Optimization of metro express stopping scheme based on OD pair of passenger flow
-
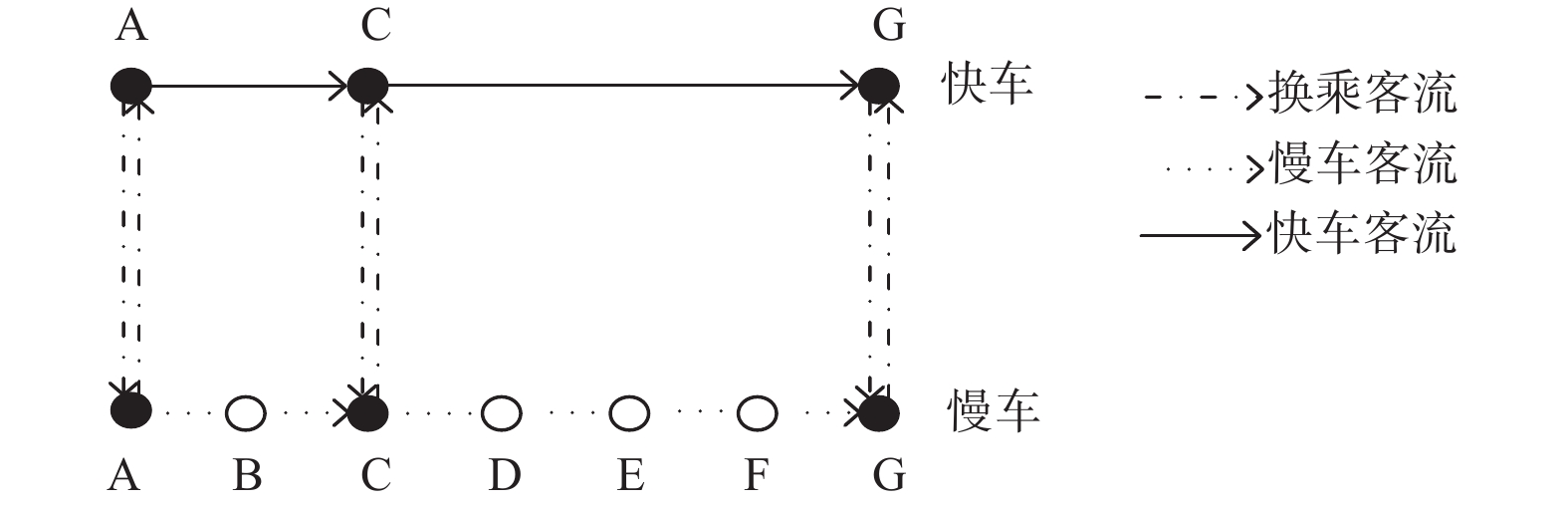
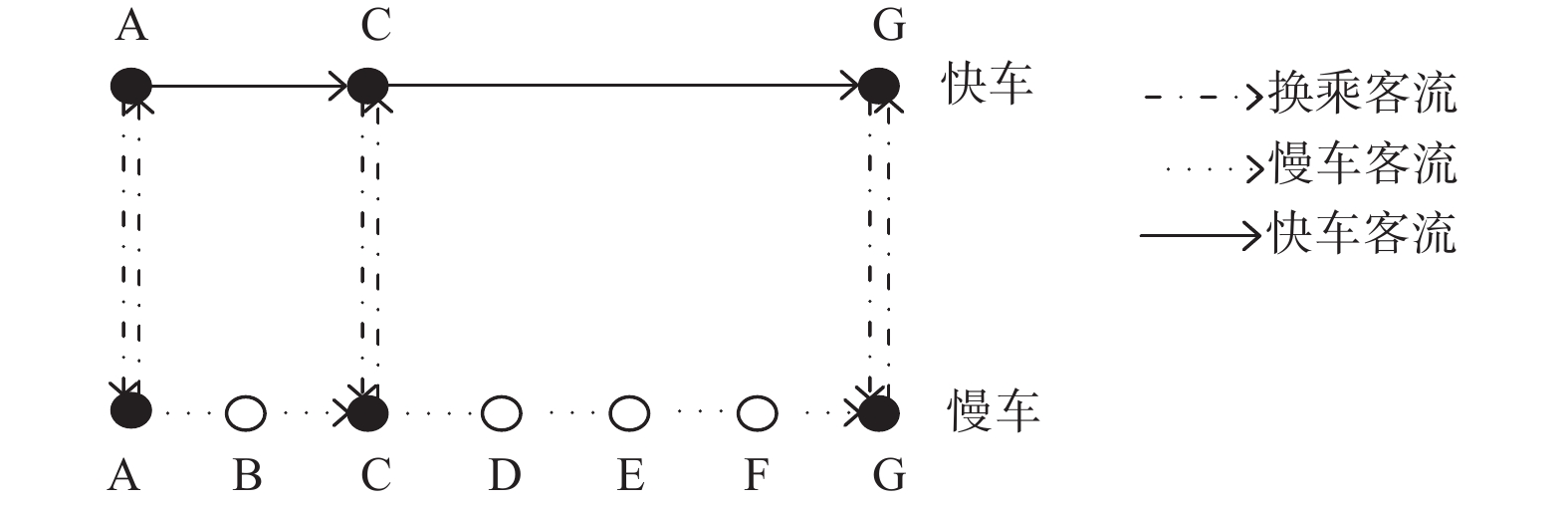
摘要: 为精细化确定轨道交通市郊线路快车停站方案,提出一套以市郊线路客流OD为核心导向的快车停站优化方案。首先,构建轨道交通区间选择费用函数,根据路径选择费用分配OD客流;其次,在客流分配的基础上,以乘客出行时间最短与企业运营成本最低为目标函数,以断面满载率、车站客流需求、优化时段发车次数约束等多重客观因素为模型约束,建立快车停站方案优化模型;最后,以S市地铁市郊线路16号线基础数据为实例验证,运用带精英策略的非支配排序的遗传算法和GA混合(GA-NSGA-II)对停站方案优化模型求解。优化结果表明,在高峰时段乘客人均出行时间节省1.074 min,每个运营日车底运用数减少6列。Abstract: In order to further determine the metro express stopping station, an optimization model of express stopping scheme based on origin-destination (OD) pair of passenger flow was established. Firstly, a road cost function was constructed to allocate OD passenger flow according to route cost. Secondly, taking the shortest travel time of passengers and the lowest operating cost of enterprises as the optimization objective, and taking multiple objective factors such as the cross section full rate, the station passenger flow demand, the number of times of the optimization period constraints as the model constraints, an express stop optimization model was builted according to passenger flow allocation. Finally, based on the basic data of metro line 16 in S city, the genetic algorithm with elite strategy and non dominated sorting, as well as GA hybrid (GA-NSGA-II) were used to solve the optimization model of stopping plan. The optimization results show that in peak hours, the per capita travel time of passengers is saved by 1.074 min, and the number of vehicles under each operation day is reduced by 6 columns.
-
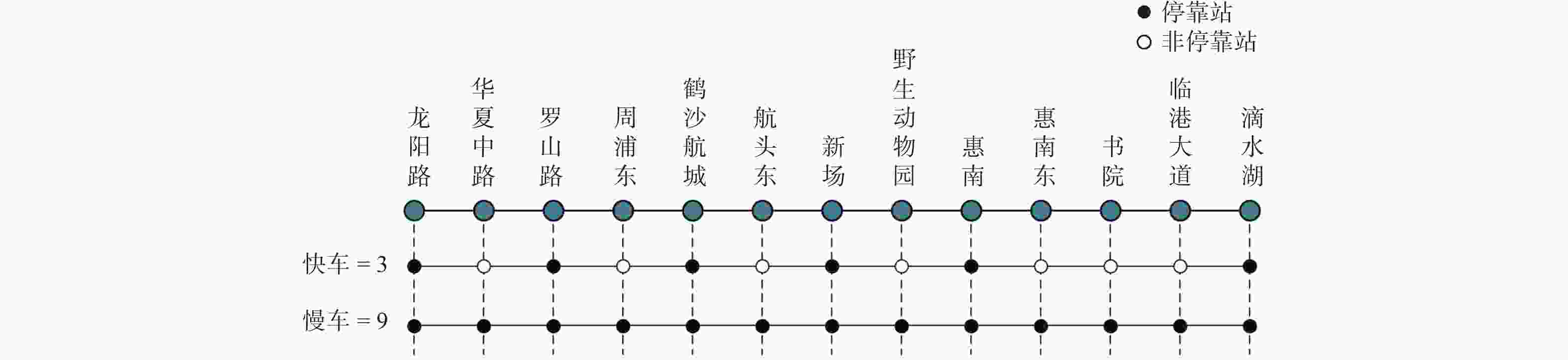
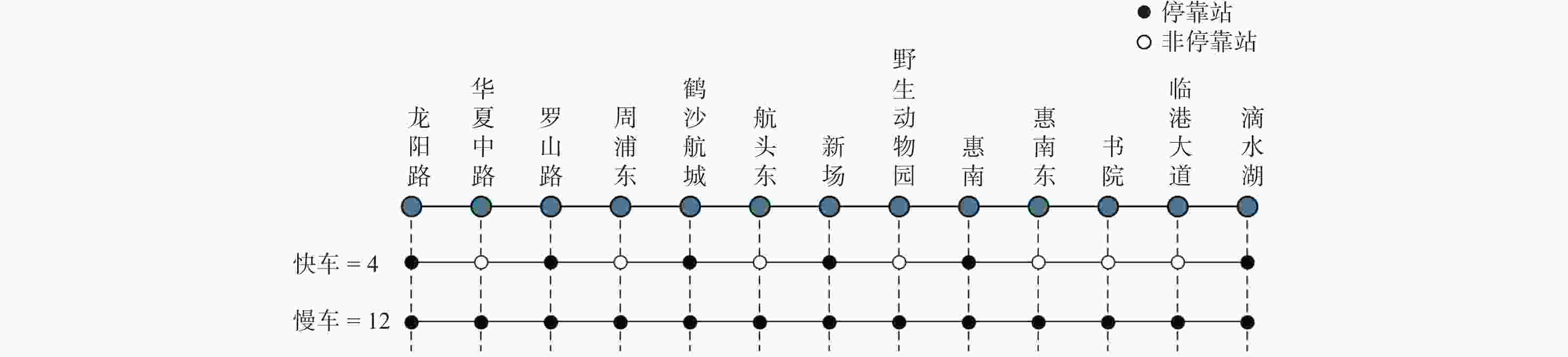
表 1 轨道交通16号线现行快车停站时刻表
Table 1. Current stop schedule for rail transit line 16
车站 往滴水湖方向车次 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 滴水湖 7:46 8:07 10:46 11:46 12:46 13:07 13:46 14:48 15:48 16:46 临港大道 7:43 
10:43 11:43 12:43 
13:43 14:43 14:43 16:43 惠南 7:26 10:26 11:26 12:26 13:26 15:26 14:26 16:26 新场 7:18 10:18 11:18 12:18 14:18 14:18 14:18 16:18 罗山路 7:06 10:06 11:06 12:06 14:06 14:06 14:06 16:06 龙阳路 7:00 7:30 10:00 11:00 12:00 12:30 14:00 14:00 14:00 16:00 车站 往龙阳路方向车次 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 滴水湖 10:00 11:00 12:00 13:00 14:00 15:00 16:00 17:00 17:45 临港大道 10:03 11:03 
13:03 14:03 15:03 16:03 17:03 
惠南 10:21 11:21 13;21 14:21 15:21 16:21 17:21 新场 10:29 11:29 13:29 14:29 15:29 16:29 17:29 罗山路 10:41 11:41 13:41 14:41 15:41 16:41 17:41 龙阳路 10:46 11:46 12:36 13:46 14:46 15:46 16:46 17:46 18:21 表 2 轨道交通16号线站间距及列车运行时分
Table 2. Distance and duration between stations of Rail Transit Line 16
区间 距离
$ \mathop l\nolimits_{ij} $/km运行时分
$ \mathop t\nolimits_{ij} $/s启动附加
时间/s停站附加
时间/s龙阳路站—华夏中路站 4.520 300 20 20 华夏中路站—罗山路站 2.612 300 20 20 罗山路站—周浦东站 5.022 240 20 20 周浦东站—鹤沙航城站 3.616 240 20 20 鹤沙航城站—航头东站 2.612 180 20 20 航头东站—新场站 3.616 240 20 20 新场站—野生动物园站 4.922 360 20 20 野生动物园站—惠南站 6.027 420 20 20 惠南站—惠南东站 5.725 360 20 20 惠南东站—书院站 10.748 600 20 20 书院站—临港大道站 6.931 360 20 20 临港大道站—滴水湖站 2.612 300 20 20 表 3 模型相关参数取值
Table 3. Values of model parameters
参数 取值 优化时长T/h 早高峰4,晚高峰5 列车单位走行距离成本/(元·km−1) 150 车底成本/(元·列−1) 6000 列车停站成本/(元·次−1) 200 停站时间/s 45 表 4 停站方案优化前后乘客总出行时间对比
Table 4. Comparison of total travel time of passengers before and after optimization
开行方案 开行前 开行后 节省 节省占比/% 乘客总旅行时间/h 23490 21970 1520 6.5 表 5 停站方案优化前后运用车辆数对比
Table 5. Comparison of the number of vehicles used before and after optimization
开行方案 开行前 开行后 节省 节省占比/% 运用车底数 158 152 6 3.8 -
[1] LIN W S, SHEU J W. Automatic train regulation for metro lines using dual heuristic dynamic programming[J] . Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F:Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit,2010,224(1):15 − 23. doi: 10.1243/09544097JRRT283 [2] JAMILI A, AGHAEE M P. Robust stop-skipping patterns in urban railway operations under traffic alteration situation[J] . Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies,2015,61:63 − 74. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2015.09.013 [3] YANG A, WANG B, HUANG J, et al. Service replanning in urban rail transit networks: Cross-line express trains for reducing the number of passenger transfers and travel time[J] . Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2020,115:102629. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2020.102629 [4] ALTAZIN E, DAUZÈRE-PÉRÈS S, RAMOND F, et al. Rescheduling through stop-skipping in dense railway systems[J] . Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies,2017,79:73 − 84. doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2017.03.012 [5] LIN D Y, KU Y H. Using genetic algorithms to optimize stopping patterns for passenger rail transportation[J] . Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering,2014,29(4):264 − 278. doi: 10.1111/mice.12020 [6] 李颖, 朱昌锋, 张正坤. 基于前景理论的城市轨道交通停站方案研究[J] . 公路交通科技,2018,16(1):85 − 92. [7] 徐沙, 罗霞. 考虑能耗的城市轨道交通快慢车停站方案优化模型[J] . 交通运输工程与信息学报,2020,18(2):154 − 162. [8] 李晓明, 李海龙, 刘晓磊, 等. 基于再生制动的城轨列车停站时间节能优化研究[J] . 现代计算机,2020(18):23 − 27. [9] 段凌林, 查伟雄, 李剑, 等. 城市轨道交通大小交路结合快慢车开行方案优化[J] . 铁道运输与经济,2020,42(5):103 − 109. [10] 熊祎, 杨桂新, 史丰收, 等. 基于客流需求的城市轨道交通动态时刻表优化模型[J] . 现代城市轨道交通,2020(3):85 − 92. [11] 汤莲花, 徐行方. 基于双层规划的市郊轨道交通多交路快慢车开行方案优化研究[J] . 交通运输系统工程与信息,2018,18(3):152 − 159. [12] FU H, NIE L, MENG L, et al. A hierarchical line planning approach for a large-scale high speed rail network: The China case[J] . Transportation Research, Part A:Policy and Practice,2015,75(5):61 − 83. [13] 王靖. 城市轨道交通市郊线路快慢车开行比例优化研究[D]. 上海: 上海工程技术大学, 2020. [14] 万浩纯, 丁小兵, 刘志钢, 等. 城市轨道交通市郊线快慢车开行方案精细性优化建模研究[J] . 城市轨道交通研究,2020,23(11):73 − 77, 83. [15] 王琳, 魏国静. 基于遗传−模拟退火算法的城市轨道交通快慢车停站方案[J] . 城市轨道交通研究,2015,18(3):96 − 100. [16] 徐俊, 梁青槐, 韩阔等. 市域快轨快慢车比例对越行站设置影响分析[J] . 铁道工程学报,2022,39(9):100 − 105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2022.09.016 -





 下载:
下载: