Study on thermal deformation behavior and constitutive model of 304 stainless steel
-
摘要:
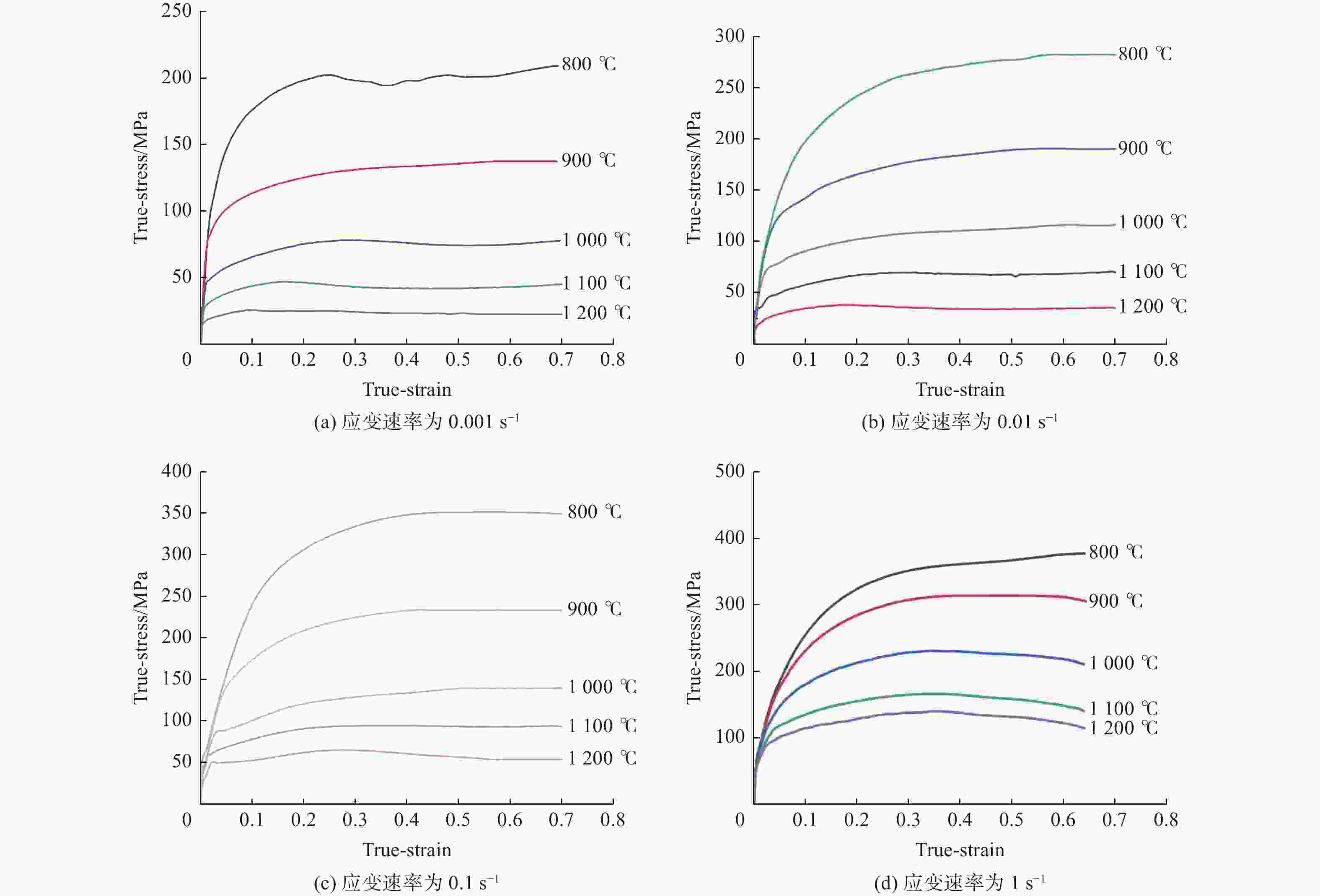
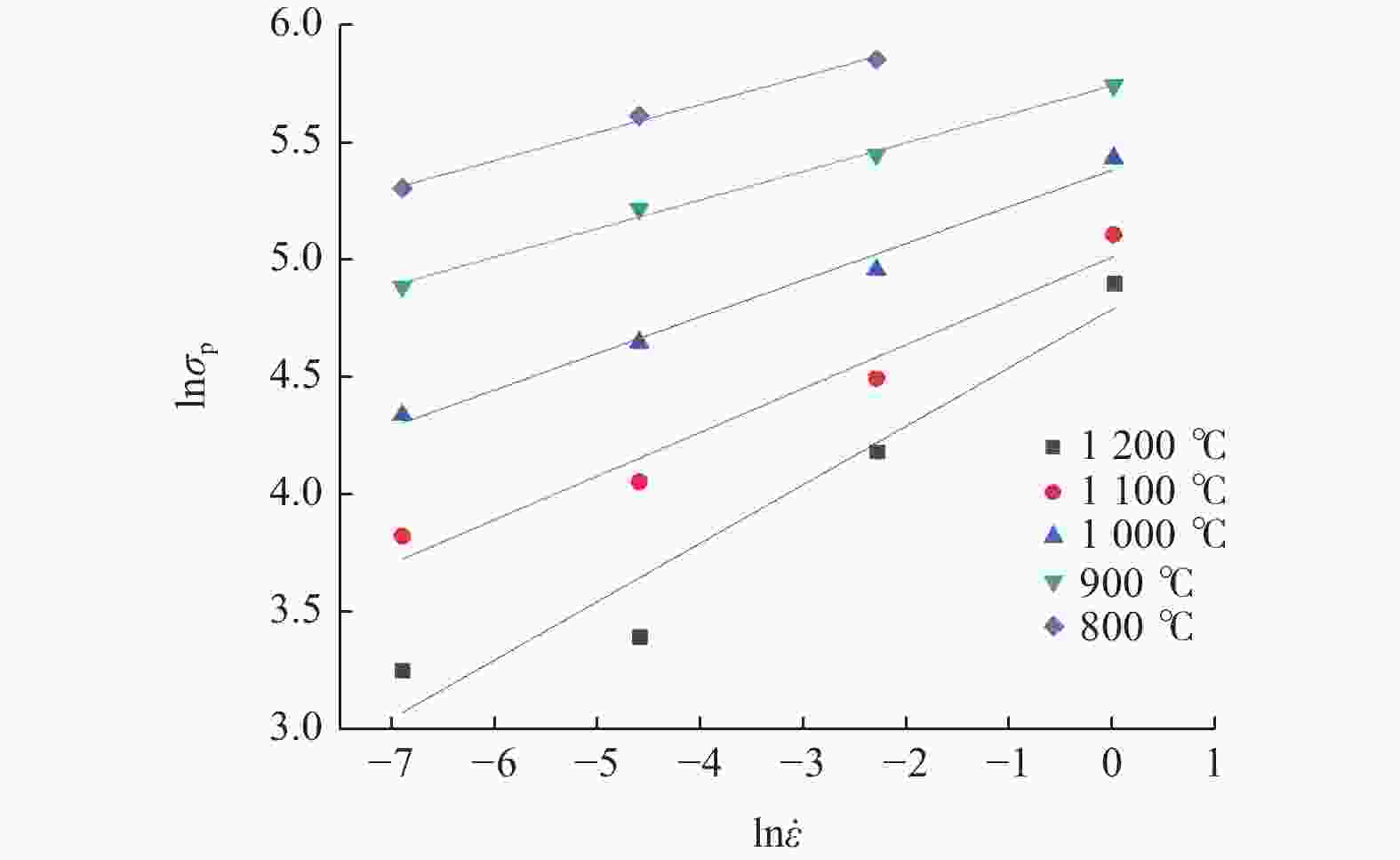
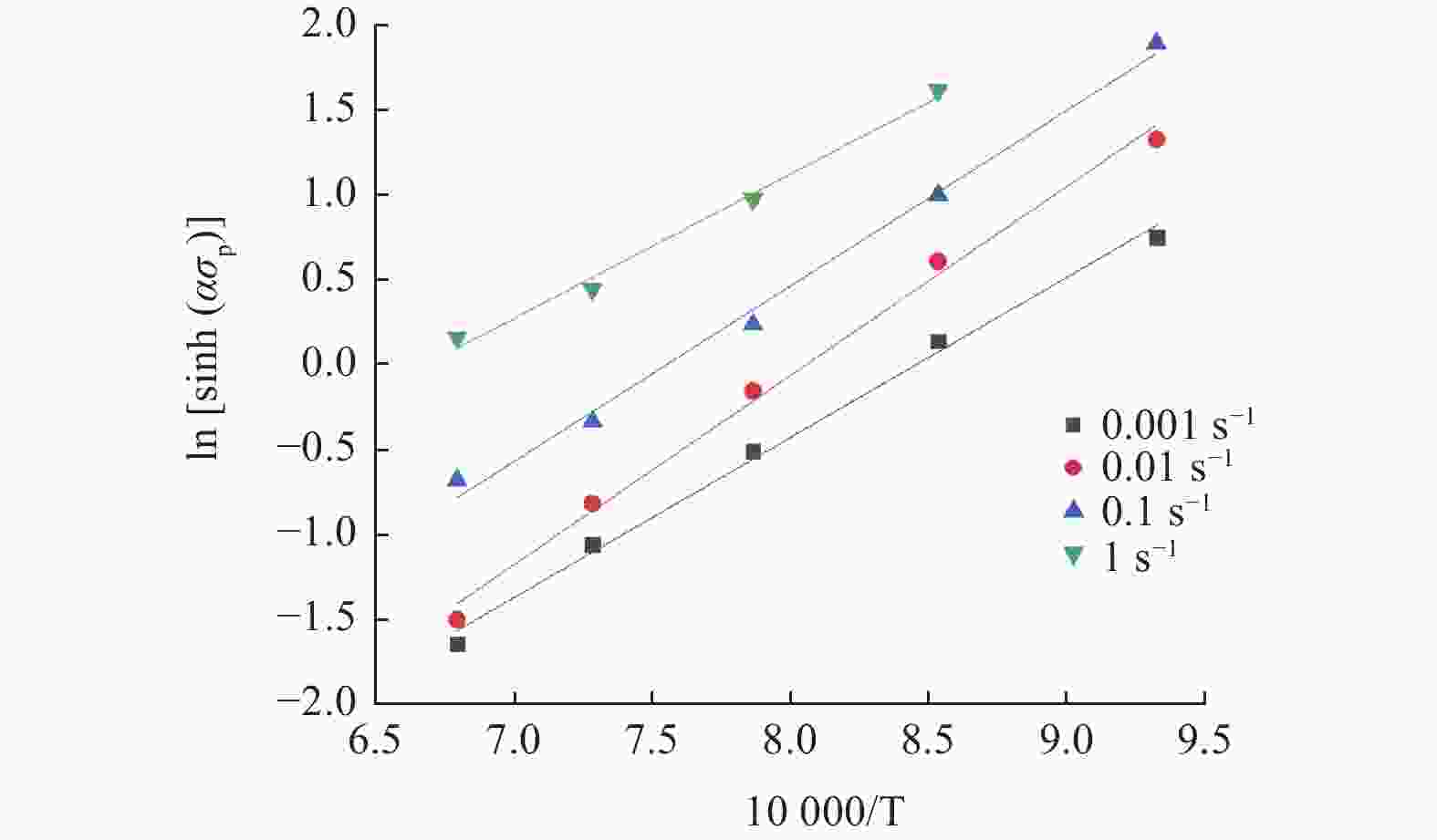
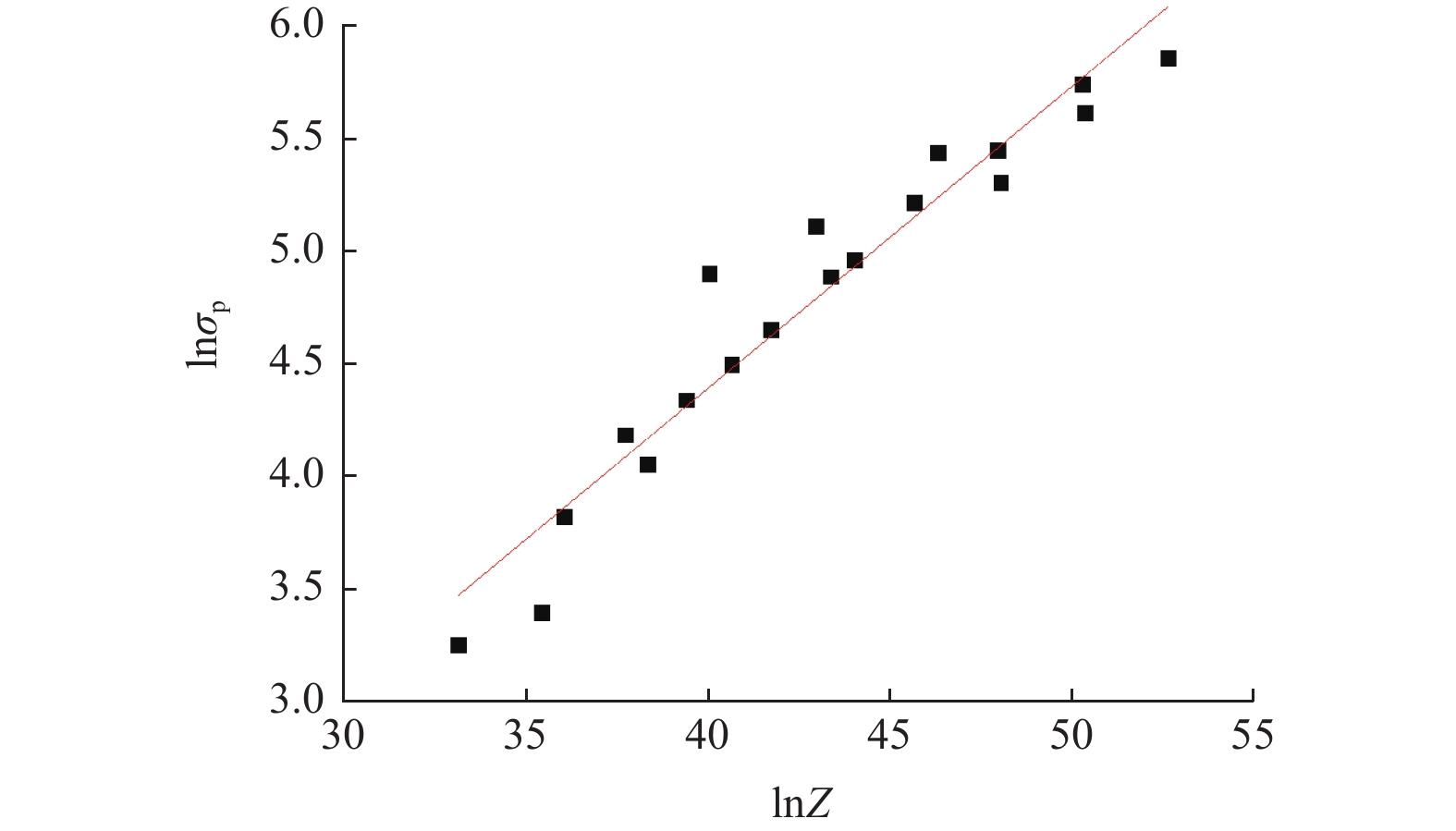
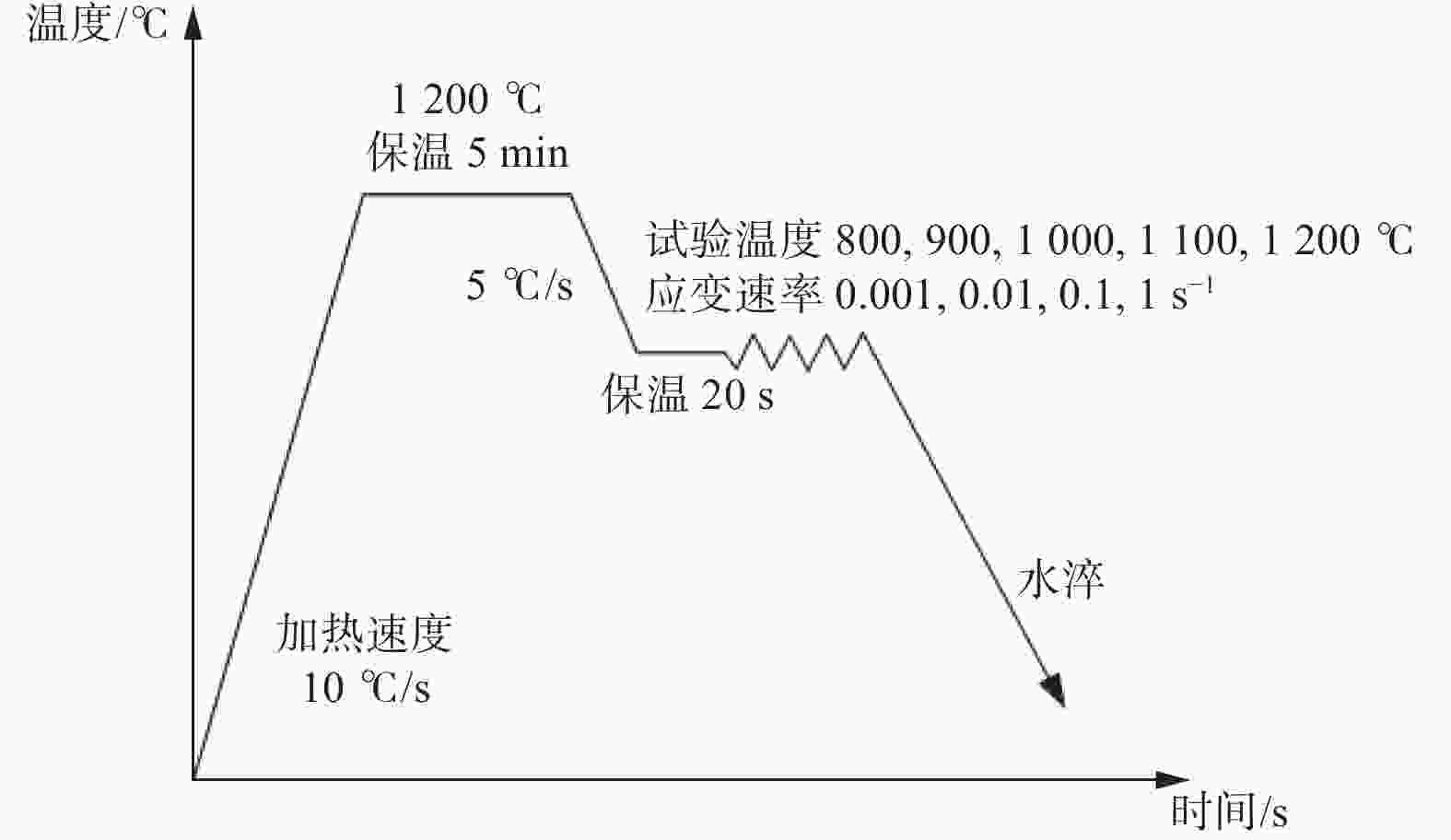
利用Gleeble−3800热/力学模拟试验机研究304不锈钢热变形行为,通过变形温度区间为800~1200 ℃,应变速率区间为0.001~1 s−1的热压缩试验,得到304不锈钢在此区间的真实应力−应变曲线. 结果表明,304不锈钢在热变形过程中,流动应力随着温度的降低和应变速率的升高而增大. 根据真实应力−应变曲线构建304不锈钢的Arrhenius本构方程,其热变形激活能为490 kJ/mol,lnZ和ln
\begin{document}${\sigma _{\rm{p}}}$\end{document} 之间的线性相关系数为0.93,说明模型应力预测值与试验值吻合较好.
Abstract:Thermal deformation behavior of 304 stainless steel was investigated by utilizing Gleeble−3800 thermo-mechanical simulator. The true stress-strain curves of 304 stainless steel were obtained through the hot compression experiment with temperature range of 800~1200 ℃ and the strain rate range of 0.001~1 s−1. The results show that the flow stress of 304 stainless steel increases with the reduction of temperature and the growth of strain rate during the hot deformation. According to the true stress-strain curves, the Arrhenius constitutive equation of 304 stainless steel was constructed. The hot deformation activation energy is 490 kJ/mol and the linear correlation coefficient between lnZ and ln
\begin{document}${\sigma _{\rm{p}}}$\end{document} is 0.93, which shows that the stress values predicted by the model are in good agreement with the experimental ones.
-
Key words:
- 304 stainless steel /
- thermal deformation /
- flow stress /
- constitutive model
-
表 1 304不锈钢材料的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of 304 stainless steel
元素 Fe C Cr Si Mn N Ni Cu Co P 质量分数 /% 69.010 0.034 18.94 0.440 1.860 0.066 9.400 0.040 0.020 0.020 -
[1] JIA B, RUSINEK A, PESCI R, et al. Simple shear behavior and constitutive modeling of 304 stainless steel over a wide range of strain rates and temperatures[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2021, 154: 103896. [2] KORI P, VADAVADAGIA B H, KHATIRKAR R K. Hot deformation characteristics of ASS-304 austenitic stainless steel by tensile tests[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 28(3): 1895–1898. [3] 周芳娟. 304不锈钢切削加工表面特性地研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2014. [4] 廖喜平, 谢其军, 胡成亮, 等. 304奥氏体不锈钢热变形行为及热加工图[J] . 锻压技术,2017,42(12):150 − 156. [5] 王艳, 王明家, 蔡大勇, 等. 高强度奥氏体不锈钢的热变形行为及其热加工图[J] . 材料热处理学报,2005,26(4):65 − 68. [6] NKHOMA R K C, SIYASIYA C W, STUMPF W E. Hot workability of AISI 321 and AISI 304 austenitic stainless steels[J] . Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2014,595(15):103 − 112. [7] PARSA M H, OHADI D. A constitutive equation for hot deformation range of 304 stainless steel considering grain sizes[J] . Materials and Design,2013,52(24):412 − 421. [8] 吴琨, 邹德宁, 韩英, 等. 304Cu奥氏体不锈钢热变形本构模型[J] . 热加工工艺,2013,42(14):15 − 17. [9] 李星星. 304不锈钢本构模型参数识别研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2012. [10] BABU K A, MANDAL S, ATHREYA C N, et al. Hot deformation characteristics and processing map of a phosphorous modified super austenitic stainless steel[J] . Materials & Design,2017,115:262 − 275. [11] CHEN Z Y, NASH P. Hot deformation behavior and processing maps for a large marine crankshaft S34MnV steel[J] . Steel Research Intertional,2018,89(3):1700321. doi: 10.1002/srin.201700321 [12] 姬忠超. GH690合金热变形行为及水室隔板制造工艺研究[D]. 上海: 上海工程技术大学, 2019. [13] 于以标, 陈乐平, 徐勇, 等. 2060-T8E30铝锂合金的热变形行为及本构模型[J] . 稀有金属材料与工程,2021,50(12):4388 − 4394. -





 下载:
下载: