Enterprise credit evaluation model based on cost sensitive XGBoost
-
摘要:
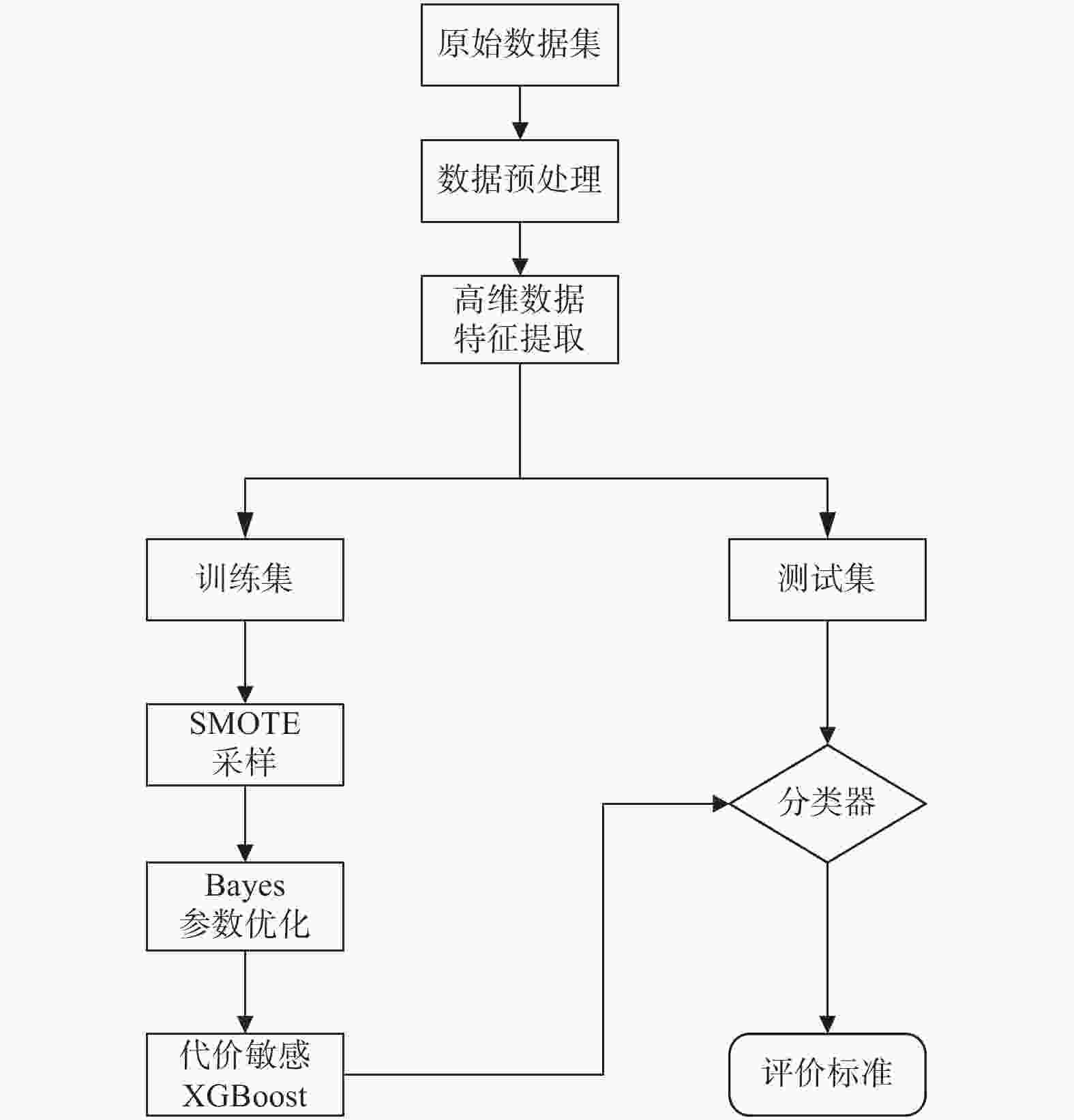
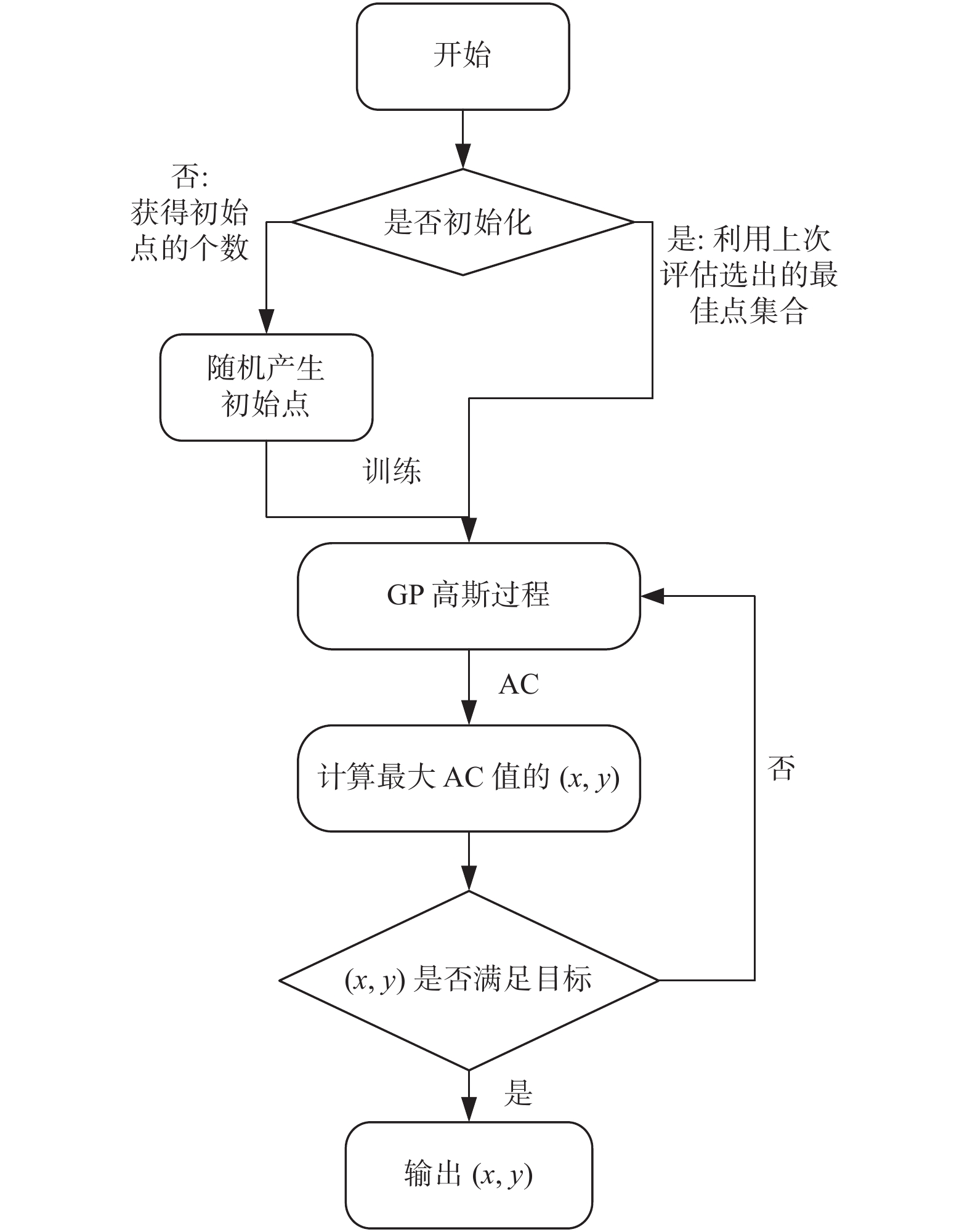
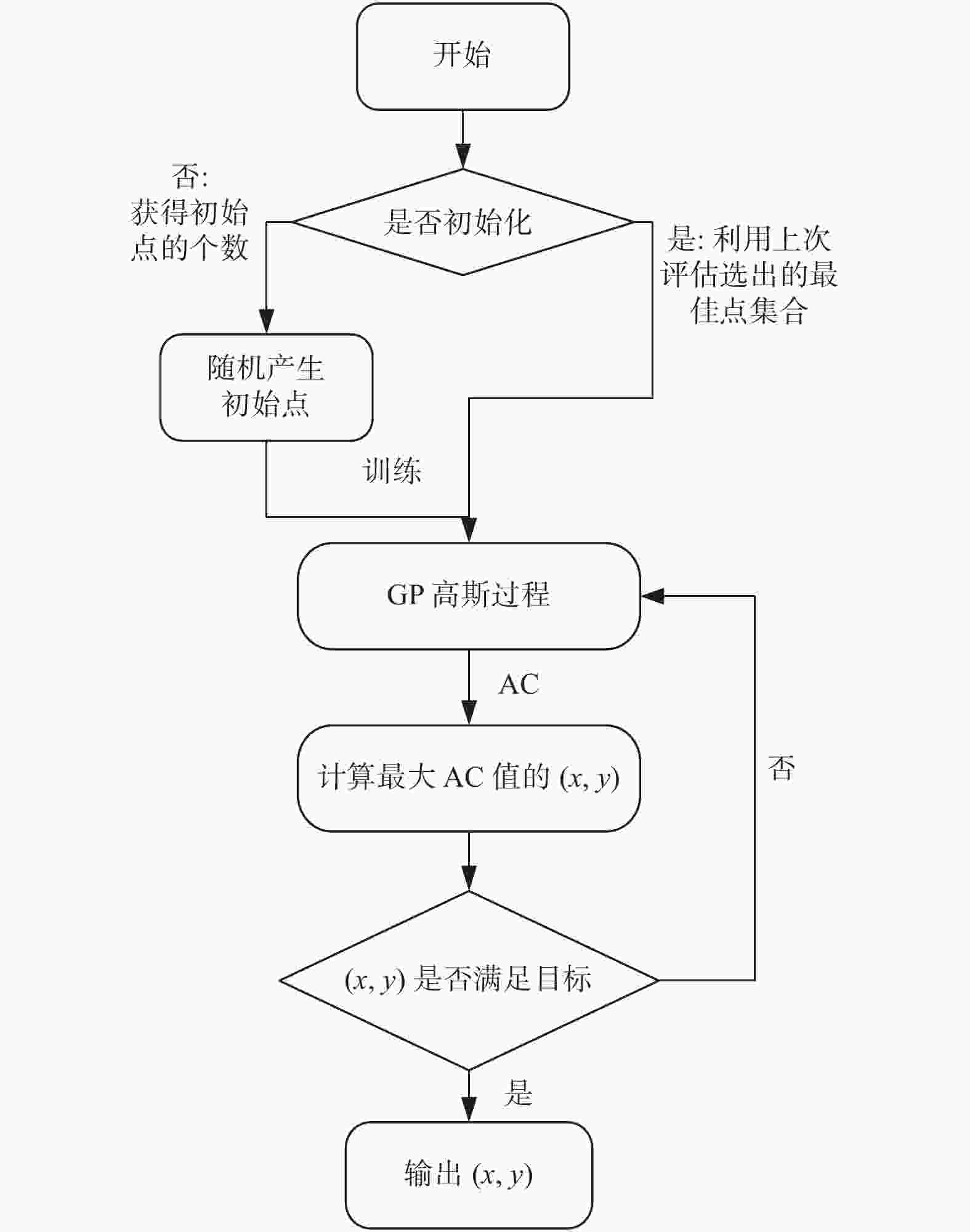
我国信用不良的企业数量远小于信用良好的企业数量,样本类别的极端不平衡导致传统的信用评估模型在训练时无法充分学习信用不良企业的特征. 为提高极端梯度提升算法(Extreme Gradient Boosting, XGBoost)在企业信用评估这种不平衡分类问题中的准确率,提出一种基于代价敏感XGBoost的企业信用评估模型. 在XGBoost算法拟合过程中,加入代价敏感损失函数迫使模型更加关注少数类的特征,并引入贝叶斯优化调整模型的重要超参数. 以我国A股市场中小板块企业2016—2020年数据为样本,实证结果表明,基于代价敏感XGBoost的企业信用评估模型能够在保证总体识别精度的情况下提高对信用不良企业的识别准确率.
Abstract:In China, the number of enterprises with bad credit is much smaller than that of enterprises with good credit. The extreme imbalance of sample categories results in the traditional credit evaluation model unable to fully learn the characteristics of bad credit enterprises during training. In order to improve the accuracy of extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) in unbalanced classification problems such as enterprise credit evaluation, an enterprise credit evaluation model based on cost sensitive XGBoost was proposed. In the process of XGBoost algorithm fitting, the cost sensitive loss function was added to force the model to pay more attention to the characteristics of minority classes, and the bayesian optimization was introduced to adjust the hyperparameters of the model. Taking the datas of small and medium-sized enterprises in China's A-share market from 2016 to 2020 as the sample, the experimental results show that the enterprise credit evaluation model based on cost sensitive XGBoost can improve the identification accuracy of bad credit enterprises while ensuring the overall identification accuracy.
-
表 1 超参数搜索域空间
Table 1. Space of hyperparameter search field
序号 参数 含义 域空间 1 max_depth 树最大深度 [1,50] 2 gamma 损失函数最小下降值 [0.001,10] 3 subsample 随机采样比例 [0.4,1.0] 4 min_child_weight 最小叶子节点权重 [4,15] 5 max_delta_step 树权重最大步长 [1,10] 6 n_estimators 弱学习器个数 [2,150] 7 colsample_bytree 随机列数占比 [0.2,1.0] 表 2 试验结果
Table 2. Experimental results
模型 Bayes−XGB/% Bayes−FL−XGB/% Bayes−WCE−XGB/% Bayes−GHM−XGB/% 训练集 TPrate 98.67 90.90 91.07 91.16 TNrate 96.53 91.55 91.52 91.85 G 97.59 91.23 91.29 91.51 AUC 97.60 91.22 91.40 91.50 测试集 TPrate 75.39 86.96 86.25 87.50 TNrate 91.06 91.13 91.29 91.22 G 82.84 89.01 88.73 89.34 AUC 84.13 89.06 88.75 89.40 -
[1] 王名豪, 梁雪春. 基于CPSO-XGboost的个人信用评估[J] . 计算机工程与设计,2019,40(7):1891 − 1895. [2] 刘志惠, 黄志刚, 谢合亮. 大数据风控有效吗?:基于统计评分卡与机器学习模型的对比分析[J] . 统计与信息论坛,2019,34(9):18 − 26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2019.09.003 [3] 夏利宇, 何晓群. 基于重抽样法处理不平衡问题的信用评级模型[J] . 管理评论,2020,32(3):75 − 84. [4] 张涛, 汪御寒, 李凯, 等. 基于样本依赖代价矩阵的小微企业信用评估方法[J] . 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(1):149 − 158. doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.19017 [5] 陈启伟, 王伟, 马迪, 等. 基于Ext-GBDT集成的类别不平衡信用评分模型[J] . 计算机应用研究,2018,35(2):421 − 427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2018.02.022 [6] KHEMAKHEM S, BEN SAID F, BOUJELBENE Y, et al. Credit risk assessment for unbalanced datasets based on data mining, artificial neural network and support vector machines[J] . Journal of Modelling in Management,2018,13(4):932 − 951. [7] 罗康洋, 王国强. 基于改进的MRMR算法和代价敏感分类的财务预警研究[J] . 统计与信息论坛,2020,35(3):77 − 85. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-3116.2020.03.011 [8] CHEN T, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2016, 785 − 794. [9] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J] . IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence,2020,42(2):318 − 327. [10] SUN Y, WONG A K C, KAMEL M S. Classification of imbalanced data: A review[J] . International journal of pattern recognition and artificial intelligence,2009,23(4):687 − 719. doi: 10.1142/S0218001409007326 [11] LI B, LIU Y, WANG X. Gradient harmonized single-stage detector[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Honolulu: American Association for Artificial Intelligence, 2019: 8577 − 8584. [12] 肖雨晴, 杨慧敏. 目标检测算法在交通场景中应用综述[J] . 计算机工程与应用,2021,57(6):30 − 41. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011-0361 [13] PELIKAN M. Bayesian optimization algorithm [M]. Berlin, Heidelberg, 2005: 31 − 48. [14] 唐红, 王栋, 宋博, 等. 基于非线性赋权XGBoost算法的航班延误分类预测[J] . 系统仿真学报,2021,33(9):2261 − 2269. [15] 史佳琪, 张建华. 基于多模型融合Stacking集成学习方式的负荷预测方法[J] . 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(14):4032 − 4042. [16] 王桂兰, 赵洪山, 米增强. XGBoost算法在风机主轴承故障预测中的应用[J] . 电力自动化设备,2019,39(1):73 − 77, 83. -





 下载:
下载: