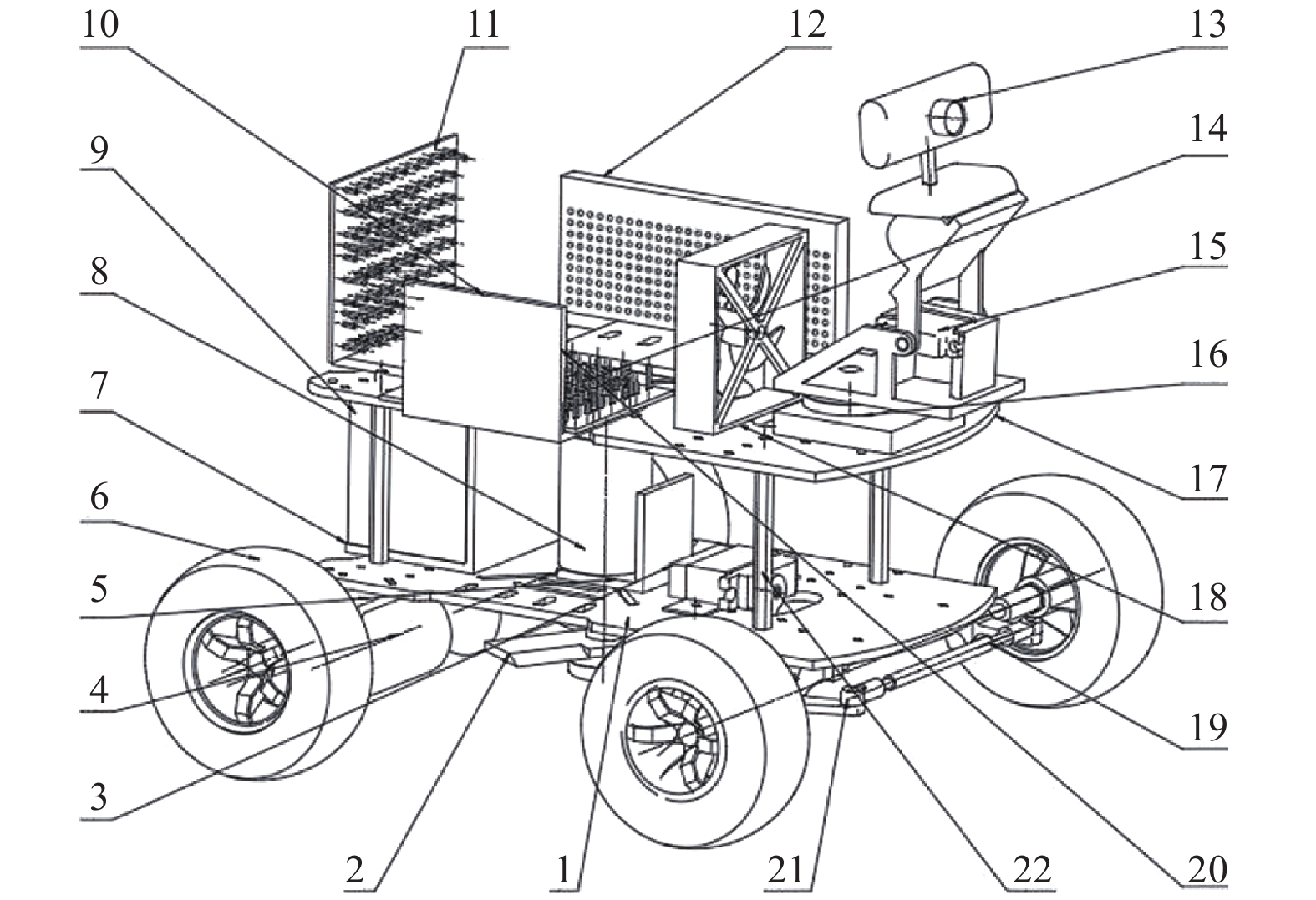
Research on Grass Recognition of Mowing System Based on Machine Vision
-
摘要: 为使割草机系统实现青草识别,规划割草机运动路径并自动进行割草工作,采用单步多框检测器(SSD)目标检测算法和卷积神经网络框架(Caffe)在工作机上训练青草识别模型. 通过树莓派(RPi)拍摄割草场地照片并传送到工作机,工作机计算青草在图片中的坐标值并返回至树莓派,树莓派再根据青草的坐标值自动计算车桥转动角度和后轮电动机运行时间及方向,调动割草机机械部分进行割草作业. 实验结果表明,较之于传统的人工机械割草机或围栏式割草机,训练的青草识别模型能正常识别青草,割草机能较好地自动规划割草路径,具有一定除草效果. 研究结果实现了机器视觉和传统机械的结合,为今后智能机械的研究提供一定思路.
-
关键词:
- 青草识别 /
- 单步多框检测器(SSD)模型 /
- 机器视觉 /
- 三维建模
Abstract: In order to realize the grass recognition in the mower system, plan the moving path of the mower and cut the grass automatically, the target detection algorithm of single shot multibox detector (SSD) and convolutional architecture for fast feature embedding (Caffe) were used to train the grass recognition model on the mower. Pictures of grass cutting field were taken by raspberry pie (RPi) and sent to the working machine. The coordinate values of the grass in the picture were calculated by the working machine and returned to raspberry pie, and the axle rotation angle, the running time and direction of the rear wheel motor according to the coordinate value of the grass were calculated automatically, and then the mechanical parts of the mower were mobilized to mow the grass. The experimental results show that compared with the traditional manual mechanical mower or fence mower, the trained grass recognition model can recognize the grass normally, and the mower can better plan the mowing path automatically, which has a certain weeding effect. The research results realize the combination of machine vision and traditional machinery, and provide some ideas for the future research of intelligent machinery. -
表 1 检测模型性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of detection models
检测算法 Map FPS 批尺寸 Boxes 输入归结 Faster R-CNN(VGG16) 73.2 7 1 6000 1000 × 600 Fast YOLO 52.7 155 1 98 448 × 448 YOLO(VGG16) 66.4 21 1 98 448 × 448 SSD300 74.3 46 1 8732 300 × 300 SSD512 76.8 19 1 24564 512 × 512 SSD300 74.3 59 8 8732 300 × 300 -
[1] 马振峰. 基于智能视觉的割草机自动控制系统设计[J] . 计算机测量与控制,2018,26(7):84 − 87, 142. [2] 徐伟锋, 刘山. 基于PLC的智能割草机器人控制系统[J] . 农业工程,2020,10(1):22 − 25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2020.01.007 [3] 谢忠华. 基于视觉导航的割草机器人运动控制[J] . 农业工程,2016,6(5):30 − 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1795.2016.05.012 [4] 马超. 浅谈我国田间机械除草现状及发展趋势[C]//中国农业机械学会第四届青年学术年会论文集. 天津: 中国农业机械学会, 2007. [5] 郭亭亭, 杨然兵, 李娟, 等. 机器视觉喷药机器人的研发[J] . 中国农机化学报,2015,36(5):215 − 219. [6] 高彦杰, 于子叶. 深度学习: 核心技术、工具与案例解析[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2018. [7] 彭红星, 黄博, 邵园园, 等. 自然环境下多类水果采摘目标识别的通用改进SSD模型[J] . 农业工程学报,2018,34(16):155 − 162. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.16.020 [8] IAN G, YOSHUA B, AARON C. 深度学习[M]. 赵申剑, 黎彧君, 符天凡, 等译. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2017. [9] Liu Wei, Anguelov Dragomir, Erhan. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector[J]. 2015. [10] 周瑶. 基于深度学习的舰船目标检测与识别[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2018. [11] 赵杰, 胡浩然, 孙启智, 等. 改进果蝇算法的运输车辆路径规划[J] . 黑龙江科技大学学报,2020,30(2):187 − 192, 204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-7262.2020.02.013 [12] 代峰燕, 高庆珊, 陈家庆, 等. 储油罐清洗机器人全覆盖路径规划研究[J] . 机械设计与制造,2020(2):263 − 266. [13] XU Y, GUAN G F, SONG Q W, et al. Heuristic and random search algorithm in optimization of route planning for robot’s geomagnetic navigation[J] . Computer Communications,2020,154:12 − 17. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2020.02.043 -






 下载:
下载: