Underground pipeline trajectory measurement method based on reduced inertial navigation
-
摘要:
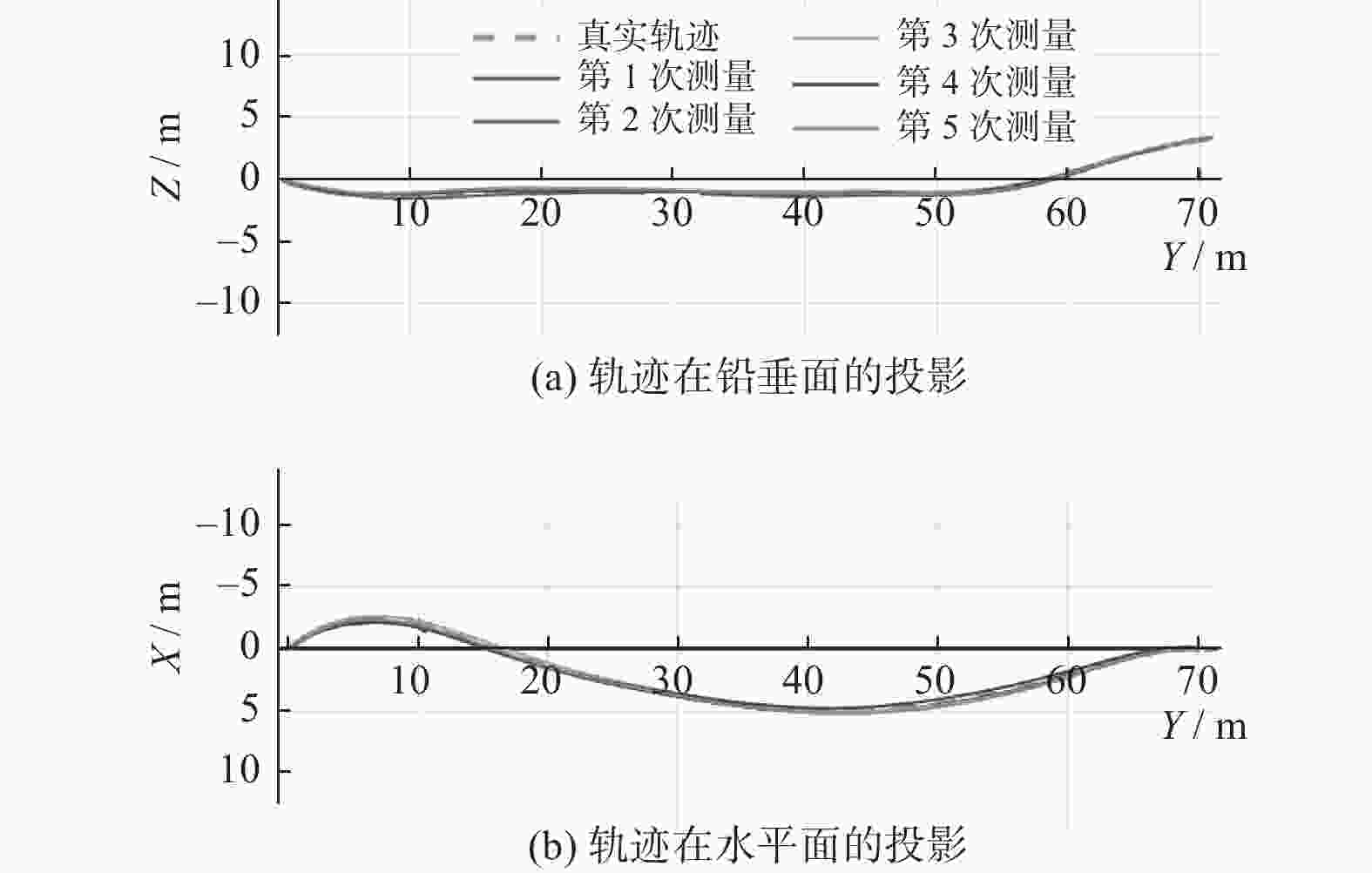
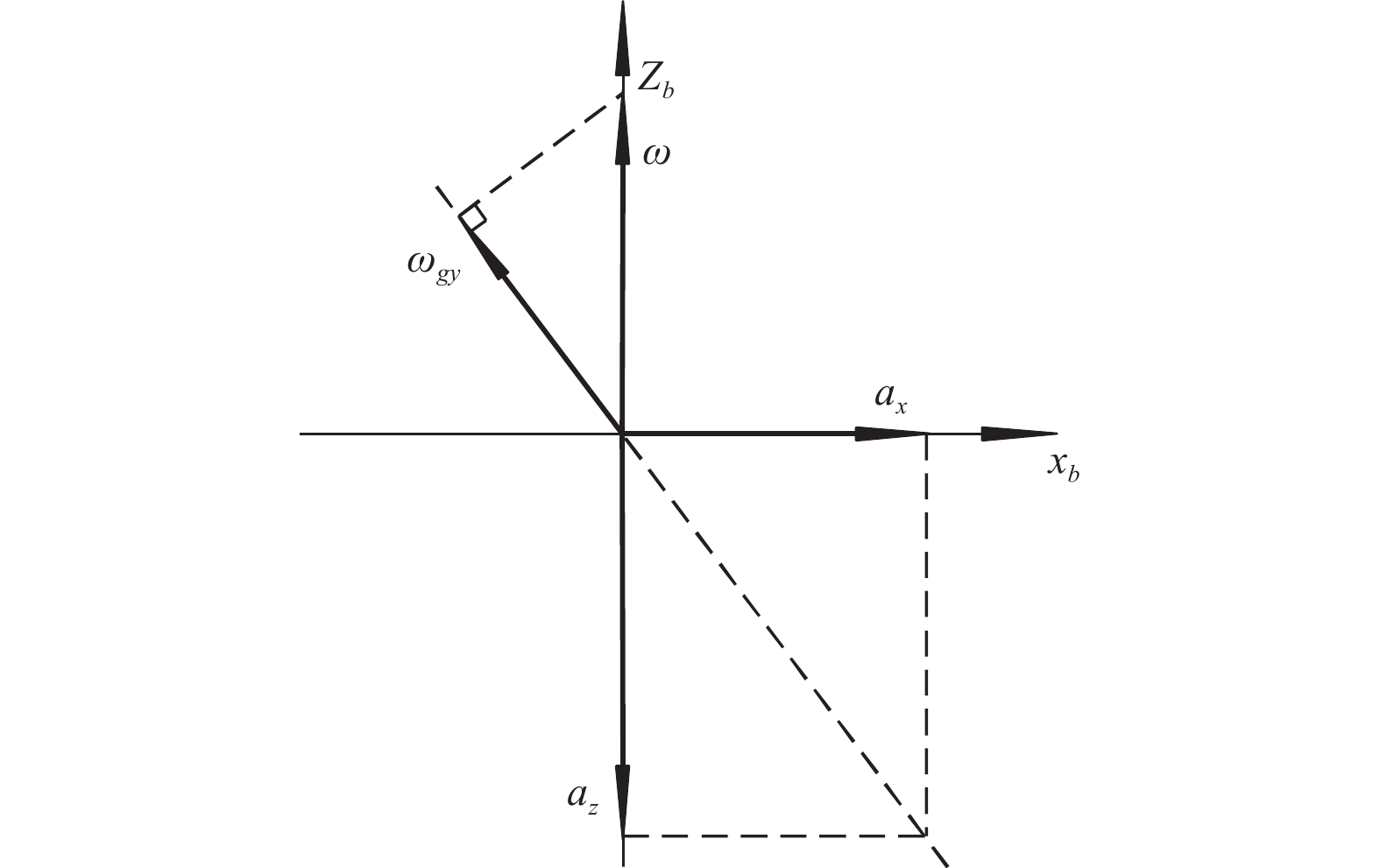
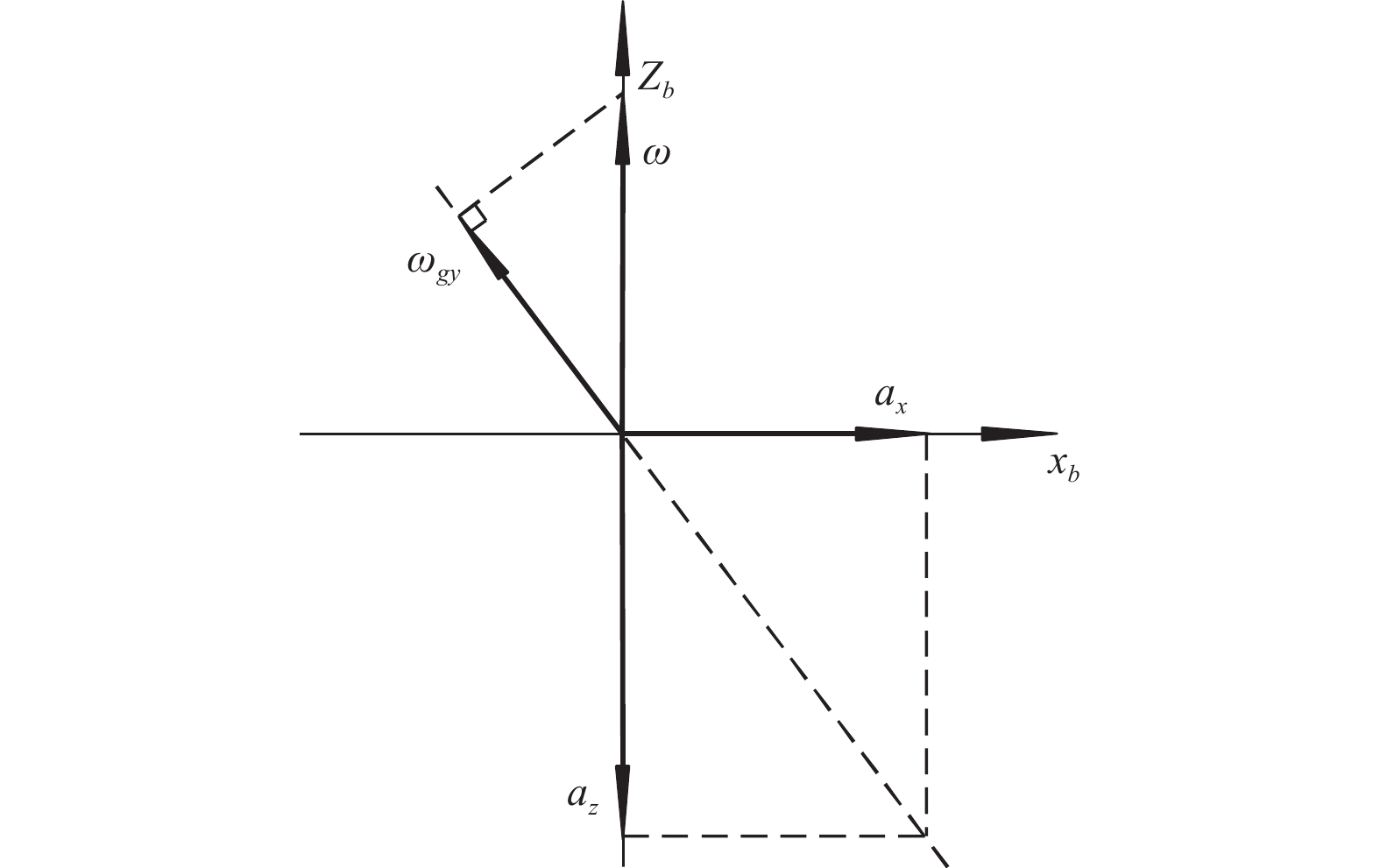
针对目前基于惯性导航原理的地下管线轨迹测量系统成本过高的缺点,通过减少惯性传感器的数量,有效降低系统成本. 首先推导了仅使用单轴角速度和双轴加速度数据还原管线轨迹的公式,然后使用具有自适应噪声的完全集成经验模态分解处理惯性传感器原始数据,最后利用所推导公式和处理后数据重建管线轨迹. 在75 m长的测试管路中,重建轨迹最大偏差小于全长的0.2%,同时传感器成本减少一半,具有较强的实用价值.
Abstract:In view of the high cost of current underground pipeline trajectory measurement system based on inertial navigation principle, the cost of the system was effectively reduced by reducing the number of inertial sensors. Firstly, the formula of using only uniaxial angular velocity and biaxial acceleration data to restore pipeline trajectory was derived. Then, the complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise was used to process the original data of inertial sensors. Finally, the pipeline trajectory was reconstructed by using the derived formula and the processed data. In the 75 m long test pipeline, the maximum deviation of the reconstruction track is less than 0.2% of the total length, and the cost of the sensor is reduced by half, which has strong practical value.
-
-
[1] 陈思静, 胡祥云, 彭荣华. 城市地下管线探测研究进展与发展趋势[J] . 地球物理学进展,2021,36(3):1236 − 1247. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0257 [2] 胡玉洋, 叶荣华, 陈长青. 宁波市深埋非开挖管线探测方法与应用研究[J] . 测绘通报,2021(S2):156 − 161. [3] 黄鹏飞. 非开挖管线精细探测方法分析[J] . 测绘通报,2021,530(5):140 − 144. [4] 卢晓龙. 超深地下管道精确定位技术的研究及应用[J] . 测绘与空间地理信息,2021,44(10):177 − 180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2021.10.048 [5] 赵显鹏. 基于MIMU/里程计的地下管线定位技术研究 [D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2020. [6] 许晓东. 地下管道定位系统及误差补偿方法的研究 [D]. 杭州: 中国计量大学, 2018. [7] 司马健. 一种基于惯性测量的管线测绘仪的设计与实现 [D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018. [8] WANG X H, SONG H. The inertial technology based 3-dimensional information measurement system for underground pipeline[J] . Measurement: Journal of the International Measurement Confederation,2012,45(3):604 − 614. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2011.08.016 [9] VERMA A, KAIWART A, DUBEY N D, et al. A review on various types of in-pipe inspection robot[J] . Materials Today:Proceedings,2021,50(5):1425 − 1434. [10] HUANG N E, SHEN Z, LONG S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J] . Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,1998,454(1971):903 − 995. [11] TORRES M E, COLOMINAS M A, Schlotthauer G, et al. A complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise[C]// Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). New Jersey: IEEE, 2011: 4144 − 4147. [12] ZHAO Y, XU J. Denoising of ECG signals based on CEEMDAN[C]// Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICICSP). New Jersey: IEEE, 2021: 430 − 433. [13] 吴全玉, 张文强, 潘玲佼, 等. 一种结合自适应噪声完备经验模态分解和盲反卷积去除脑电中眼电伪迹的新方法[J] . 数据采集与处理,2020,35(4):720 − 729. [14] 孙苗, 吴立, 袁青, 等. 基于CEEMDAN的爆破地震波信号时频分析[J] . 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(3):76 − 82. [15] 汤俊, 李垠健, 高鑫. 基于CEEMDAN的GNSS变形监测去噪方法[J] . 大地测量与地球动力学,2021,41(4):408 − 412. -







 下载:
下载: