Location and mapping of lidar and vision sensor fusion
-
摘要:
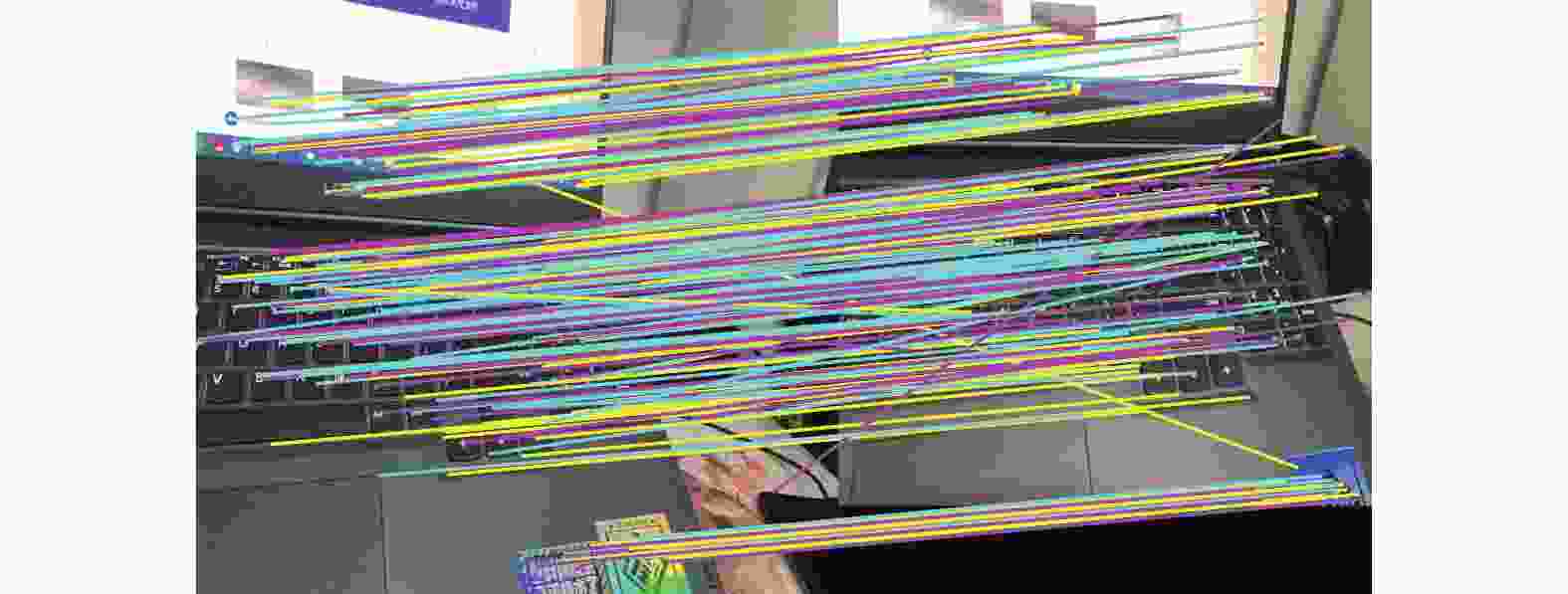
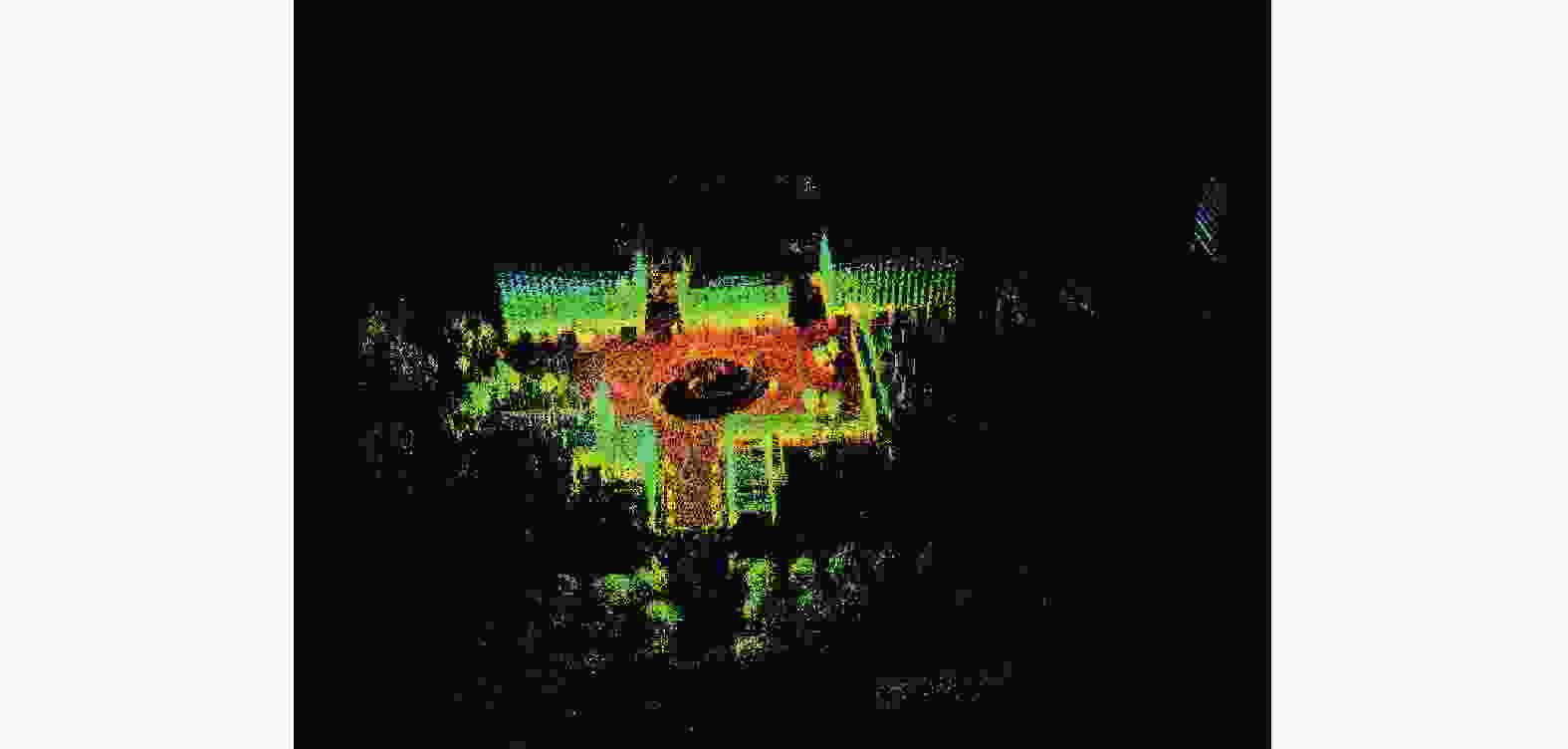
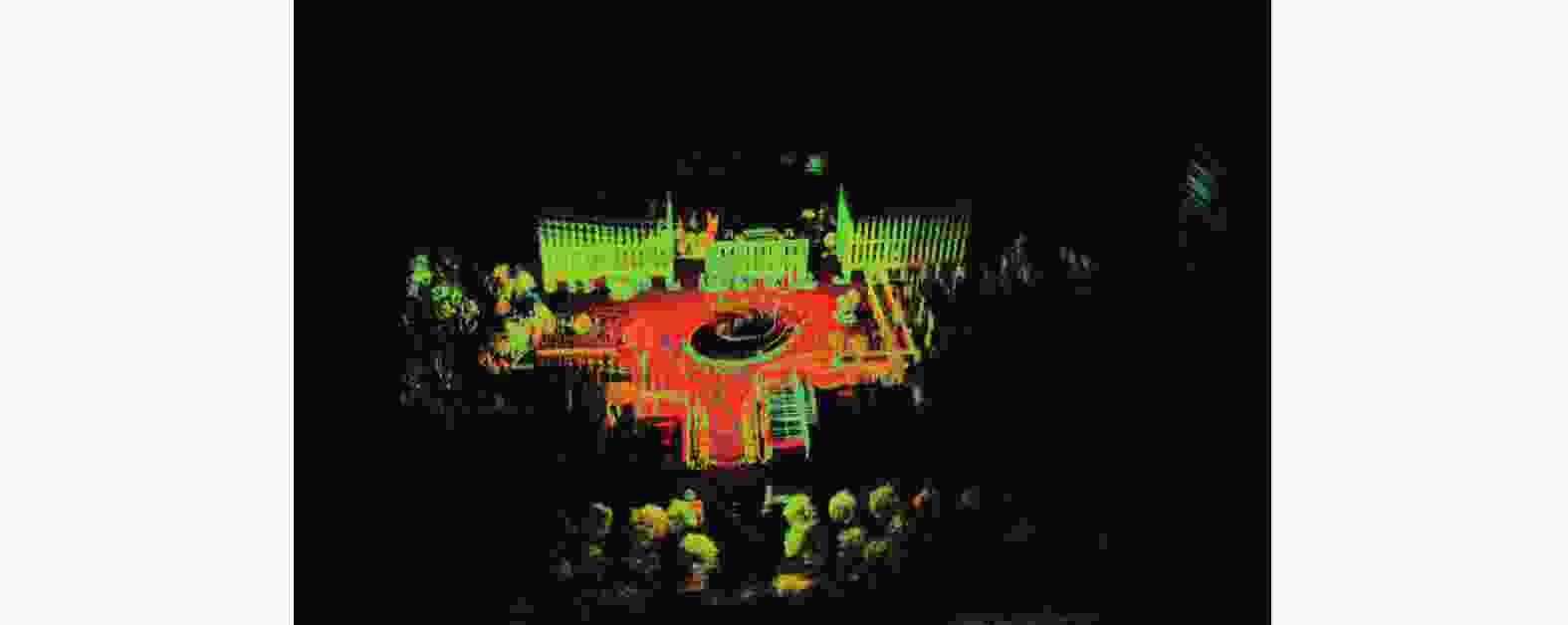
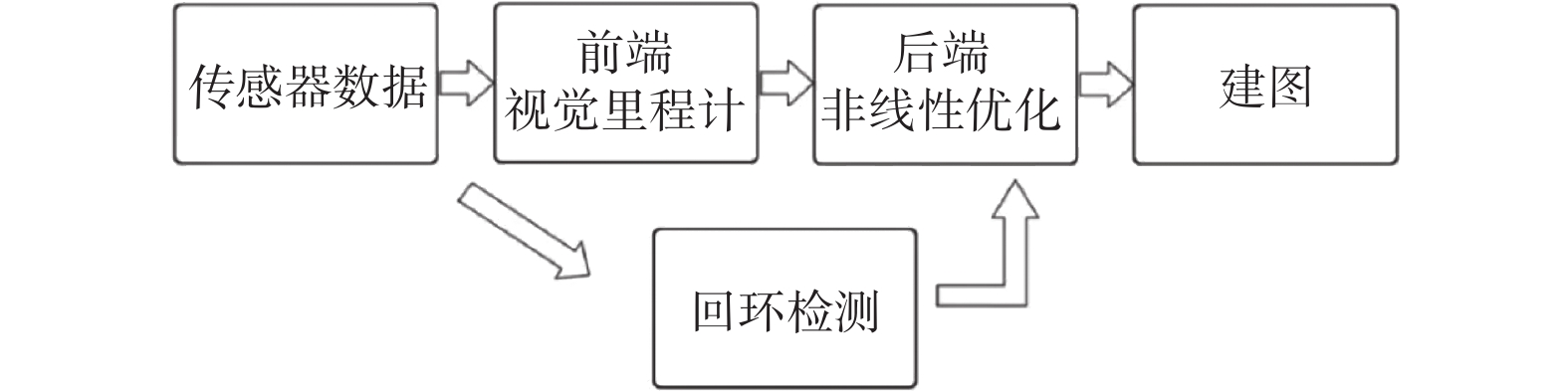
定位与建图是自动驾驶的关键技术之一. 激光传感器或视觉传感器具有局限性,通过多传感器融合可以发挥不同传感器各自的优点,提高定位与建图的精度和鲁棒性. 通过优化Harris算法对图像进行角点提取,利用关键帧对特征点匹配算法进行优化,然后利用非线性最小二乘法进行后端优化. 通过试验平台进行定位与建图试验,对算法进行验证,并用EVO工具对定位误差进行分析. 结果表明,提出后端优化算法误差比单一传感器定位误差减少13%.
Abstract:Location and mapping is one of the key technologies for autonomous driving. With limitations of lidar sensors or vision sensors, the advantages of different sensors can be brought into play through multi-sensor fusion and the accuracy and robustness of location and mapping can be improved. The Harris algorithm was optimized for corner extraction, the key frame was used to optimize the feature point matching algorithm, and then the nonlinear least square method was used for back-end optimization. The location and mapping experiments were carried out on the test platform to verify the algorithm, and the positioning error was analyzed with the EVO tool. The result shows that the error of the proposed back-end optimization algorithm is 13% less than that of a single sensor.
-
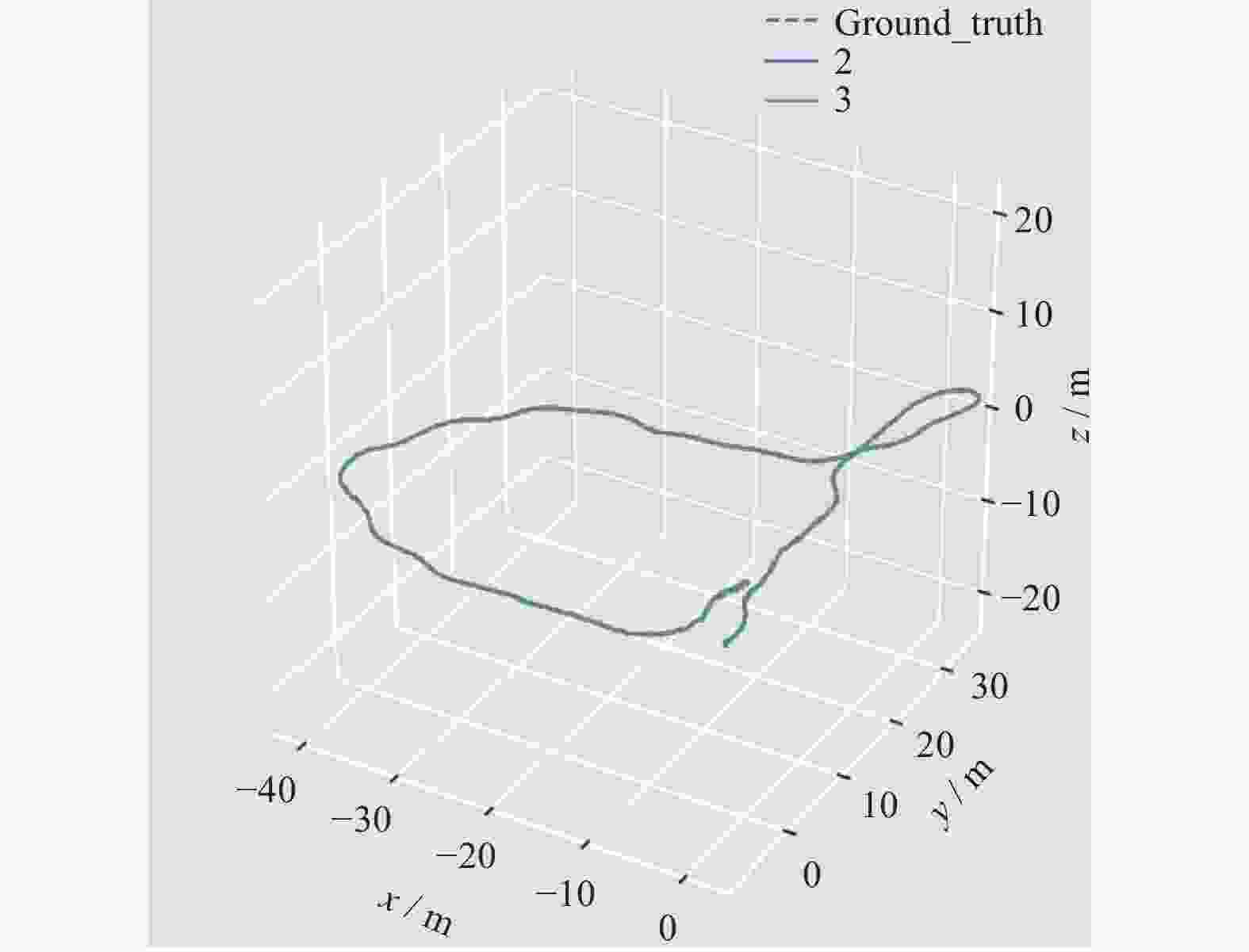
表 1 激光视觉传感器定位误差和单一传感器比较
Table 1. Comparison of positioning accuracy between laser vision sensor and single sensor
算法 最大误差 最小误差 平均误差 中值误差 均方根方差 LOAM 2.5137 2.3267 2.4539 2.4429 2.3535 OURS 2.1764 1.9965 2.0368 2.0466 2.0036 -
[1] GRAETER J, WILCZYNSKI A, LAUER M. LIMO: Lidar-Monocular Visual Odometry[C]//Proceedings of IEEE, 2019: 7872 − 7879. [2] SHIN Y S, PARK Y S, KIM A. Direct visual SLAM using sparse depth for camera-lidar system[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Brisbane: IEEE, 2018: 1−8. [3] HUANG S S, MA Z Y, MU T, et al. Lidar-monocular visual odometry using point and line features[C]//Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris: IEEE, 2020: 33−42. [4] SILVA V D, ROCHE J, KONDOZ A. Fusion of LiDAR and camera sensor data for environment sensing in driverless vehicles[J] . arXiv,2017. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1710.06230 [5] ZUO X X, GENEVA P, YANG Y L, et al. Visual-inertial localization with prior LiDAR map constraints[J] . IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2019,4(4):3394 − 3401. [6] JI Z, SINGH S. Visual-lidar odometry and mapping: low-drift, robust, and fast[C]//Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Seattle: IEEE, 2015: 345−351. [7] ZHANG J, SINGH S. Laser-visual-inertial odometry and mapping with high robustness and low drift[J] . Journal of Field Robotics,2018,35(8):1242 − 1264. doi: 10.1002/rob.21809 [8] SHAO W Z, VIJAYARANGAN S, LI C, et al. Stereo visual inertial LiDAR simultaneous localization and mapping[C]//Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Macau: IEEE, 2019: 370−377. [9] ZUO X, GENEVA P, LEE W, et al. LIC-fusion: LiDAR-inertial-camera odometry[C]//Proceedings of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Kyongju: IEEE, 2019: 1−4. [10] 张伟伟, 陈超, 徐军. 融合激光与视觉点云信息的定位与建图方法[J] . 计算机应用与软件,2020,37(7):114−119. -





 下载:
下载: