Distortion compensation method for high-precision point cloud model
-
摘要:
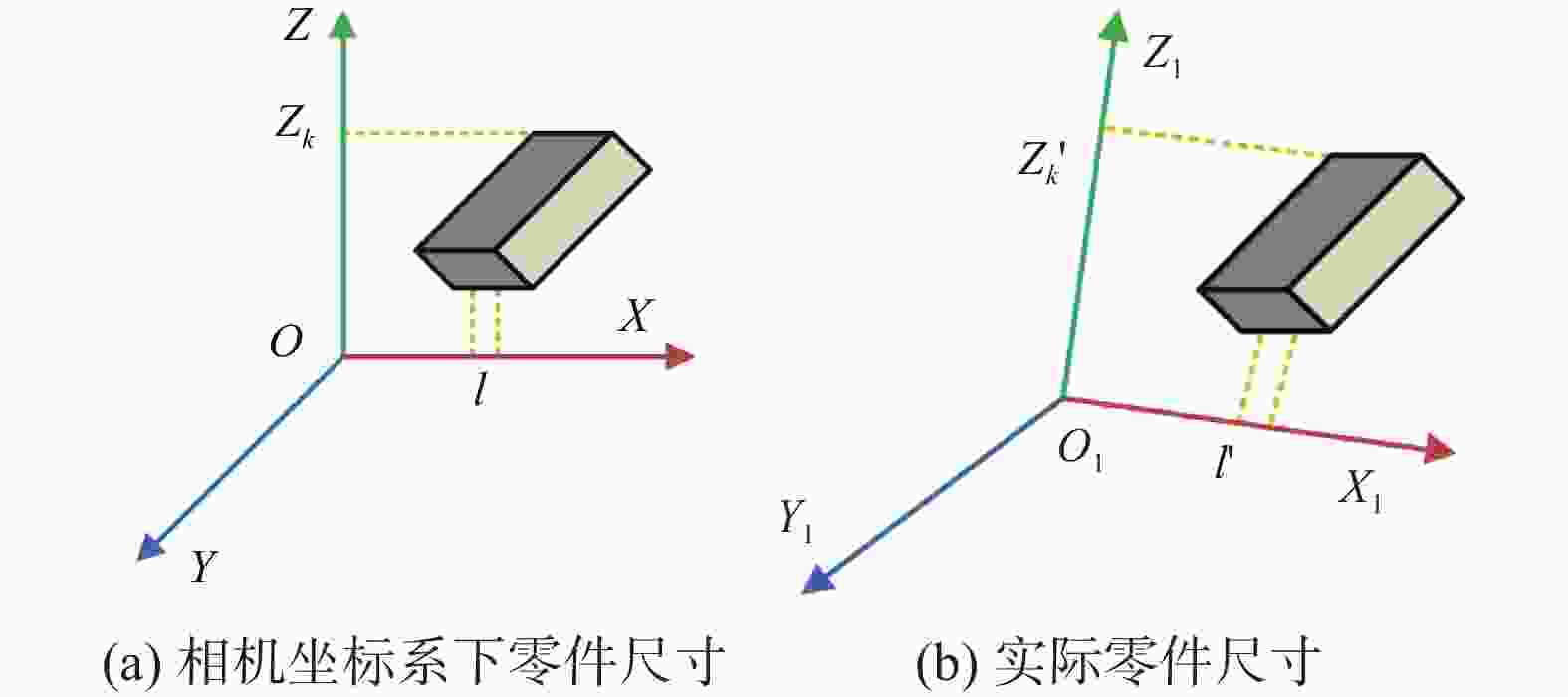
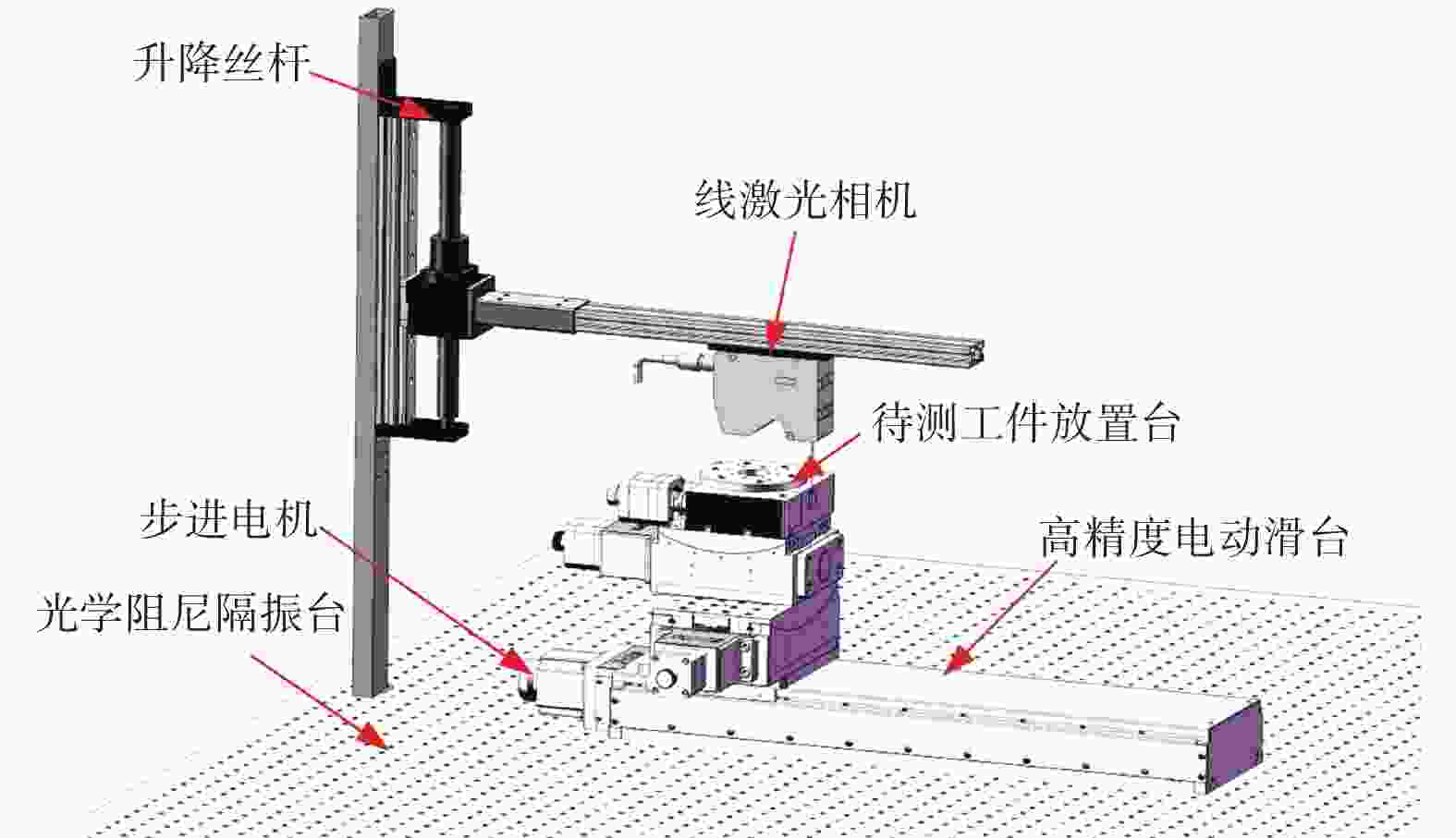
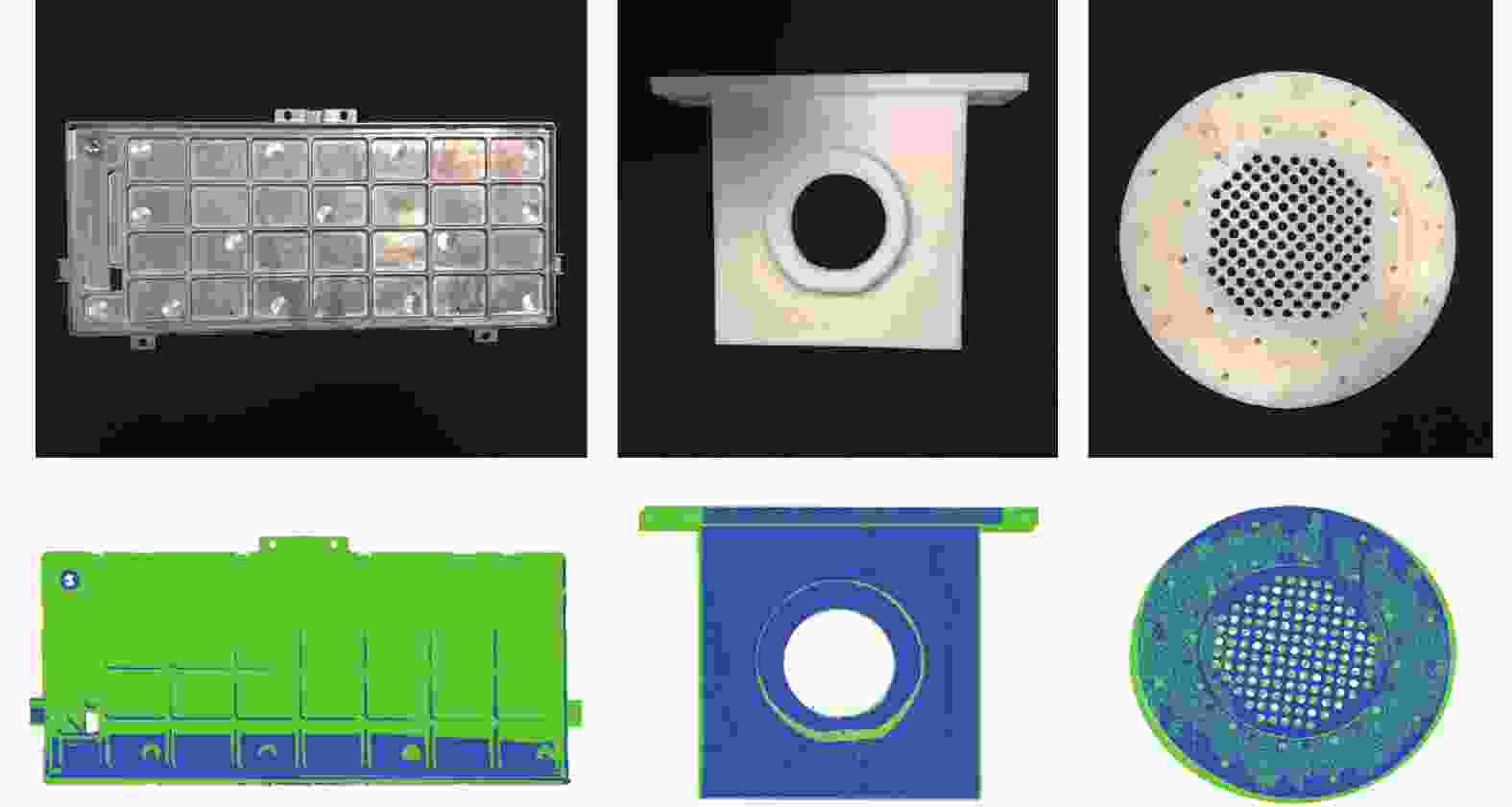
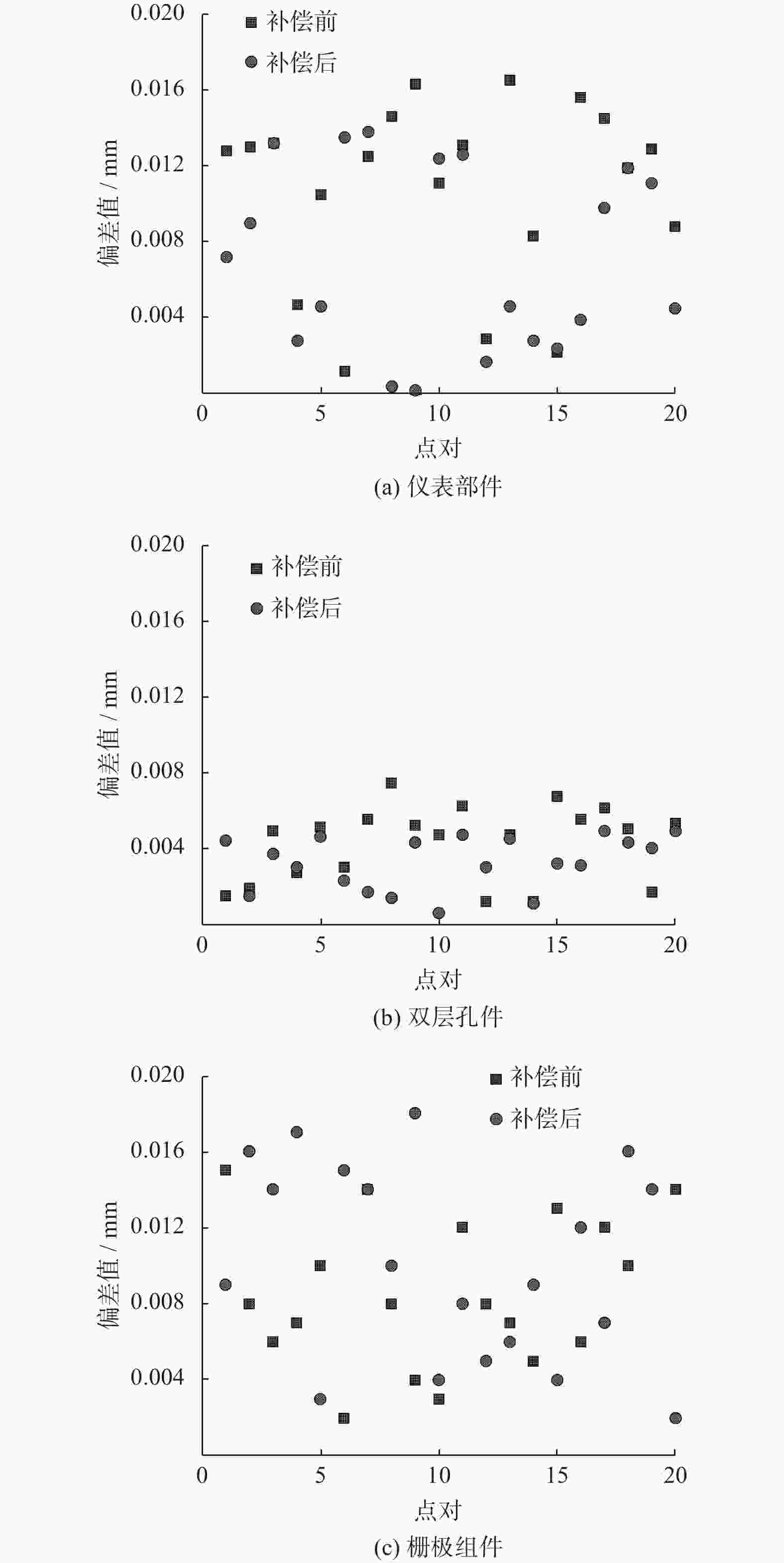
点云模型的准确获取与畸变补偿是三维激光扫描技术检测零部件的关键. 提出一种通过畸变补偿获得高精度三维点云模型方法. 利用线激光重构零部件三维点云模型,对模型中存在的夹角误差进行畸变补偿,实现高精度的点云数据获取. 搭建试验平台,选取仪表部件、双层孔件及栅极组件等不同材质及结构的试验对象,通过对比分析发现,畸变补偿后的均方根差分别减少0.009、0.036、0.024 mm. 结果表明点云模型畸变补偿方法有效,同时具有很好的通用性.
Abstract:Accurate acquisition and distortion compensation of point cloud model was the key to 3D laser scanning technology for inspection of parts. A method of obtaining high-precision 3D point cloud model by distortion compensation is proposed. The 3D point cloud model of parts was reconstructed by using a line laser, and the distortion compensation was applied to the included angle error in the model to achieve high-precision point cloud data acquisition. The test platform was established, and the test objects with different materials and structures were selected such as instrument parts, double-layer hole parts and grid components. Through comparative analysis, it has been found that the root-mean-square differences after the distortion compensation were reduced by 0.009, 0.036 and 0.024 mm respectively. The results verified the effectiveness of the distortion compensation method for the point cloud model and its good generality.
-
Key words:
- line laser /
- point cloud model /
- distortion compensation
-
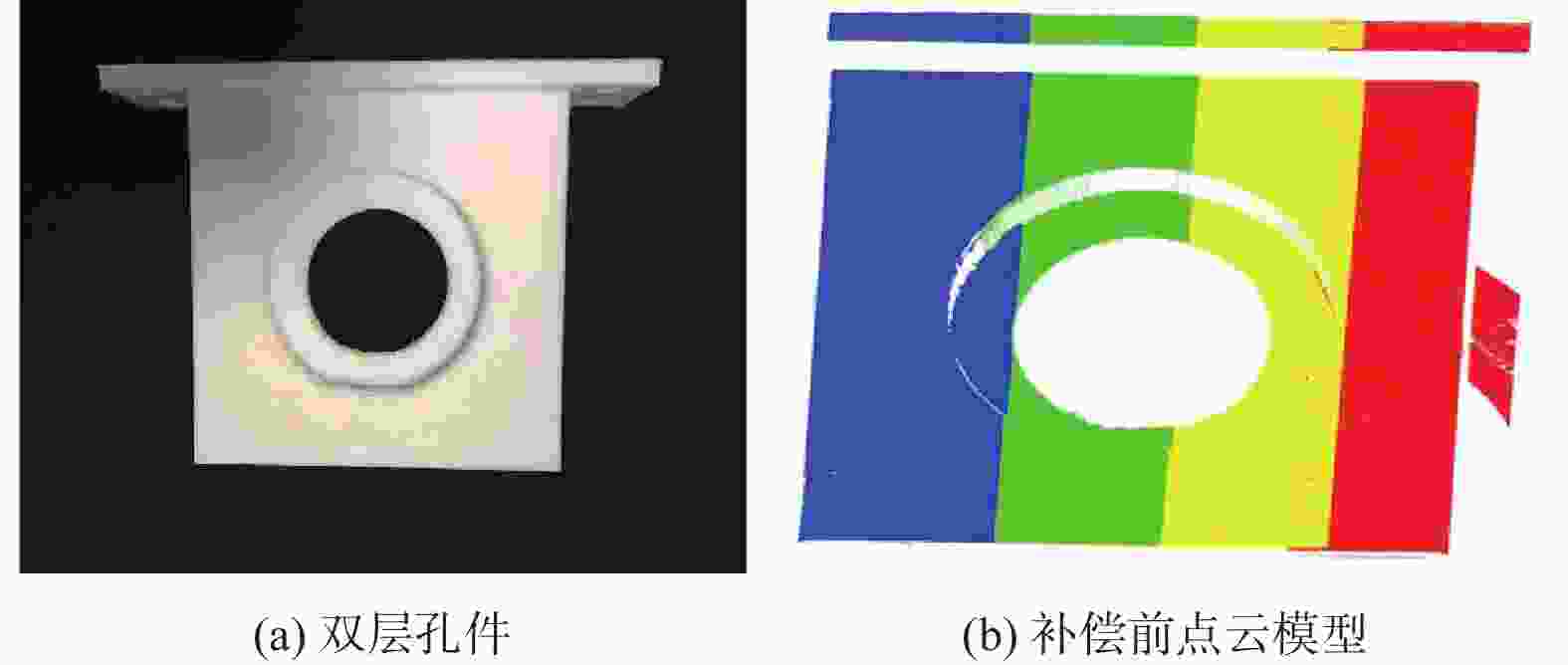
表 1 双层孔件相关参数
Table 1. Relevant parameters of double-layer hole parts
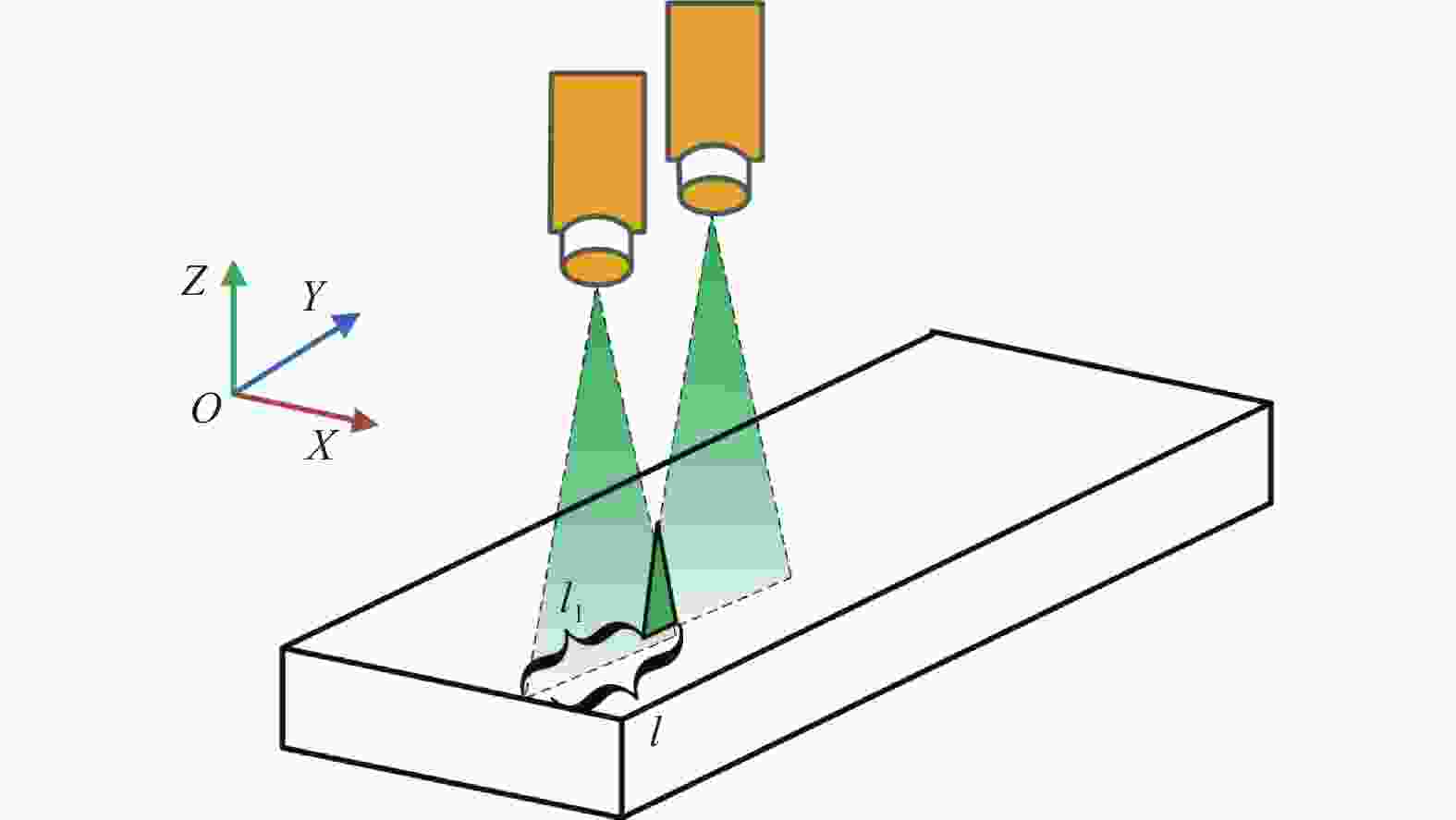
mm 双层孔件底部底座与
球孔面存在高度差L1遮挡造成点云数据缺
失部分的长度L2深度信息差L3 相机线宽L4 每次点云扫描的
理论宽度L5每次点云扫描的
实际宽度L65.000 3.010 12×10−3 16.000 16.000 16.006 表 2 双层孔件线激光扫描倾斜角
Table 2. linear laser scanning inclination angle of double-layer hole parts
(°) 线激光入射角 倾斜角$ {\theta _x} $ 倾斜角$ {\theta _y} $ 倾斜角$ {\theta _z} $ 35.000 4.000 0.040 1.569 表 3 双层孔件的测量结果
Table 3. Measurement results of double-layer hole parts
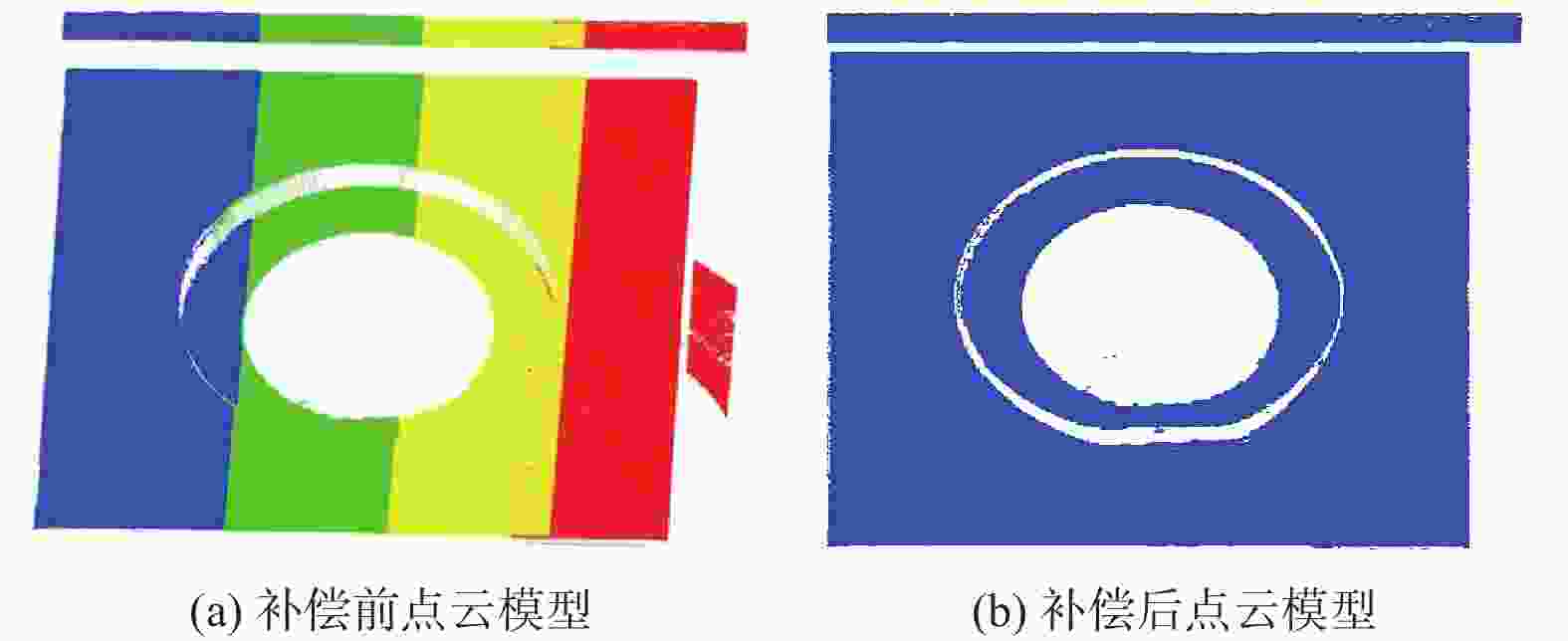
mm 畸变补偿 尺寸参数 标准值 试验1 试验2 试验3 试验4 试验5 均方根差 补偿前 大孔直径
小孔直径
孔面长度
孔面宽度30.00
20.00
50.00
50.0029.85
19.82
49.88
50.1229.78
19.87
49.88
50.1029.78
19.83
49.91
50.1029.85
19.87
49.89
50.1429.72
19.82
49.91
50.080.21
0.16
0.10
0.11补偿后 大孔直径
小孔直径
孔面长度
孔面宽度30.00
20.00
50.00
50.0029.88
19.90
49.98
50.0129.82
19.90
49.99
50.0329.84
19.87
49.97
50.0329.88
19.87
49.98
50.0129.80
19.86
49.98
50.020.16
0.12
0.02
0.02 -
[1] BUONAMICI F, CARFAGNI M, FURFERI R, et al. Reverse engineering modeling methods and tools: A survey[J] . Computer-Aided Design and Applications,2018,15(3):443 − 464. doi: 10.1080/16864360.2017.1397894 [2] HELLE R H, LEMU H G. A case study on use of 3D scanning for reverse engineering and quality control[J] . Materials Today:Proceedings,2021,45(6):5255 − 5262. [3] YU F, WEI Y X, YU H G. Research on target recognition method based on laser point cloud data[J] . Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics,2020,928:1305 − 1310. [4] CHAO W, YONG K C. Smart scanning and near real-time 3D surface modeling of dynamic construction equipment from a point cloud[J] . Automation in Construction,2015,49(B):239 − 249. [5] NGUYEN C, CHOI Y. Comparison of point cloud data and 3D CAD data for on-site dimensional inspection of industrial plant piping systems[J] . Automation in Construction,2018,91:44 − 52. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2018.03.008 [6] JOVANCEVIC I, PHAM H H, ORTEU J J, et al. 3D point cloud analysis for detection and characterization of defects on airplane exterior surface[J] . Journal of Nondestructive Evaluation,2017,36(4):74. doi: 10.1007/s10921-017-0453-1 [7] XIAO J H, ZHANG J H, ADLER B, et al. Three-dimensional point cloud plane segmentation in both structured and unstructured environments[J] . Robotics and Autonomous Systems,2013,61(12):1641 − 1652. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2013.07.001 [8] WANG J, LI L P, SHI S S, et al. Fine exploration and control of subway crossing karst area[J] . Applied Sciences,2019,9(13):2588. doi: 10.3390/app9132588 [9] CALIGNANO F, VEZZETTI E. Soft tissue diagnosis in maxillofacial surgery: A preliminary study on three-dimensional face geometrical features-based analysis[J] . Aesthetic Plastic Surgery,2010,34(2):200 − 211. doi: 10.1007/s00266-009-9410-4 [10] FARAHANI N, BRAUN A, JUTT D, et al. Three-dimensional imaging and scanning: current and future applications for pathology[J] . Journal of Pathology Informatics,2017,8(1):1 − 10. doi: 10.4103/jpi.jpi_47_16 [11] SUN S P, LI C Y, CHEE P W, et al. Three-dimensional photogrammetric mapping of cotton bolls in situ based on point cloud segmentation and clustering[J] . ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing,2020,160:195 − 207. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.12.011 [12] WANG Y W, CHEN Y F. Non-destructive measurement of three-dimensional plants based on point cloud[J] . Plants,2020,9(5):571. doi: 10.3390/plants9050571 [13] LI Y D, GU P H. Automatic localization and comparison for free-form surface inspection[J] . Journal of Manufacturing Systems,2006,25(4):251 − 268. doi: 10.1016/S0278-6125(08)00007-1 [14] WANG J J, XU L J, LI X L, et al. A proposal to compensate platform attitude deviation's impact on laser point cloud from airborne LiDAR[J] . IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation & Measurement,2013,62(9):2549 − 2558. [15] BARNFATHER J D, ABRAM T. Efficient compensation of dimensional errors in robotic machining using imperfect point cloud part inspection data[J] . Measurement,2018,117:176 − 185. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2017.12.021 [16] GONG C, YIN X, LIANG J, et al. A compensation filter method for extracting surface characteristic from optical point cloud [J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2019, 31(2). DOI: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab42f0. [17] BALLIT A, MOUGHARBEL I, GHAZIRI H, et al. Visual sensor fusion with error compensation strategy toward a rapid and low-cost 3D scanning system for the lower residual limb[J] . IEEE Sensors Journal,2020,20(24):15043 − 15052. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3011172 -





 下载:
下载: