Analysis of pumping test and optimization design of excavation dewatering in complex geological environment
-
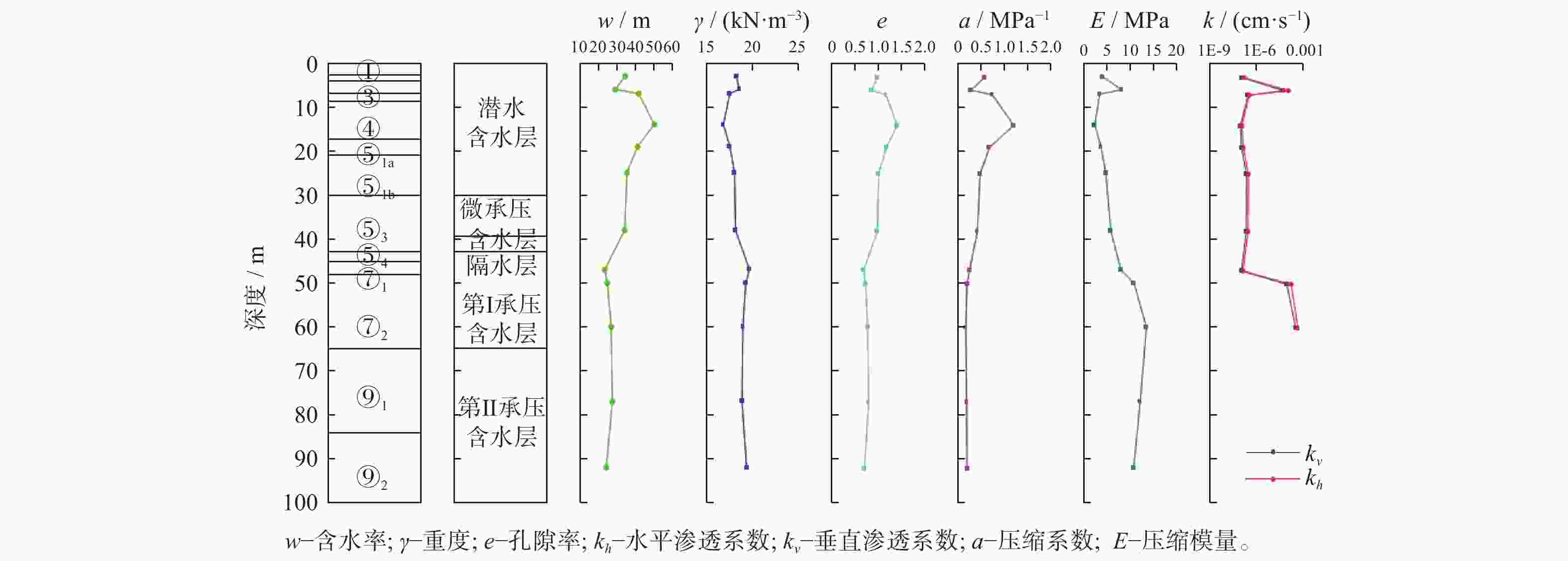
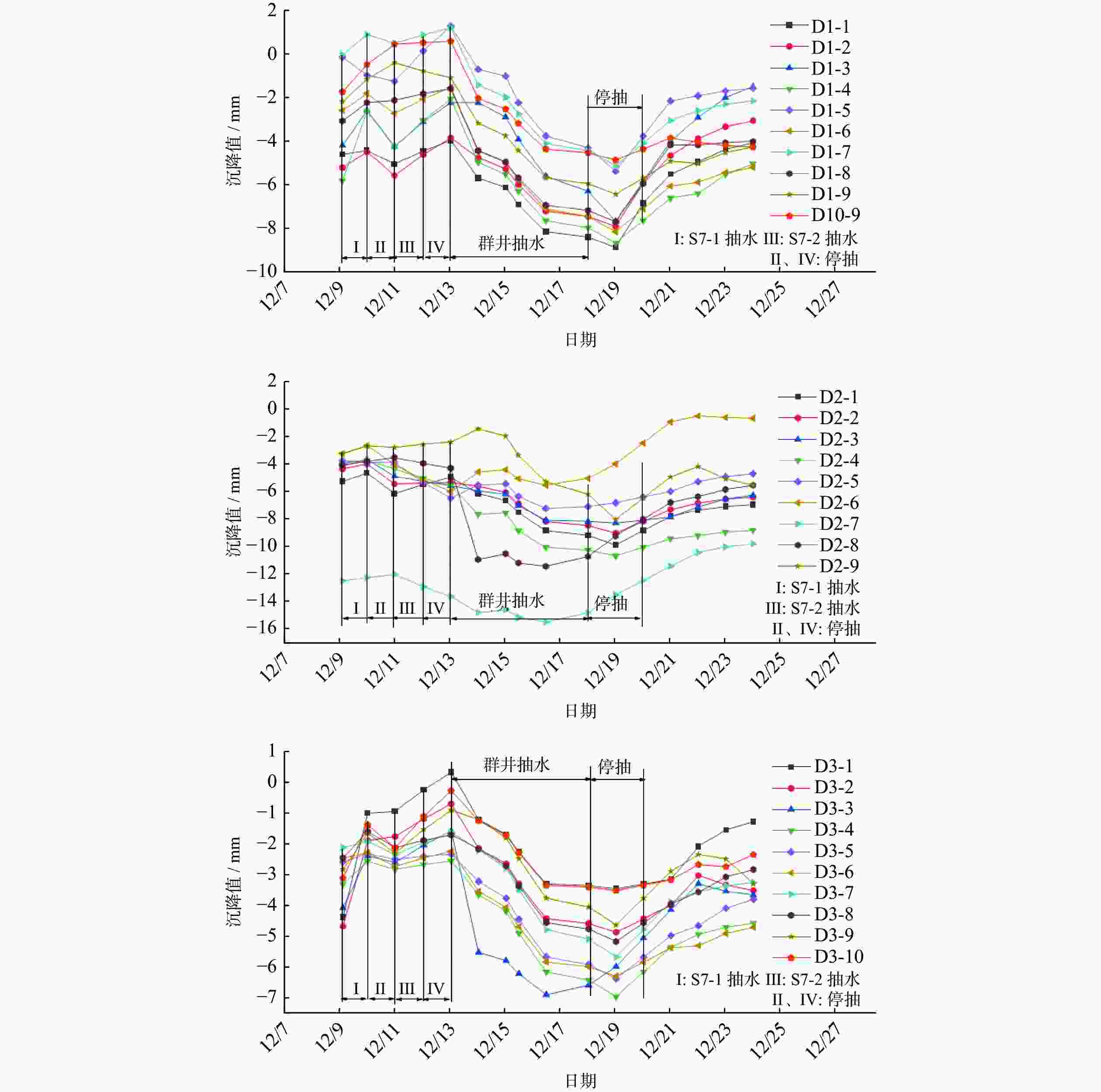
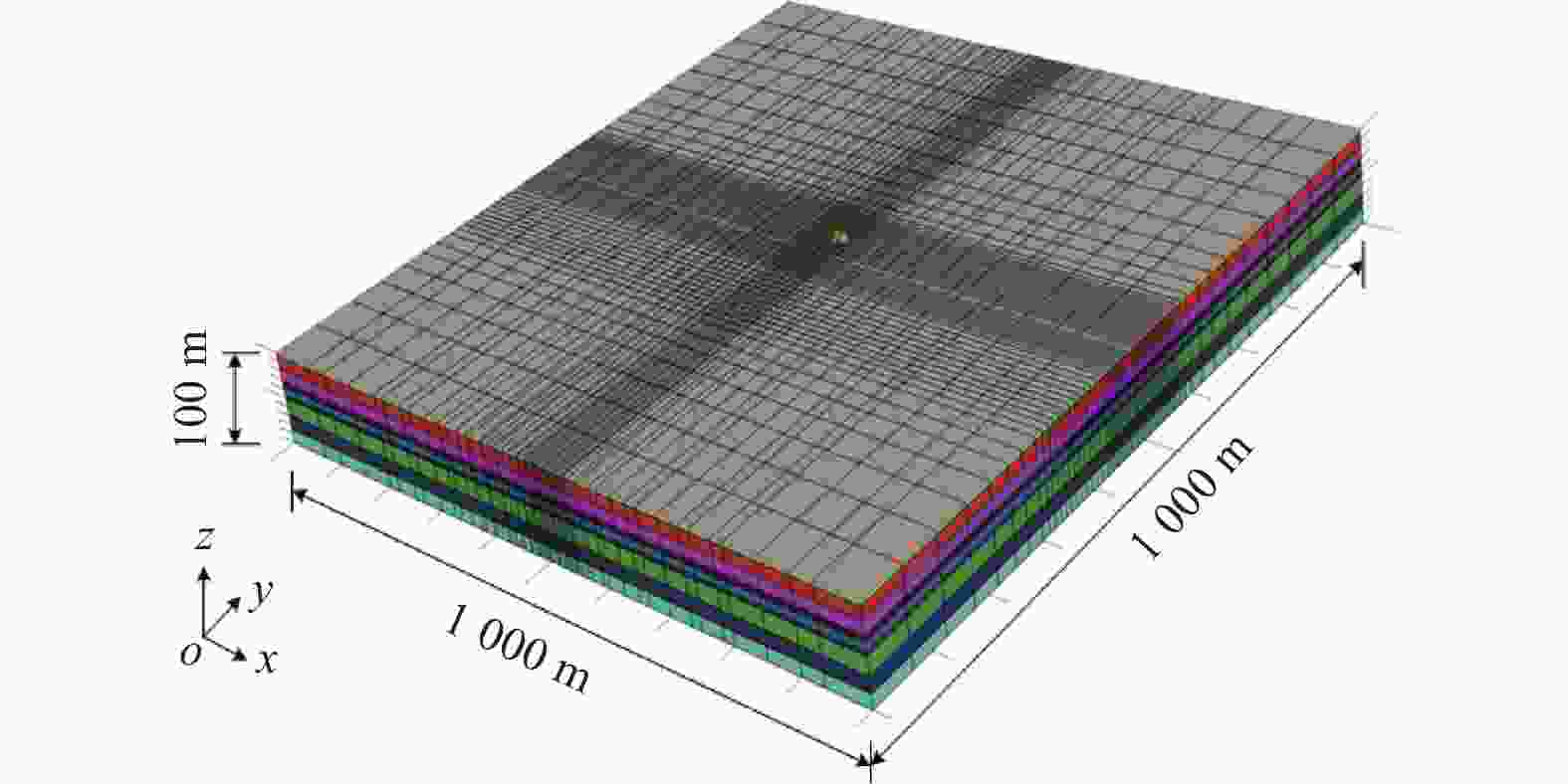
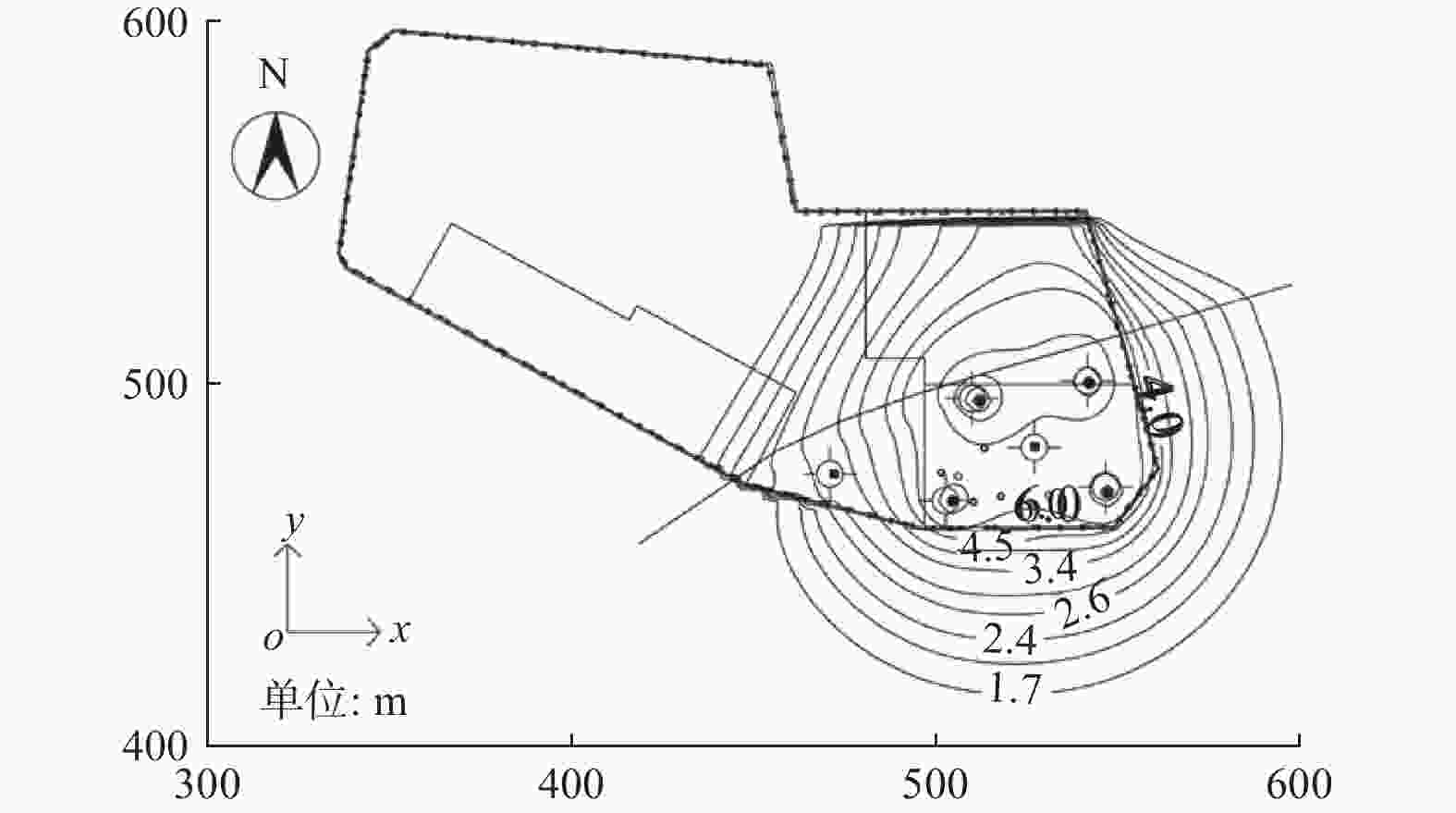
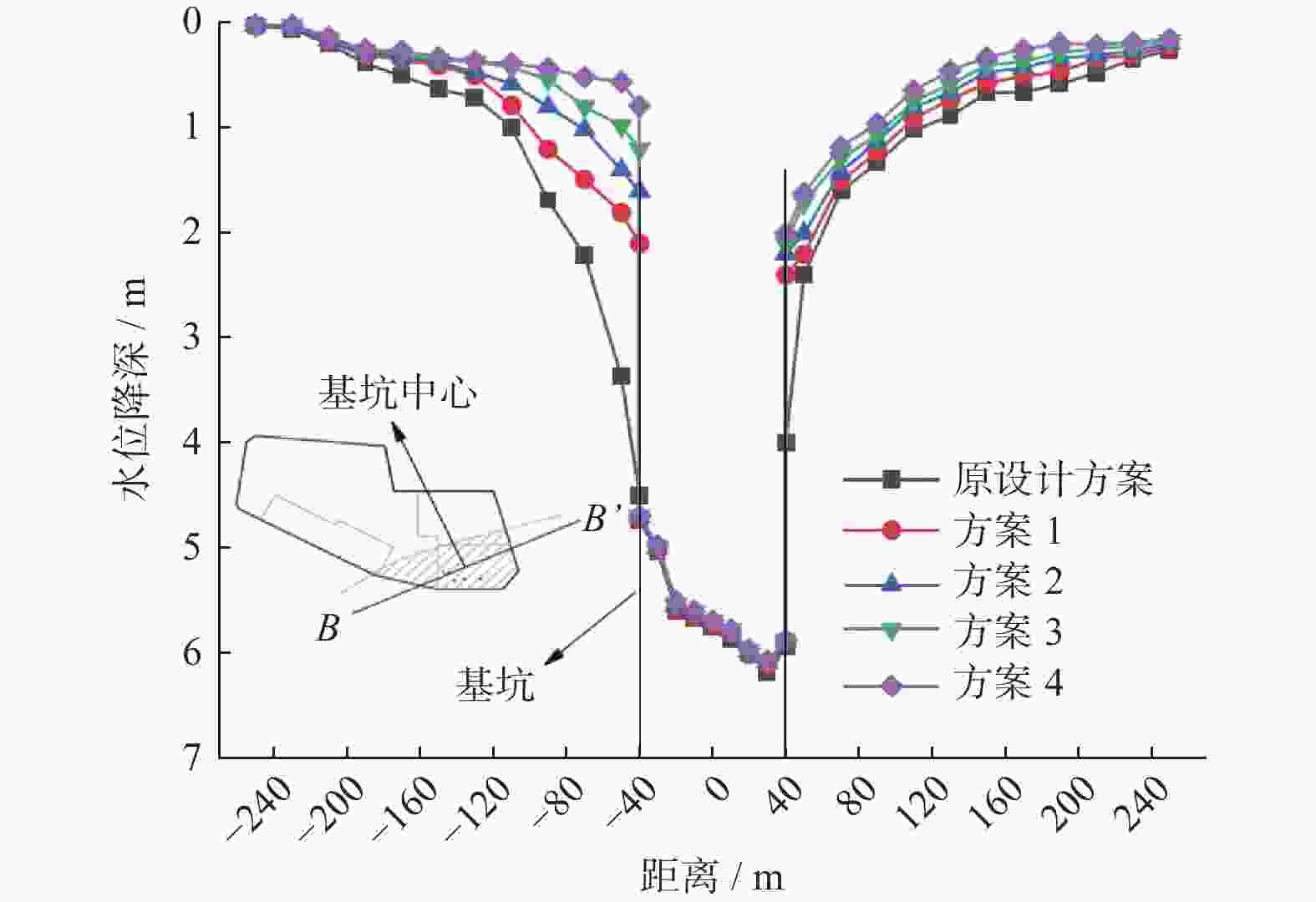
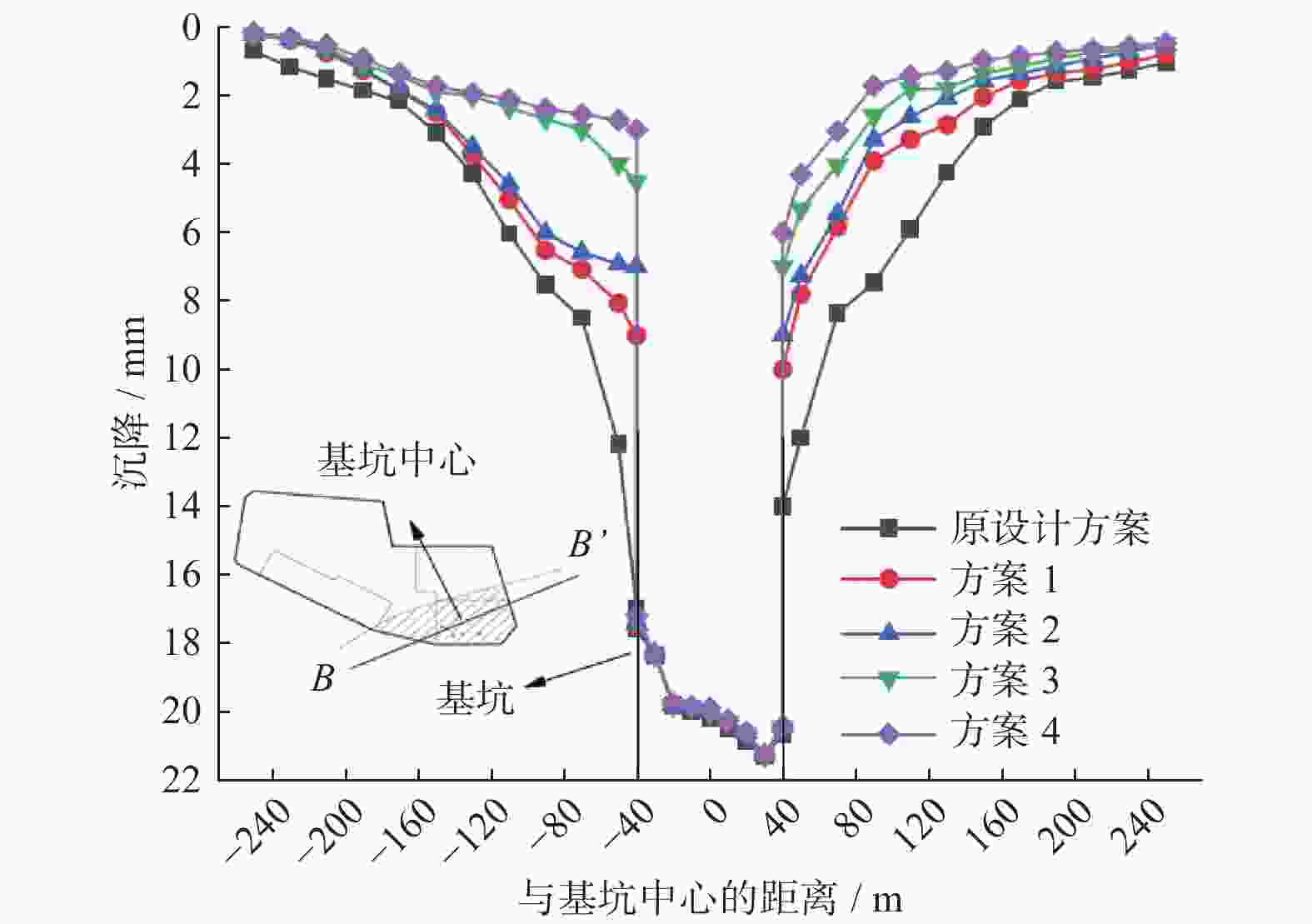
摘要: 针对复杂巨厚的承压含水层中的深基坑降水问题,以上海某基坑降水工程为依托,对基坑开挖前抽水试验的实测数据,采用数值模拟的方法进行反演验证,获得各含水层的水文地质参数,预测现有地下连续墙深度下基坑降水引起的坑外地表沉降。对比分析4种不同地下连续墙深度下基坑外水位降深及降水引起的地表沉降,结果表明:现有方案下地下连续墙深度下基坑降水引起的地表沉降较大;地下连续墙深度越大,降水引起的地表沉降越小;地下连续墙的深度大于抽水井的深度时,降水引起的地表沉降变化较小。综合考虑工程对环境影响及地下连续墙造价,得到最优化的地下连续墙深度为48.8 m。Abstract: Aiming at the dewatering of deep excavation pit in complex and thick confined aquifers, relied on an engineering case in Shanghai, the measured data of pumping test before excavation were verified by numerical simulation, the hydrogeological parameters of each aquifer were obtained through the inversion and verification of the measured data. The ground settlement caused by dewatering with the preliminary designed diaphragm wall was predicted by the verified model, and the comparison of groundwater drawdown and ground settlement under four different diaphragm wall depths was analyzed. The results indicate that ground settlement caused by pumping is large with the existed design of the diaphragm wall depths. The greater the depth of the diaphragm wall, the smaller the ground settlement caused by dewatering. When the diaphragm wall depth is greater than the pumping well depth, the variation of the ground settlement caused by dewatering is small. Considering the environmental effects and the diaphragm wall cost, the optimal depth determined is 48.8 m for the diaphragm wall.
-
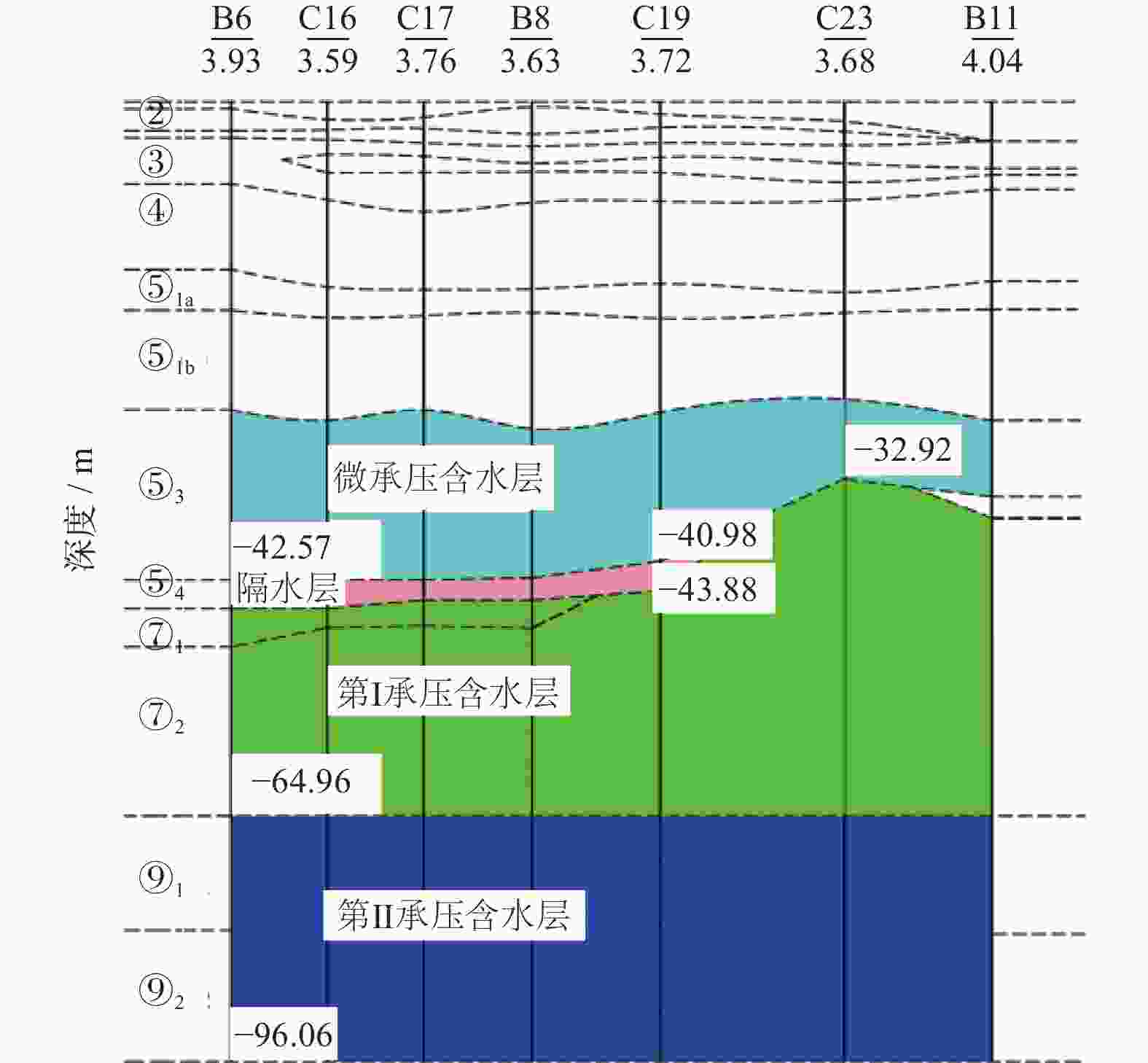
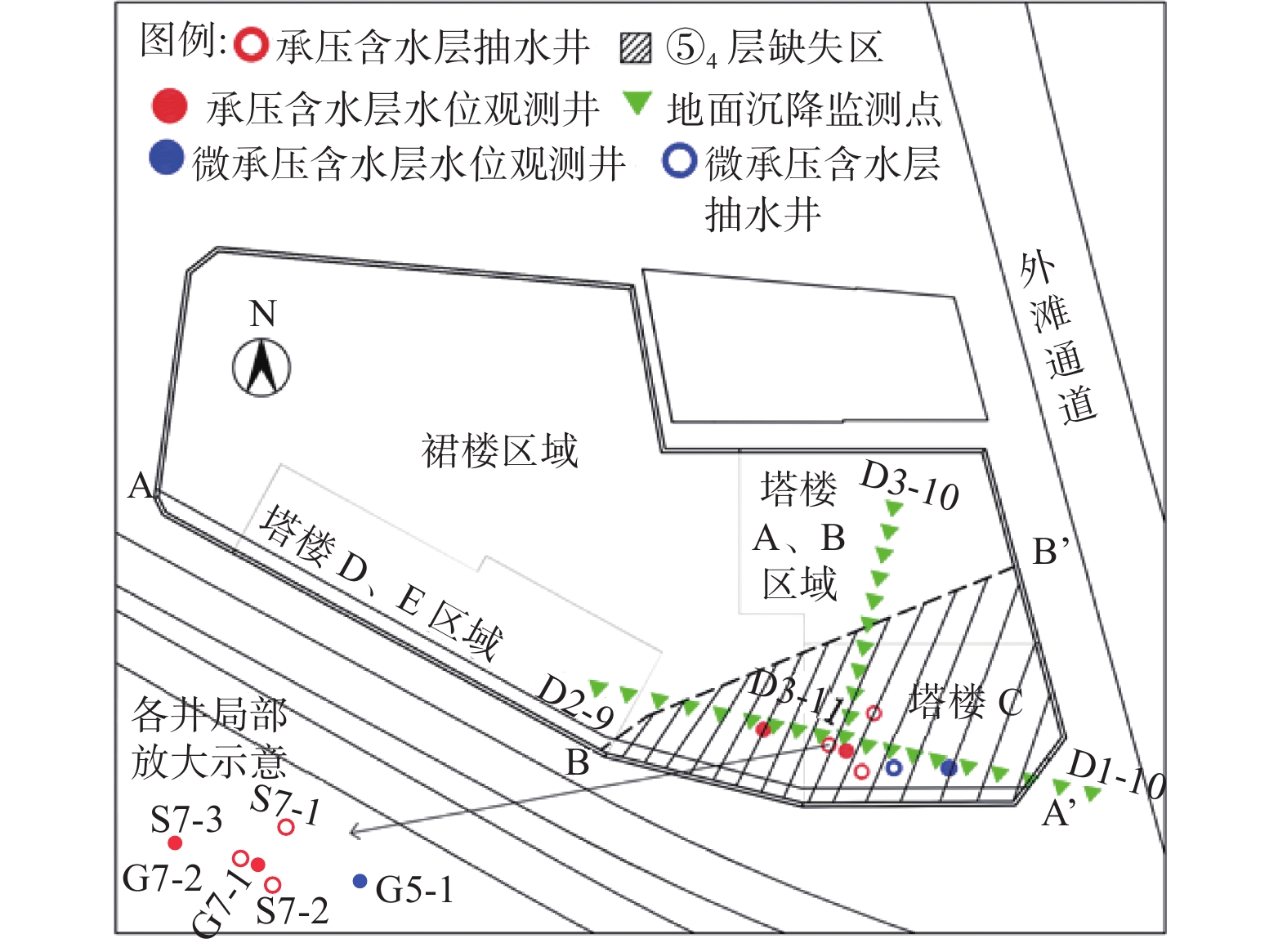
表 1 试验井结构
Table 1. Test well structure
类型 井号 井数 深度/m 孔径/m 管径/m 滤管埋深/m 抽水井 S7-1 ~ S7-3 3 50 650 273 39~49 观测井 G7-1 ~ G7-2G5-1 2
150
36650
650273
27339~49
30~35表 2 试验主要参数
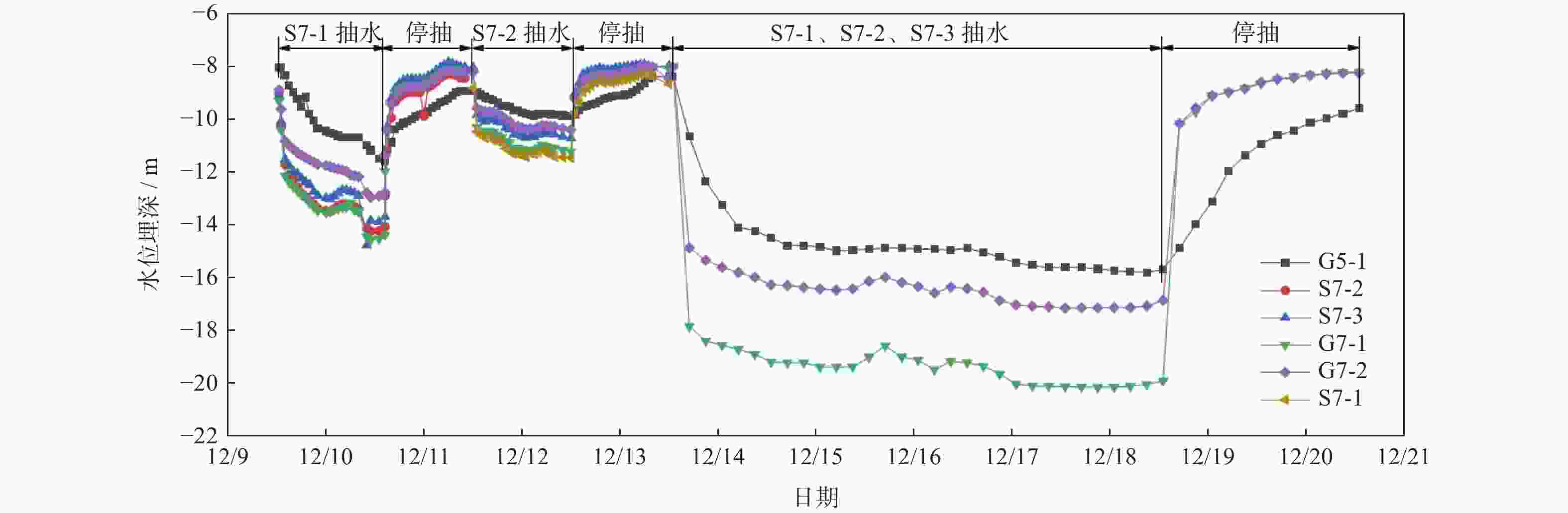
Table 2. Main parameters of field test
类别 抽水井 日期 抽水时间/d 恢复时间/d 平均流量/(m3·h−1) 单井抽水 S7-1
S7-220101209—20101210
20101211—201012121.083
10.895
1.04241.50
25.25群井抽水 S7-1
S7-2
S7-320201213—20101218 5 2 37.85
20.49
22.97 -
[1] 刘蓉, 赵勇, 王庆明, 等. 海河平原区浅层地下水位健康修复目标研究[J] . 水利学报,2022,53(9):1105 − 1115. [2] 刘祥勇, 宋享桦, 谭勇, 等. 南通富水砂性地层地铁深基坑抽水回灌现场试验研究[J] . 岩土工程学报,2020,42(7):1331 − 1340. [3] WU Y X, ZHENG Q, ZHOU A, et al. Numerical evaluation of the ground response induced by dewatering in a multi-aquifer system[J] . Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(5):101209. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2021.101209 [4] 袁斌, 武永霞, 廖少明, 等. 基于数值模拟的富水砂砾地层深基坑降水方案优化[J] . 工程勘察,2017,45(1):34 − 39. [5] 郁志伟, 张克胜, 孙志国, 等. 软土地区含承压水层深基坑抽降水设计及模拟分析[J] . 建筑结构,2023,53(S1):2946 − 2951. [6] 连正, 申玉生, 资晓鱼, 等. 圆砾地层深大基坑施工降水设计及应用研究[J] . 都市快轨交通,2021,34(2):104 − 110. [7] 骆祖江, 李兆, 任虎俊. 矿井涌水量预测数值模拟研究[J] . 煤炭科学技术,2015,43(1):33 − 36. -





 下载:
下载: