Instance segmentation method based on improved Mask R−CNN for the stacked automobile parts
-
摘要:
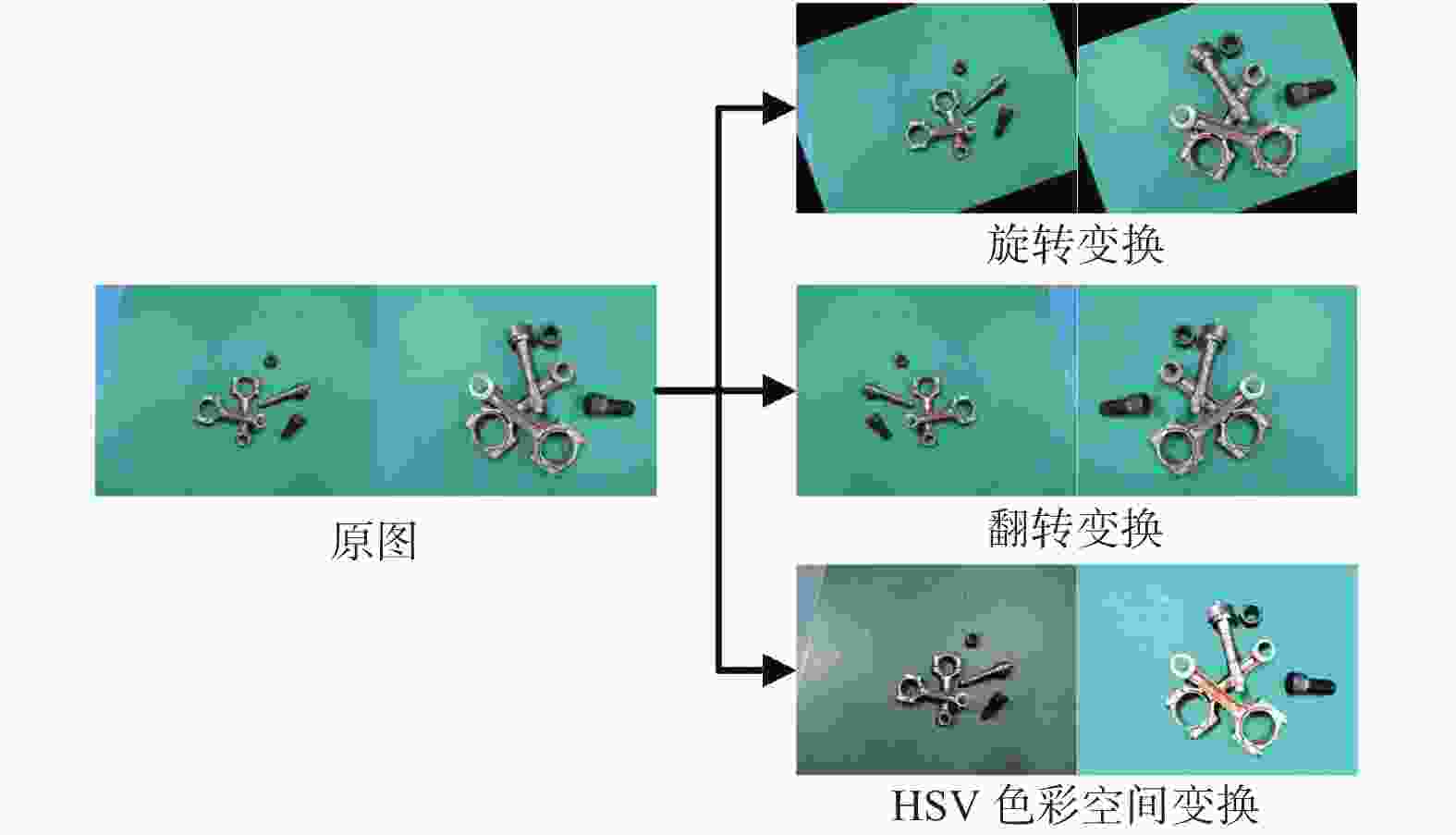
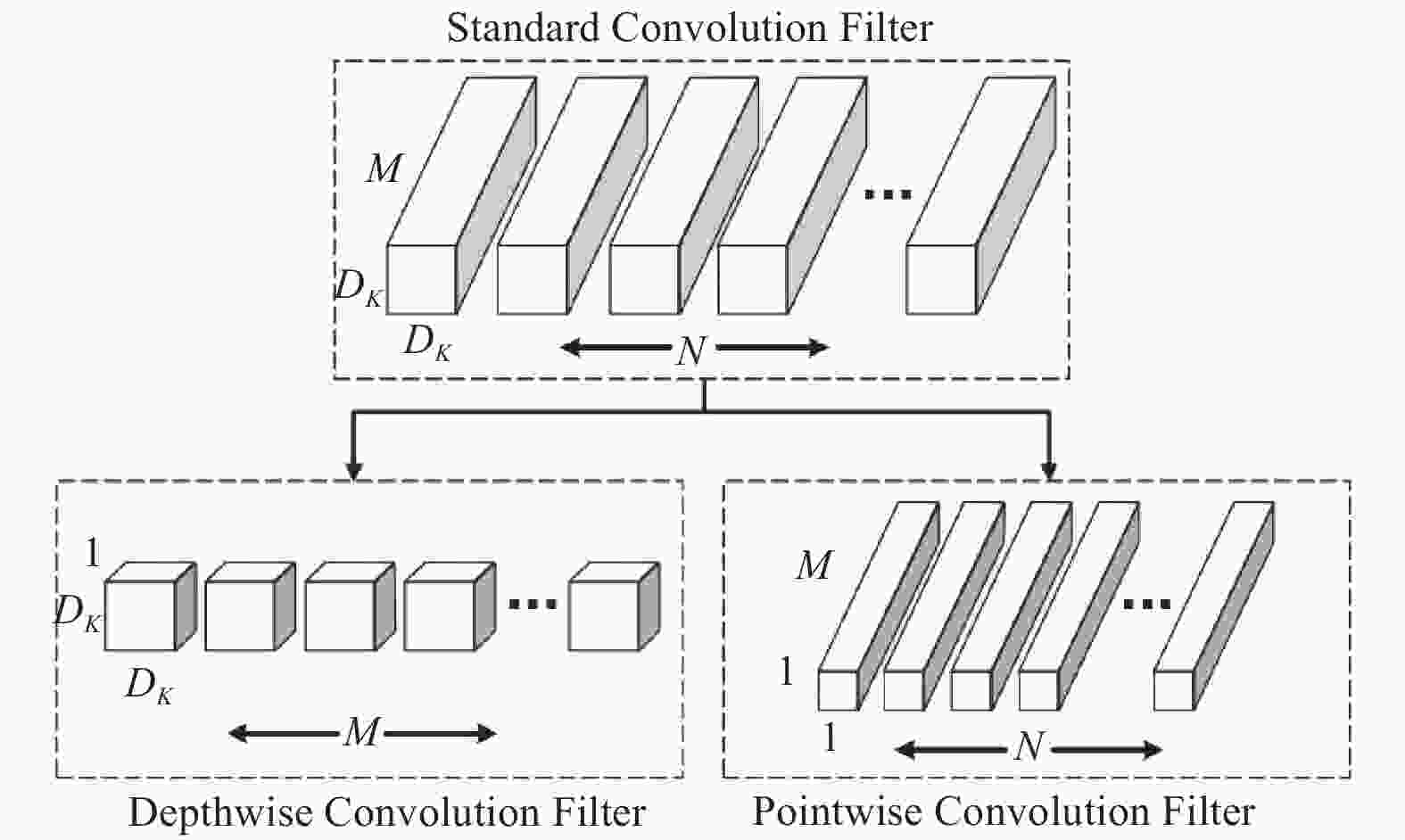
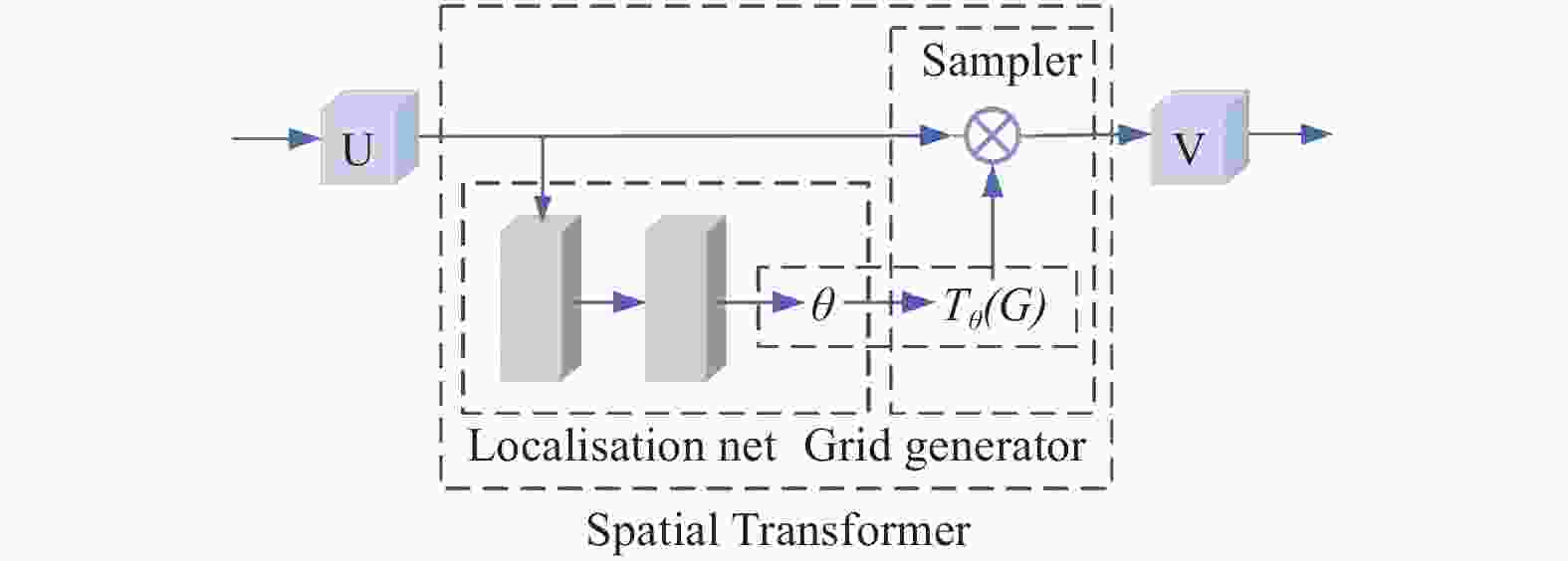
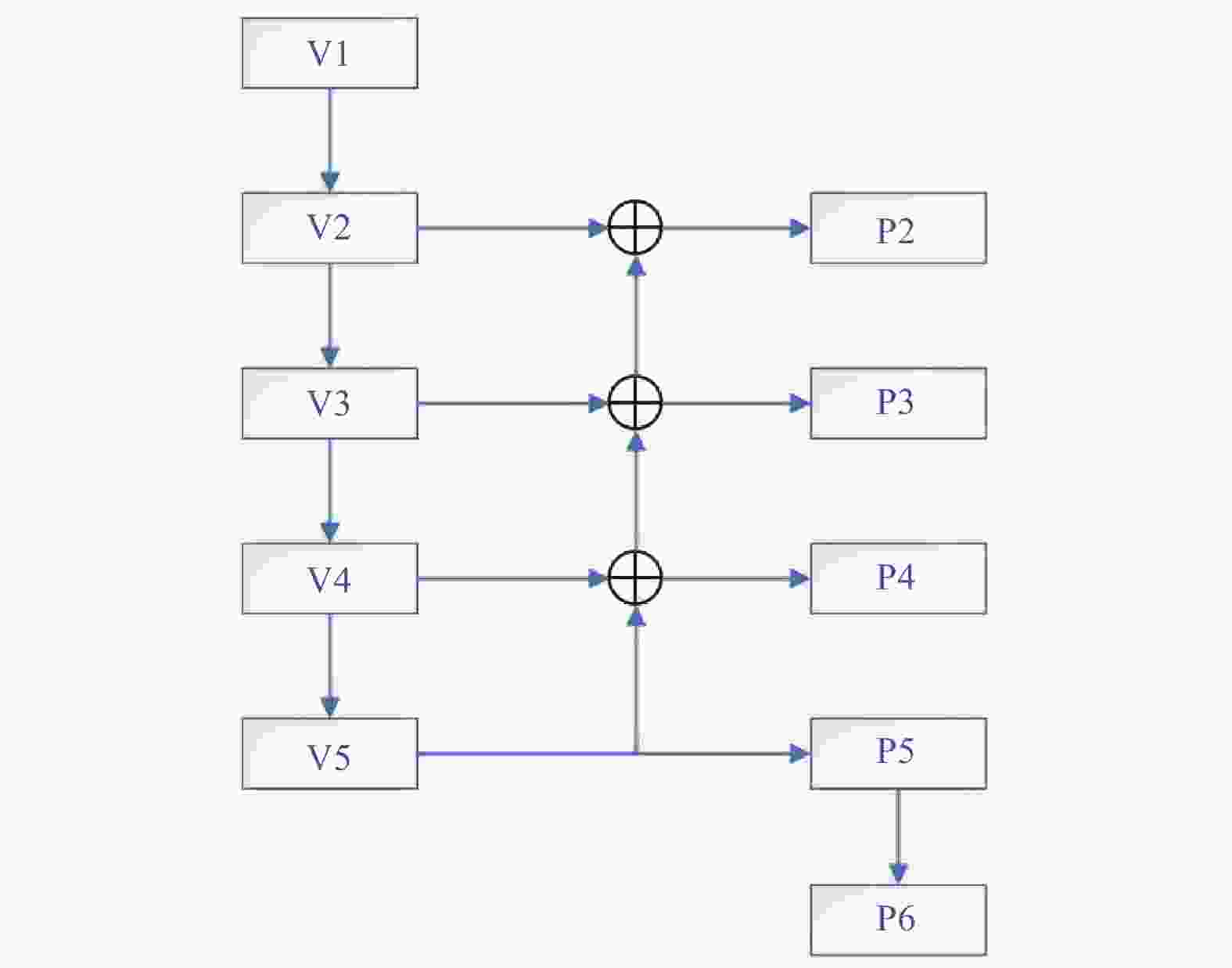
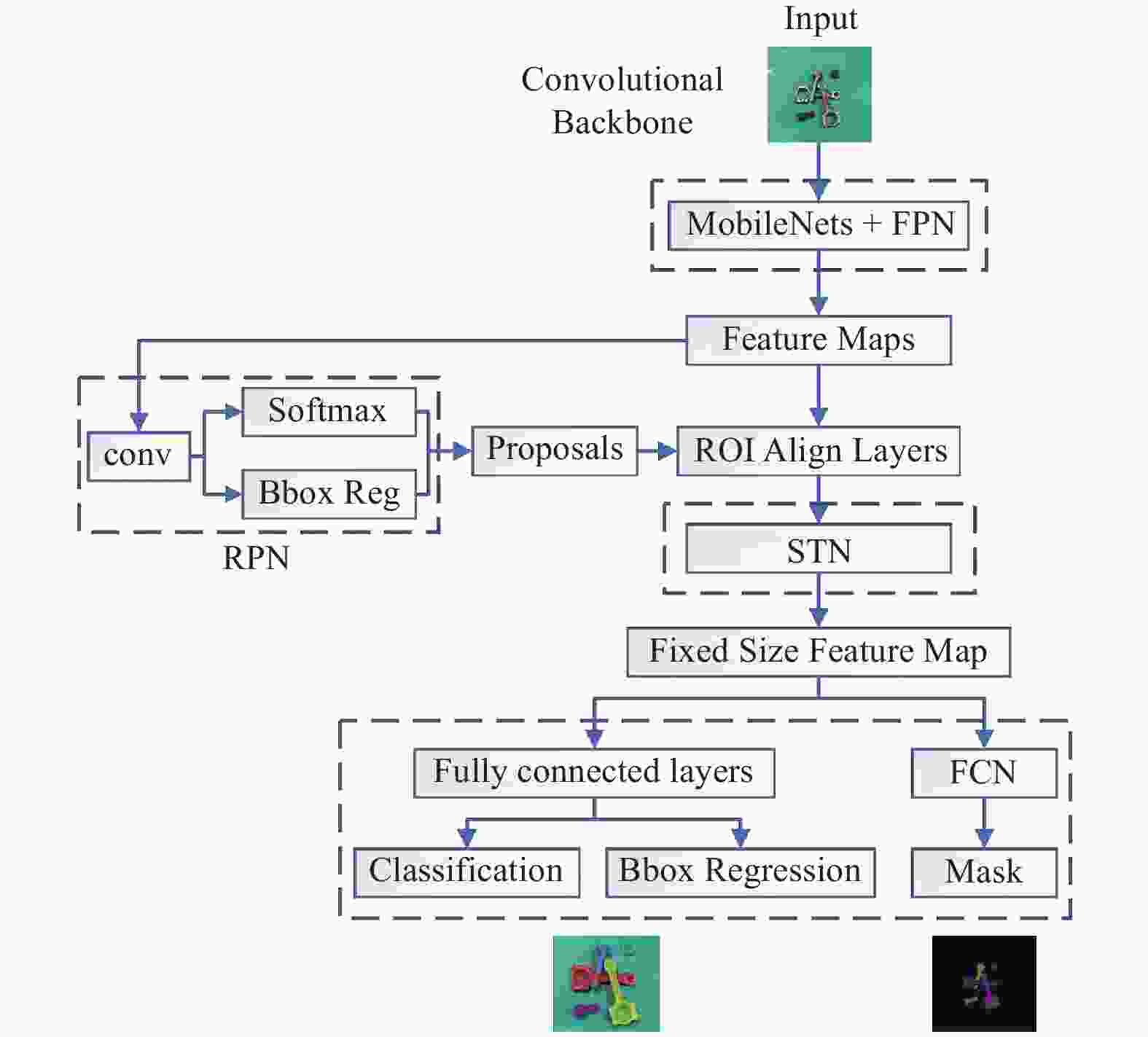
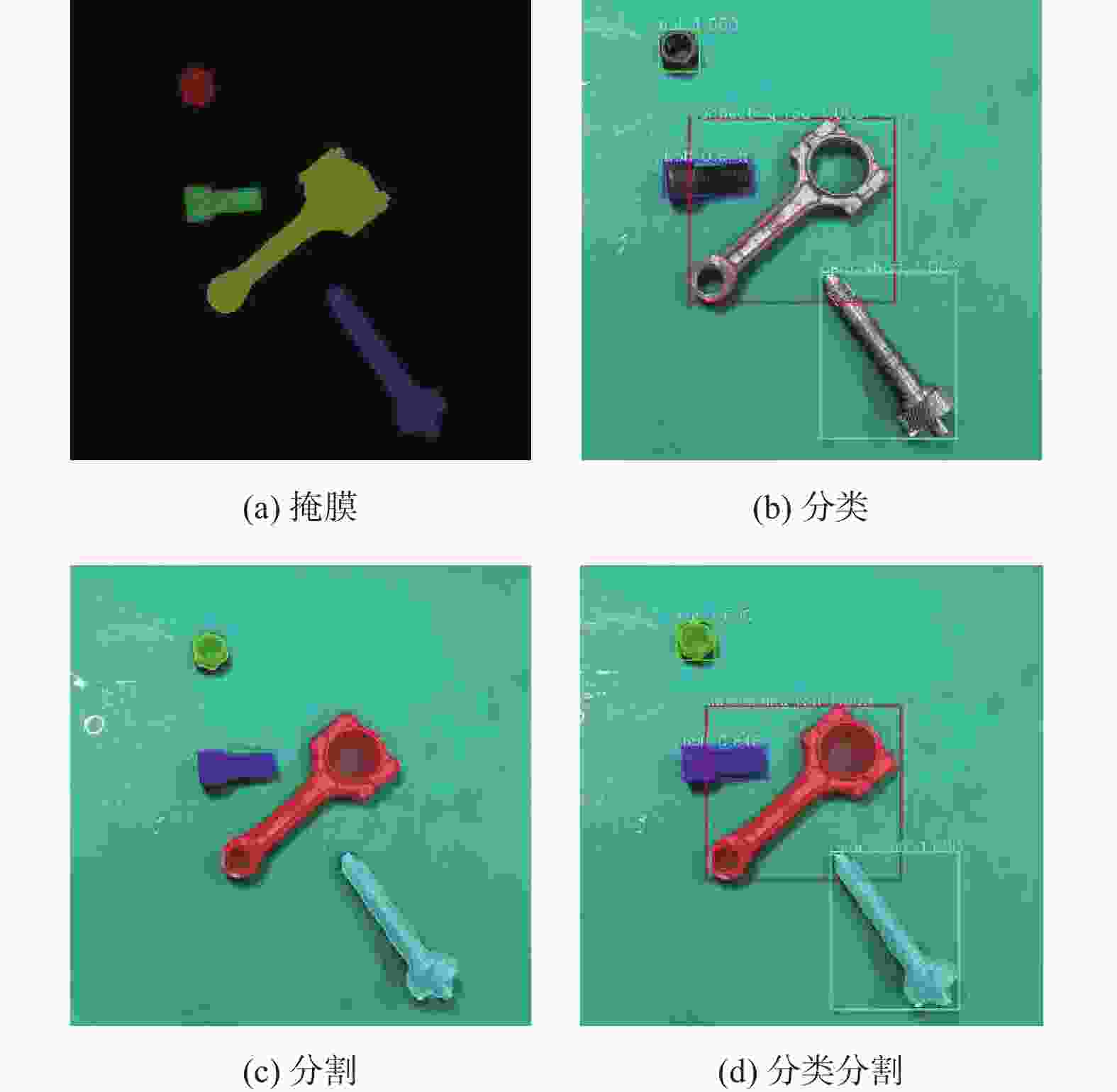
针对堆叠汽车零件识别检测与分割速度慢、精度低及鲁棒性差等问题,提出一种基于改进Mask R−CNN算法对堆叠汽车零件快速检测与实例分割的方法. 首先,对Mask R−CNN中的特征提取网络进行优化,将ResNet + 特征金字塔网络(Feature Pyramid Networks,FPN)替换成MobileNets + FPN作为骨干网络,有效减少网络参数并压缩模型体积,提高模型检测的速度;然后,通过在Mask R−CNN的ROI Align结构后加入空间变换网络(Spatial Transformer Networks,STN)模块,保证模型的检测精度. 试验结果表明,改进后压缩了模型的尺寸,识别检测速度提升了1倍;模型的平均精度均值(Mean Average Precision,mAP)较改进前也有所提升. 对未经训练的新样本进行检测,结果表明该模型速度上优于Mask R−CNN,且更轻量和精准,能够快速准确地实现对堆叠汽车零件检测与分割,验证了改进模型的实际可行性.
-
关键词:
- 实例分割 /
- 堆叠 /
- MobileNets模型 /
- 空间变换网络
Abstract:Aiming at the problems of slow speed, low accuracy and poor robustness in recognition, detection and segmentation of stacked automobile parts, a fast detection and instance segmentation method based on improved Mask R−CNN algorithm was proposed. Firstly, the feature extraction network of Mask R-CNN was optimized, and ResNet + Feature Pyramid Networks (FPN) was replaced by MobileNets + FPN as the backbone network, which effectively reduced network parameters, compressed model volume and improved model detection speed. Then,Spatial Transformer Networks (STN) module was added after the ROI Align structure of Mask R-CNN to ensure the detection accuracy of the model. The experimental results show that the size of the model is compressed and the detection speed is doubled. The mean Average Precision (mAP) of the model is also improved. The detection of untrained new samples shows that the model is better than Mask R−CNN in speed, lighter and more accurate, and can quickly and accurately detect and segment stacked automobile parts, which verifies the practical feasibility of the improved model.
-
Key words:
- instance segmentation /
- stacked /
- MobileNets model /
- spatial transformer networks (STN)
-
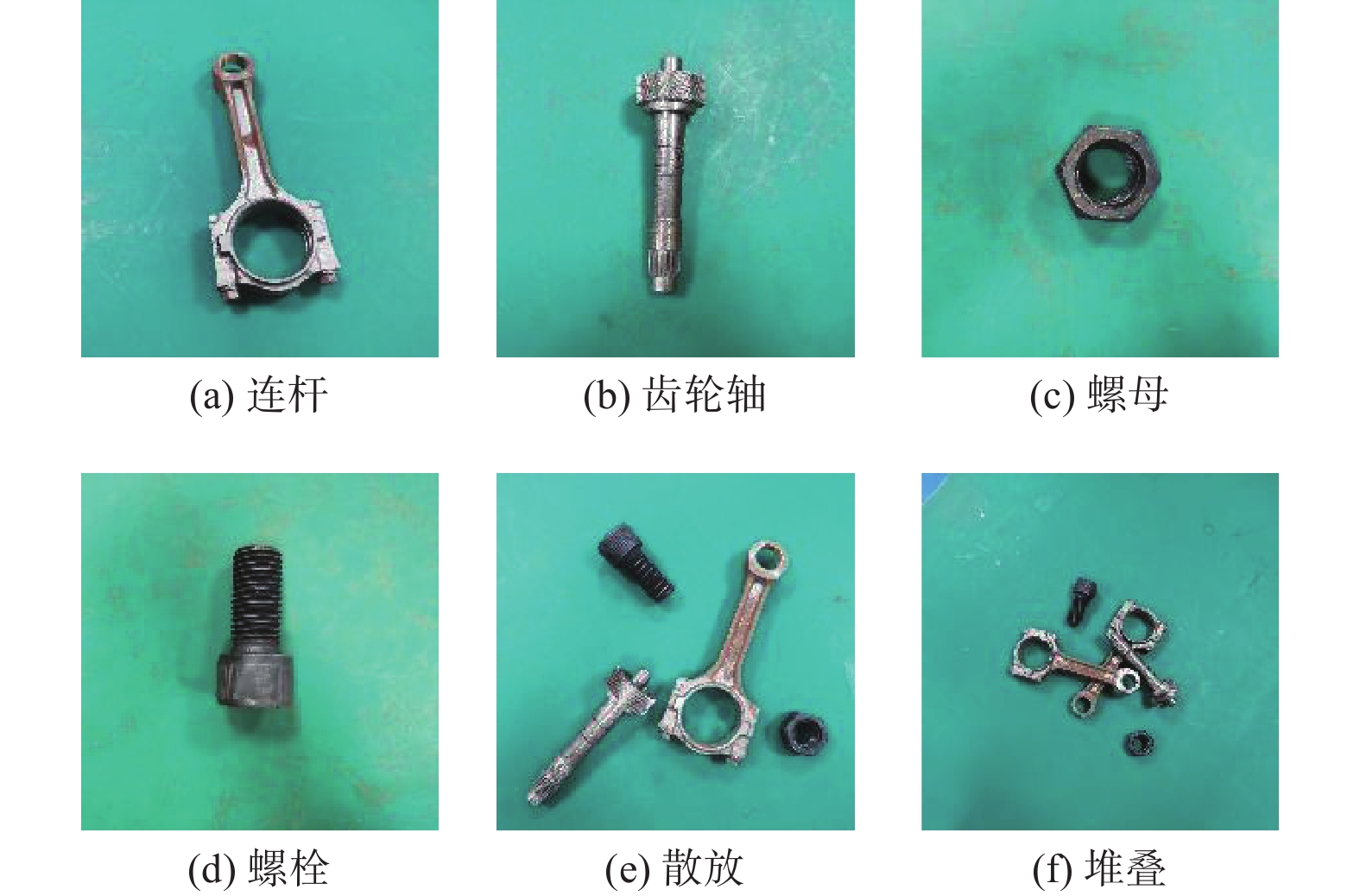
表 1 训练集、验证集和测试集的组成
Table 1. Composition of training, validation and test set
种类 零件数量 训练集 验证集 测试集 连杆 1981 788 1196 齿轮轴 906 354 538 螺栓 895 365 527 螺母 873 366 531 表 2 数据集格式
Table 2. Dataset format
数据集文件 相应功能 imgs 训练图像 label_viz 标注后分割图像 mask 标注后掩膜图像 yaml 标注后位置文件 表 3 修改后MobileNets的5个阶段
Table 3. Five stages of modified MobileNets
阶段 输入 卷积类型 滤波器尺寸/步长 输出 1 224 × 224 × 3 Conv 3 × 3 × 3 × 32/2 V1 112 × 112 × 32 Convd 3 × 3 × 32/1 112 × 112 × 32 Conv 1 × 1 × 32 × 64/1 2 112 × 112 × 64 Convd 3 × 3 × 64/2 V2 56 × 56 × 64 Conv 1 × 1 × 64 × 128/1 56 × 56 × 128 Convd 3 × 3 × 128/1 56 × 56 × 128 Conv 1 × 1 × 128 × 128/1 3 56 × 56 × 128 Convd 3 × 3 × 128/2 V3 28 × 28 × 128 Conv 1 × 1 × 128 × 256/1 28 × 28 × 256 Convd 3 × 3 × 256/1 28 × 28 × 256 Conv 1 × 1 × 256 × 256/1 4 28 × 28 × 256 Convd 3 × 3 × 256/2 V4 14 × 14 × 256 Conv 1 × 1 × 256 × 512/1 14 × 14 × 512 Convd × 5 3 × 3 × 512/1 14 × 14 × 512 Conv × 5 1 × 1 × 512 × 512/1 5 14 × 14 × 512 Convd 3 × 3 × 512/2 V5 7 × 7 × 512 Conv 1 × 1 × 512 × 1024/1 7 × 7 × 1024 Convd 3 × 3 × 1024/1 7 × 7 × 1024 Conv 1 × 1 × 1024 × 1024/1 表 4 改进前后模型大小及检测时间对比
Table 4. Comparison of model size and detection time before and after improvement
参数 Mask R−CNN 改进的Mask R−CNN 模型大小/MB 249.9 92.8 单张图片检测时间/s 3.8 1.7 表 5 改进前后识别准确率对比
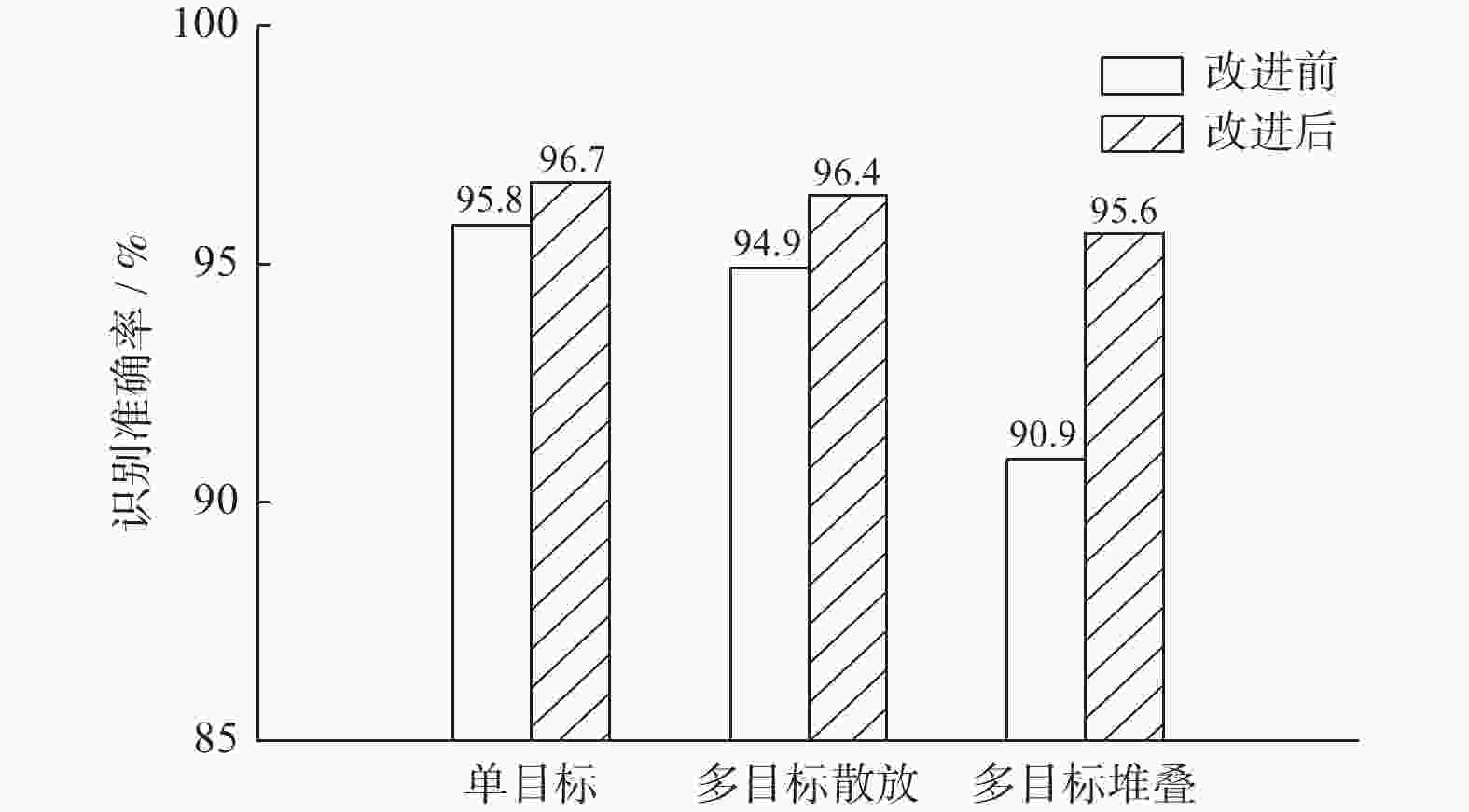
Table 5. Comparison of recognition accuracy before and after improvement
模型 类别 测试样本数量 正确识别零件数量 误识别及未识别零件数量 识别准确率/% 改进前 单目标 120 115 5 95.8 多目标散放 120 397 21 94.9 多目标堆叠 120 451 45 90.9 改进后 单目标 120 116 4 96.7 多目标散放 120 401 17 96.4 多目标堆叠 120 474 22 95.6 -
[1] 刘学平, 李玙乾, 刘励, 等. 自适应边缘优化的改进YOLOV3目标识别算法[J] . 微电子学与计算机,2019,36(7):59 − 64. [2] 余永维, 韩鑫, 杜柳青. 基于Inception-SSD算法的零件识别[J] . 光学精密工程,2020,28(8):1799 − 1809. [3] HE K M, GKIOXARI G, DOLLAR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[J] . IEEE Transactions on Pattern AnalysisMachine Intelligence,2017(99):1. [4] 魏中雨, 黄海松, 姚立国. 基于机器视觉和深度神经网络的零件装配检测[J] . 组合机床与自动化加工技术,2020(3):74 − 77,82. [5] YANG Z X, DONG R X, XU H, et al. Instance Segmentation Method Based on Improved Mask R-CNN for the Stacked Electronic Components[J] . Electronics,2020,9(6):1. [6] GUO D, KONG T, SUN F C, et al. Object discovery and grasp detection with a shared convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Stockholm: IEEE, 2016: 2038−2043. [7] 王德明, 颜熠, 周光亮, 等. 基于实例分割网络与迭代优化方法的3D视觉分拣系统[J] . 机器人,2019,41(5):637 − 648. [8] ZHANG H, LAN X, BAI S, et al. A multi-task convolutional neural network for autonomous robotic grasping in object stacking scenes[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Macau: IEEE, 2019: 6435−6442. [9] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J] . IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(6):1137 − 1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [10] LIN T Y, DOLLAR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 936−944. [11] XIE S, GIRSHICK R, DOLLAR P, et al. Aggregated Residual Transformations for Deep Neural Networks[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 5987−5995. [12] HOWARD A G, ZHU M L, CHEN B, et al. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications[EB/OL]. (2017−04−17)[2021−10−17]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.04861.pdf. [13] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A, et al. Spatial transformer networks[C]//Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal: IEEE, 2015: 2017–2025. [14] NAIR V, HINTON G E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. Haifa: IMLS, 2010: 807–814. [15] LIN T-Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]//Proceedings of Computer Vision – ECCV 2014. Zurich: Springer, 2014: 740−755. -






 下载:
下载: