Research on trajectory tracking control based on radial basis neural network PID and model predictive control
-
摘要:
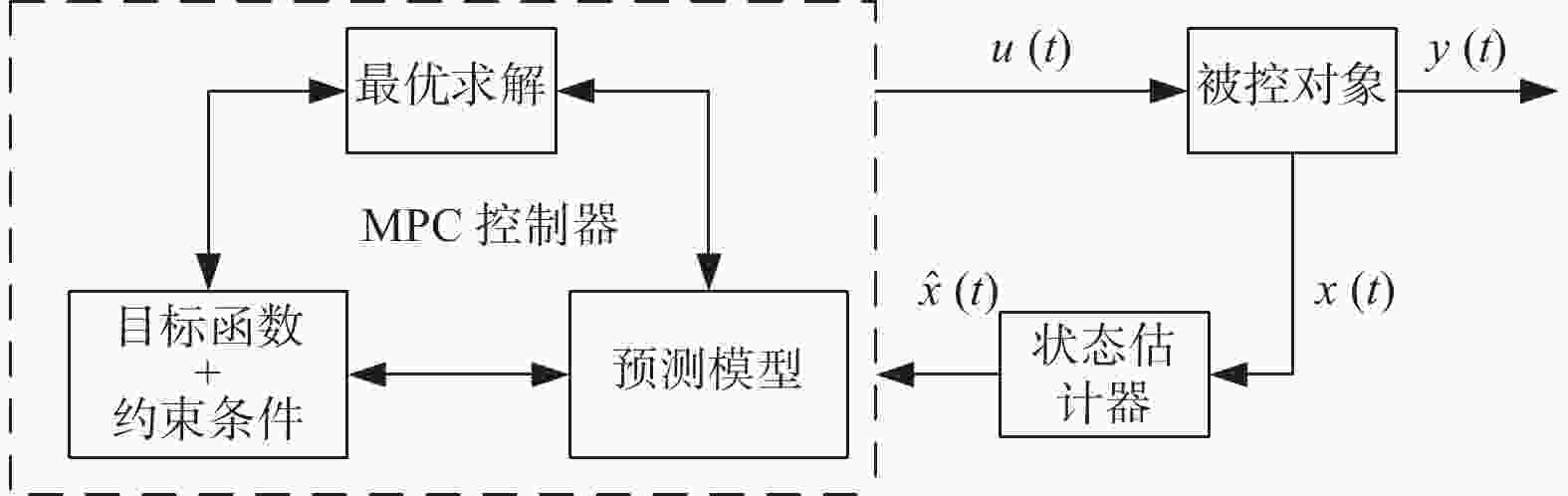
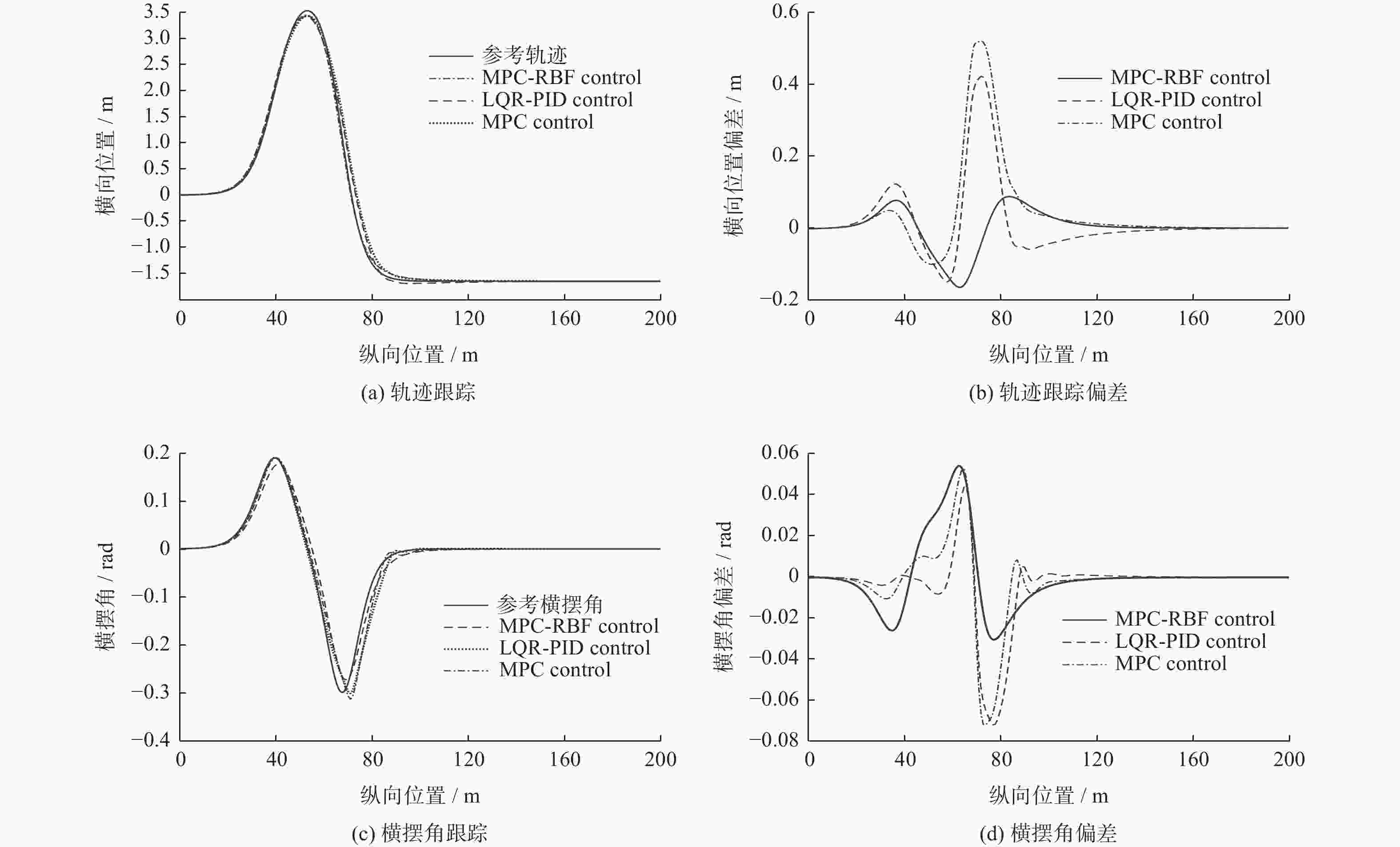
为提高无人驾驶车辆的稳定性和鲁棒性,提出一种基于径向基函数神经网络自适应比例积分微分(RBFNN−PID)算法和模型预测控制(MPC)算法相结合的车辆轨迹跟踪控制方法. 基于自适应RBFNN−PID算法、MPC算法以及车辆动力学模型,建立智能车辆纵向速度控制和横向控制的仿真模型并将其结合起来. 在此基础上,以横向MPC控制和LQR−PID控制算法为基准,验证所提出的控制方法在轨迹跟踪方面的优越性. 仿真结果表明,新方法比对照组具有更高的精度. 最后,对新控制方法的硬件在环验证表明,该轨迹跟踪控制算法在轨迹跟踪精度和稳定性方面具有一定的有效性和先进性.
Abstract:In order to improve the stability and robustness of self-driving vehicle, a trajectory tracking control method was proposed based on the combination of self-adaptive proportional integral derivative (PID) of radial basis function neural network (RBFNN−PID) and model predictive control (MPC). A simulation model of intelligent vehicle longitudinal speed control and lateral control was established based on self-adaptive RBFNN−PID algorithm, MPC algorithm and vehicle dynamics model. Based on that, the lateral MPC and LQR−PID control algorithm were used as benchmarks to demonstrate the superiority of the presented control method in trajectory tracking. The simulation results show that the presented control method has higher accuracy than the comparing group. Finally, the hardware-in-the-loop verification of the proposed control method is carried out. The results show that the proposed trajectory tracking control algorithm is effective and advanced in trajectory tracking accuracy and stability.
-
表 1 车辆动力学参数
Table 1. Vehicle dynamics parameters
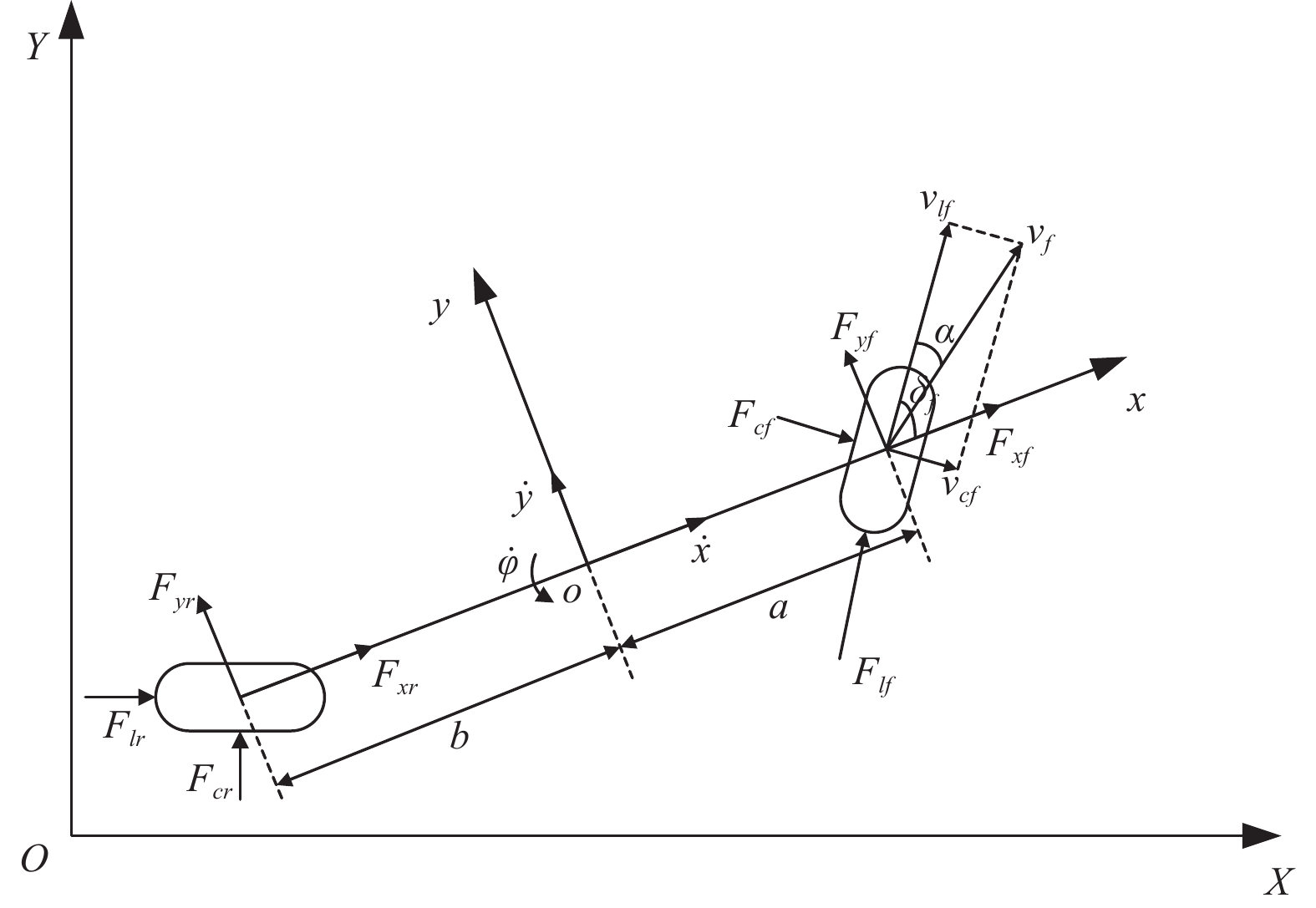
参数 数值 轴距/mm a=1015, b=1895 车身尺寸/mm L=3850, W=2080 绕z轴转动惯量/(kg·m2) 1536.7 整车质量/kg 1413 轮胎侧偏刚度/(N·rad−1) Ccf =−148970, Ccr =−82204 表 2 控制器参数
Table 2. Controller parameters
参数 数值 Np 30 Nc 15 T/s 0.01 δf /(°) −15~15 Δδf /(°) −0.5~0.5 Q diag(30,1,5,1) R 6 表 3 车道1前方车辆行驶信息
Table 3. Vehicle driving informations ahead of lane 1
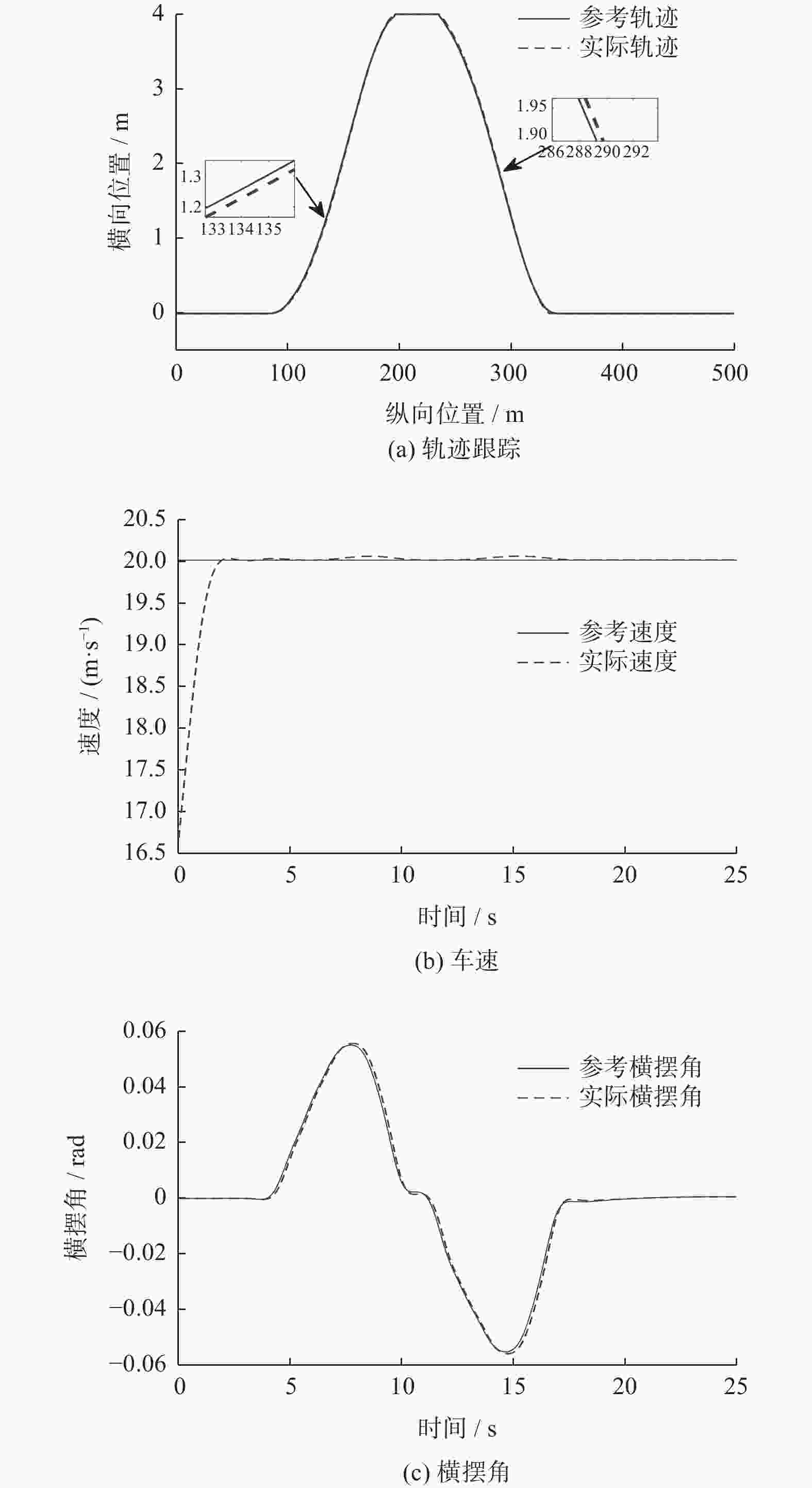
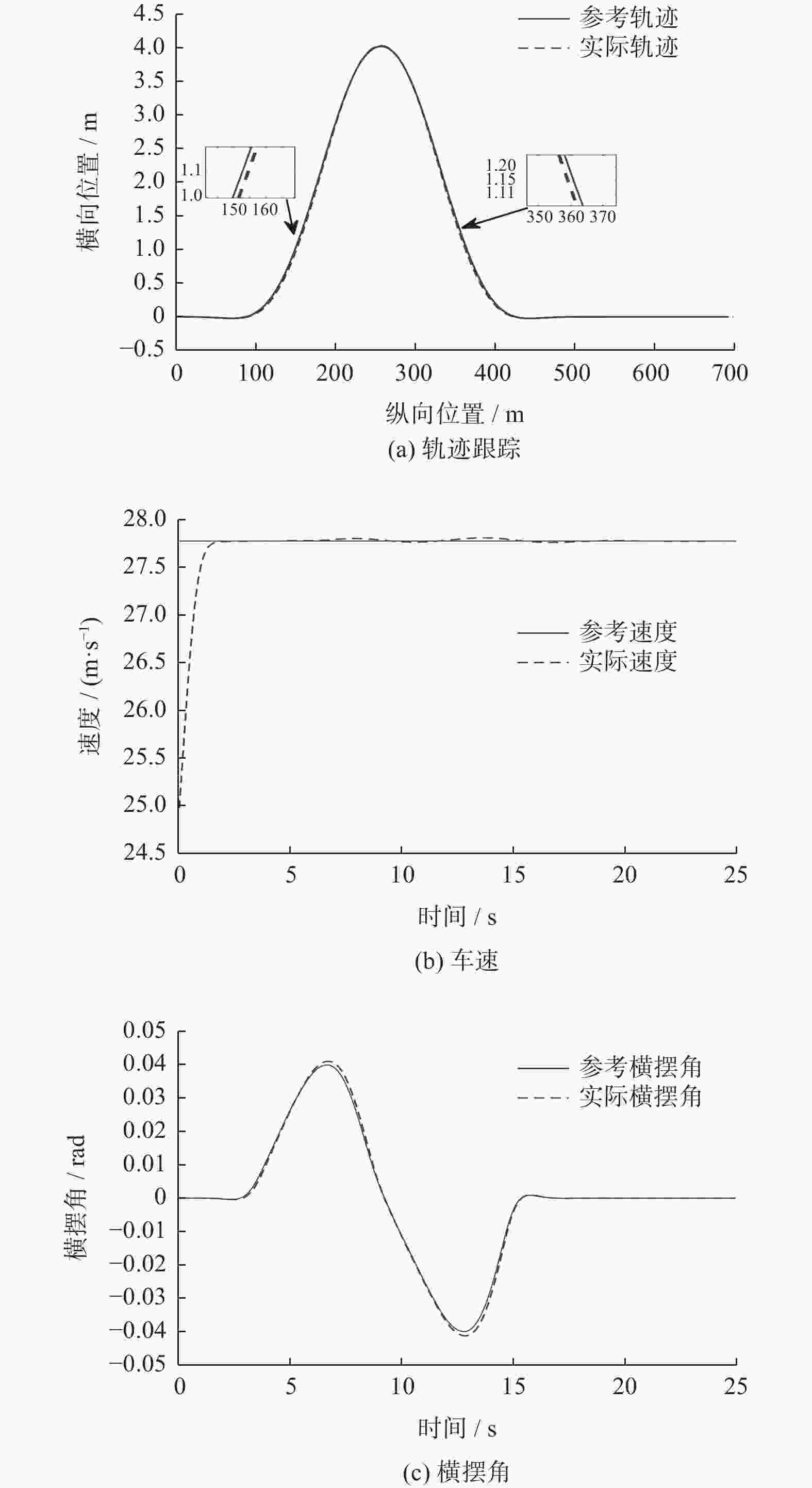
场景 状态信息 数值 场景一 车速/(km·h−1) 54 横向位置/m 0 纵向位置/m 0 场景二 车速/(km·h−1) 80 横向位置/m 0 纵向位置/m 0 表 4 不同车速仿真误差
Table 4. Simulation error of different speed
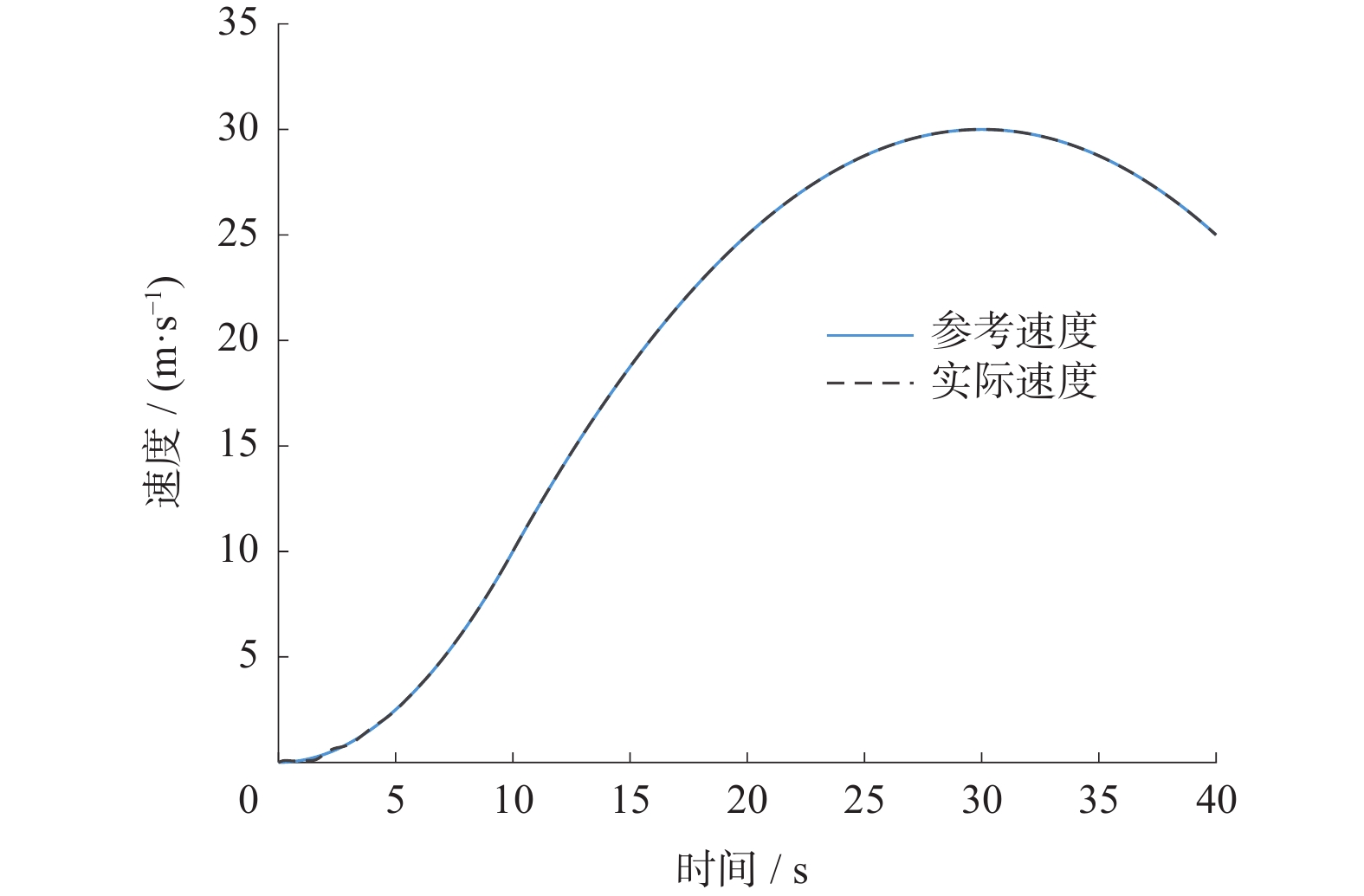
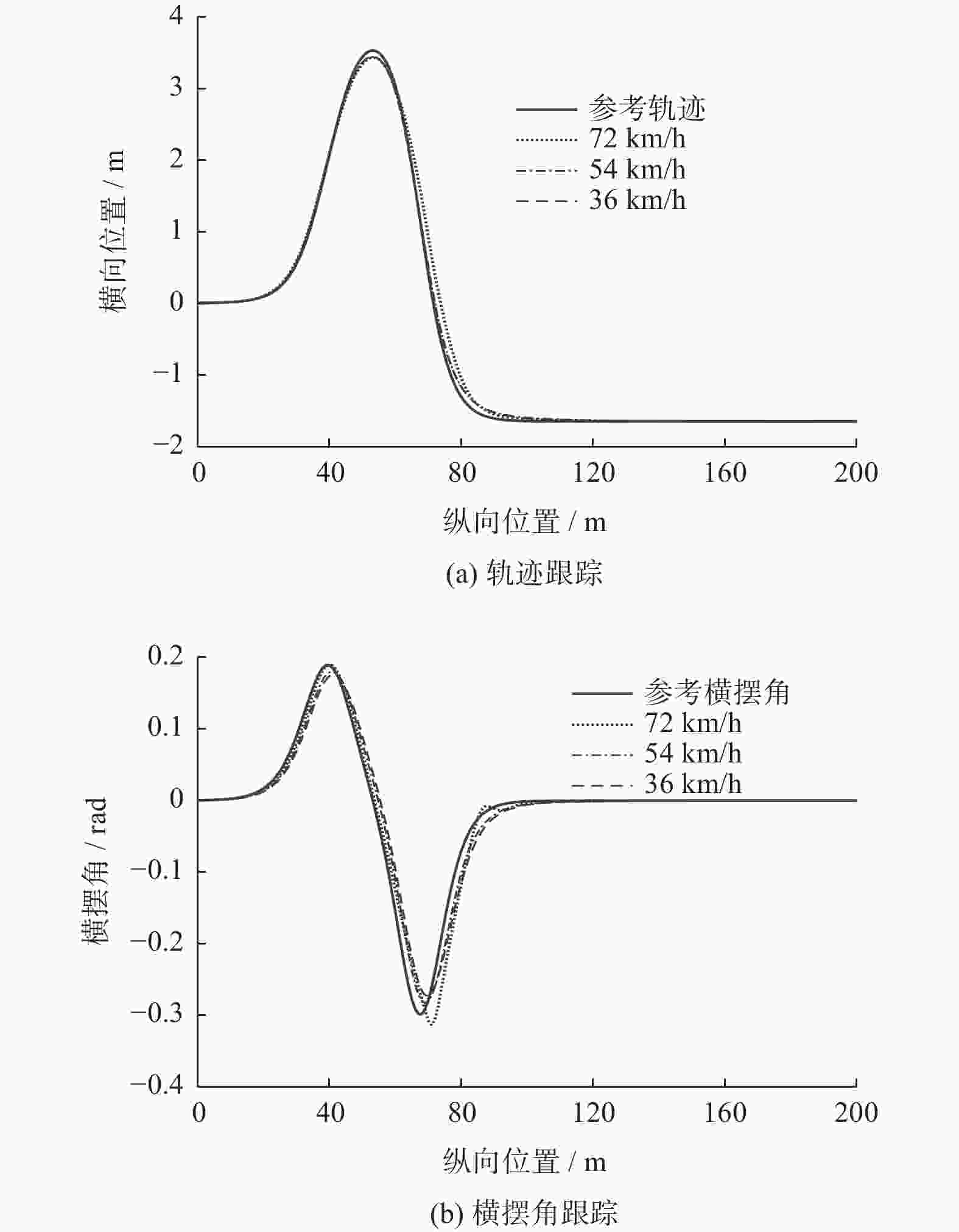
速度/(km•h−1) 轨迹跟踪情况 最大横向偏差/m 最大航向偏差/rad 最大速度偏差/(km•h−1) 72 良好 0.06 0.004 0.188 100 良好 0.10 0.002 0.150 -
[1] BADUE C, GUIDOLINI R, CARNEIRO R V, et al. Self-driving cars: A survey[J] . Expert Systems with Applications,2020:113816. [2] 陈慧岩, 熊光明, 龚建伟. 无人驾驶汽车概论[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2014. [3] AGRIESTI S, BREVI F, GANDINI P, et al. Impact of driverless vehicles on urban environment and future mobility[J] . Transportation Research Procedia,2020,49:44 − 59. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2020.09.005 [4] 张琨. 智能汽车自主循迹控制策略研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013. [5] 聂枝根, 王万琼, 赵伟强, 等. 基于轨迹预瞄的智能汽车变道动态轨迹规划与跟踪控制[J] . 交通运输工程学报,2020,20(2):147 − 160. [6] 姜岩, 龚建伟, 熊光明, 等. 基于运动微分约束的无人车辆纵横向协同规划算法的研究[J] . 自动化学报,2013,39(12):2012 − 2020. [7] 罗鹰, 冒兴蜂. 智能汽车换道避障路径规划与跟踪控制研究[J] . 机械设计与制造,2019(7):139 − 143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2019.07.035 [8] 龚建伟, 姜岩, 徐威. 无人驾驶车辆模型预测控制[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2014. [9] 陈虹. 模型预测控制[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. [10] ALCALA E, PUIG V, QUEVEDO J. LPV-MPC control for autonomous vehicles[J] . IFAC-PapersOnLine,2019,52(28):106 − 113. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2019.12.356 [11] BAO C J, FENG J W, WU J, et al. Model predictive control of steering torque in shared driving of autonomous vehicles[J] . Science Progress,2020,103(3):1 − 22. [12] PAUCA O, CARUNTU C F, LAZAR C. Predictive control for the lateral and longitudinal dynamics in automated vehicles[C]//2019 23rd International Conference on System Theory, Control and Computing (ICSTCC). Sinaia: IEEE, 2019: 797-802. [13] 张正华. 基于神经网络的无人驾驶车辆轨迹跟踪控制[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2019. [14] 肖宗鑫, 李晓杰, 肖宗烁, 等. 基于RBF神经网络优化的无人驾驶车辆增量线性模型预测轨迹跟踪控制研究[J] . 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2021,35(3):36 − 45. -






 下载:
下载: