Research on FT fuel engine characteristics using neural network
-
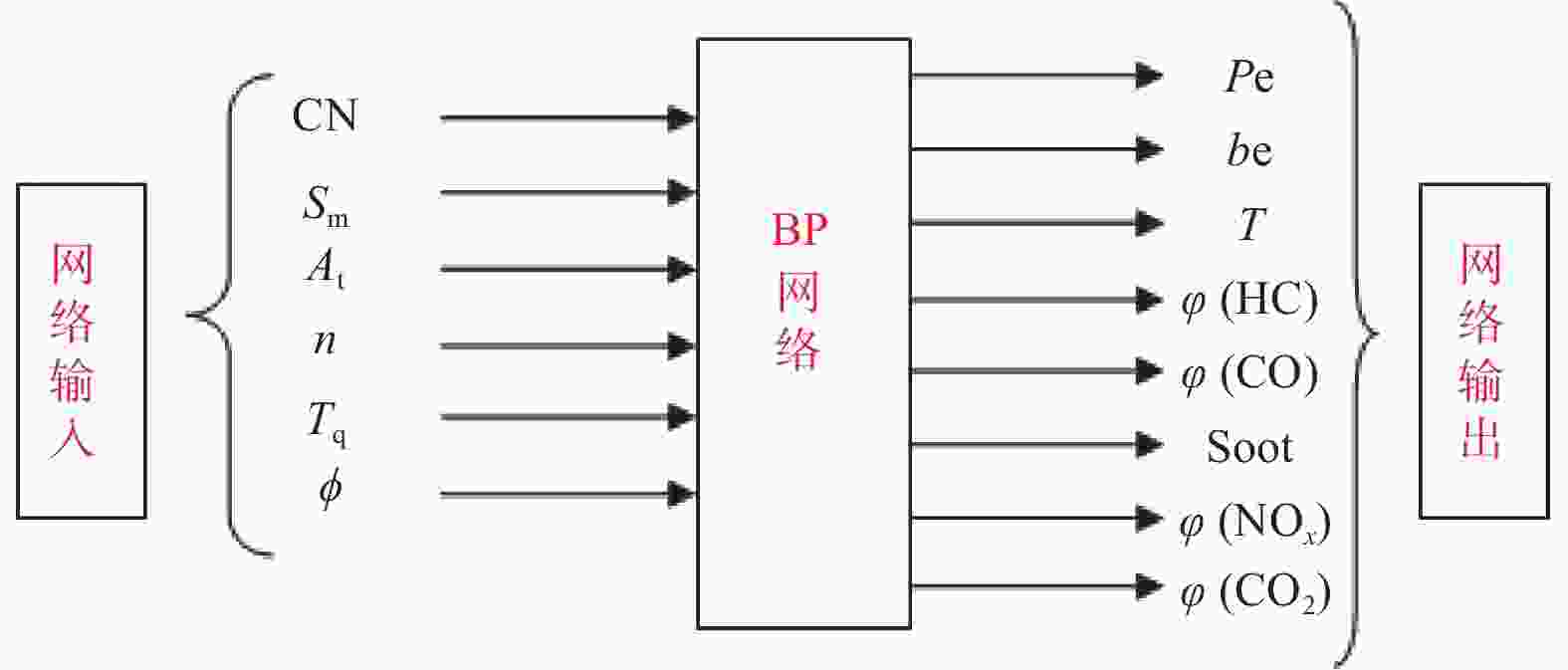
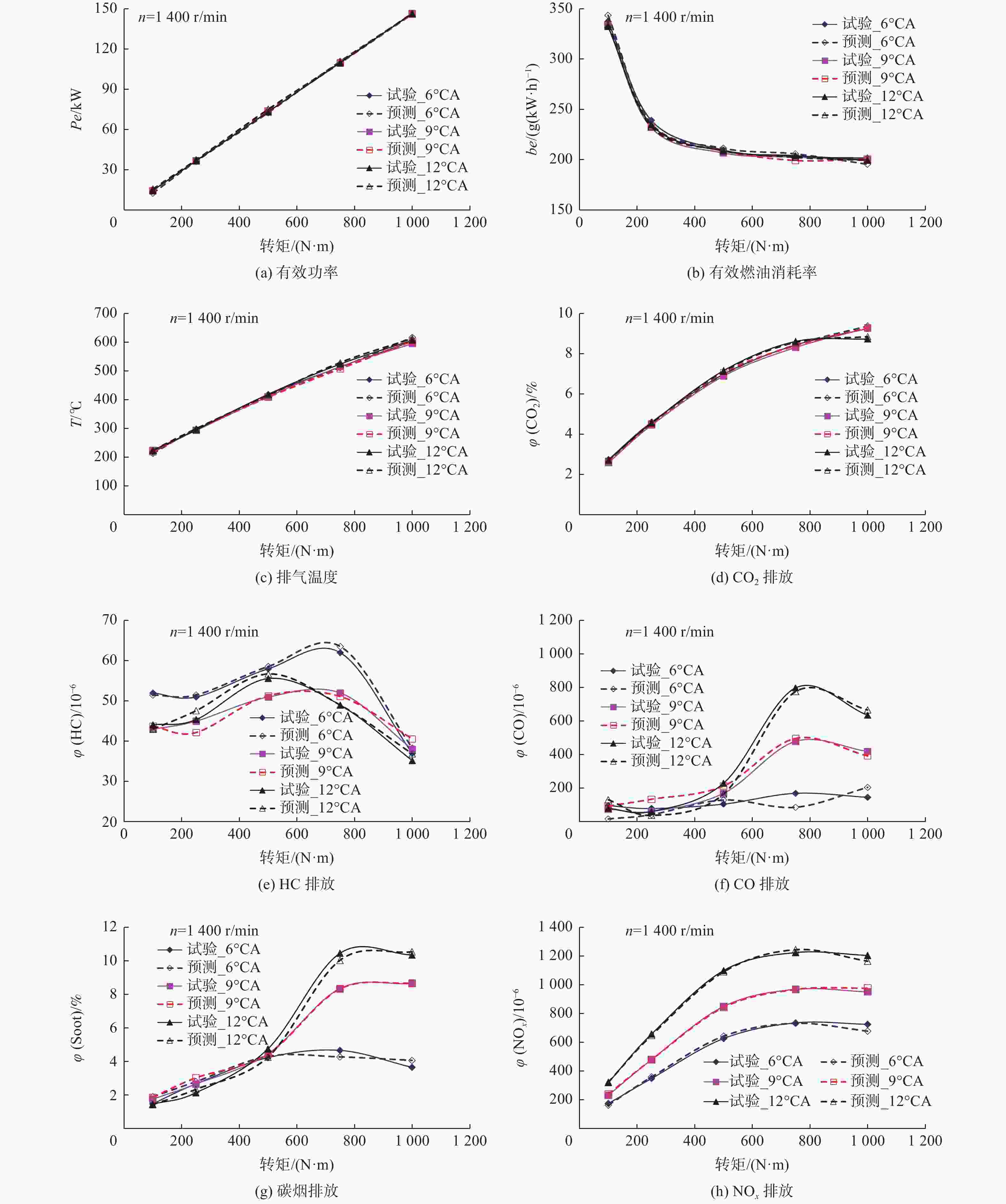
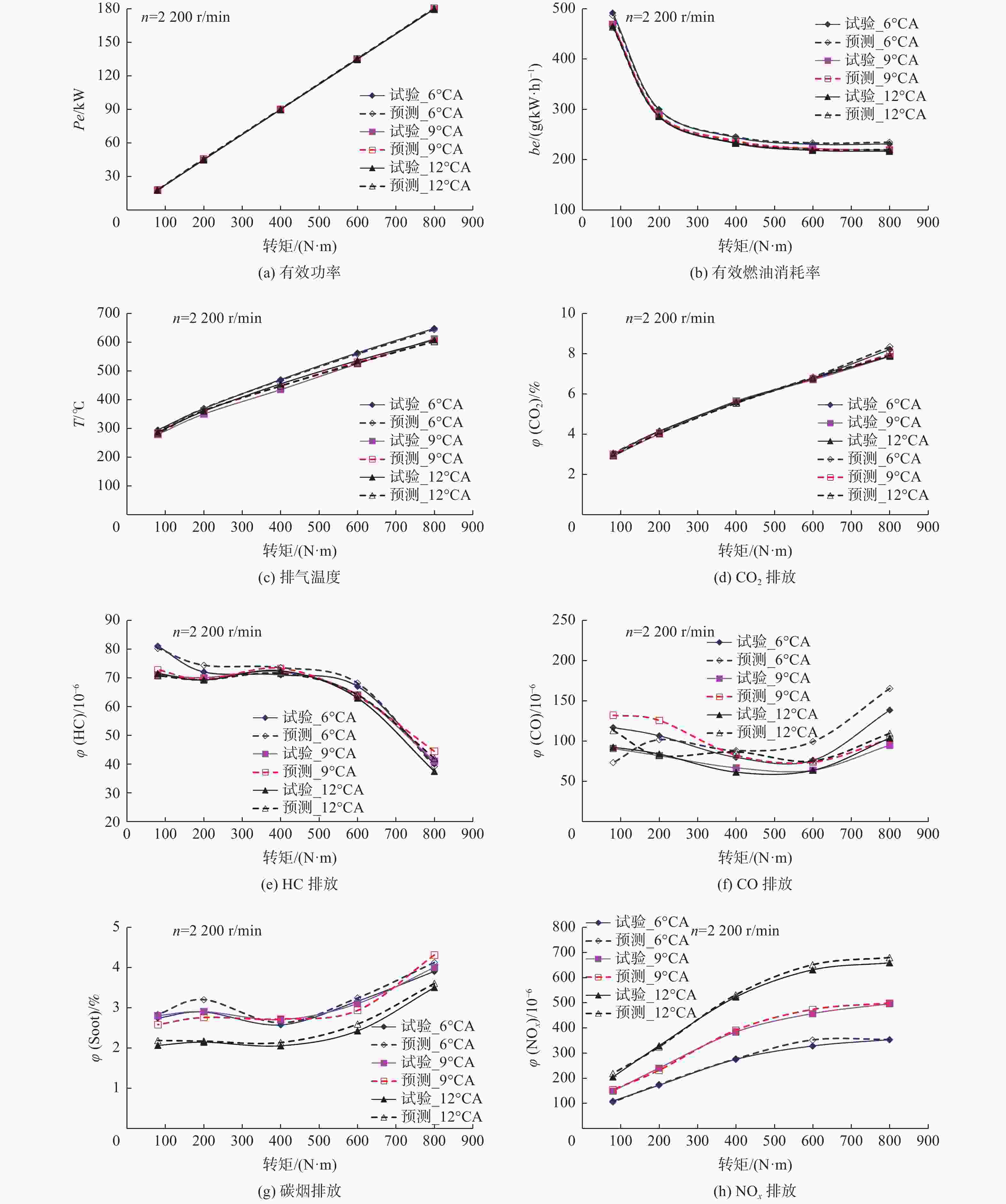
摘要: 基于反向传播(Back Propagation,BP)神经网络强大的非线性逼近和自学习能力,设计3层网络模型,采集发动机台架试验数据作为样本进行模型训练和检验. 以发动机转速、转矩、供油提前角和以天然气为原料的费托燃油(GTL)与柴油混合燃料特性参数十六烷值、硫含量、芳香烃含量为输入,建立BP神经网络模型预测GTL发动机特性. 结果表明,采用该模型可同时预测GTL发动机功率、油耗、排温、HC、CO、CO2、NOx和碳烟排放等特性;与试验数据对比,预测结果的相对误差基本在5%以内,表明该模型具有较高的模型精度和良好的泛化能力.Abstract: Based on the strong nonlinear approximation and self-learning ability of Back Propagation (BP) neural network, a three-layer network model was designed, and the engine bench test data were collected as the samples to train and verify the model. The engine speed, torque, fuel supply advance angle and the characteristic parameters of the fuel mixture of Fischer-Tropsch gas-to-liquid (GTL) and diesel, such as cetane number, sulfur content and aromatic hydrocarbon content, were taken as inputs. The BP neural network model was established to predict the characteristics of GTL engine. The results show that the model can predict the power, fuel consumption, exhaust temperature, HC, CO, CO2, NOx and soot emission of GTL engine at the same time. Compared with the experimental data, the relative error of the prediction results is nearly within 5%, which shows that the model has high model accuracy and good generalization ability.
-
Key words:
- back propagation (BP) neural network /
- Fischer-Tropsch fuel /
- engine /
- emission /
- model
-
表 1 柴油和GTL混合燃料的理化特性
Table 1. Properties of diesel and GTL fuels
理化
参数密度
@15 ℃/(kg∙L−1)十六
烷值CN硫
质量分数/%总芳烃
质量分数/%低热值/
(MJ∙kg−1)黏度@40 ℃/
(mm2∙s−1)C质量分数
/%H质量分数
/%测试
方法ASTM
D4052ASTM
D613ASTM
D2622EN 12916 ASTM
D4868ASTM
D445SH/T
0656SH/T 0656 柴油 0.8392 51.7 0.0403 27.7 42.9 2.665 86.0 14.0 GTL 0.7790 75.0 0.0003 1.4 43.6 2.740 84.9 15.1 表 2 试验发动机主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters of test engine
参数 说明 型式 六缸、四冲程、增压中冷 缸径 × 行程 114 mm × 135 mm 活塞总排量 8.27 L 压缩比 18∶1 标定功率(转速) 184 kW (2200 r/min) 最大转矩(转速) 1000 N·m(1400 r/min) 喷油嘴(6个) 6 孔 × 0.24 mm 表 3 主要试验设备
Table 3. Main test equipments
设备 型号 生产商 发动机控制台 EIM301D 杭州奕科机电 测功机 PECD9400 小野电测 空气流量计 文丘里式流量计 ABB 油耗仪 MF−2200 小野电测 气体排放分析仪 PROVIT5600 AVL 消光式烟度计 AVL439 AVL 表 4 不同中间层神经元数网络训练结果
Table 4. Training results of network with different middle layer neuron numbers
神经元数量 目标误差 训练次数
/次训练误差 5 0.001 1000 0.0091 15 0.001 1000 0.0013 25 0.001 462 9.9982e-04 30 0.001 279 9.9990e-04 35 0.001 128 9.9936e-04 表 5 网络训练输出参数的计算值与试验值的统计参数
Table 5. Statistical parameters of calculated and experimental values of network outputs
统计
参数$\varphi $(NOx) $\varphi $(Soot) $\varphi $(HC) $\varphi $(CO) $\varphi $(CO2) be Pe T RMSE 0.3006 0.0057 0.0612 5.1100 0.0019 0.1281 0.0088 0.0689 MRE 2.0367 5.9316 2.5862 12.2872 1.1072 1.1358 0.7635 1.2239 R2 0.99959 0.99837 0.99903 0.99960 0.99971 0.99942 0.99998 0.99977 表 6 网络预测各输出参数相对误差
Table 6. Relative errors of output parameters by network predict
参数 φ(NOx) φ (碳烟) φ (HC) φ (CO) φ (CO2) be Pe T 相对误差 2.9 4.8 2.8 13.7 1.4 0.7 0.7 1.4 -
[1] 夏勇, 商斌梁, 张振仁, 等. 神经网络在内燃机故障诊断中的应用研究[J] . 机械科学与技术,2000,19:108 − 110. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-8728.2000.01.040 [2] 侯志祥, 吴义虎, 邓华, 等. 车用汽油机过渡工况空燃比的神经网络控制研究[J] . 内燃机工程,2006,27(5):33 − 36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0925.2006.05.008 [3] 杨继红, 张宗杰, 方昌良. 柴油机运行工况的神经网络分析[J] . 柴油机设计与制造,2000(3):21 − 24. [4] 高洪滨, 欧阳光耀, 张萍. 基于BP神经网络的柴油机气缸压力重构[J] . 内燃机工程,2005,26(1):68 − 70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0925.2005.01.017 [5] 张向军, 桂长林. 内燃机摩擦学智能设计中人工神经网络的应用[J] . 机械科学与技术,2001,20(3):459 − 460. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-8728.2001.03.058 [6] 侯国祥, 徐凯, 朱梅林, 等. 应用神经网络-蒙特卡罗法的可靠性分析方法[J] . 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2002,30(4):84 − 86. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.2002.04.029 [7] BALAWENDER K, USTRZYCKI A, LEJDA K, et al. Modeling of unburned hydrocarbon emission in a DI diesel engine using neural networks [C]//Proceedings of SAE Powertrains, Fuels & Lubricants Meeting. Krakow: Society of Automotive Engineers, 2020. [8] ARCAKLIOGLU E, CELIKTEN I. A diesel engine's performance and exhaust emissions[J] . Applied Energy,2005,80(1):11 − 22. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2004.03.004 [9] SAYIN C, ERTUNC H M, HOSOZ M, et al. Performance and exhaust emissions of a gasoline engine using artificial neural network[J] . Applied Thermal Engineering,2007,27(1):46 − 54. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2006.05.016 [10] CANAKCI M, ERDIL A, ARCAKLIOGLU E. Performance and exhaust emissions of a biodiesel engine[J] . Applied Energy,2006,83(6):594 − 605. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2005.05.003 [11] 李捷辉, 周大伟, 段畅. BP神经网络在双燃料发动机排放预测中的应用[J] . 机械设计与制造,2018(3):127 − 130. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2018.03.038 [12] 孙俊, 高孝洪. BP网络在双燃料发动机排放预测中的应用研究[J] . 武汉理工大学学报(交通科学与工程版),2003,27(3):350 − 353. [13] VOSLOO A C. Fischer-Tropsch: A futuristic view[J] . Fuel Processing Technology,2001,71(1-3):149 − 155. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3820(01)00143-6 [14] 张德丰. MATLAB神经网络应用设计[M]. 2版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2011: 79. [15] WU T, HUANG Z, ZHANG W, et al. Physical and chemical properties of GTL-diesel fuel blends and their effects on performance and emissions of a multi-cylinder di compression ignition engine[J] . Energy and Fuels,2007,21(4):1908 − 1914. doi: 10.1021/ef0606512 -





 下载:
下载: