Numerical analysis of fully coupled thermoporoelastic behavior of two-dimensional saturated porous media flat plate under LTNE condition
-
摘要:
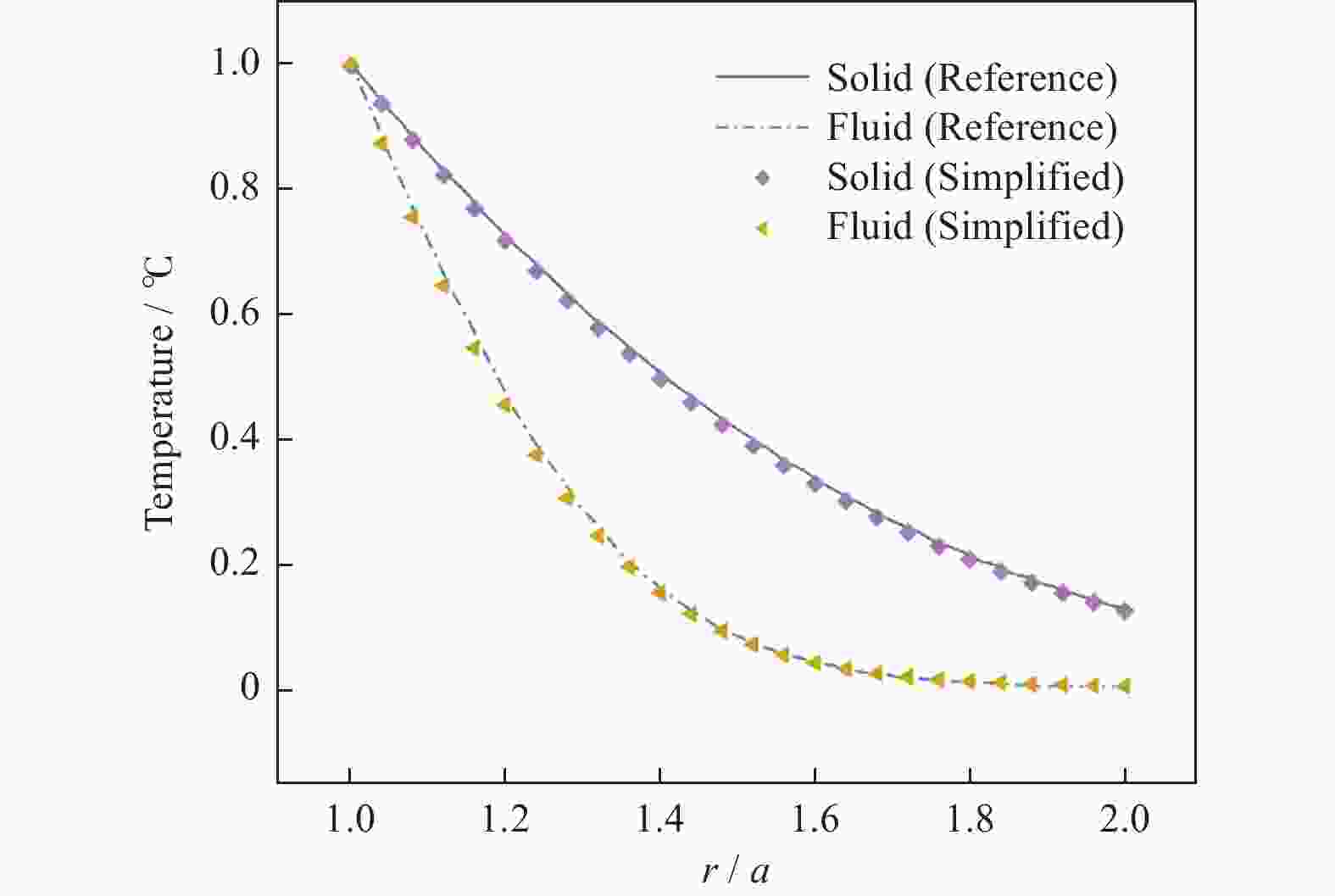
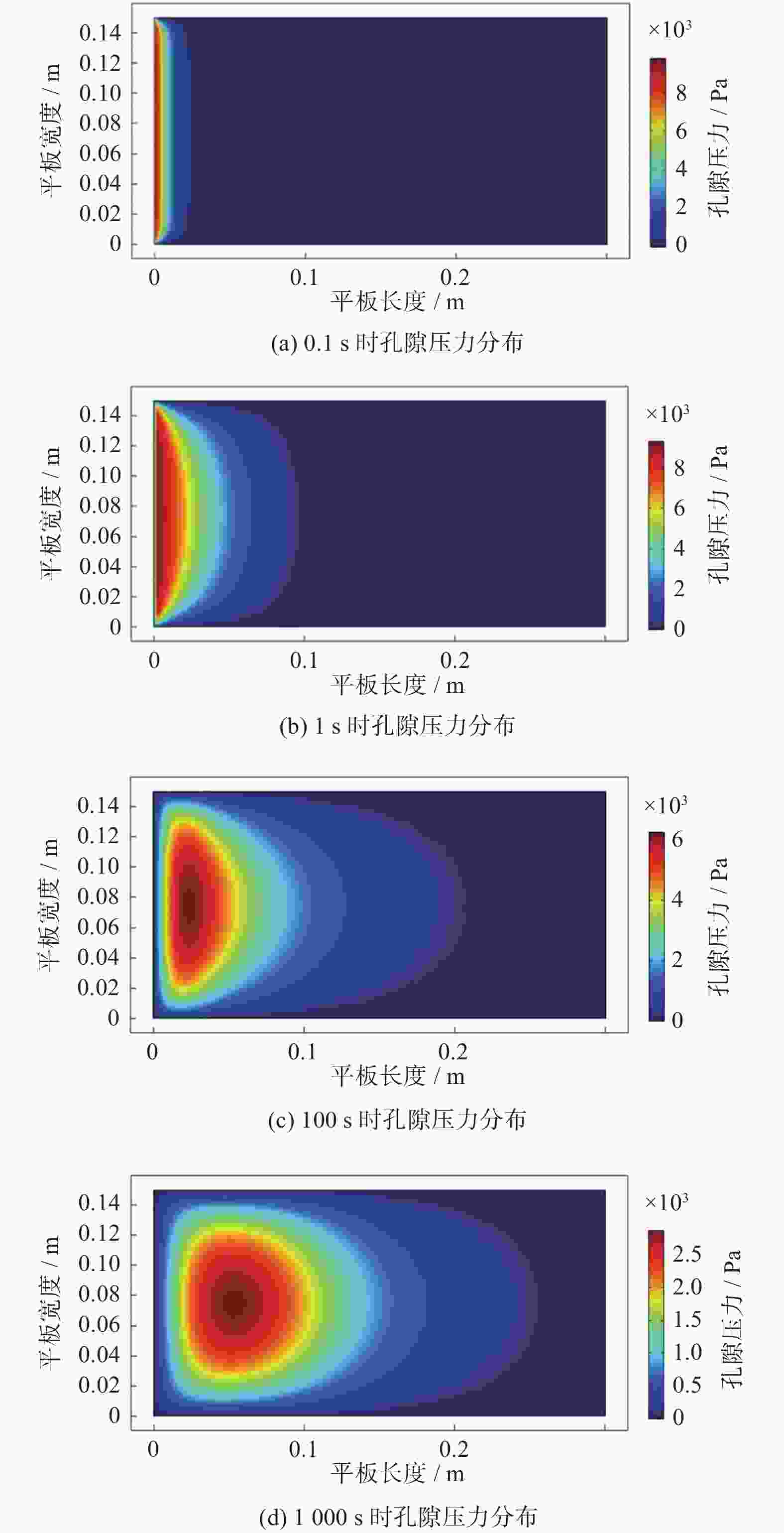
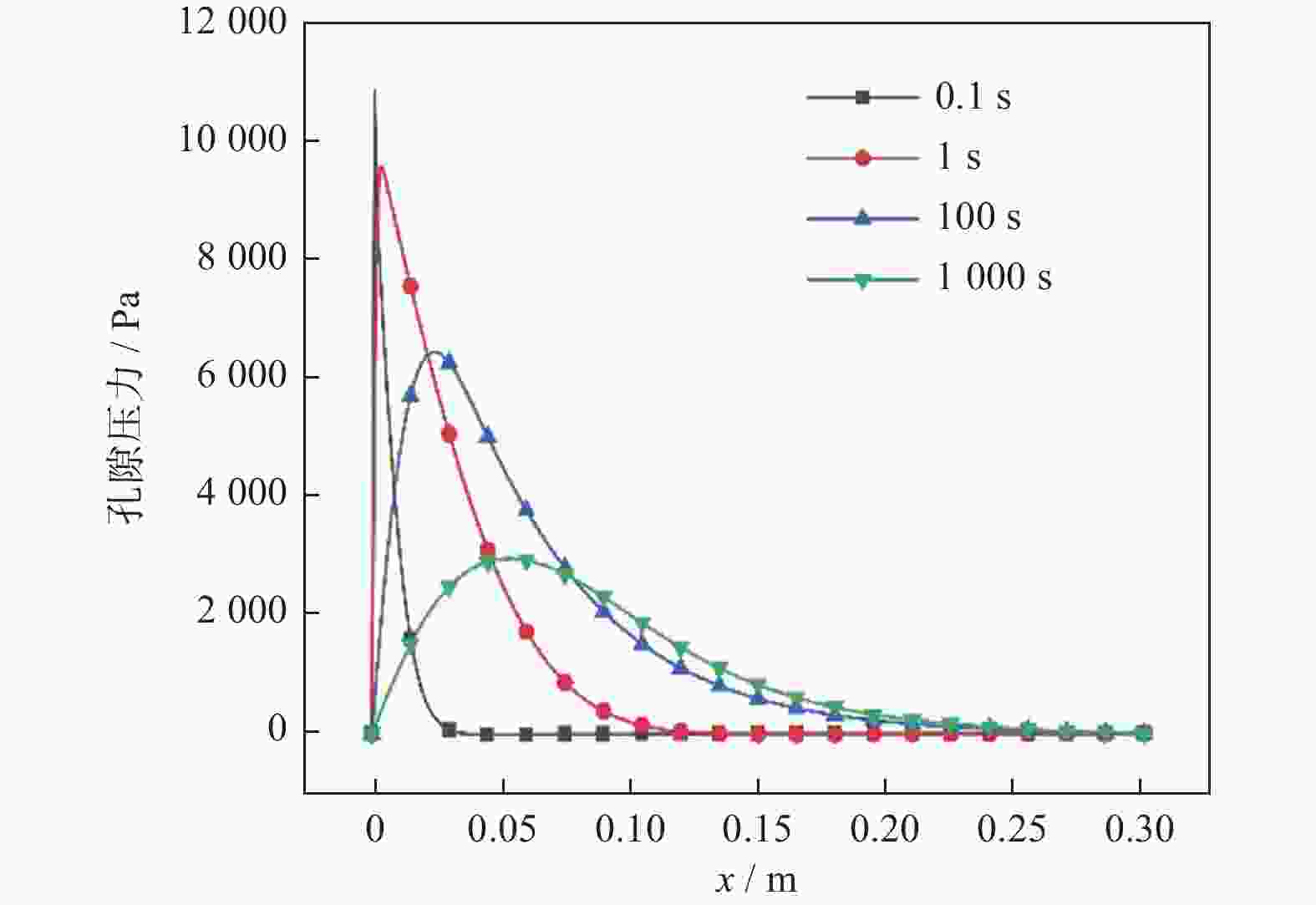
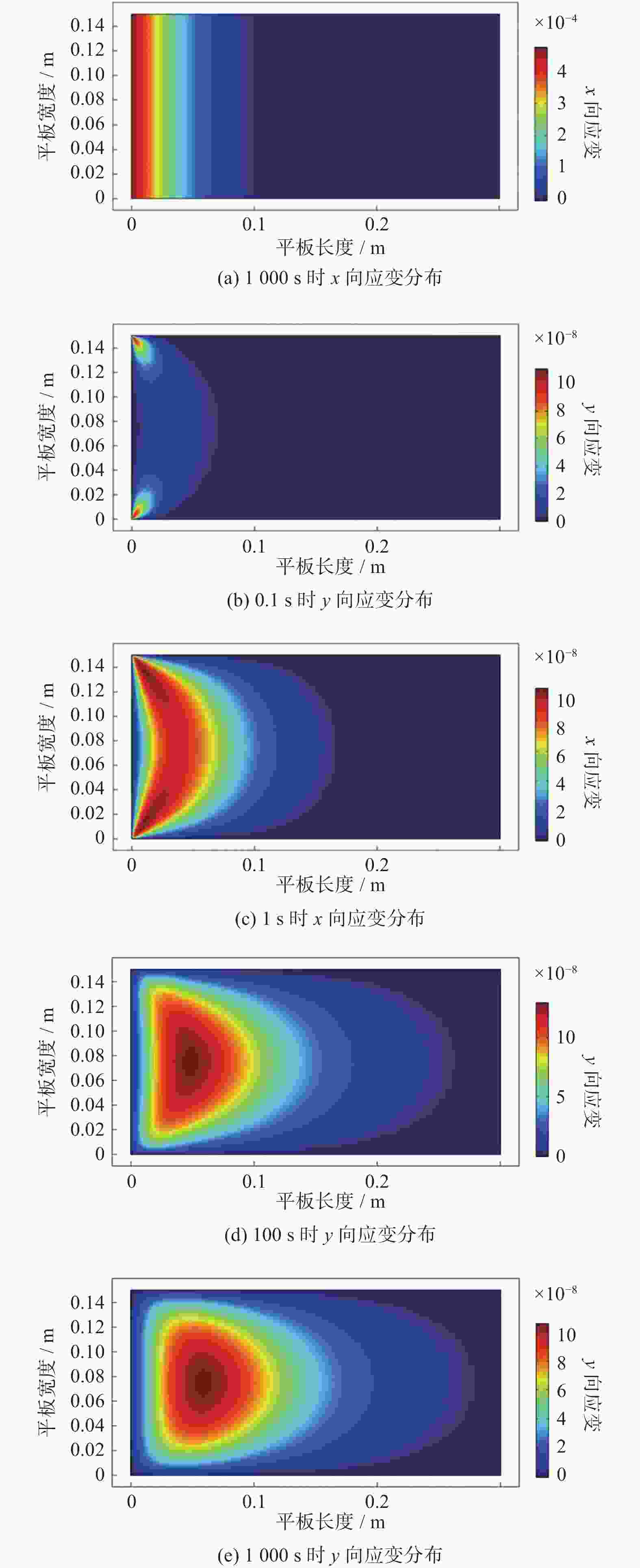
针对目前多孔介质热流固耦合数学模型多为不完全耦合模型,且物理模型多为一维或一维轴对称模型的现状,对二维饱和多孔介质平板热流固完全耦合问题进行数学建模和数值分析. 采用强耦合方式实现热流固3个物理场的完全耦合. 在平板左侧施加30 ℃流体和固体温度边界条件及固定位移边界条件,平板其他边界温度场和位移场假设为自然边界条件,平板四周加载0 Pa的孔隙压力边界条件. 利用COMSOL Multiphysics有限元分析软件的偏微分方程(PDEs)模式实现上述完全耦合模型的求解,得到渗流场、应变场以及双温度场的数值解. 数值结果表明,随时间增加,流体和固体温度、应变及孔隙压力沿x轴方向传递,同时发现x轴方向应变远大于y轴方向应变. 此外,随时间增加,y轴方向应变和孔隙压力最大值逐渐减小. 研究建立的数学模型和数值解有助于深入认识二维饱和多孔介质热流固完全耦合力学行为.
Abstract:Most of current thermoporoelastic models of porous media are incomplete coupled ones, and the physical models mostly adopt one-dimensional or one-dimensional axisymmetric models. In view of this point, a fully coupled model of a two-dimensional saturated porous media flat plate was presented and the corresponding numerical simulation was carried out. The fully coupled of three physical fields (heat, fluid flow, and solid stress/deformation) were realized by means of strong coupling. The boundary conditiorns were assumed as follows: As for the temperature field and the displacement field, 30 ℃ fluid and solid temperature boundary conditions and fixed displacement boundary conditions were exerted on the left side of the plate, and naturual boundary conditions were prescribed on the other sides of the plate. Meanwhile, 0 Pa pore pressure boundary conditions were loaded around the plate. The numerical solutions of flow field, strain field and two temperature fields were obtained by the PDEs pattern of COMSOL Multiphysics FEA software. Numerical results showed that fluid and solid temperature, strain and pore pressure transfer along the x-axis direction with increasing time, and the strain in the x-direction is much larger than that in the y-direction. In addition, it was found that the maximum values of y-direction strain and pore pressure gradually decrease with time. The presented mathematical model and numerical solutions are of benefit to provide deep insights into the fully thermoporoelastic coupled behavior of two-dimensional saturated porous media.
-
表 1 不同网格数下孔隙压力的相对误差
Table 1. Relative error of pore pressure under different grid numbers
网格数量
坐标$ 180\times 80 $ $ 190 \times 90 $ $ 200 \times 100 $ (0.1,0.075) $ 7.963\;73 \times {10^{ - 8}} $ $ 7.963\;66\times {10}^{-8} $ $ 7.963\;11 \times {10^{ - 8}} $ y向应变相对误差/% $- 0.000\;88$ $- 0.006\;91$ (0.2,0.075) $ {\text{1}}{{.453\;65}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 8}} $ $ {\text{1}}{{.453\;72}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 8}} $ $ {\text{1}}{{.453\;39}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 8}} $ y向应变相对误差/% $0.00482$ $- 0.022\;71$ (0.3,0.075) $ {\text{2}}{{.418\;16}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 9}} $ $ {\text{2}}{{.418\;43}} \times {\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 9}} $ $ \text{2}{.417\;34}\times {\text{10}}^{-9} $ y向应变相对误差/% $0.01116$ $- 0.04509$ 表 2 流体和固体物性参数
Table 2. Fluid and solid physical parameters
参数/单位 取值 Lame常数$ G $/$ {\text{GPa}} $ $ 6.8 $ Lame常数$ \lambda $/$ \text{GPa} $ $ 3.8 $ Biot系数$ {\alpha }_{\text{B}} $ $ 0.74 $ 流度c/(m2·s−1) $ 1.4\times {10}^{-3} $ 排空体积模量$ K/{\text{GPa}} $ $ 8.4 $ 参考温度$ {T_{\text{0}}/{\textit{℃ }}} $ $ 30 $ 固体密度$ {\rho _{\text{s}}} $/$ ({\text{kg}}\cdot{{\text{m}}^{{-3}}}) $ $ 2\;600 $ 流体密度$ {\rho _{\text{f}}} $/$ ({\rm{kg\cdot m}}^{{-3}} )$ $ 1\;000 $ 孔隙度$ \phi $ $ 0.4 $ 固体体积热膨胀系数$ {\beta _{\text{T}}} $/K−1 $ 3.3 \times {10^{ - 5}} $ 固体温度对孔隙压力的贡献系数$ {a_{ {P }{ {T }_{\text{S} } } } } $/Pa−1 $ - 7.17 \times {10^{ - 5}} $ 流体温度对孔隙压力的贡献系数${a_{ {P }{ {T }_{\text{f} } } }}$/Pa−1 $ - 4.78 \times {10^{ - 5}} $ 固体热导率$ {k_{\text{s}}} $/(W·(m·K)−1) $ 2.4 $ 流体热导率$ {k_{\text{f}}} $/(W·(m·K)−1) $ 0.6 $ 恒容热容$ C_{\text{s}}^{\left( {\text{v}} \right)} $/(J·(kg·K)−1) $ 920 $ 恒压热容$ {C}_{\text{f}}^{\left(\text{p}\right)} $/(J·(kg·K)−1) $ 4\;200 $ 固液界面传热系数$ h $/(W·(m3·K)−1) $ 50 $ 孔隙压力随时间变化量的贡献系数${a}_{PP }$/Pa−1 $ 1.4\times {10}^{-3} $ -
[1] JIANG P X, REN Z P. Numerical investigation of forced convection heat transfer in porous media using a thermal non-equilibrium model[J] . International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow,2001,22:102 − 110. doi: 10.1016/S0142-727X(00)00066-7 [2] VAFAI K, KIM S J. Forced convection in a channel filled with a porous medium: An exact solution[J] . Journal of Heat Transfer,1989,111:1103 − 1106. doi: 10.1115/1.3250779 [3] NIELD D A, BEJAN A. Convection in porous media [M]. fifth edition. Berlin: Springer, 2017. [4] 马德正, 李培超, 张恒运. 锂离子电池隔膜在压缩过程中的流固耦合效应[J] . 储能科学与技术,2021,10(2):483 − 490. [5] NAIR R, ABOUSLEIMAN Y, ZAMAN M. A finite element thermoporoelastic model for dualporosity media[J] . International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,2004,28:875 − 898. doi: 10.1002/nag.336 [6] WU B S, ZHANG X, JEFFREY R G, et al. A semi-analytic solution of a wellbore in a nonisothermal low-permeability porous medium under non-hydrostatic stresses[J] . International Journal of Solids and Structures,2012,49(13):1472 − 1484. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.02.035 [7] ABOUSLEIMAN Y, EKBOTE S. Solutions for the inclined borehole in a thermoporoelastic transversely isotropic medium[J] . Journal of Applied Mechanics,2005,72(1):102 − 114. doi: 10.1115/1.1825433 [8] 路朗, 辛成运, 刘忠鑫. 多孔介质局部非热平衡模型研究综述[J] . 热能动力工程,2019,34(7):1 − 8. [9] 陈帅, 李波波, 张尧, 等. 页岩气储层微观渗流机理研究[J] . 中国科学: 技术科学,2021,51(5):580 − 590. [10] LI P C, ZHANG J L, WANG K Y, et al. Heat transfer characteristics of thermally developing forced convection in a porous circular tube with asymmetric entrance temperature under LTNE condition[J] . Applied Thermal Engineering,2019,154:326 − 331. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.03.109 [11] 周峰, 刘琪英, 王晨光, 等. 基于COMSOL的果糖脱水传热传质数值模拟[J] . 太阳能学报,2019,40(6):1677 − 1683. [12] LI P C, ZHANG J L, WANG K Y, et al. Analysis of thermally developing forced convection heat transfer in a porous medium under local thermal non-equilibrium condition: A circular tube with asymmetric entrance temperature[J] . International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2018,127:880 − 889. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.08.081 [13] YUE F L, LI P C, Zhao C Y. Numerical investigation of thermally developing non-Darcy forced convection in a porous circular duct with asymmetric entrance temperature under LTNE condition[J] . Transport in Porous Media,2021,136(2):639 − 655. doi: 10.1007/s11242-020-01533-7 [14] WANG K Y, TAVAKKOLI F, VAFAI K. Analysis of gaseous slip flow in a porous micro-annulus under local thermal non-equilibrium condition: An exact solution[J] . International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2015,89:1331 − 1341. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2015.06.001 [15] KUZNETSOV A V, NIELD D A. Forced convection in a channel partly occupied by a bidisperse porous medium: Asymmetric case [J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2010, 53(23/24): 5167−5175. [16] GAO J J, DENG J G, LAN K, et al. Porothermoelastic effect on wellbore stability in transversely isotropic medium subjected to local thermal non-equilibrium[J] . International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2017,96:66 − 84. [17] YASSER M, MEHDI M. Analytical investigation of heat transfer enhancement in a channel partially filled with a porous material under local thermal non-equilibrium condition[J] . International Journal of Thermal Sciences,2011,50(12):2386 − 2401. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2011.07.008 [18] CHIKH S, BOUMEDIEN A, BOUHADEF K, et al. Analytical solution of non-Darcian forced convection in an annular duct partially filled with a porous medium[J] . International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,1995,38:1543 − 1551. doi: 10.1016/0017-9310(94)00295-7 [19] XU Z G, GONG Q. Numerical investigation on forced convection of tubes partially filled with composite metal foams under local thermal non-equilibrium condition[J] . International Journal of Thermal Sciences,2018,133:1 − 12. [20] TONG F G, JING L R, ZIMMERMAN R W. A fully coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical model for simulating multiphase flow, deformation and heat transfer in buffer material and rock masses[J] . International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences,2010,47(2):205 − 217. [21] LEWIS R W, ROBERTS P J, SCHREFLFLER B A. Finite element modeling of two phase heat and fluid flow in deforming porous media[J] . Transport in Porous Media,1989,4:319 − 334. doi: 10.1007/BF00165778 [22] GELET R, LORET B, KHALILI N. Borehole stability analysis in a thermoporoelastic dual porosity medium[J] . International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences,2012,50:65 − 76. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.12.003 [23] GHASSEMI A, NYGREN A, CHENG A. Effects of heat extraction on fracture aperture: a poro- thermoelastic analysis[J] . Geothermics,2008,37:525 − 539. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2008.06.001 [24] BOER R D. 多孔介质理论发展史上的重要成果 [M]. 刘占芳, 严波, 译. 重庆: 重庆大学出版社, 1995. [25] 孔祥言, 李道伦, 徐献芝, 等. 热−流−固耦合渗流的数学模型研究[J] . 水动力学研究与进展,2005,20(2):269 − 275. [26] ZHANG Z, CHENG X. A fully coupled THM model based on a non-equilibrium thermodynamic approach and its application[J] . International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,2017,41(4):527 − 554. doi: 10.1002/nag.2569 [27] YANG Y, KLAUS G, TOM S. Thermo-osmosis effect in saturated porous medium[J] . Transport in Porous Media,2014,104(2):253 − 271. doi: 10.1007/s11242-014-0332-5 [28] LI W D, CHEN M, JIN Y, et al. Effect of local thermal non-equilibrium on thermoporoelastic response of a borehole in dual-porosity media[J] . Applied Thermal Engineering,2018,142:166 − 183. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.06.055 [29] HE L W, JIN Z H. A local thermal nonequilibrium poroelastic theory for fluid saturated porous media[J] . Journal of Thermal Stresses,2010,33:799 − 813. doi: 10.1080/01495739.2010.482358 -





 下载:
下载: