Modal analysis simulation and experimental research of an industrial robot
-
摘要:
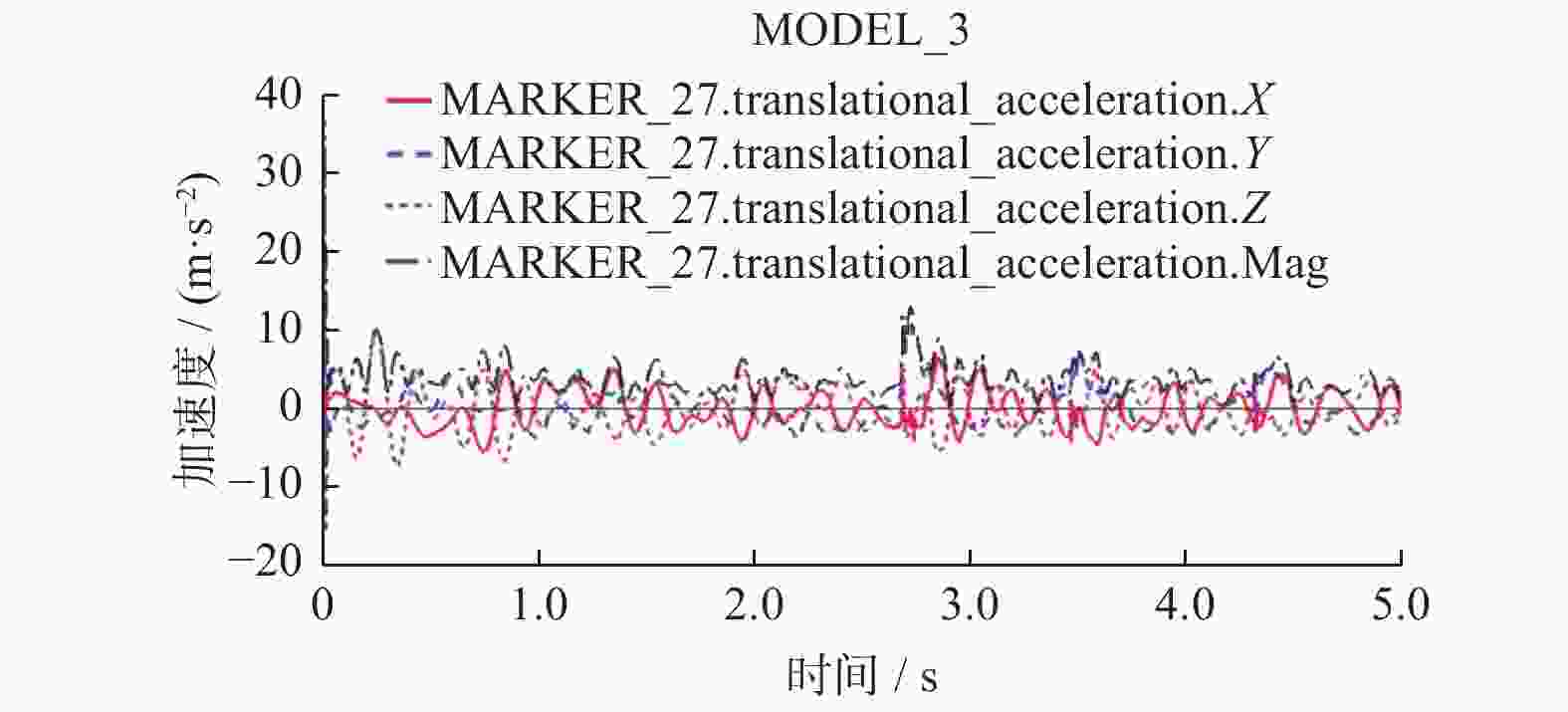
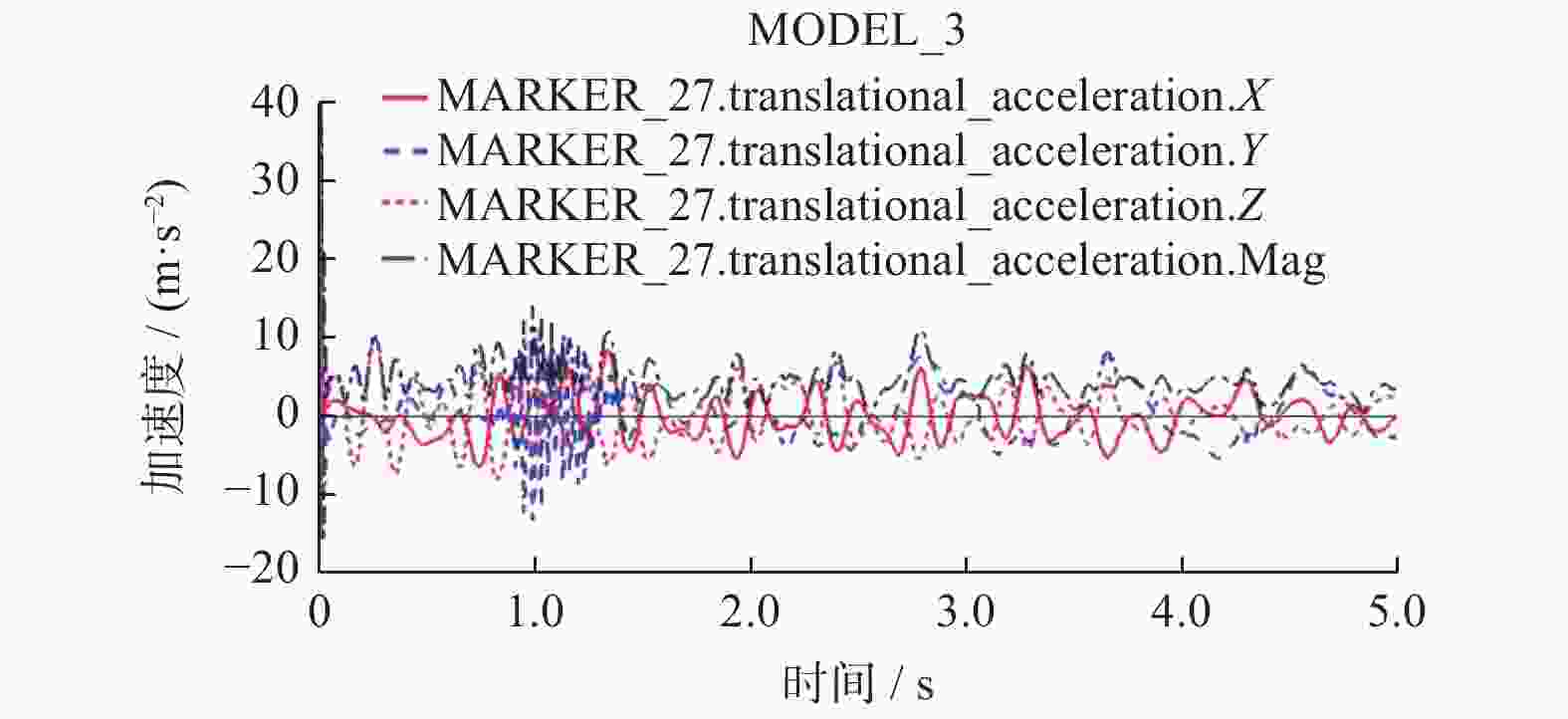
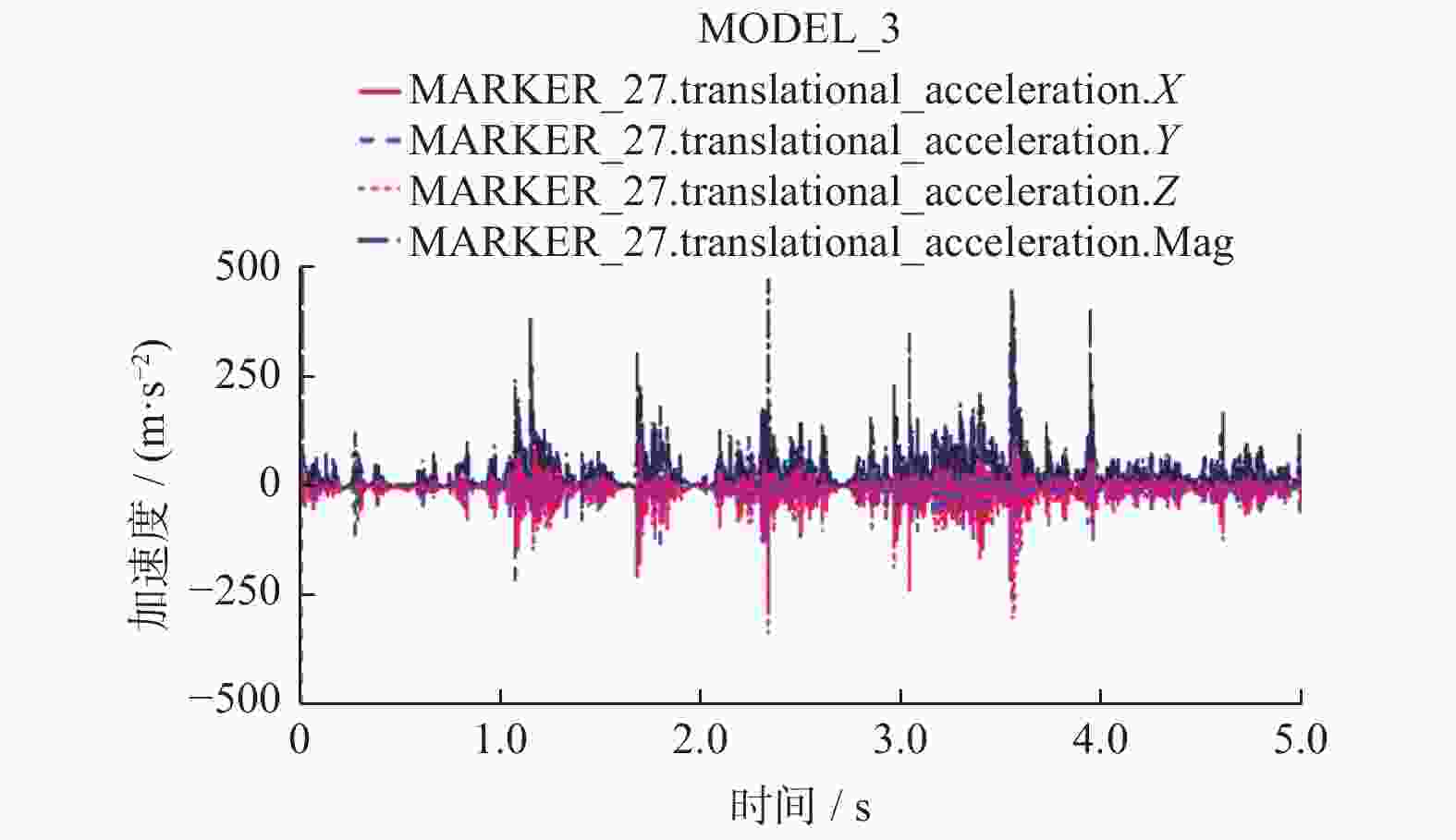
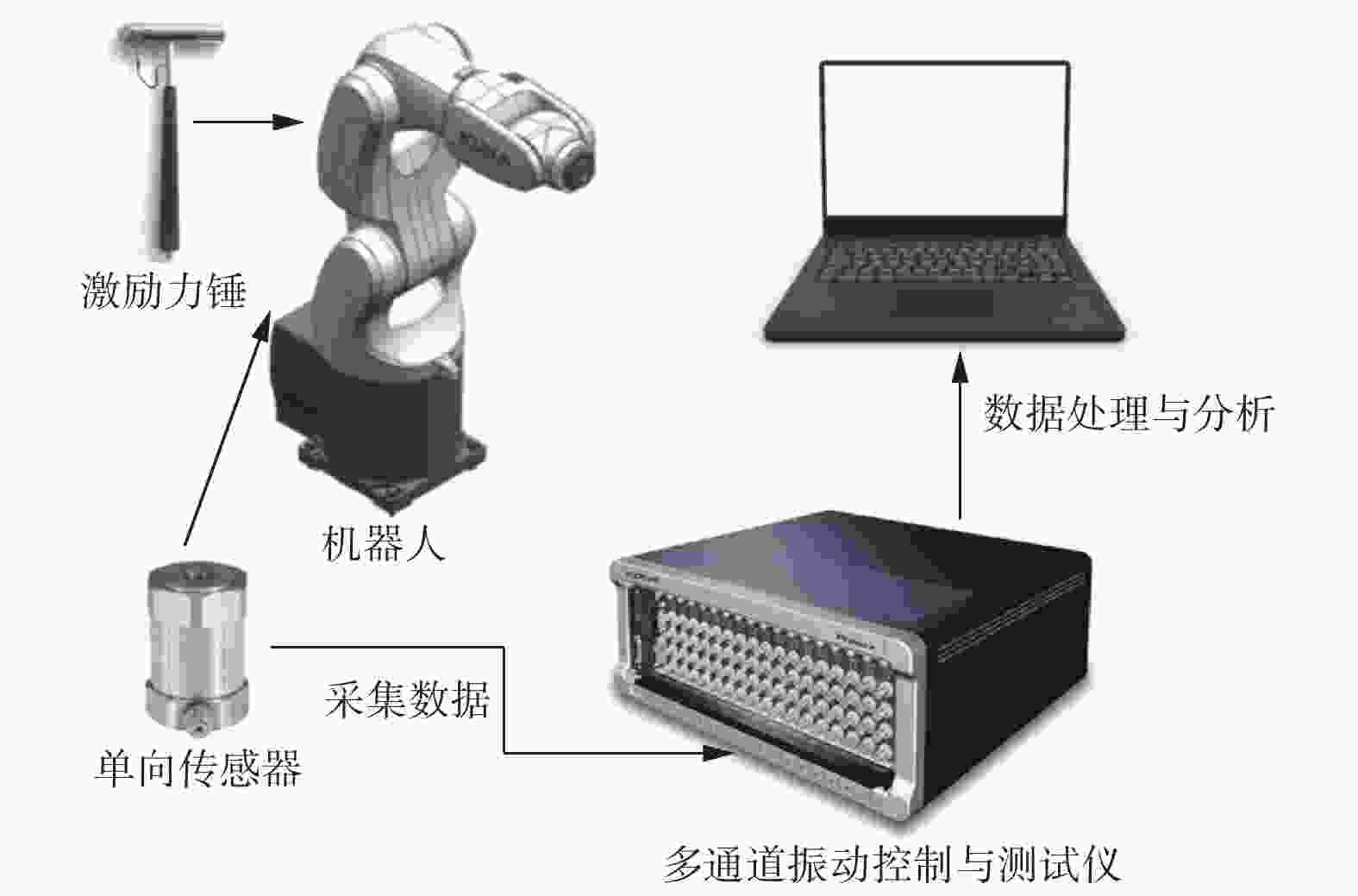
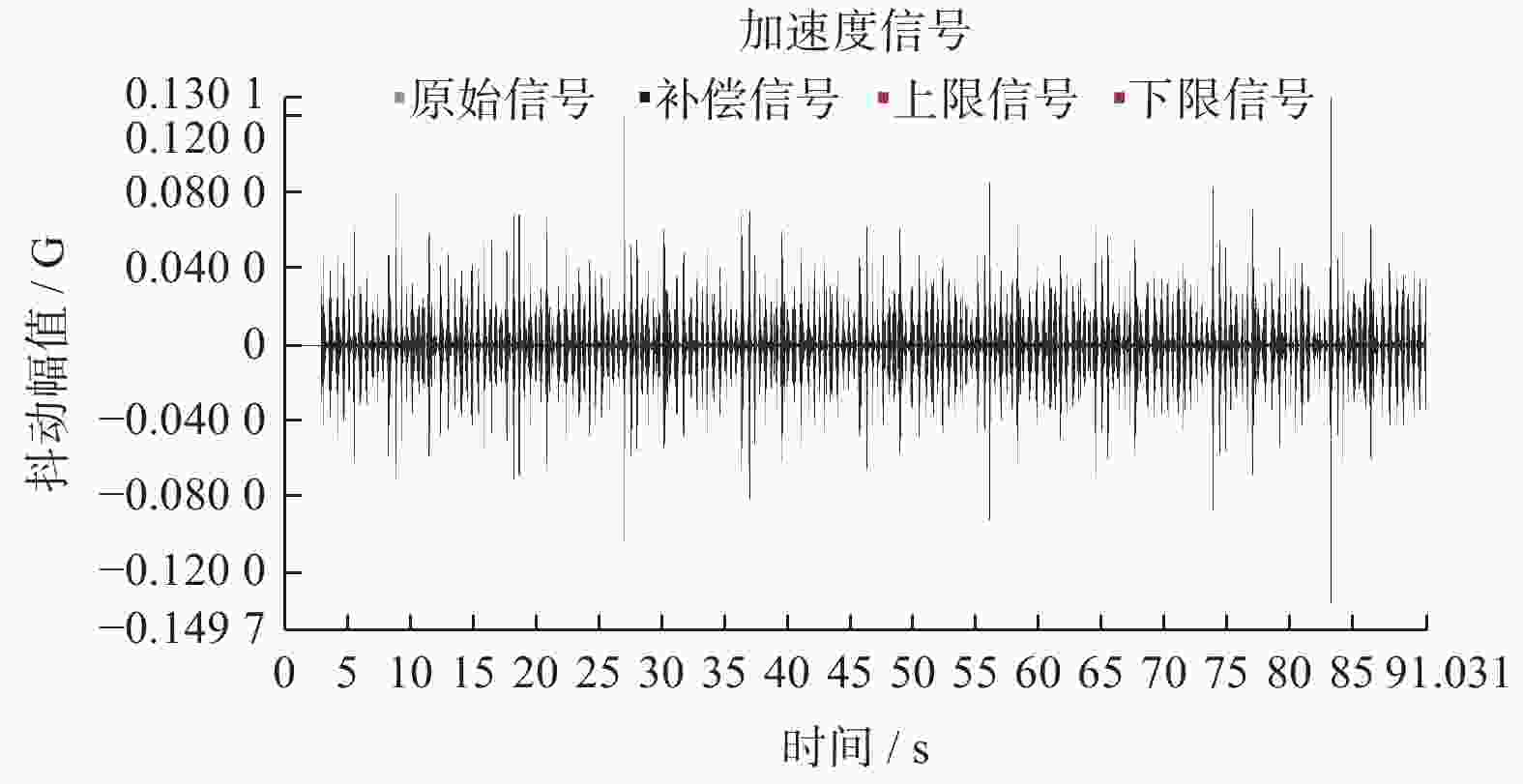
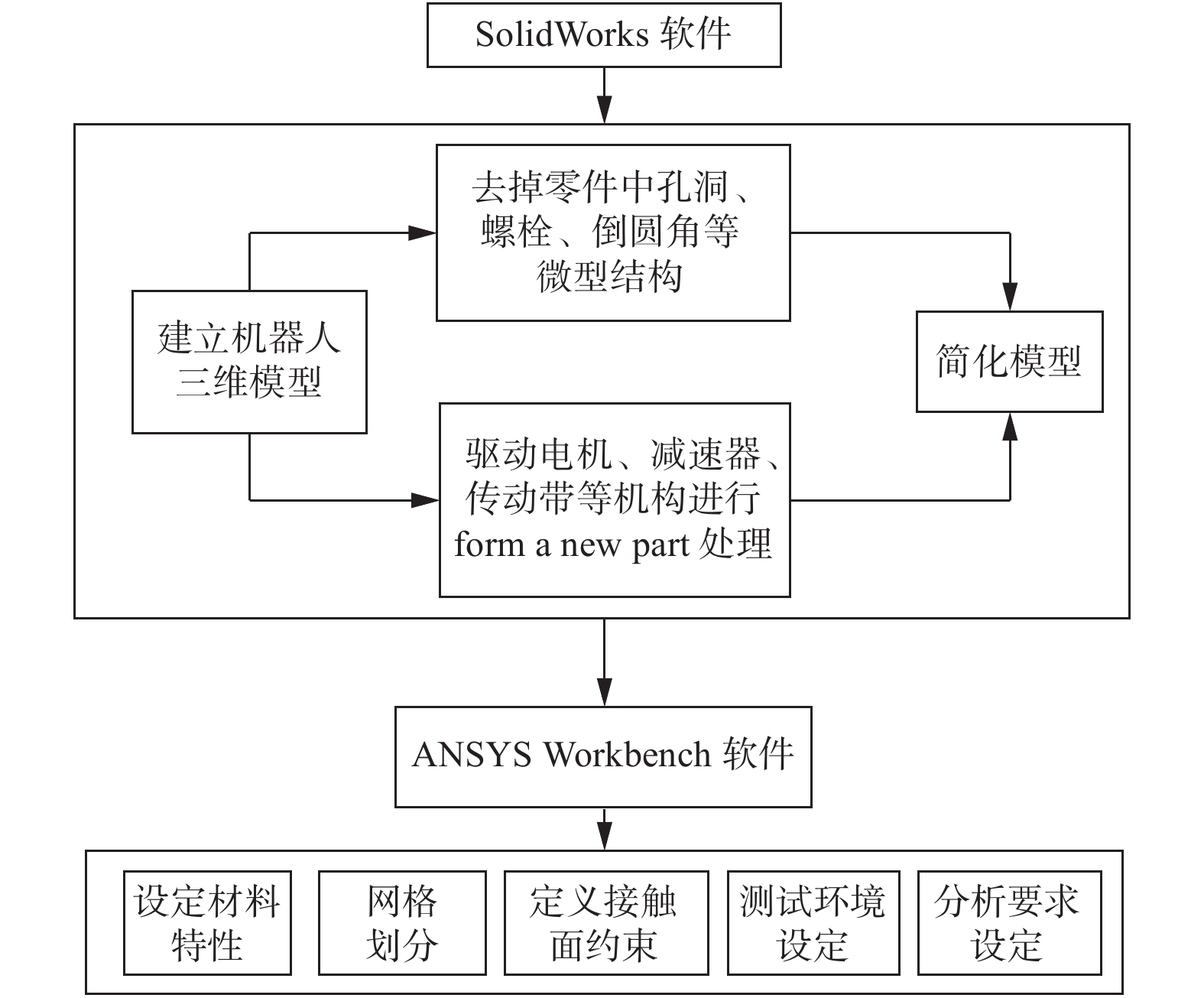
以某工业机器人为研究对象,基于模态理论,通过仿真和试验方法开展机器人的模态分析. 首先建立典型姿态下机器人的三维模型,利用ANSYS Workbench软件与ADAMS软件分析机器人的理论模态,得到固有频率和模态振型等动态特性,并确定了振动薄弱部位. 其次使用力锤法开展机器人试验模态分析,并对机器人进行振动试验验证仿真结果的正确性. 最后针对振动表现剧烈部位提出优化方案. 分析结果表明:该机器人关节2、关节3易引起低频振动,且机器人小臂相对其他部件刚性较弱. 研究结果可对机器人优化设计与工作性能改进提供理论和试验参考.
Abstract:Based on modal theory, modal analysis of an industrial robot was carried out by simulation and experimental methods. Firstly, a three-dimensional model of the robot was established in a typical posture, ANSYS Workbench software and ADAMS software were used to analyze the theoretical mode of the robot, dynamic characteristics such as natural frequency and mode shape were obtained, and the weak vibration part was determined. Secondly, the hammer method was used to carry out the modal analysis of the robot experiment and the vibration test of the robot was used to verify the correctness of the simulation results. Finally, the optimization solution was proposed for parts with severe vibration. The analysis results show that the robot joint 2 and joint 3 are prone to low-frequency vibration, and the rigidity of the small robot arm is relatively weak compared with other parts. The results can provide theoretical and experimental references for robot optimal design and work performance improvement.
-
Key words:
- robot /
- modal simulation /
- experimental model /
- dynamic characteristics
-
表 1 机器人材料属性
Table 1. Material properties of robot
材料 结构钢 密度/(kg•m−3) 7850 泊松比 0.3 杨氏模量/ GPa 200 各关节的接触特性 bonded 约束 表 2 机器人前4阶固有频率及模态振型描述
Table 2. Description of robot’s four natural frequencies and mode shapes
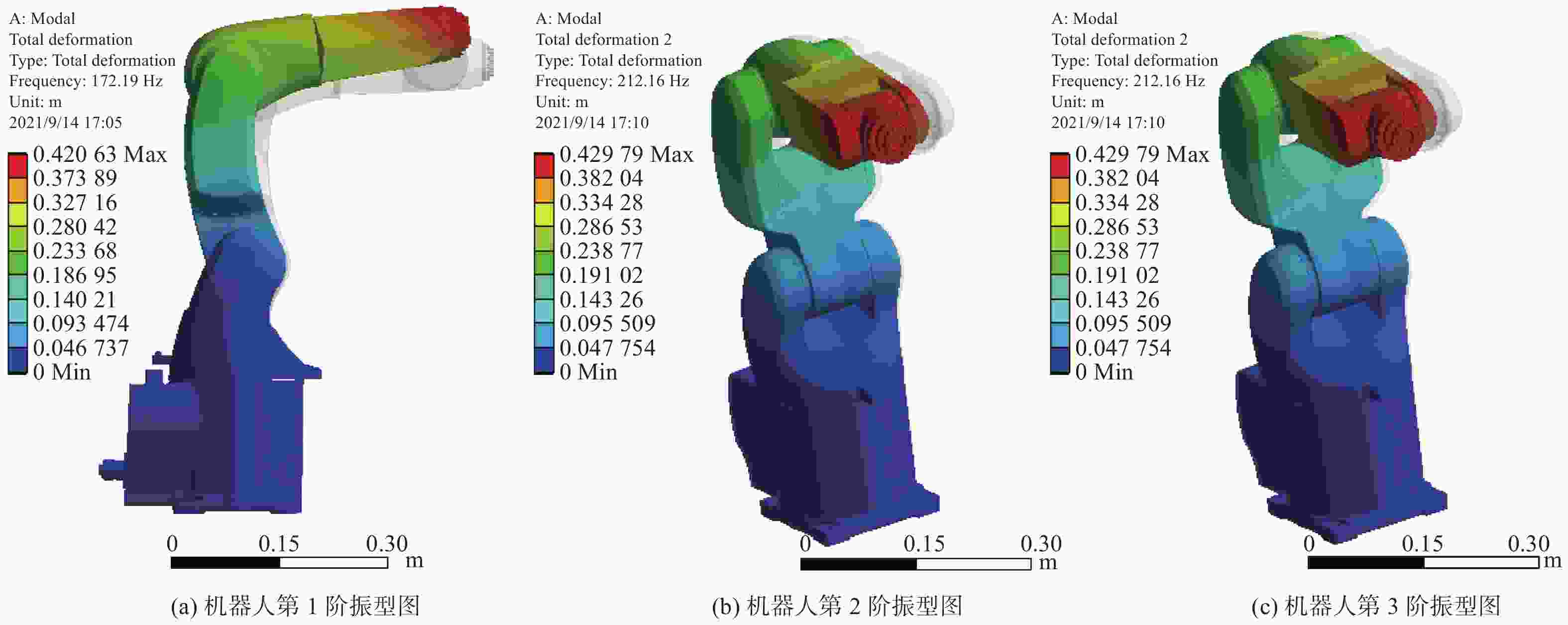
模态阶次 固有频率 / Hz 振型表现 第1阶模态 172.19 机器人大臂、小臂和腕部
绕着关节2的俯仰转动第2阶模态 212.16 大臂绕着关节2的俯仰运
动和小臂及腕部绕着关节
3的左右摆动第3阶模态 461.02 机器人大臂、小臂和腕部
绕关节2的左右摆动第4阶模态 467.79 机器人腕部、小臂与末端
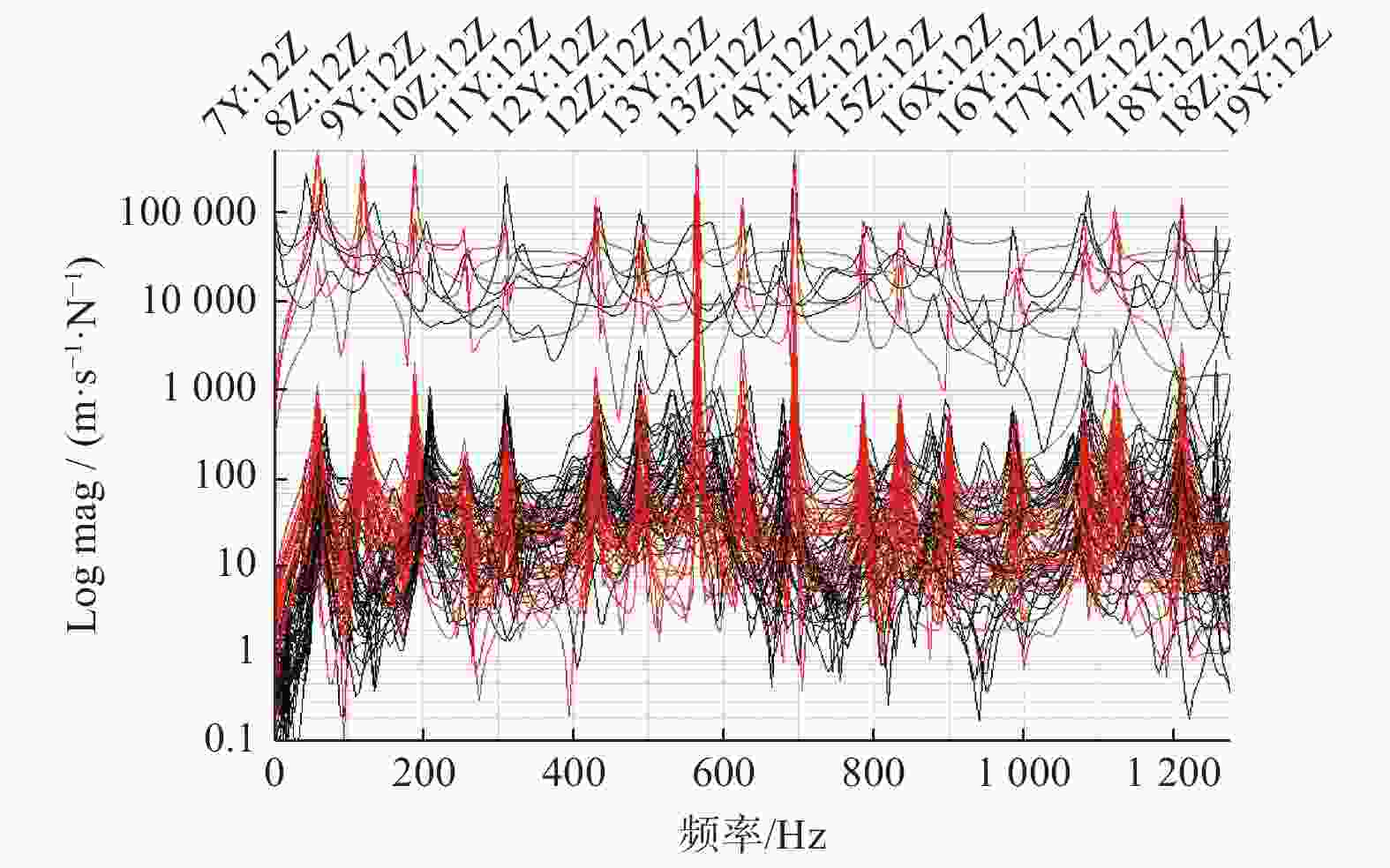
执行器随关节3的俯仰运动表 3 机器人试验获得的前6阶固有频率
Table 3. Six order natural frequencies obtained by robot test
模态阶次 固有频率 / Hz 阻尼 / % 1 186.20 0.367 2 210.70 9.106 3 479.68 0.452 4 489.03 6.490 5 1173.95 2.237 6 1250.98 0.945 表 4 机器人前4阶固有频率
Table 4. Four natural frequencies of robot
模态阶次 固有频率/Hz 误差/% 数值模态 试验模态 1 172.19 186.20 7.52 2 212.16 210.70 0.65 3 461.02 479.68 3.89 4 467.79 489.03 4.34 -
[1] ZAGHBANI I, LAMRAOUI M, SONGMENE V, et al. Robotic high speed machining of aluminum alloys[J] . Advanced Materials Research,2011,188:584 − 589. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.188.584 [2] MEJRI S, GAGNOL V, LE T P, et al. Dynamic characterization of machining robot and stability analysis[J] . International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2016,82(1−4):351 − 359. [3] 李柳林. 机器人样机设计制造及振动测试[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2012. [4] MOUSAVI S, GAGNOL V, BOUZGARROU B C, et al. Dynamic modeling and stability prediction in robotic machining[J] . International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2017,88(9−12):3053 − 3065. [5] 梁君, 赵登峰. 模态分析方法综述[J] . 现代制造工程,2006(8):139 − 141. [6] 田东升, 胡明, 邹平, 等. 基于ANSYS的六自由度工业机器人模态分析[J] . 机械与电子,2009(2):59 − 62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2257.2009.02.019 [7] 李向良. 基于ADAMS和Workbench的高空作业臂性能仿真分析[J] . 河北工程大学学报(自然科学版),2017,34(4):99 − 102, 108. [8] 王斌锐, 方水光, 严冬明. 机器人手臂的刚柔耦合建模及摆动模态对比[J] . 中国机械工程,2012,23(17):2092 − 2097. [9] 徐稀文, 平雪良, 陈鲁刚, 等. 弧焊机器人大臂结构模态分析[J] . 机械设计与制造,2012(6):151 − 153. [10] PAN W D. Flexible multibody dynamic simulation [D]. Iowa City: The University of Iowa, 1998. [11] 满建财, 周雷, 张伟玲. 基于ABAQUS的并联码垛机器人模态分析[J] . 起重运输机械,2013(11):51 − 54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0785.2013.11.021 [12] LIAO X P, GONG C L, LIN Y Z, et al. The finite element modal analysis of the base of welding robot [C]//2010 3rd International Conference on Advanced Computer Theory and Engineering(ICACTE). Chengdu: IEEE, 2010. [13] 周恩德, 王喜顺, 方海涛, 等. 八自由度智能喷涂机器人的结构设计与模态分析[J] . 机械与电子,2017,35(5):76 − 80. [14] 周正干, 李然, 贠超, 等. 实验模态技术在机器人动态特性分析中的应用[J] . 华北工学院学报,2000, 21(4):290 − 295. [15] 陈骏, 陈威. 桁架机器人动态特性分析及实验研究[J] . 机械工程与自动化,2018(2):86 − 87, 89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6413.2018.02.033 [16] SIRIGULENG B, ZHANG W, LIU T, et al. Vibration modal experiments and modal interactions of a large space deployable antenna with carbon fiber material and ring-truss structure[J] . Engineering Structures,2019,207:109932. -





 下载:
下载: