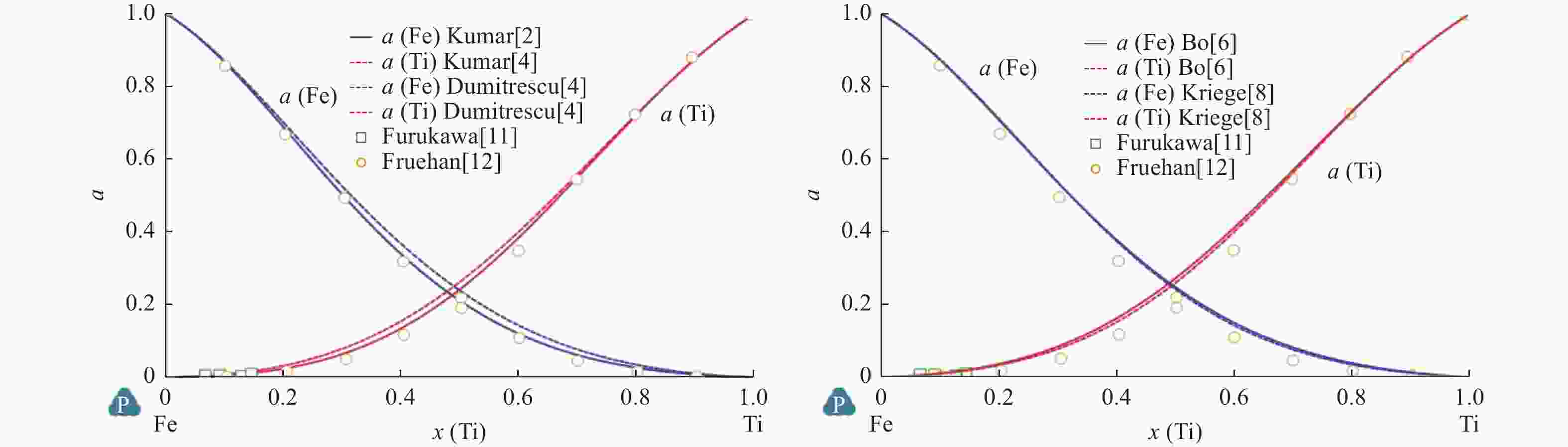
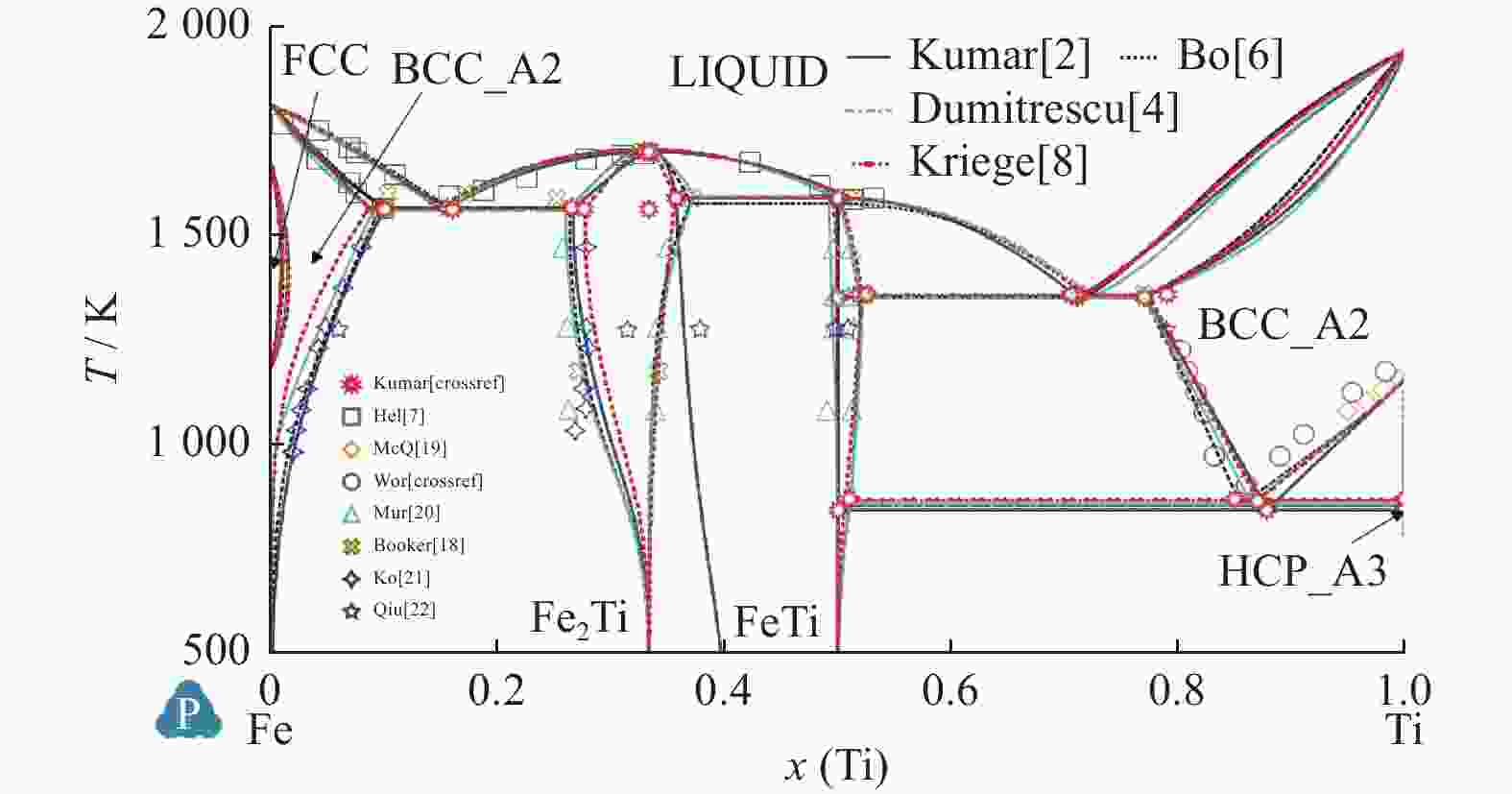
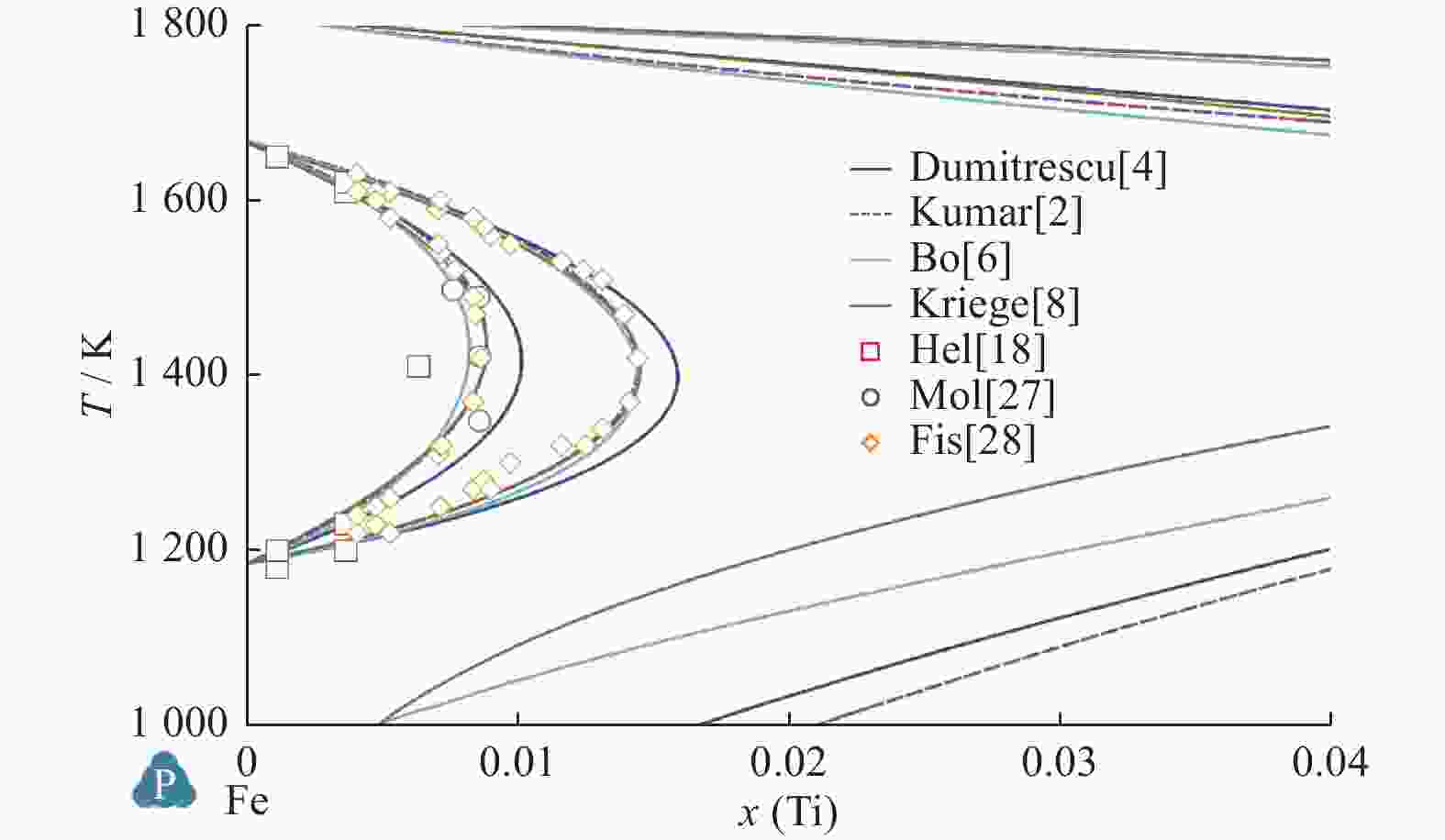
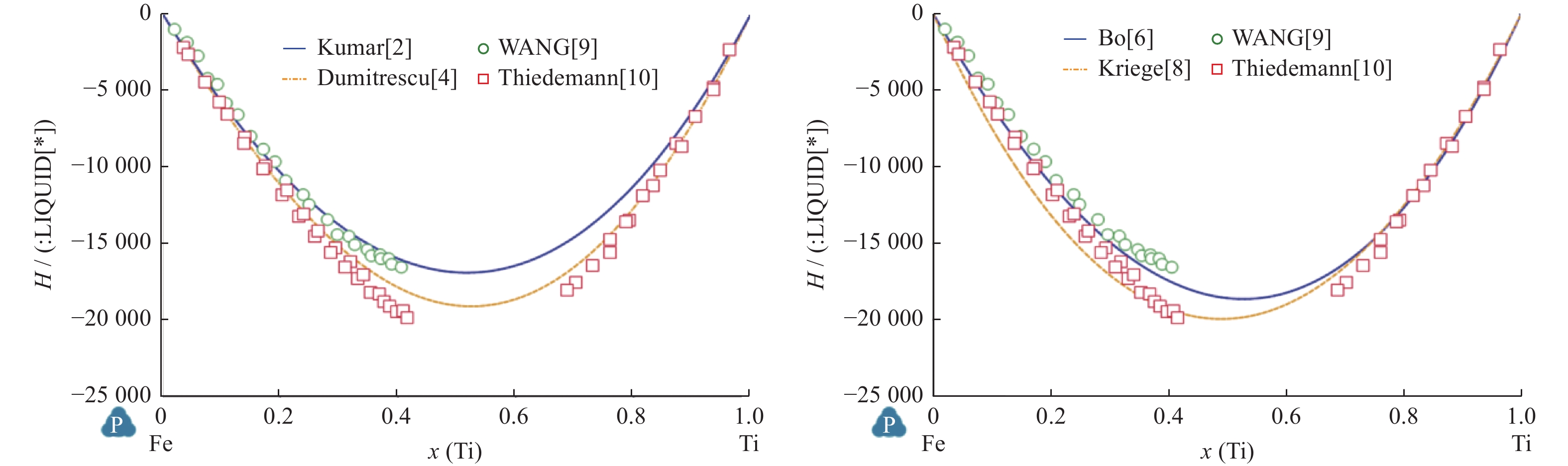
Comparison of Fe-Ti binary system thermodynamic assessments
-
摘要: Fe-Ti二元系作为多组元Fe合金和多组元Ti合金的子系统,其热力学性质研究是将其拓展到多维应用的基础. 利用CALPHAD方法,选取近几十年来最具代表性的5篇Fe-Ti二元系评估研究论文,复现各评估研究的计算结果,比较不同评估对稳定相的热力学建模的相异性和对最终评估结果的影响,同时指出某些评估中存在的问题.Abstract: As a subsystem of multi-principal-elements Fe alloys and multi-principal-elements Ti alloys, the thermodynamic properties of the Fe-Ti binary system are the basis for expanding it to multi-dimensional applications. By using CALPHAD method, five of the most representative Fe-Ti binary system assessment research articles in recent decades were selected and the calculation conclusions of these research were reproduced. Meanwhile, the dissimilarities of the thermodynamic modeling of stable phases of different assessments and the impact on the final evaluation results were compared, and some problems in the evaluation were pointed out.
-
Key words:
- Fe-Ti binary system /
- thermodynamic assessment /
- sublattice model /
- CALPHAD method /
- phase stability
-
表 1 溶液相热力学参数计算值
Table 1. Calculated thermodynamic parameters of solution phase
相 参数 Kumar等[2] Jonsson[3] Dumitrescu等[4] Keyzer等[5] Bo等[6] LIQUID L0 $ -6\;758 + 9.809T $ $ -64\;457 $ $ -71\;374 + 8.25T $ $ -76\;247 + 17.845T $ $ -74\;300 + 17.839T $ L1 $ -4\;731 $ $ 7\;434-4.5T $ $ 7\;900-6.069T $ $ 8\;299.849-6.101T $ L2 $ 12\;155 + 0.25T $ $ 4\;345-2.844T $ BCC_A2 L0 $ -579 + 14.954T $ $ -58\;134 + 6.887T $ $ -59\;098 + 11.5T $ $ -68\;488 + 23.825T $ $ -69\;241.924 + 25.246T + $
$0.000\;1{T}^{2} + 120\;000{T}^{-1}$L1 $ -6\;059 $ $ -12\;879 + 6.828T $ $ -1\;769 + T $ $ 5\;467-5.083T $ $ 5\;018.986-4.992T $ L2 $ 5\;602 + 3.5T $ $ 25\;262-15.83T $ $ 23\;028.241-13.110T $ FCC_A1 L0 $ -5\;030 + 5.487T $ $ -50\;400 $ $ -51\;625 + 11T $ $ -56\;022 + 8.356T $ $ -52\;149.856 + 9.265T $ L1 $ -1\;950-6T $ $ 4\;773-4.029T $ $ 4\;755.9-4.982T $ L2 $ 14\;875 $ $ 30\;021-12.614T $ $ 29\;205.228-11.046T $ HCP_A3 L0 $ 15\;132-8.668T $ $ -20\;019 + 23.08T $ $ -28\;750 + 11T $ $ -10\;000 + 15T $ $ -2\;500 + 35.004T $ L1 $ -1\;700-6T $ L2 $ 15\;000 $ 表 2 FeTi相热力学参数计算值
Table 2. Calculated thermodynamic parameters of FeTi phase
作者 FeTi相描述形式 热力学参数 Kumar等[2] 化学计量化合物 $-53\;650 + 7.495T + {H}^{\mathrm{S}\mathrm{E}\mathrm{R} } + \displaystyle \sum { {}_{}{}^{0}G}^{\mathrm{S}\mathrm{E}\mathrm{R} }$ Jonsson[3] 化学计量化合物 $-63\;646 + 243.681T-449\;929T{\rm{ln}}T-0.00\;843{T}^{2} + 102\;000{T}^{-1} + {H}^{\mathrm{S}\mathrm{E}\mathrm{R} }$ Dumitrescu等[4] 化学计量化合物 $-90\;800 + 409T-73.5\;538T{\rm{ln}}T-0.01\;017{T}^{2} +$
$ 124\;200{T}^{-1} + {H}^{\mathrm{S}\mathrm{E}\mathrm{R}} $Keyzer等[5] 双亚点阵模型 ${G}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}:\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i} }^{}=76\;218-46.685T + 8.663T\rm{ln}T-0.007\;151{T}^{2} + 1.121\;169{\text{×} } {10}^{-6}{T}^{3}$ $ {L}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e},\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}:\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}}^{1}=-13\;764 $
$ {L}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e},\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}:Ti}^{0}=-6\;097 $
$ {L}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e},\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}:\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}}^{1}=12\;256 $
$ {\mathrm{T}\mathrm{C}}_{\mathrm{B}2}=-1\;325 $Bo等[6] 双亚点阵模型 $ -30\;028.003 + 4.495T $ $ {L}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e},\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}:\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}}=-5\;001.5 $
$ {L}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e},\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}:\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}}=11\;000 $表 3 Fe2Ti相热力学参数计算值
Table 3. Calculated thermodynamic parameters of Fe2Ti phase
作者 热力学模型 亚点阵点位 热力学参数 Kumar等[2] 三亚点阵模型 Fe:Ti:Fe $ -429\;782 + 120.875T $ Fe:Fe:Fe $ 69\;869 $ Va:Ti:Fe $-3\;556\;573 + 109.065T$ Va:Fe:Fe $ 60\;724 $ Josson[3] 三亚点阵模型 Fe:Fe:Fe $12{\text{×} }({}_{}{}^{0}{G}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e} }^{} + 8\;426)$ Fe:Ti:Fe $12{\text{×} }(-34\;938 + 137.773-24.517\;77T\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}T$
$-0.003\;39{T}^{2} + 41\;400{T}^{-1})$Fe:Fe:Ti $2{G}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}:\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}:\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e} }^{ {\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e} }_{2}\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i} }-{G}_{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}:\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}:\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i} }^{ {\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e} }_{2}\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i} } + 2.4{\text{×} }{10}^{6} + 46.105T$ Fe:Ti:Ti $ 6{G}^{\mathrm{F}\mathrm{e}\mathrm{T}\mathrm{i}} + 28\;193 $ Dumitrescu等[4] 双亚点阵模型 Fe:Fe $ 15\;000 $ Ti:Fe $ 15\;000 $ Fe:Ti $-90\;800 + 409T-73.553\;18-0.010\;17{T}^{2}$
$ + 124\;200{T}^{-1} $Ti:Ti $ 15\;000 $ Fe,Ti:Va $ -38\;000 $ Va:Fe,Ti $ 16\;000 $ Keyzer等[5] 三亚点阵模型 摩尔吉布斯自由能函数G $-78\;603 + 349.967\;5T-64.502T\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}T$
$-0.0241\;491{T}^{2} + 3.936\;825{\text{×} }10^{-6}{T}^{3} + 7\;620{T}^{-1}$Fe,Ti:Fe:Fe $ 3\;177 $ Fe:Fe,Ti:Fe $ 18\;000 $ Fe:Fe:Fe,Ti $ 6\;000 $ Bo等[6] 双亚点阵模型 摩尔吉布斯自由能函数G $ -85\;500 + 410.041T-73.553T\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}T $
$-0.010\;17{T}^{2} + 124\;212.42{T}^{-1}$相 $ {\beta }_{0} $ $ {\beta }_{1} $ $ {\beta }_{2}^{} $ $ {\beta }_{3}^{} $ $ {K}_{T}^{\text{'}} $ FeTi $5.164 \;3{\text{×} }{10}^{12}$ $9.329{\text{×} }{10}^{14}$ $-12.781 \;5{\text{×} }{10}^{19}$ $423.456{\text{×} }{10}^{23}$ $ 3.1 $ Fe2Ti $4.971 \;7{\text{×} }{10}^{12}$ $5.245{\text{×} }{10}^{14}$ $0.322 \;8{\text{×} }{10}^{19}$ $1.237 \;8{\text{×} }{10}^{23}$ $ 4 $ 表 5 金属间相生成焓计算值与实验数据对比
Table 5. Comparation between calculated enthalpy of formation and experimental data in intermetallic phases
相 x(Ti) 温度/K 生成焓 $\Delta H$/(kJ•mol−1) Kumar等[2] Jonsson[3] Dumitrescu等[4] 试验值及来源 FeTi $0.500$ $ 1\;450 $ $ -27.51 $ $-31.691$ $ -29.868 $ $ -31.1 $,Gacchon等[13] FeTi $0.500$ $ 1\;513 $ $ -27.29 $ $-31.639$ $ -29.816 $ $ -27.8 $,Dinsdale等[14] Fe2Ti $0.311$ $ 1\;514 $ $ -31.81 $ $-31.510$ $ -26.863 $ $ -27.6 $,Gacchon等[13] Fe2Ti $0.330$ $ 1\;413 $ $ -34.52 $ $-33.930$ $ -29.273 $ $ -25.4 $,Dinsdale等 [14] 表 6 Fe-Ti二元系中温度和摩尔分数计算值与试验测量值
Table 6. Calculated values and experimental measured value of temperature and mole fraction of Fe-Ti system
平衡反应 Kumar等[2] Jonsson[3] Dumitrescu等[4] Bo等[6] Kriegel等[8] 试验[15] 试验[16] 试验[17] L$ \leftrightarrow $BCC_Fe + Fe2Ti T=1 565.4 K T=1 564 K T=1 562 K T=1 559 K
x(Ti)=0.26T=1 564.3 K
x(Ti)=0.277T=1 562 K T=1 599 K
xTi=0.25Cong.melt Fe2Ti T=1 699.5 K T=1 704 K T=1 692.5 K T=1 706 K
x(Ti)=0.329T=1 700.8 K
x(Ti)=0.333T=1 700 K T=1 696 K FeTi$ \leftrightarrow $Fe2Ti + L T=1 589.5 K T=1 593 K T=1 612 K T=1 592 K
x(Ti)=0.492T=1 588.4 K
x(Ti)=0.356T=1 590 K T=1 589 K
x(Ti)=0.37L$ \leftrightarrow $FeTi + BCC_Ti T=1 351 K T=1 346 K T=1 355 K T=1 352 K
x(Ti)=0.77T=1 356.5 K
x(Ti)=0.774T=1 353 K
x(Ti)=0.78BCC_Ti$ \leftrightarrow $FeTi + HCP_Ti T=840.65 K T=859 K T=856.4 K T=856 K
x(Ti)=0.9 995T=864.8 K T=848 K
x(Ti)>0.99 -
[1] KAUFMAN L, NESOR H. Coupled phase diagrams and thermochemical data for transition metal binary systems — I[J] . Calphad,1978,2(1):55 − 80. doi: 10.1016/0364-5916(78)90005-6 [2] KUMAR K C H, WOLLAIITS P, DELAEY L. Thermodynamic reassessment and calculation of Fe-Ti phase diagram[J] . Calphad,1994,18(2):223 − 234. doi: 10.1016/0364-5916(94)90028-0 [3] JONSSON S. Assessment of the Fe-Ti system[J] . Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B,1998,29(2):361 − 370. doi: 10.1007/s11663-998-0113-z [4] DUMITRESCU L F S, HILLERT M, SOUNDERS N. Comparison of Fe-Ti assessments[J] . Journal of Phase Equilibria,1998,19(5):441 − 448. doi: 10.1361/105497198770341923 [5] De KEYZER J, CACCIAMANI G, DUPIN N, et al. Thermodynamic modeling and optimization of the Fe–Ni–Ti system[J] . Calphad,2009,33(1):109 − 123. doi: 10.1016/j.calphad.2008.10.003 [6] BO H, WANG J, DUARTE L, et al. Thermodynamic re-assessment of Fe–Ti binary system[J] . Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2012,22(9):2204 − 2211. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61450-7 [7] GRIMVALL G. Thermophysical Properties of Materials[M]. Elsevier, 1999. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-044482794-4/50007-3. [8] KRIEGEL M J, WETZEL M H, FABRICHNAYA O, et al. Binary Ti–Fe system. Part II: Modelling of pressure-dependent phase stabilities[J] . Calphad,2022,76:102383. doi: 10.1016/j.calphad.2021.102383 [9] WANG H, LÜCK R, PREDEL B. Calorimetric determination of the enthalpy of mixing of liquid iron-titanium alloys[J] . Zeitschrift fuer Metallkunde,1991,82(8):659 − 665. [10] THIEDEMANN U, QIN J, SCHAEFERS K, et al. Mixing enthalpy measurements of liquid Fe-Ti alloys by levitation alloying calorimetry and calculation of the thermodynamic properties of mixing.[J] . ISIJ International,1995,35(12):1518 − 1522. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.35.1518 [11] FURUKAWA T, KATO E. Thermodynamics of binary liquid iron-titanium alloys by mass spectrometry[J] . Transactions of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan,1976,16(7):382 − 387. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational1966.16.382 [12] FRUEHAN R J. Activities in liquid Fe-AI-O and Fe-Ti-O alloys[J] . Metallurgical Transactions,1970,1:3403 − 3410. [13] GACHON J C, NOTIN M, HERTZ J. The enthalphy of mixing of the intermediate phases in the systems FeTi, CoTi, and NiTi by direct reaction calorimetry[J] . Thermochimica Acta,1981,48(1/2):155 − 164. doi: 10.1016/0040-6031(81)87031-1 [14] DINSDALE A T, CHART T G, PUTLAND F H. Enthalpies of formation of binary phases in the Fe-Ni system[R]. National Physical Laboratory: Middlesex, 1985. [15] MURRAY J L. The Fe−Ti (iron-titanium) system[J] . Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams,1981,2(3):320 − 334. doi: 10.1007/BF02868286 [16] BOOKER P H. Ternary phase equilibria in the systems Ti-Fe-C, Ti-Co-C and Ti-Ni-c : Phase equilibria of the type metal carbonitride + graphite + nitrogen in the systems Ti-C-N, Zr-C-N, and Hf-C-N[EB/OL]. 1979. [17] VANTHYNE R J, KESSLER H D, HANSEN M. The systems titanium-chromium and titanium-iron[J] . Transactions of the American Society for Metals,1952,44:974 − 989. [18] HELLAWELL A. The constitution of manganese base alloys with metals of the second transition series[J] . Journal of the Less Common Metals,1959,1(5):343 − 347. doi: 10.1016/0022-5088(59)90036-0 [19] MCQUILLAN A D. The application of hydrogen equilibriumpressure measurements to the investigation of titanium alloy systems[J] . Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals,1951(79):73 − 88. [20] MURAKAMI Y, KIMURA H, NISHIMURA Y. An investigation on the titanium-iron-carbon system (1st report). on the titanium-iron system[J] . Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals,1957,21(11):665 − 669. [21] KO M, NISHIZAWA T. Effect of magnetic transition on the solubility of alloying elements in alpha iron[J] . Journal of the Japan Institute of Metals,1979,43(2):118 − 126. [22] QIU C, JIN Z P. An experimental study and themodynamic evaluation of the Fe-Ti-W system at 1 000°C[J] . Scripta Metallurgica et Materialia,1993,28(1):85 − 90. doi: 10.1016/0956-716X(93)90542-Z [23] RAUB E, RAUB C J, RÖSCHEL E, et al. The α-Ti-Fe solid solution and its superconducting properties[J] . Journal of the Less Common Metals,1967,12(1):36 − 40. doi: 10.1016/0022-5088(67)90066-5 [24] MATYKA J, FAUDOT F, BIGOT J. Study of iron solubility in α titanium[J] . Scripta Metallurgica,1979,13(7):645 − 648. doi: 10.1016/0036-9748(79)90126-1 [25] BALESIUS A, GONSER U. Precision phase analysis[J] . Journal de Physique: Colloque,1976,37:C6 − 397. [26] STUPEL M M, BAMBERGER M, RON M. The solubility of iron in α-titanium in the temperature range 360~580 °C[J] . Journal of the Less Common Metals,1986,123(1/2):1 − 7. doi: 10.1016/0022-5088(86)90109-8 [27] MOLL S, OGILVIE R. Solubility and diffusion of titanium in iron[J] . Transactions of AIME,1959,215:613 − 618. [28] FISCHER W, LORENTZ K, FABRITIUS H, et al. Investigation of phase transformations in iron alloys using a magnetic balance[J] . Arch Eisenhüttenwes,1966,37:78 − 87. [29] DUMITRESCU L, HILLERT M. Reassessment of the solubility of TiC and TiN in Fe[J] . Isij International,1999,39:84 − 90. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.39.84 [30] FENG Q, DUAN B, MAO L, et al. Thermodynamic assessment of Ti-Al-Fe-V quaternary system applied to novel titanium alloys designing[J] . Metals,2022,12(3):444. doi: 10.3390/met12030444 [31] ZHANG G, ZHENG W, ZHAO Z, et al. Thermodynamic modeling of the Fe-Mn-Ti system[J] . Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion,2021,42(3):363 − 372. doi: 10.1007/s11669-021-00889-7 [32] WITUSIEWICZ V T, BONDAR A, HECHT U, et al. Experimental study and thermodynamic re-modelling of the constituent binaries and ternary B–Fe–Ti system[J] . Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,800:419 − 449. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.341 [33] HU T, ZENG Y, HUANG X M, et al. Experimental investigation of phase relationship in Ti–Fe-Hf ternary system[J] . Calphad,2019,67:101669. doi: 10.1016/j.calphad.2019.101669 [34] CHEN Y, CHENG L, TANG B. Binary diffusion behaviour in Ti– X (X = Al, Mo, V, Cr, Fe) alloys[J] . International Journal of Materials Research,2018,109(6):569 − 572. doi: 10.3139/146.111642 [35] LU X G, Selleby M, Sundman B. Implementation of a new model for pressure dependence of condensed phases in Thermo-Calc[J] . Calphad,2005,29(1):49 − 55. doi: 10.1016/j.calphad.2005.04.001 -






 下载:
下载: