Virtual screening of phospholipase PLA2G1B inhibitors based on molecular docking and pharmacophore
-
摘要:
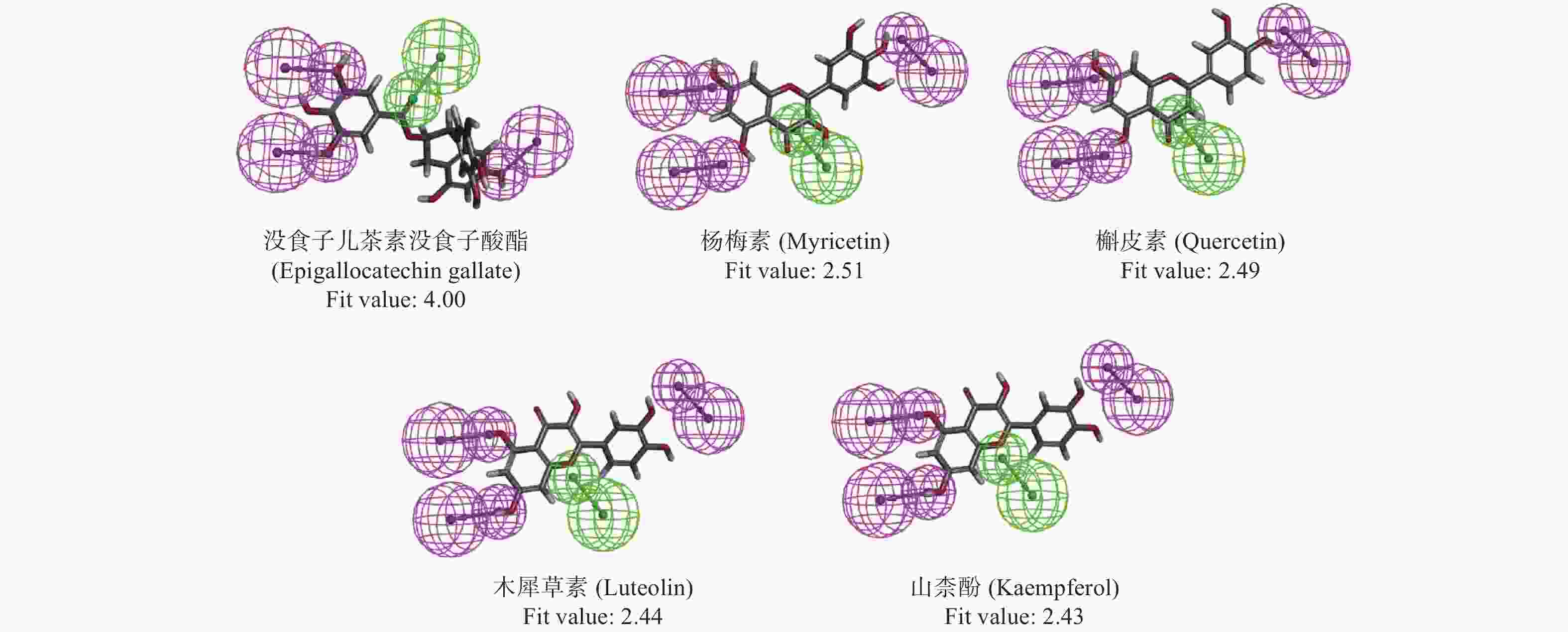
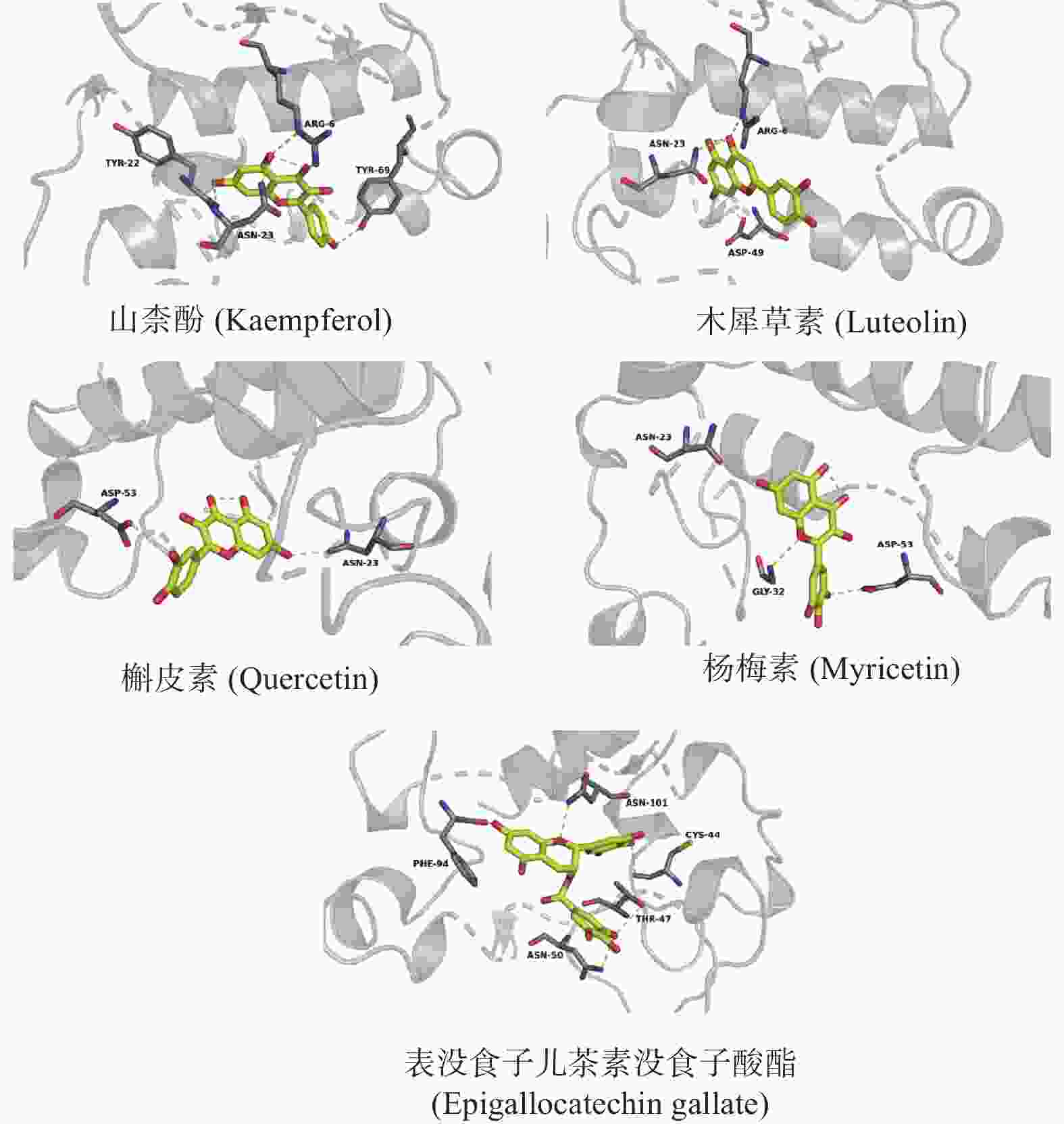
磷脂酶PLA2G1B 与饮食诱导肥胖及相关代谢紊乱密切联系,研究表明一些天然类黄酮化合物对磷脂酶有抑制作用. 采用整合分子对接和药效团策略筛选PLA2G1B靶向小分子抑制剂. 对5种类黄酮化合物与PLA2G1B靶标进行分子模拟对接,分析其相互作用,建立基于配体分子共同特征(HipHop)的药效团模型,应用该模型对ZINC数据库中小分子化合物进行筛选,并对匹配评分良好的化合物进行类药性和药代动力学性质(ADME)预测分析. 结果表明,山柰酚、木犀草素、槲皮素、杨梅素和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯与PLA2G1B均能较好结合,结合能为−7.17~−6.17 kJ/mol;所构建的药效团模型含有3个氢键供体和1个氢键受体4个特征元素;通过对ZINC数据库中10 897个小分子的筛选,共得到722个分子,命中率为6.6%. 其中匹配评分>2.5的29个化合物均满足Lipinski规则,大部分化合物的ADME参数良好. 研究结果为PLA2G1B抑制剂设计及先导化合物发现提供了参考数据.
-
关键词:
- PLA2G1B抑制剂 /
- 类黄酮 /
- 分子对接 /
- 药效团 /
- 虚拟筛选
Abstract:Phospholipase PLA2G1B is closely related to diet-induced obesity and related metabolic disorders. Studies have shown that some natural flavonoid compounds can inhibit phospholipase. An integrated molecular docking and pharmacophore strategy was used to screen PLA2G1B-targeted small molecule inhibitors. Molecular docking of five flavonoid compounds with PLA2G1B were possessed, and their interaction patterns were analyzed. A pharmacophore model based on common ligand molecular characteristics (HipHop) was established, which was used to screen small molecular compounds from ZINC database. The drug-likeness and pharmacokinetic properties (ADME) of the compounds with good fit values were predicted. The results show that kaempferol, luteolin, quercetin, myricetin and epigallocatechin gallate can bind PLA2G1B well, with the binding energies of −7.17~−6.17 kJ/mol. The pharmacophore model consisted of three hydrogen bond donors and one hydrogen bond receptor. By screening 10 897 small molecules in ZINC database, a total of 722 molecules with a hit rate of 6.6% were obtained. The 29 compounds with fit values higher than 2.5 are all meeting Lipinski's rule, and most of the compounds have good ADME parameters. These results can provide reference data for the design of PLA2G1B inhibitors and discovery of lead compounds.
-
Key words:
- PLA2G1B inhibitor /
- flavonoid /
- molecular docking /
- pharmacophore /
- virtual screening
-
表 1 分子对接结合自由能和氢键作用结果
Table 1. Results of binding energies and hydrogen bond interactions by molecular docking
化合物名称 结合能/(kJ·mol−1) 氢键作用 山柰酚(Kaempferol) −7.17 ARG−6、ASN−23、TYR−22、TYR−69 木犀草素(Luteolin) −6.80 AGR−6、ASN−23、ASP−49 槲皮素(Quercetin) −6.32 ASP−53和ASN−23 杨梅素(Myricetin) −6.19 ASN−23、ASP−53、GLY−32 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(Epigallocatechin gallate) −6.17 ASN−101、CYS−44、THR−47、ASN−50、PHE−94 表 2 10 个基于分子共同特征的药效团的结果参数
Table 2. Parameters of ten common features of pharmacophore
模型编号 特征元素 评分 最高匹配 01 DDDA 56.532 4 02 DDDA 56.430 4 03 DDAA 56.207 4 04 DDDA 56.017 4 05 DDAA 56.013 4 06 DDDA 55.571 4 07 DDDA 55.571 4 08 DDAA 55.532 4 09 DDAA 55.532 4 10 DDAA 55.532 4 表 3 基于药效团筛选、类药性及ADME分析得到29个小分子各项得分值
Table 3. Scores of each index of 29 molecules obtained based on pharmacophore screening, drug-likeness and ADME analysis
序号 化合物 匹配评分 Lipinski规则 Veber规则 Absorption Solubility BBB CYP2D6 PPB 1 ZINC001151173718 3.17 Yes No 3 4 4 False False 2 ZINC001454282551 3.06 Yes Yes 3 5 4 False False 3 ZINC001558022086 3.01 Yes Yes 1 5 4 False False 4 ZINC001363316402 2.94 Yes Yes 2 4 4 False False 5 ZINC001179227552 2.92 Yes Yes 1 4 4 False False 6 ZINC001363491746 2.91 Yes Yes 0 4 3 False False 7 ZINC000824680228 2.91 Yes No 2 4 4 False False 8 ZINC001294455752 2.83 Yes Yes 1 5 4 False False 9 ZINC000825929851 2.82 Yes No 2 4 4 False False 10 ZINC001176845653 2.75 Yes No 3 4 4 False False 11 ZINC001130958954 2.67 Yes No 3 5 4 False False 12 ZINC000347737500 2.66 Yes Yes 2 5 4 False False 13 ZINC001411973522 2.66 Yes Yes 1 5 4 False False 14 ZINC001442587981 2.65 Yes Yes 3 5 4 False False 15 ZINC001434077453 2.62 Yes Yes 2 5 4 False False 16 ZINC001362720157 2.62 Yes Yes 2 5 4 False False 17 ZINC000824680227 2.61 Yes No 2 4 4 False False 18 ZINC001434077450 2.61 Yes Yes 2 5 4 False False 19 ZINC001346217825 2.61 Yes Yes 3 5 4 False False 20 ZINC001138190537 2.60 Yes Yes 1 5 4 False False 21 ZINC000337596865 2.60 Yes Yes 1 5 4 False False 22 ZINC001179227551 2.58 Yes Yes 1 4 4 False False 23 ZINC001142378276 2.57 Yes Yes 3 5 4 False False 24 ZINC001051505747 2.54 Yes No 3 5 4 False False 25 ZINC001090398382 2.54 Yes No 3 4 4 False False 26 ZINC001592749923 2.54 Yes No 3 5 4 False False 27 ZINC000352614243 2.53 Yes No 3 5 4 False False 28 ZINC001168946047 2.51 Yes No 1 5 4 False False 29 ZINC001133116414 2.51 Yes No 3 5 4 False False -
[1] WANG Y, XUE H, SUN M, et al. Prevention and control of obesity in China[J] . Lancet Glob Health,2019,7(9):1166 − 1167. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30276-1 [2] BRAY G A, KIM K K, WILDING J P H. Obesity: A chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the world obesity federation[J] . Obesity Reviews,2017,18(7):715 − 723. doi: 10.1111/obr.12551 [3] CASH J G, KONANIAH E, HEGDE N, et al. Therapeutic reduction of lysophospholipids in the digestive tract recapitulates the metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery and promotes diabetes remission[J] . Molecular Metabolism,2018,16:55 − 64. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.07.009 [4] HUANG J B, WANG Y J, XIE Z W, et al. The anti-obesity effects of green tea in human intervention and basic molecular studies[J] . European Journal of Clinical Nutrition,2014,68(10):1075 − 1087. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2014.143 [5] 贾旭东. 茶类黄酮类功能及其应用[J] . 国外医学(卫生学分册),2001,28(6):369 − 371. [6] SABE V T, NTOMBELA T, JHAMBA L A, et al. Current trends in computer aided drug design and a highlight of drugs discovered via computational techniques: A review[J] . European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2021,224:113705. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.113705 [7] WANG L L, HAI Y, AN L J, et al. Rapid screening the potential mechanism-based inhibitors of CYP3A4 from tripterygium wilfordi based on computer approaches combined with in vitro bioassay[J] . Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry,2017,25(10):2689 − 2700. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2017.03.037 [8] SHARMA P, JOSHI T, JOSHI T, et al. In silico screening of potential antidiabetic phytochemicals from phyllanthus emblica against therapeutic targets of type 2 diabetes[J] . Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2020,248:112268. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112268 [9] RICHMOND B L, HUI D Y. Molecular structure and tissue-specific expression of the mouse pancreatic phospholipase A2 gene[J] . Gene,2000,244(1/2):65 − 72. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00006-8 [10] HUI D Y. Group 1B phospholipase A2 in metabolic and inflammatory disease modulation[J] . Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA): Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids,2019,1864(6):784 − 788. [11] WANG S, NOH S K, KOO S I. Green tea catechins inhibit pancreatic phospholipase A2 and intestinal absorption of lipids in ovariectomized rats[J] . Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2006,17(7):492 − 498. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2006.03.004 [12] MOON H, CHOI H H, LEE J Y, et al. Quercetin inhalation inhibits the asthmatic responses by exposure to aerosolized-ovalbumin in conscious guinea-pigs[J] . Archives of Pharmacal Research,2008,31(6):771 − 778. doi: 10.1007/s12272-001-1225-2 [13] LäTTIG J, BöHL M, FISCHER P, et al. Mechanism of inhibition of human secretory phospholipase A2 by flavonoids: rationale for lead design[J] . Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design,2007,21(8):473 − 483. doi: 10.1007/s10822-007-9129-8 -





 下载:
下载: