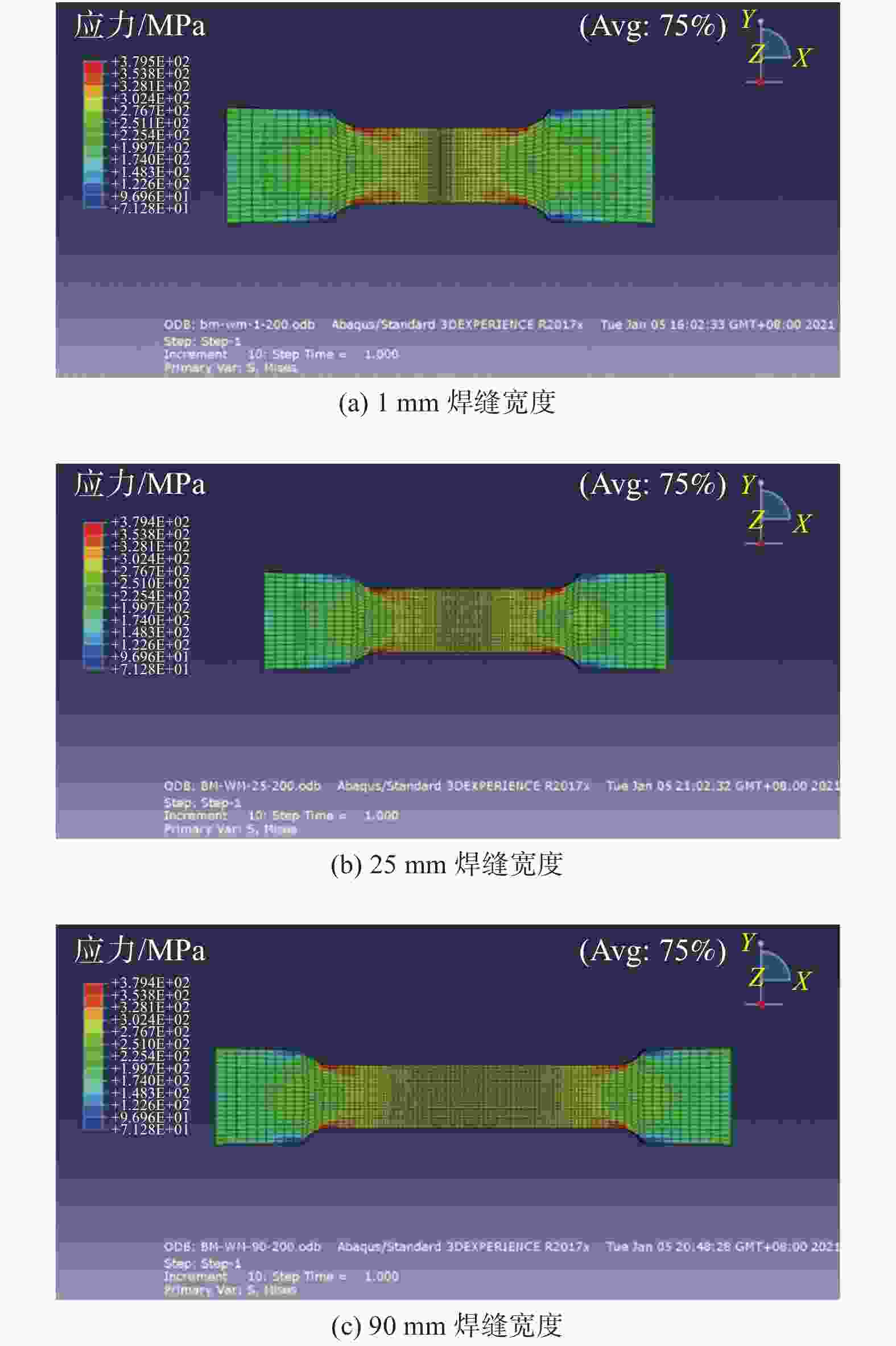
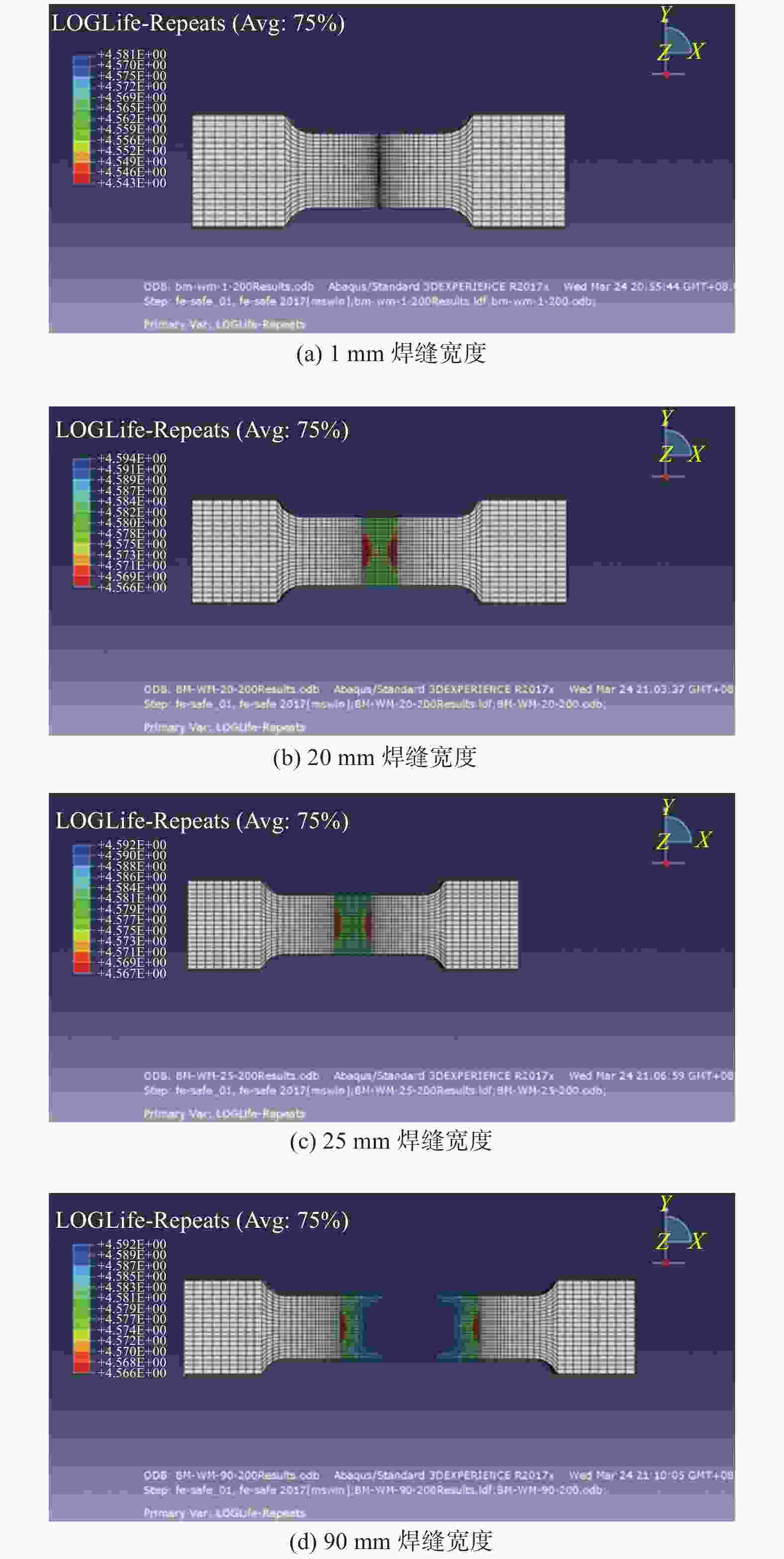
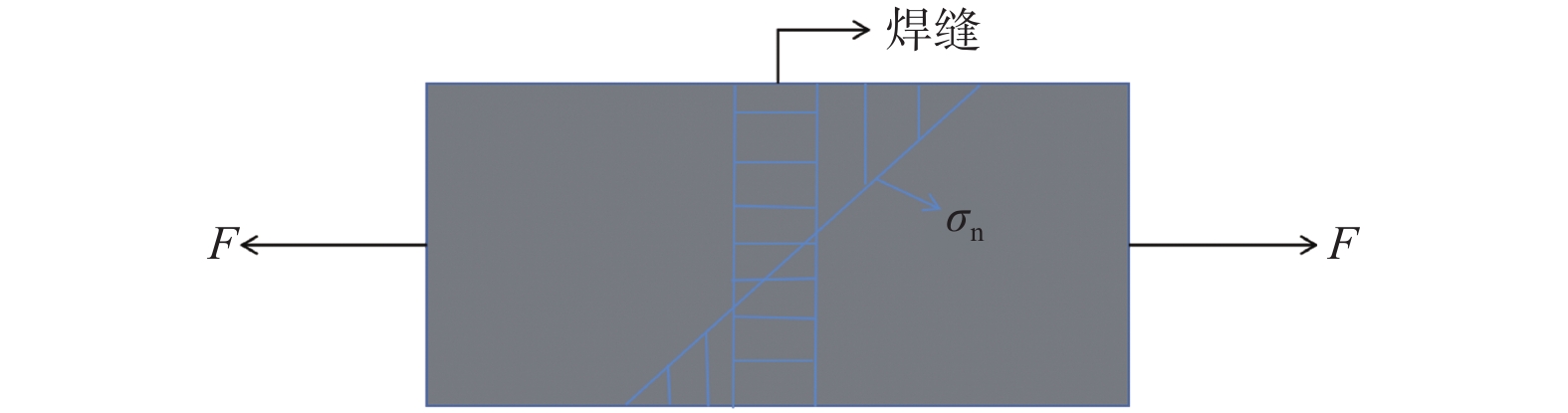
摘要: 基于建立的Q235A钢对接接头3D实体模型进行有限元分析,模拟焊缝宽度对焊缝对接接头疲劳强度的影响. 使用ABAQUS CAE软件建立8种不同焊缝宽度几何模型,对模型进行网格划分并计算结构应力. 基于网格不敏感结构应力法分析对接接头的应力,使用ABAQUS软件中Fe-safe模型进行疲劳寿命预测. 模拟结果表明:对接接头焊缝的疲劳性能先随焊缝宽度增大而增强,随着焊缝宽度的继续增大,疲劳性能反而有逐渐减弱的趋势.
-
关键词:
- 对接接头 /
- 焊缝宽度 /
- 疲劳寿命 /
- 网格不敏感结构应力法
Abstract: Finite element analysis based on the establishment of a 3D solid model of the butt joint of Q235A steel was conducted, and the influence of weld width on the fatigue strength of the butt joint was simulated. Eight geometric models of different weld widths were established by ABAQUS CAE software. The meshing of the model was carried out and the structural stress was calculated. The stress of butt joint was analyzed based on mesh insensitive structural stress method. The Fe-safe model of ABAQUS software was used to predict the fatigue life. The simulation results show that the fatigue properties of butt joint weld firstly increase with the increase of weld width, and then gradually decrease with the increase of weld width.-
Key words:
- butt joint /
- weld width /
- fatigue life /
- mesh insensitive structural stress method
-
表 1 材料力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of materials
材料 屈服强度/MPa 抗拉强度/MPa 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 Q235A 225 450 200000 0.3 JM56 430 ( ≥400 ) 480 210000 0.3 表 2 材料化学组成成分
Table 2. Chemical constituents of materials
% 材料 C Mn Si S P Q235A ≤0.220 ≤1.400 ≤0.350 ≤0.050 ≤0.045 JM56 0.060~0.150 1.400~1.850 0.800~1.150 ≤0.025 ≤0.035 表 3 对接接头应力集中系数
Table 3. Stress concentration factors of butt joints
应力集中系数 焊缝宽度/mm 1 10 20 25 30 50 70 90 SCF 1.535 1.521 1.517 1.516 1.517 1.525 1.526 1.529 表 4 疲劳强度与性能
Table 4. Fatigue strength and performance
焊缝宽度/mm 应力/MPa 疲劳寿命/次 损伤比 累积损伤比 1 200 4.226E+06 0.156 0.384 210 3.486E+06 0.096 220 3.149E+06 0.132 10 200 4.380E+06 0.150 0.371 210 3.621E+06 0.091 220 3.235E+06 0.130 20 200 4.558E+06 0.145 0.359 210 3.691E+06 0.085 220 3.352E+06 0.129 25 200 4.571E+06 0.143 0.348 210 3.721E+06 0.081 220 3.345E+06 0.124 30 200 4.550E+06 0.145 0.359 210 3.658E+06 0.086 220 3.262E+06 0.128 50 200 4.465E+06 0.148 0.368 210 3.436E+06 0.090 220 3.165E+06 0.130 70 200 4.454E+06 0.148 0.371 210 3.398E+06 0.091 220 3.109E+06 0.132 90 200 4.332E+06 0.151 0.378 210 3.298E+06 0.092 220 3.168E+06 0.135 -
[1] 陈传尧. 疲劳与断裂[M]. 武汉: 华中科技大学出版社, 2002: 1 − 90. [2] 方洪渊. 焊接结构学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2008: 78 − 112. [3] BONI L, LANCIOTTI A, POLESE C. “Size effect” in the fatigue behavior of Friction Stir Welded plates[J] . International Journal of Fatigue,2015,80(3):238 − 245. [4] JAURRIETA M A, ALONSO A, CHICA J A, et al. Tubular Structures X[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Tubular Structures. Abingdon: TaylorFrancis, 2017: 365 – 374. [5] 张欣, 高世一, 吴文兵, 等. 焊缝余高对焊接接头疲劳寿命影响的有限元分析[J] . 热加工工艺,2017,46(1):189 − 194. [6] 冯继军. 焊接结构件的疲劳分析[J] . 焊接技术,2017,46(6):78 − 80. [7] DONG P S, HONG J K,JESUS A M. Analysis of recent fatigue data using the structural stress procedure in ASME Div 2 rewrite[J] . Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology,2007,19(3):355 − 362. [8] DONG P. A structural stress definition and numerical implementation for fatigue analysis of welded joints[J] . International Journal of Fatigue,2001,23(10):865 − 876. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(01)00055-X [9] ZERBST U, HENSEL J. Application of fracture mechanics to weld fatigue[J] . International Journal of Fatigue,2020,2(3):139 − 141. [10] 李林平, 梁军, 赵雷, 等. 高、低匹配对G115/T92异种钢接头组织与力学性能的影响[J] . 机械工程材料,2018,42(10):51 − 57. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl201810010 [11] 吴松林, 薛钢, 曲占元. 低匹配对接接头尺寸设计原则研究[J] . 材料开发与应用,2014,29(1):14 − 17. [12] 赵峰. 基于网格不敏感结构应力的铝合金焊接接头疲劳性能分析[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学, 2013. [13] 罗超, 张锦华, 王琰, 等. 板厚对不锈钢车体激光叠焊接头抗剪强度和疲劳强度的影响[J] . 焊接,2021(2):57 − 61. -





 下载:
下载: