|
[1]
|
BAO X, GUO S, XIAO N, et al. A cooperation of catheters and guidewires-based novel remote-controlled vascular interventional robot[J] . Biomedical Microdevices,2018,20(20):2 − 19. doi: 10.1007/s10544-017-0241-9
|
|
[2]
|
GUO S X, WANG Y, XIAO N, et al. Study on real-time force feedback for a master-slave interventional surgical robotic system[J] . Biomedical Microdevices,2018,20(37):2 − 10. doi: 10.1007/s10544-018-0278-4
|
|
[3]
|
袁雷, 肖飞, 沈建清, 等. 基于扰动观测器的不确定非线性系统非奇异终端滑模控制[J] . 控制与决策,2014,29(2):353 − 357.
|
|
[4]
|
冒建亮, 李奇, 朱海荣. 一种连续非奇异快速终端滑模控制方法[J] . 控制与决策,2016,31(10):1873 − 1878.
|
|
[5]
|
REN C, LI X, YANG X, et al. Extended state observer-based sliding mode control of an omnidirectional mobile robot with friction compensation[J] . IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2019,66(12):9480 − 9489. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2892678
|
|
[6]
|
TRAN X T, OH H, KIM I R, et al. Attitude stabilization of flapping micro-air vehicles via an observer-based sliding mode control method[J] . Aerospace Science and Technology,2018,76:386 − 393. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.01.045
|
|
[7]
|
DEVIKA K B, THOMAS S. Sliding mode controller design for MIMO nonlinear systems: A novel power rate reaching law approach for improved performance[J] . Journal of the Franklin Institute,2018,355(12):5082 − 5098. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.05.034
|
|
[8]
|
ZHAO L, ZHANG H, YANG Y, et al. Integral sliding mode control of a bilateral teleoperation system based on extended state observers[J] . International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems,2017,15:2118 − 2125. doi: 10.1007/s12555-016-0441-8
|
|
[9]
|
YANG C, GUO S, BAO X, et al. A vascular interventional surgical robot based on surgeon’s operating skills[J] . Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing,2019,57:1999 − 2010.
|
|
[10]
|
LIU H, WANG H, YANG X, et al. Mechanism design of the minimally invasive vascular interventional surgery robot system[C]//Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) and IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM). Ningbo: IEEE, 2017: 225−230.
|





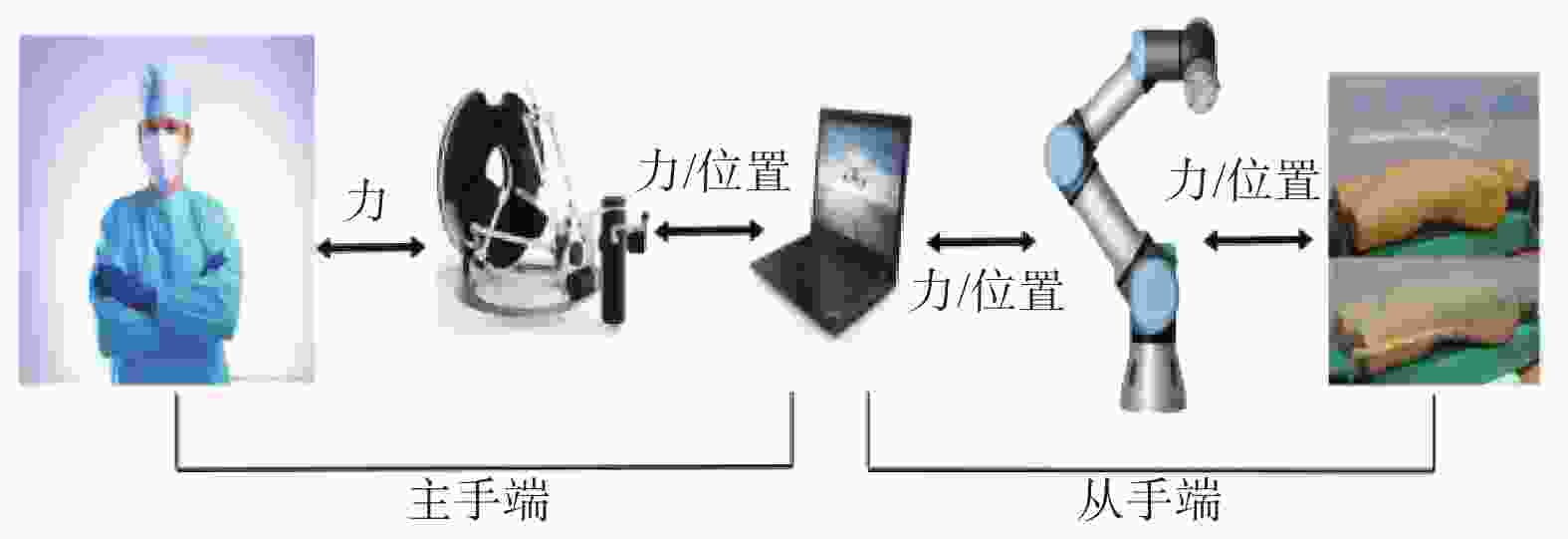
 下载:
下载: