Modeling and analysis of rate-dependent hysteresis characteristics of Maxwell reluctance actuator based on Prandtl−Ishlinskii model
-
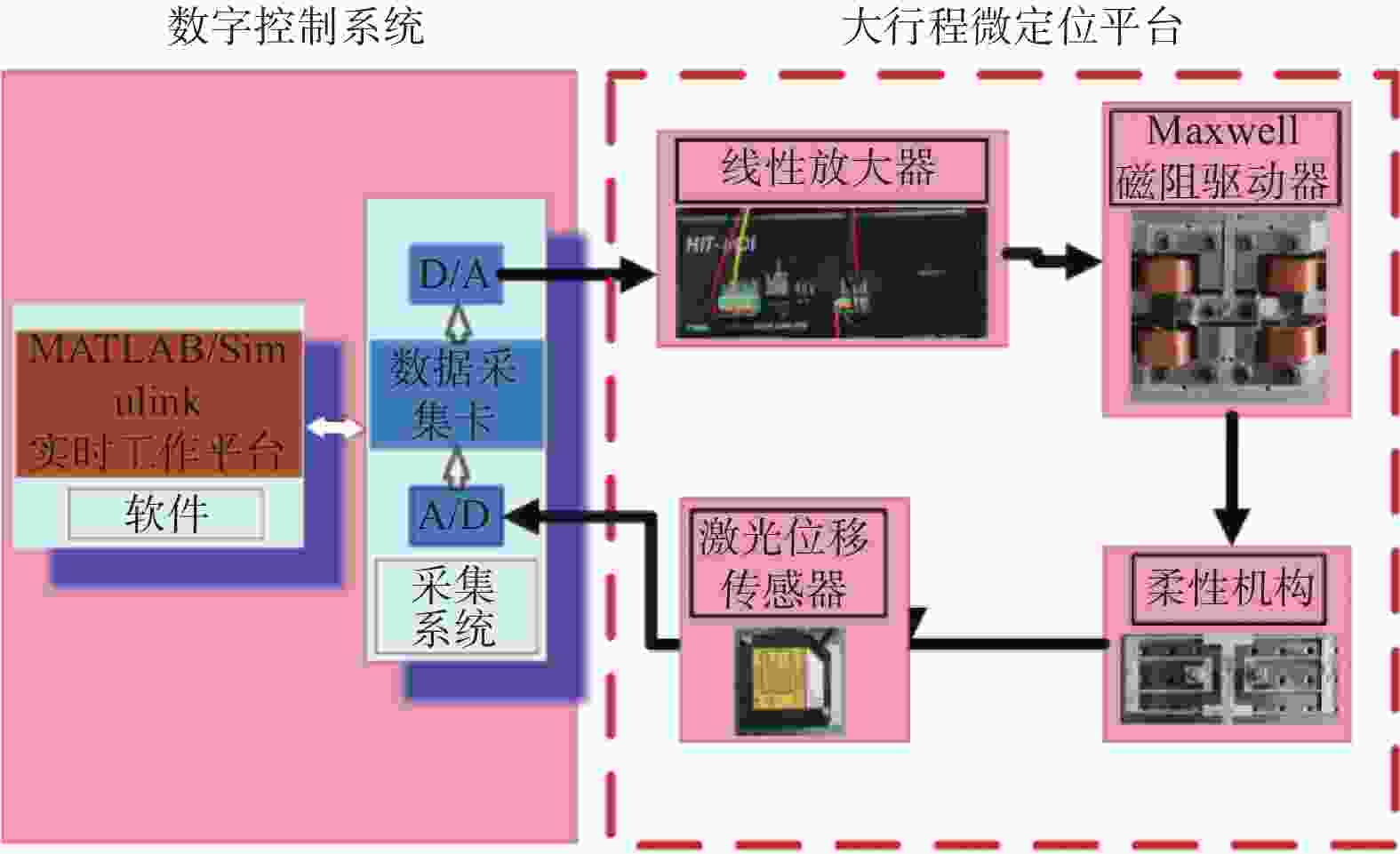
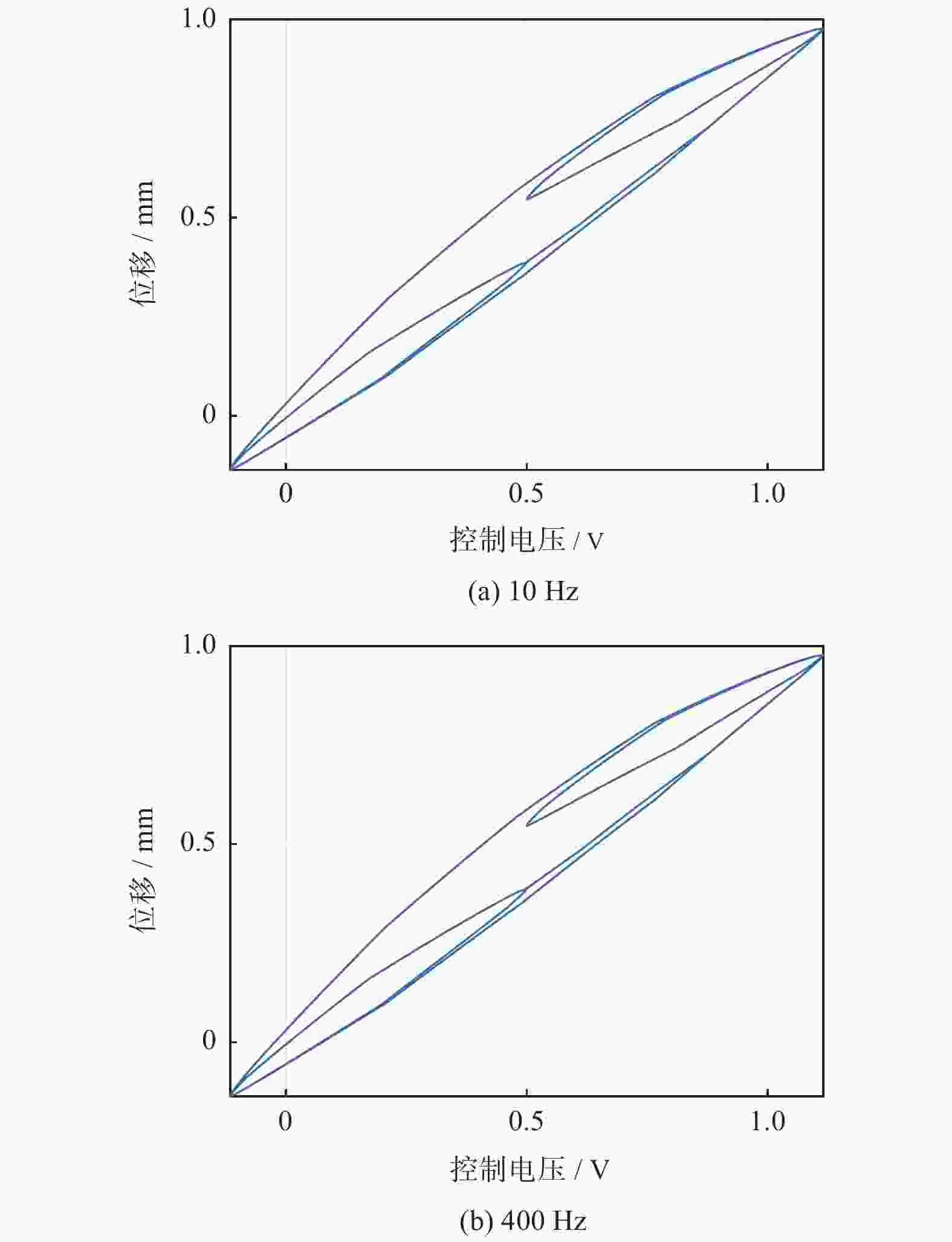
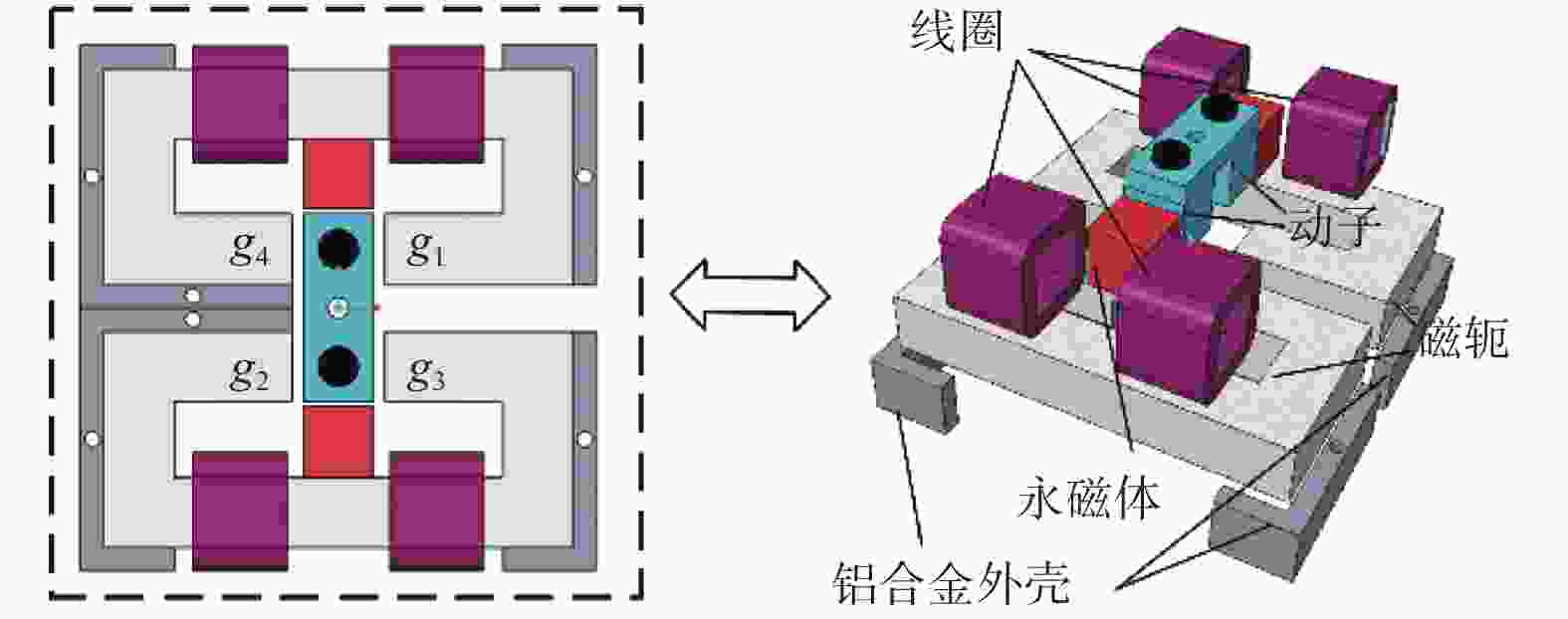
摘要: 为克服麦克斯韦磁阻驱动器材料内部磁场强度与磁感应强度之间强烈的磁滞非线性以及大气隙下漏磁增加等因素引发的驱动器控制电压与输出位移之间的磁滞特性,提出一种率相关改进型Prandtl−Ishlinskii(P−I)模型对磁阻驱动器的磁滞特性进行建模. 分析磁阻驱动器结构及其磁路和磁力模型,同时搭建基于柔性机构的磁阻驱动微定位平台试验系统,验证磁滞模型. 为克服驱动器磁滞非线性,优化改进传统P−I模型,使其具有描述非对称率相关磁滞特性的能力,并利用粒子群算法完成参数辨识. 通过对比试验验证所建模型对于磁阻驱动器磁滞非线性的描述能力. 结果表明,不同频率输入信号下率相关P−I模型输出与实际输出之间的均方根误差均小于0.0049 mm,仅为整体行程的0.245%, 证明了该模型的有效性和高精度.
-
关键词:
- 麦克斯韦磁阻驱动器 /
- 磁滞 /
- Prandtl-Ishlinskii模型 /
- 率相关
Abstract: In order to overcome the strong hysteresis nonlinearity between the internal magnetic field strength and magnetic induction strength of Maxwell reluctance actuator materials and the hysteresis between the actuator control voltage and output displacement caused by the increase of magnetic leakage under the long air gap, a rate-dependent improved Prandtl−Ishlinskii (P−I) model was proposed to model the hysteresis characteristics of reluctance actuator. The structure, magnetic circuit and magnetic force model of reluctance actuator were analyzed, and the experimental system of reluctance actuator micropositioning stage based on flexible mechanism was built for the verification of hysteresis model. In order to overcome the hysteresis nonlinearity of the actuator, the traditional P−I model was optimized and improved to make it have the ability to describe the asymmetric rate-dependent hysteresis characteristics, and the particle swarm optimization algorithm was used to complete the parameter identification. The comparative experiment was used to verify the ability of the rate-dependent P−I model to describe the hysteresis nonlinearity of the reluctance actuator. The results show that the root mean square error between the output of rate-dependent P−I model and the actual output under different frequency input signals is less than 0.0049 mm, which is only 0.245% of the overall stroke, and the effectiveness and high precision of the model are proved. -
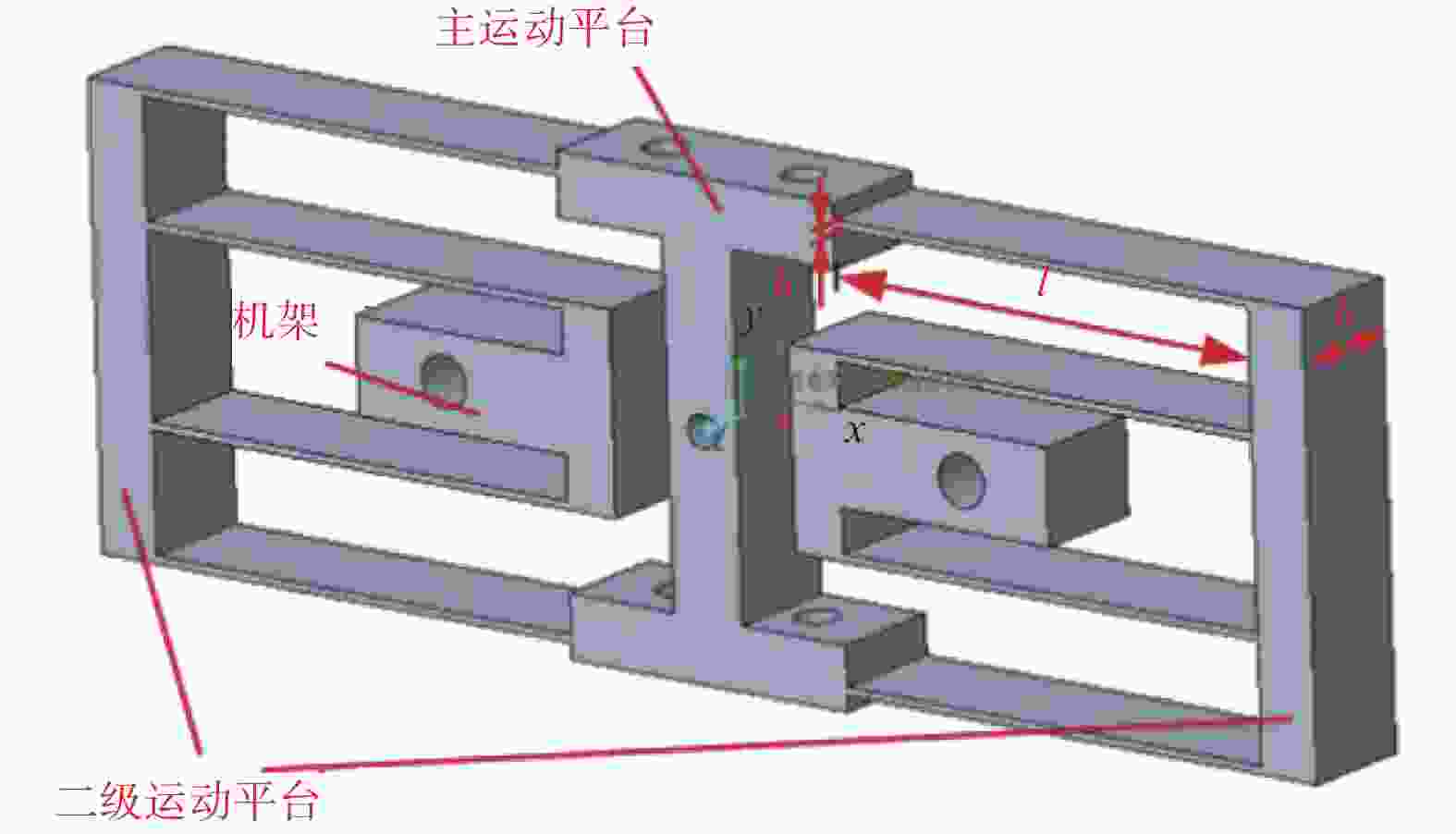
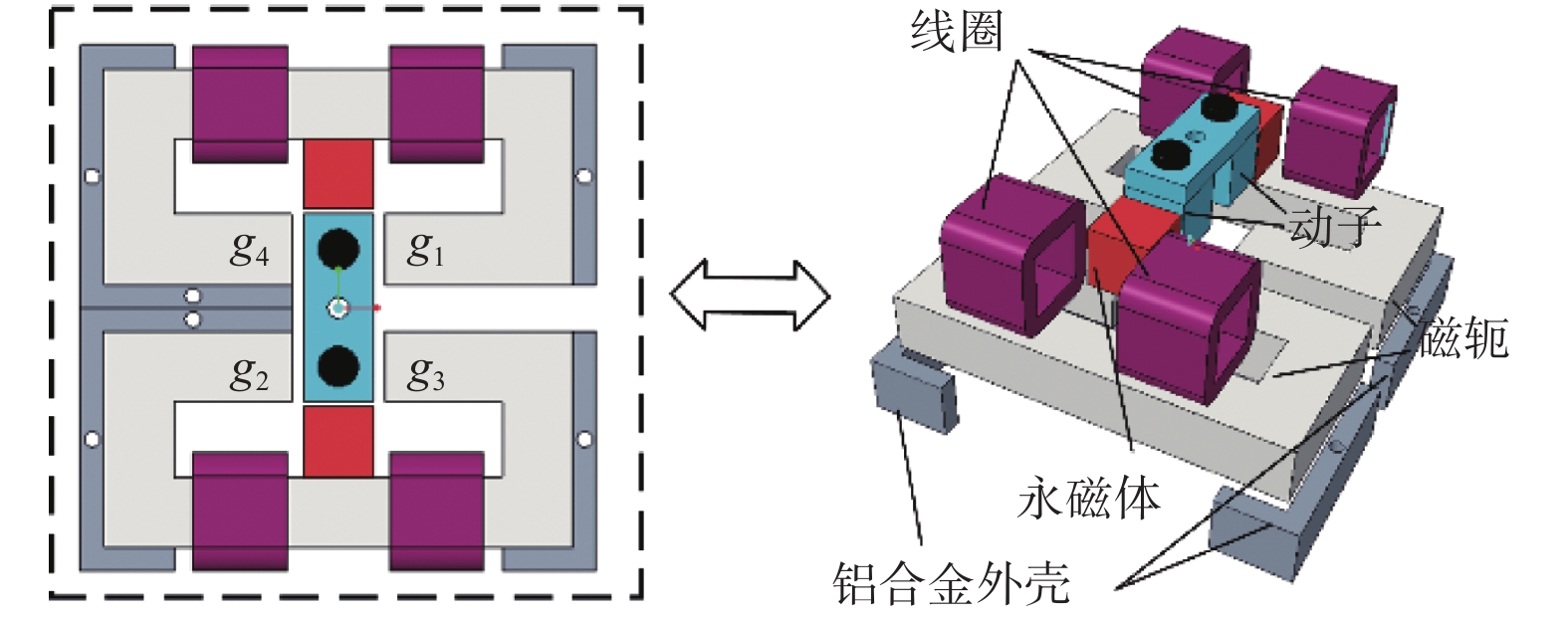
表 1 磁阻驱动器结构尺寸
Table 1. Dimensions of reluctance actuator
尺寸/mm 磁轭 永磁体 动子 长 100 15 18 宽 46 15 15 高 15 15 15 垂直磁通方向横截面/mm2 15×15 15×15 15×15 表 2 率相关P−I模型参数
Table 2. Parameters of rate-dependent P−I model
序号i ri pi ai δ/ζ 1 0 0.0762 0.0762 0.0915 2 1.5 0.1198 0.1807 0.2398 3 3 0.1490 4 4.5 0.1746 5 6 0.0470 6 7.5 0.1345 7 9 0.1054 8 10.5 0.1114 9 12 0.0425 10 13.5 0.0088 表 3 不同频率下模型输出与实际输出间的均方根误差
Table 3. Root mean square error (RMSE) between model output and actual output at different frequencies
信号频率/Hz 率相关模型/mm 率无关模型/mm 1 0.0049 0.0048 5 0.0030 0.0236 10 0.0041 0.0509 -
[1] 谢晓丹, 王博超, 吴丹. 电磁驱动快速刀具伺服机构的电磁场和驱动力[J] . 清华大学学报(自然科学版),2008,48(8):1298 − 1301. [2] KATALENIC A , BOEIJ J D, BUTLER H, et al. Linearization of a current-actuator reluctance actuator with hysteresis compensation[J] . Mechatronics,2013,23(2):163 − 171. [3] ZHU Z, CHEN L, TO S. A novel direct drive electromagnetic XY nanopositioning stage[J] . CIRP Annals,2005,70(1):415 − 388. [4] 邹亮, 李庆民, 许家响, 等. 考虑漏磁效应的永磁饱和型故障限流器磁路建模与实验研究[J] . 中国电机工程学报,2012,32(21):137 − 145. [5] 向洪岗, 陈德桂, 李兴文, 等. 基于三维磁场分析建立电磁铁等效磁路的研究[J] . 西安交通大学学报,2003,37(8):4. [6] 毛剑琴, 丁海山. 率相关迟滞非线性系统的智能化建模与控制[J] . 中国科学:信息科学,2009,39(3):289 − 304. [7] 贺一丹, 王贞艳, 何延昭, 等. 压电陶瓷作动器的改进Duhem迟滞建模[J] . 压电与声光,2021,43(3):431 − 434. doi: 10.11977/j.issn.1004-2474.2021.03.029 [8] RAKOTONDRABE M. Bouc-Wen modeling and inverse multiplicative structure to compensate hysteresis nonlinearity in piezoelectric actuators[J] . IEEE Transactions on Automation Science & Engineering,2011,8(2):428 − 431. [9] KATALENIC A. Control of reluctance actuators for high-precision positioning[D]. Eindhoven: Eindhoven University of Technology, 2013. [10] CRUZ-HERNANDEZ J M, HAYWARD V. Phase control approach to hysteresis reduction[J] . IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology,2001,9(1):17 − 26. doi: 10.1109/87.896742 [11] ANG W, KHOSLA P, RIVIERE C. Feedforward controller With inverse rate-dependent model for piezoelectric actuators in trajectory-tracking applications[J] . IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics,2007,12(2):134 − 142. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2007.892824 [12] TAN U, LATT W, WIDJAJA F, et al. Tracking control of hysteretic piezoelectric actuator using adaptive rate-dependent controlle[J] . Sensors and Actuators A: Physical,2009,150:116 − 123. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2008.12.012 [13] LU X D, TRUMPER D L. Ultrafast tool servos for diamond turning[J] . CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology,2005,54(1):383 − 388. doi: 10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60128-0 [14] CSENCSICS E , SCHLARP J , SCHITTER G . Bandwidth extension of hybrid-reluctance-force-based tip/tilt system by reduction of eddy currents[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM). Munich: IEEE, 2017. [15] YANG M J, GU G Y, ZHU L M. Parameter identification of the generalized Prandtl–Ishlinskii model for piezoelectric actuators using modified particle swarm optimization[J] . Sensors and Actuators A: Physical,2013,189:254 − 265. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2012.10.029 -





 下载:
下载: