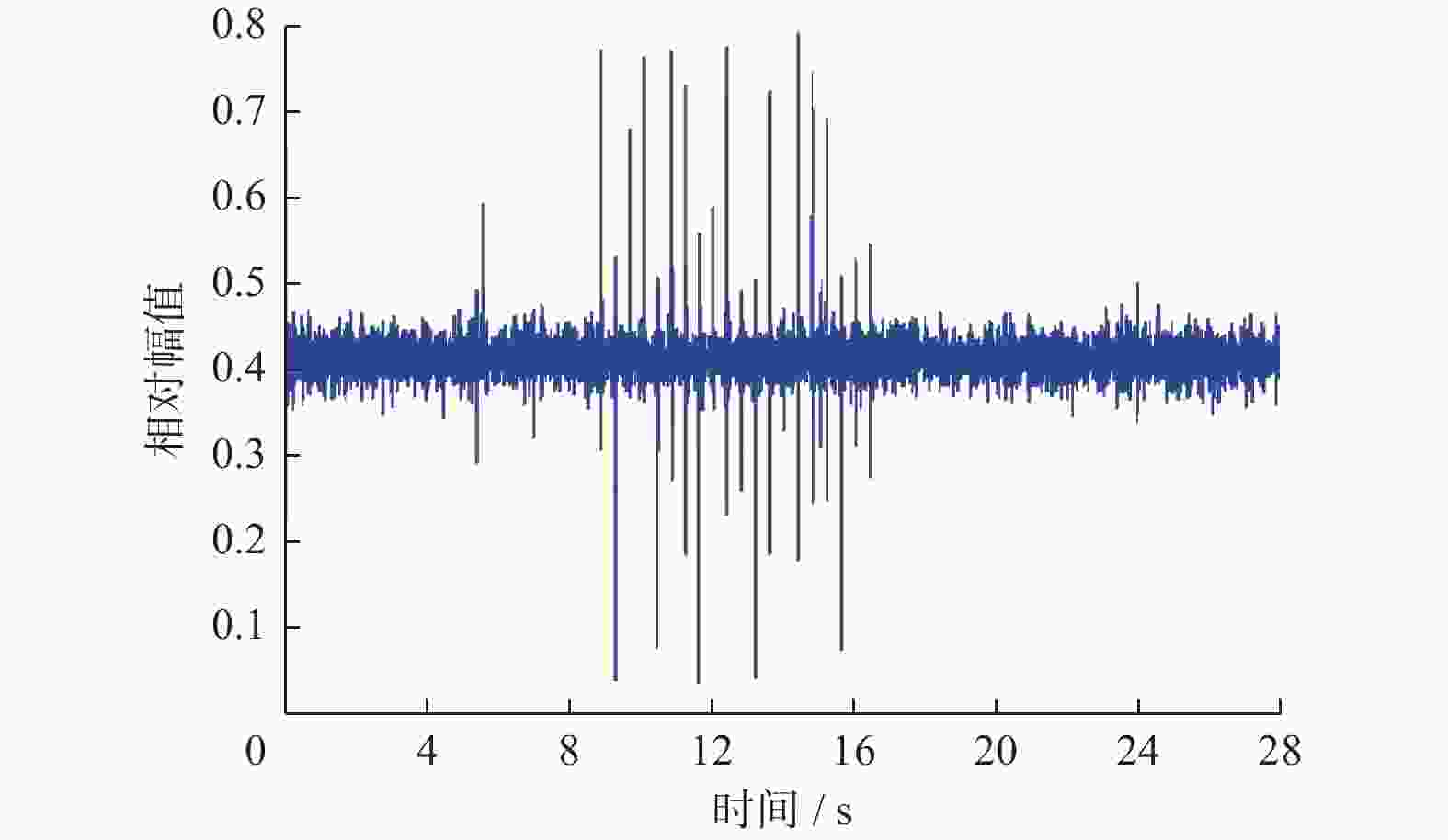
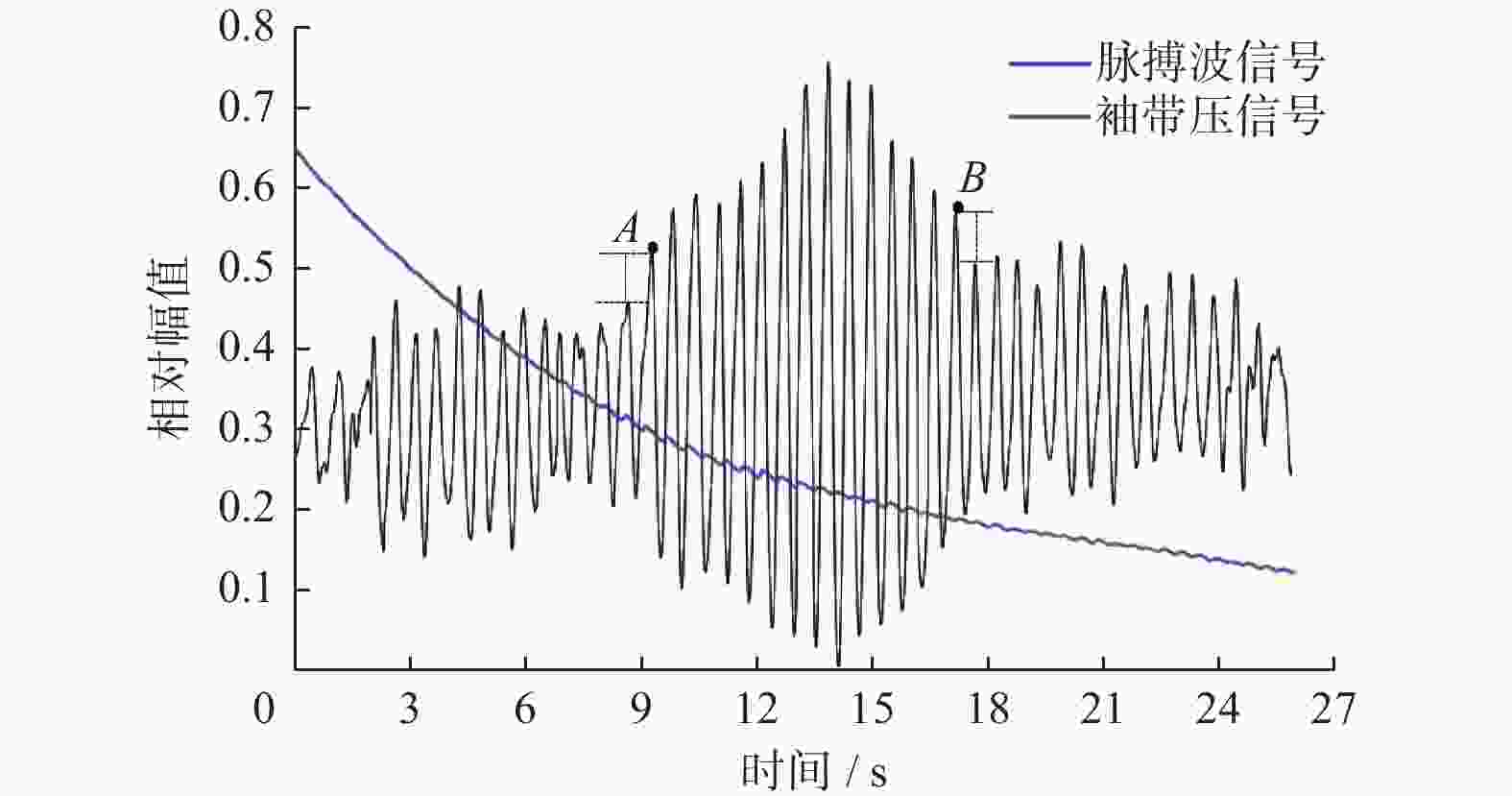
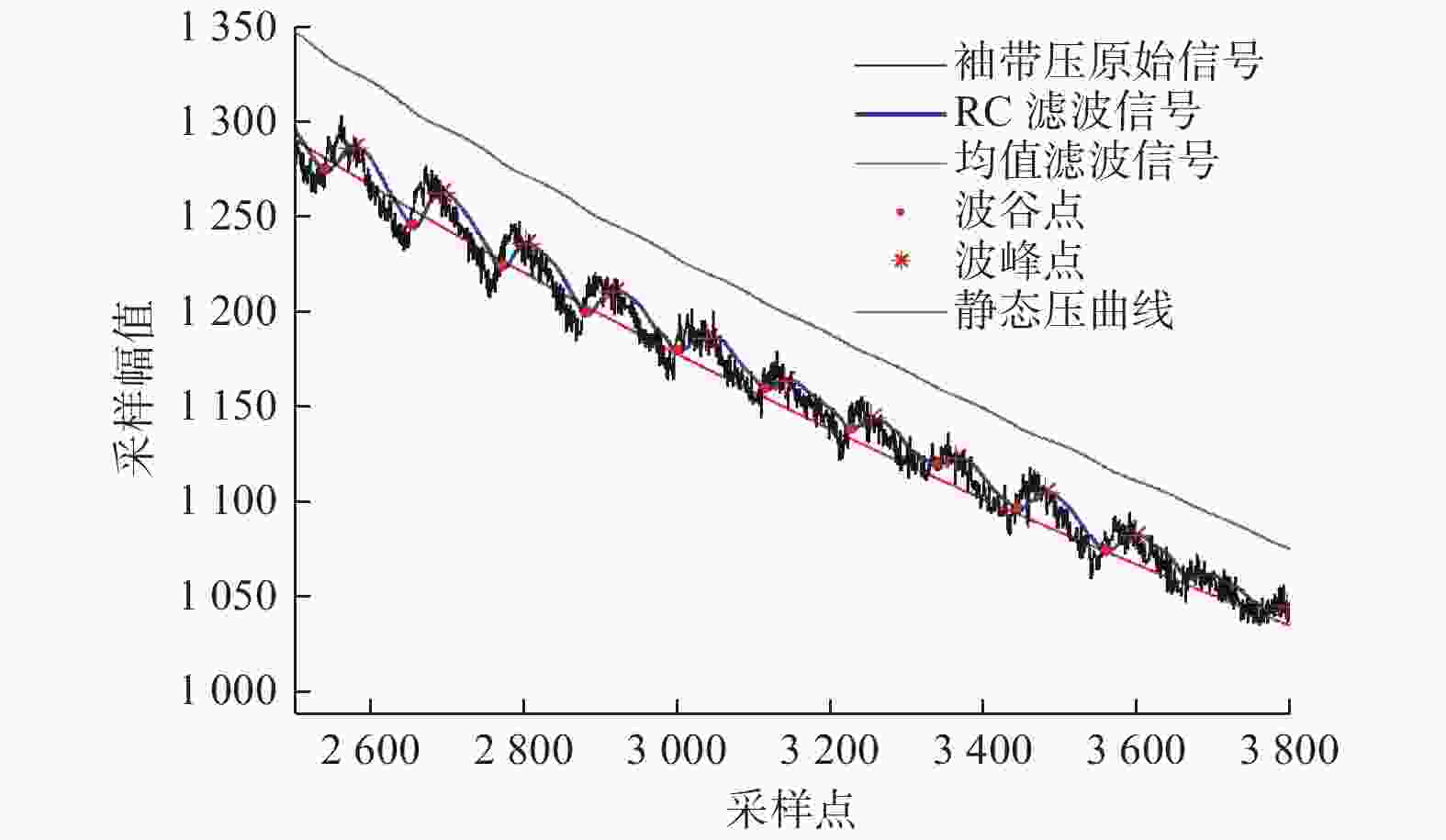
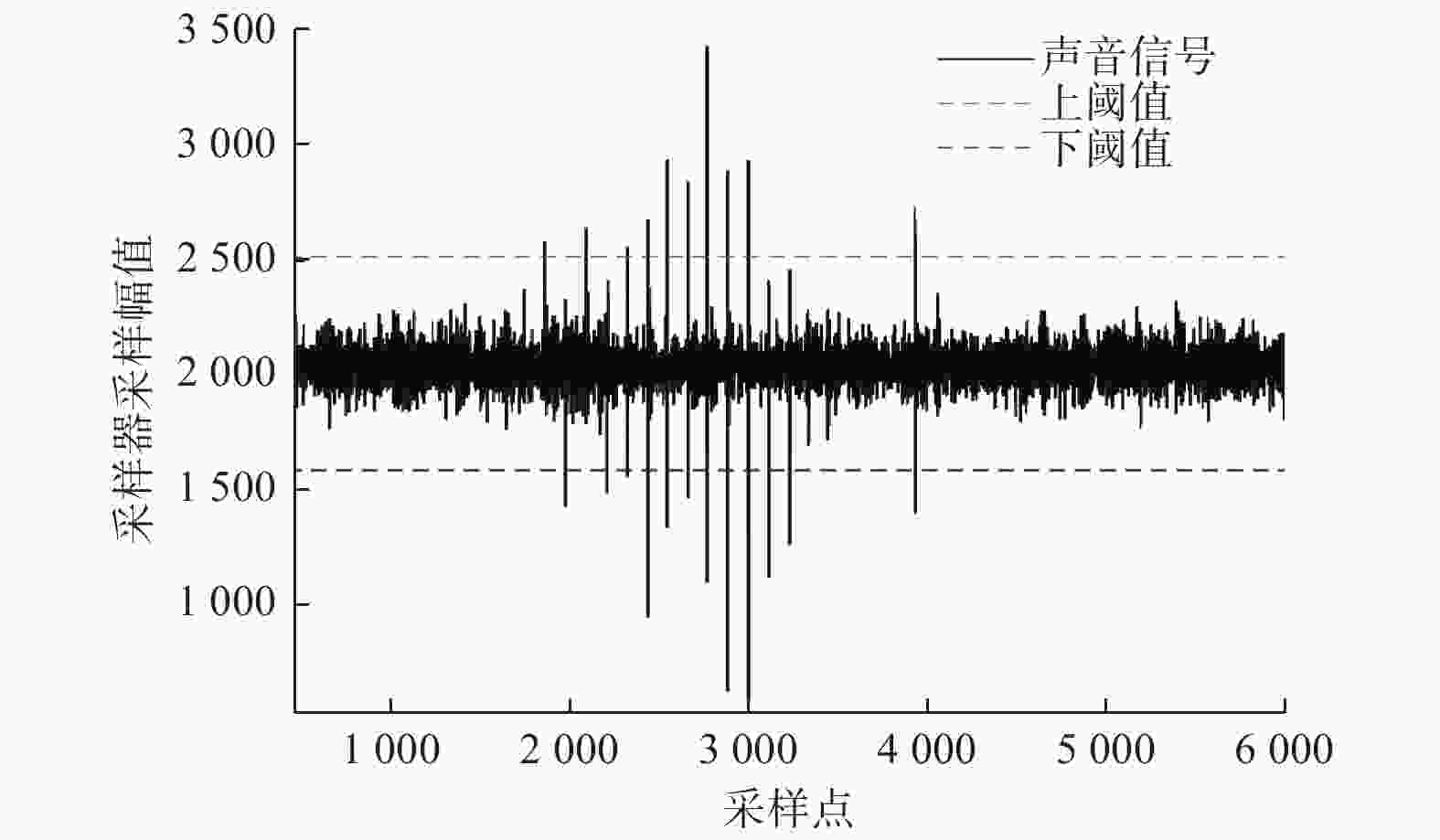
Self-adaptive segmental recognition of Korotkoff sound for blood pressure measurement method
-
摘要:
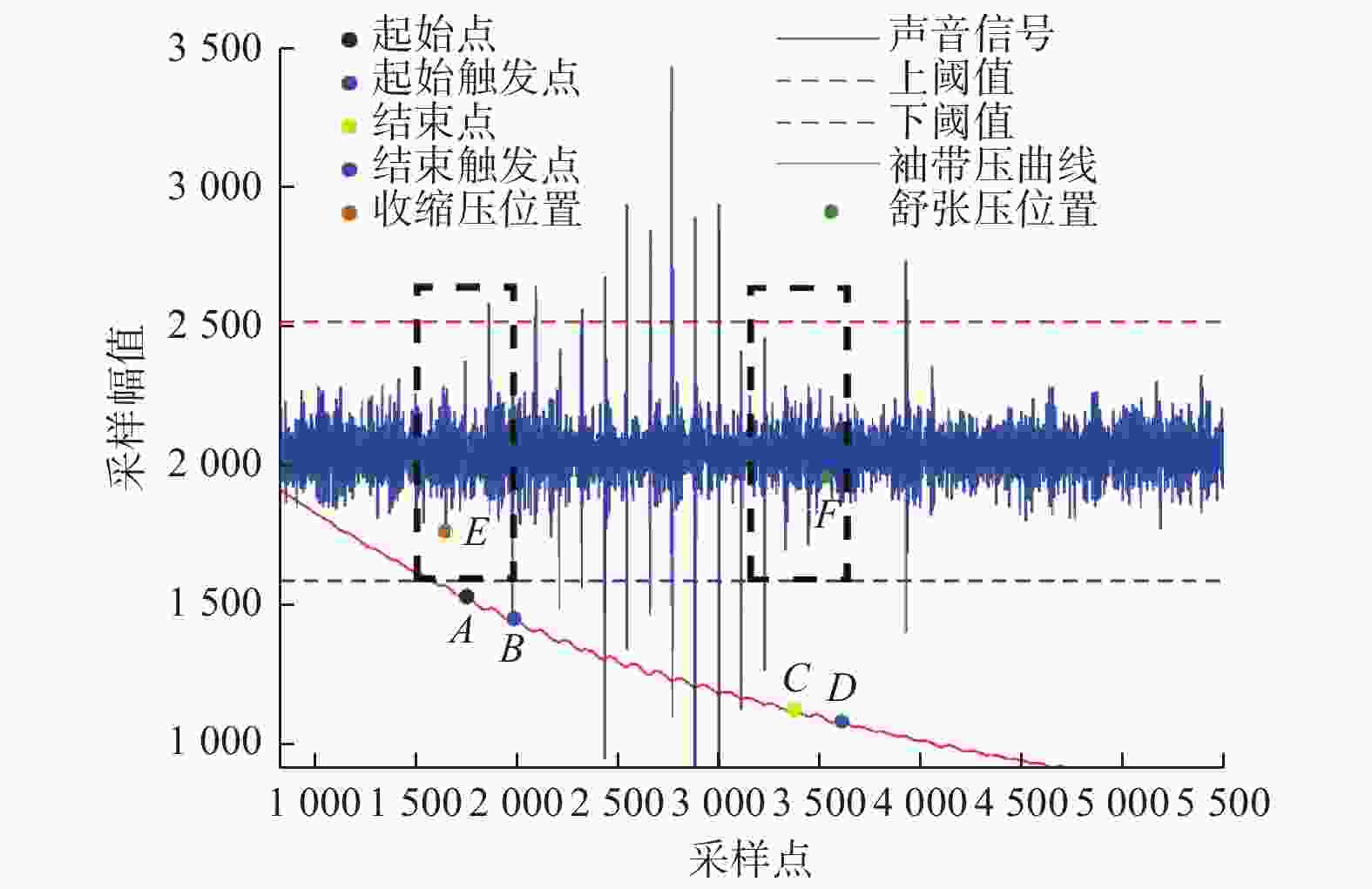
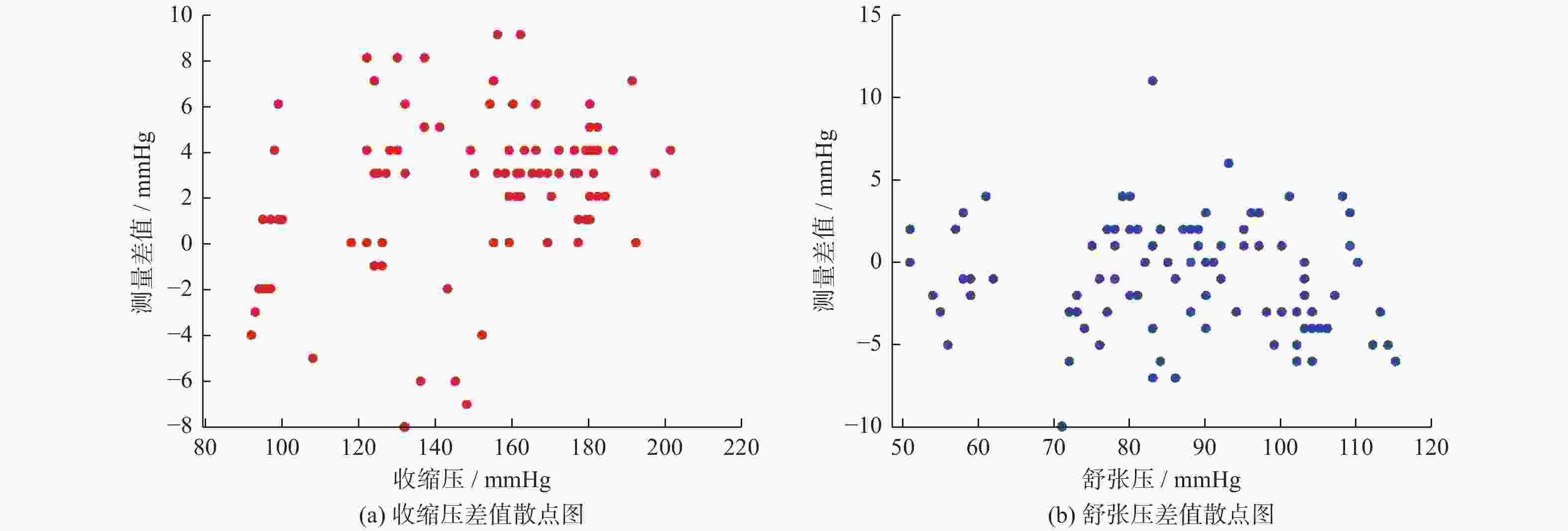
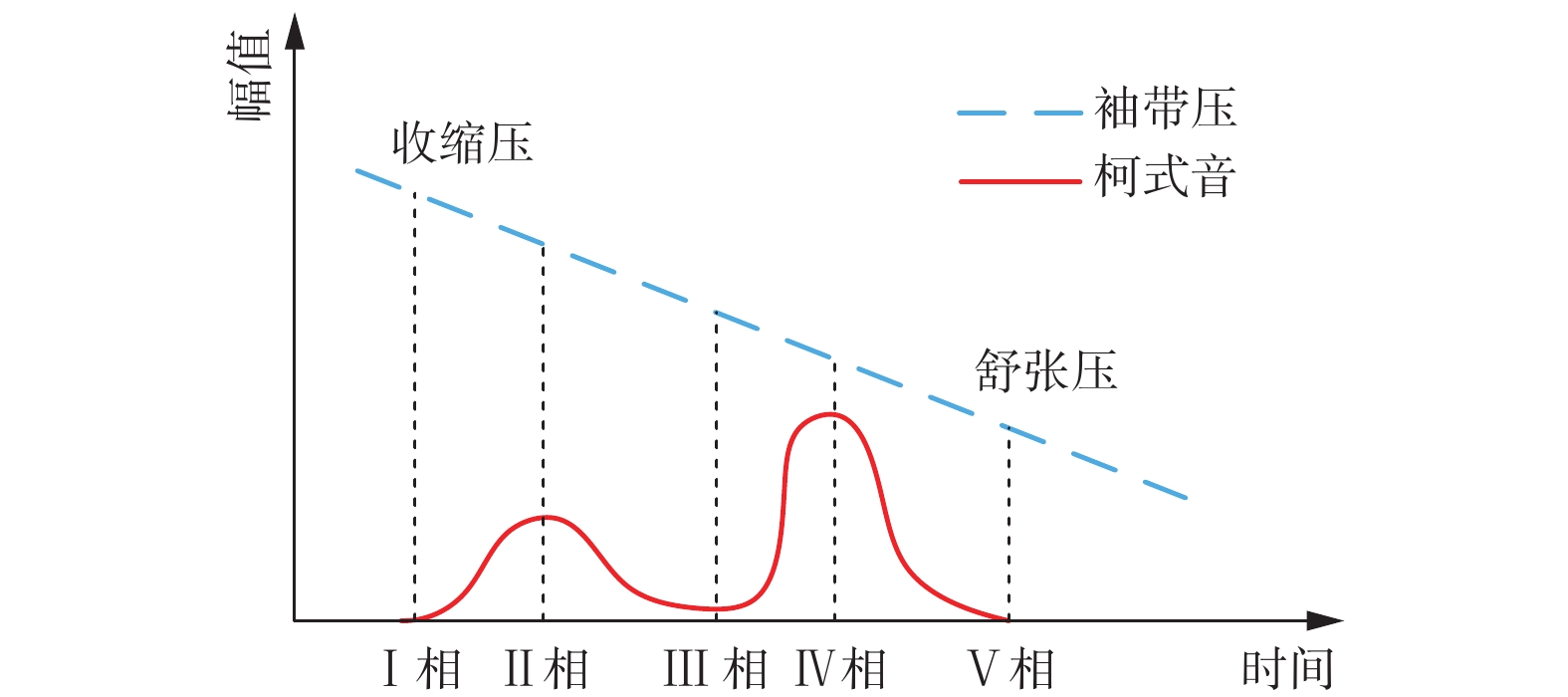
为提高电子血压计测量准确性,根据柯式音法原理,提出自适应分段识别柯式音的测量方案. 先利用双重ADC采集声音和压力信号,实时拟合出静压力方程,然后识别压力信号中的突变点,对柯式音信号进行分段. 随后基于正态分布3σ原则自适应计算阈值,完成中间段柯式音特征点的提取. 最后以心率作为搜索步长识别出收缩压和舒张压点. 试验表明:基于此方法的血压计收缩压标准差为2.18 mmHg,收缩压标准偏差为2.74 mmHg,舒张压标准差为−0.93 mmHg,舒张压标准偏差为2.24 mmHg,证明该方案准确性和稳定性更高,为柯式音电子化测量的优化改进提供了方向.
Abstract:In order to improve the measurement accuracy of electronic sphygmogram, a measure scheme using self-adaptive segmental recognition of Korotkoff sound was proposed based on the principle of Korotkoff sound method. Firstly, the dual ADC was used to collect sound and pressure signals, and the static pressure equation was fitted in real time. Then, the abrupt point in the pressure signal was identified and the signal of Korotkoff sound was segmtioned. Then, the threshold value is calculated adaptively based on the normal distribution 3σ principle, and the feature points of the middle segment Korotkoff sound were extracted. Finally, heart rate was used as the search step to identify systolic and diastolic blood pressure points. The experimental results show that the standard deviation of systolic blood pressure based on this method is 2.18 mmHg (1 mmHg=133.322 Pa), the standard deviation of systolic blood pressure is 2.74 mmHg, the standard deviation of diastolic blood pressure is −0.93 mmHg, and the standard deviation of diastolic blood pressure is 2.24 mmHg, which prove that the scheme has higher accuracy and stability, and provide a direction for the optimization and improvement of electronic measurement of Korotkoff sound.
-
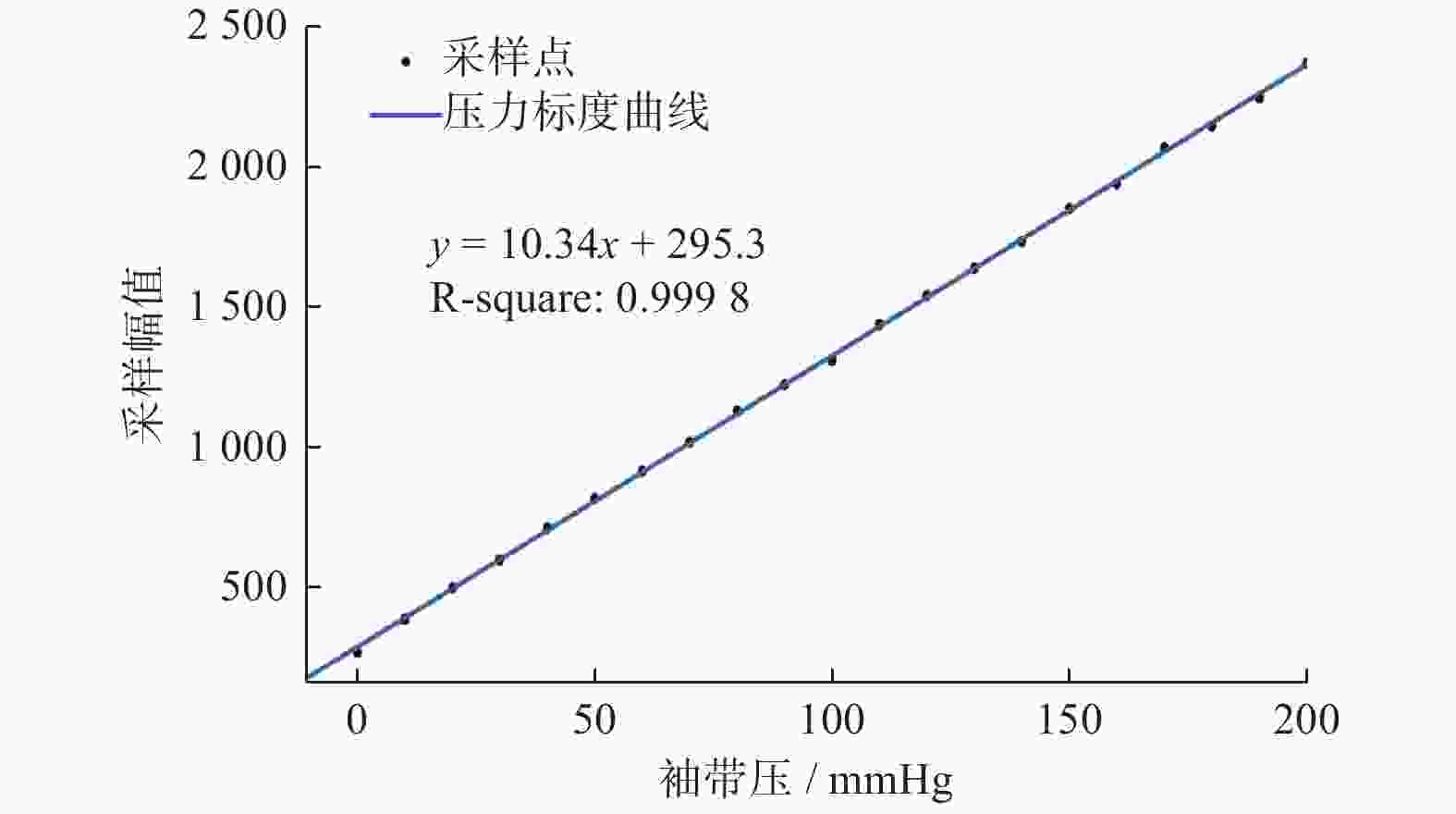
表 1 压力和采样幅值均值对应数据表
Table 1. Corresponding data table of pressure and mean sampling amplitude
压力/mmHg 均值 压力/mmHg 均值 0 276.2922535 70 1021.816901 10 394.4190141 80 1131.584507 20 505.1126761 90 1225.926056 30 604.2922535 100 1312.355634 40 717.4401408 110 1440.239437 50 821.4859155 120 1542.116197 60 919.4683099 130 1640.271127 表 2 不同方法柯式音识别率和误差率
Table 2. Recognition rate and error rate of different methods
柯式音数量 类型 固定阈值法 自适应阈值法 自适应阈值分段法 检出 检出率/% 误差率/% 检出 检出率/% 误差率/% 检出 检出率/% 误差率/% 30 柯式音 22 73.3 26.7 22 73.3 26.7 29 96.7 3.3 加噪声 28 93.3 46.7 21 70.0 30.0 32 106.7 6.7 34 柯式音 26 76.5 23.5 26 76.5 23.5 32 94.1 5.9 加噪声 38 111.8 58.8 26 76.5 23.5 33 97.1 2.9 38 柯式音 30 78.9 21.1 30 78.9 21.1 35 92.1 7.9 加噪声 36 94.7 36.8 31 81.6 18.4 35 92.1 7.9 42 柯式音 34 81.0 19.0 34 81.0 19.0 41 97.6 2.4 加噪声 42 100.0 38.1 34 81.0 19.0 42 100.0 0.0 46 柯式音 38 82.6 17.4 38 82.6 17.4 44 95.7 4.3 加噪声 51 110.9 45.7 37 80.4 15.2 49 106.5 6.5 -
[1] 中国高血压联盟《动态血压监测指南》委员会. 2020中国动态血压监测指南[J] . 中国循环杂志,2021,36(4):313 − 328. [2] 刘爽, 李恩有. 动脉血压监测的临床应用[J] . 医学综述,2017,23(9):1771 − 1774, 1781. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2017.09.022 [3] 付莹. 无创连续血压测量技术的研究进展分析[J] . 中国医疗器械信息,2020,26(2):11, 89. [4] 罗堪, 都可钦, 林友华, 等. 基于示波法的电子血压计设计与实现[J] . 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2018,32(5):177 − 182. [5] 白旭东, 迟戈, 金丹, 等. 间接动态血压监测医疗器械产品现状研究[J] . 中国医疗器械信息,2021,27(1):28 − 29, 147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6586.2021.01.012 [6] 万福瑞, 樊翔, 朱鹏志, 等. 血压测量技术发展综述[J] . 世界最新医学信息文摘(连续型电子期刊),2020,20(31):19 − 20. [7] 袁苑, 薛雷, 何金胜. 基于柯氏音识别法的自动血压测量系统[J] . 电子测量技术,2012,35(2):76 − 79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2012.02.019 [8] 王宁波. 基于柯式音法的电子血压计设计与实现[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2017. [9] 黄海霞, 陈洪波, 陈真诚. 基于柯氏音的电子血压计系统设计[J] . 医疗卫生装备,2013,34(6):1 − 3. [10] 曹俊魏, 程云章. 基于脉搏波信号的无创血压测量的研究进展与展望[J] . 生物医学工程研究,2021,40(2):220 − 224. [11] 许永峰, 贺玉成, 周林. 软件滤波的示波血压测量算法及Android实现[J] . 华侨大学学报 (自然科学版),2017,38(4):567 − 572. [12] 胡欣宇, 王昕波, 赵召龙, 等. 基于柯氏音法与示波法结合的新型血压测量系统[J] . 软件,2017,38(3):78 − 81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6970.2017.03.016 [13] 郝德国. 基于柯氏音与示波法结合的血压计设计与实现[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2012. [14] 庞宇, 蒋伟, 王志成, 等. 基于变幅度系数法的腕式血压测量系统设计[J] . 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,35(2):169 − 176. [15] 李芹. 电子血压计临床准确性评价标准综述[J] . 数字通信世界,2019(6):241, 212. -






 下载:
下载: