Wind power prediction method based on IWOA-ELM
-
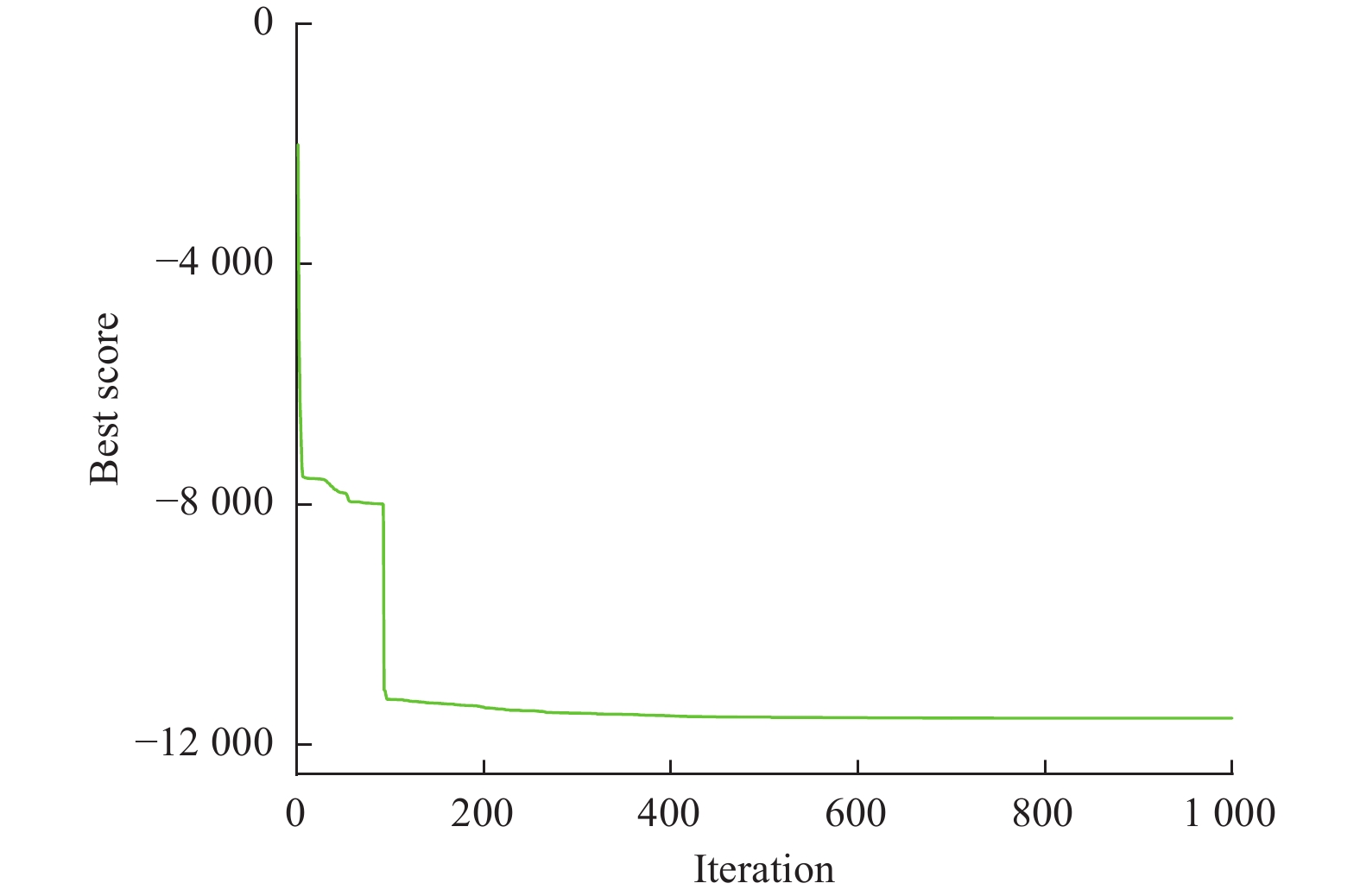
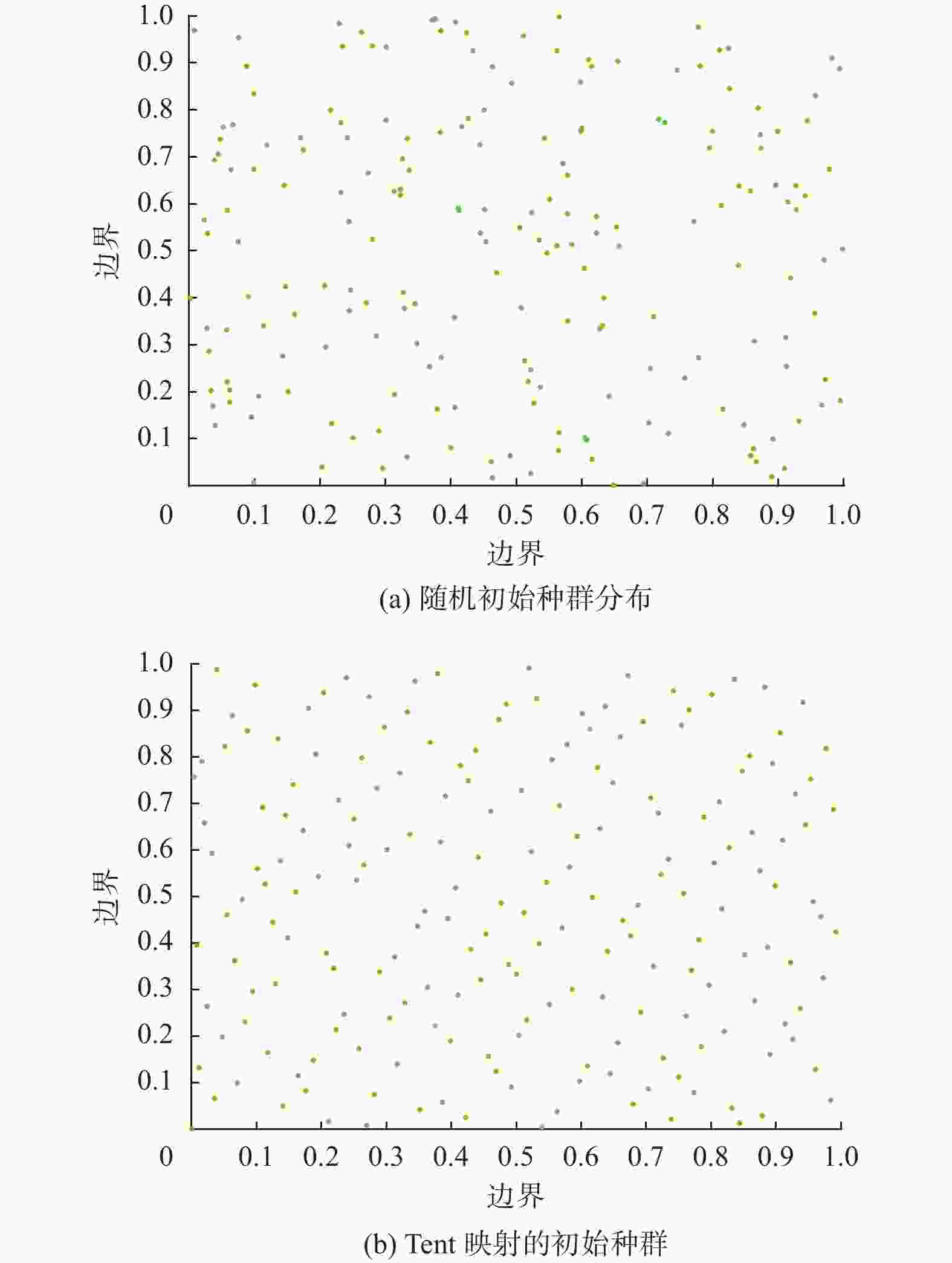
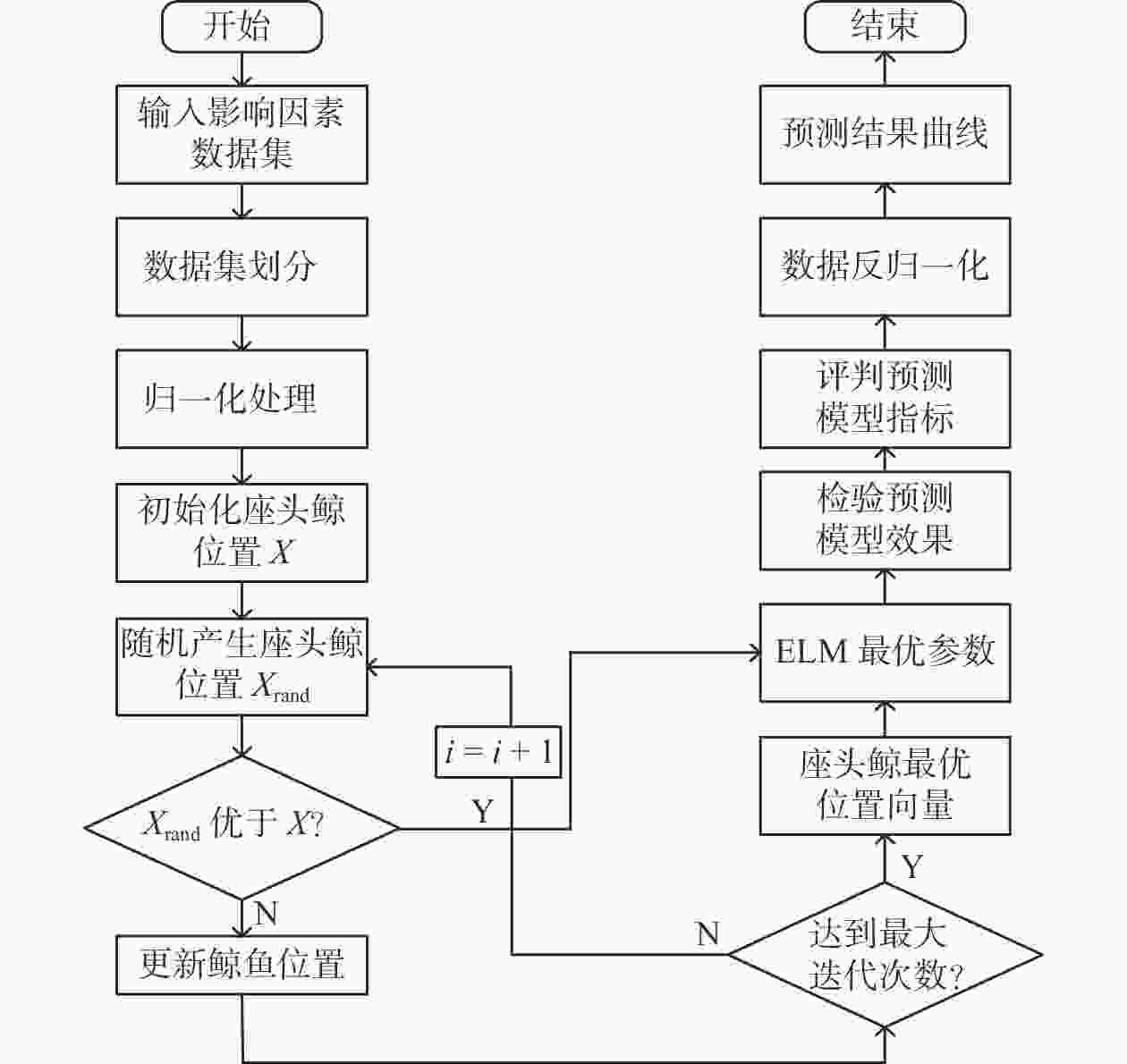
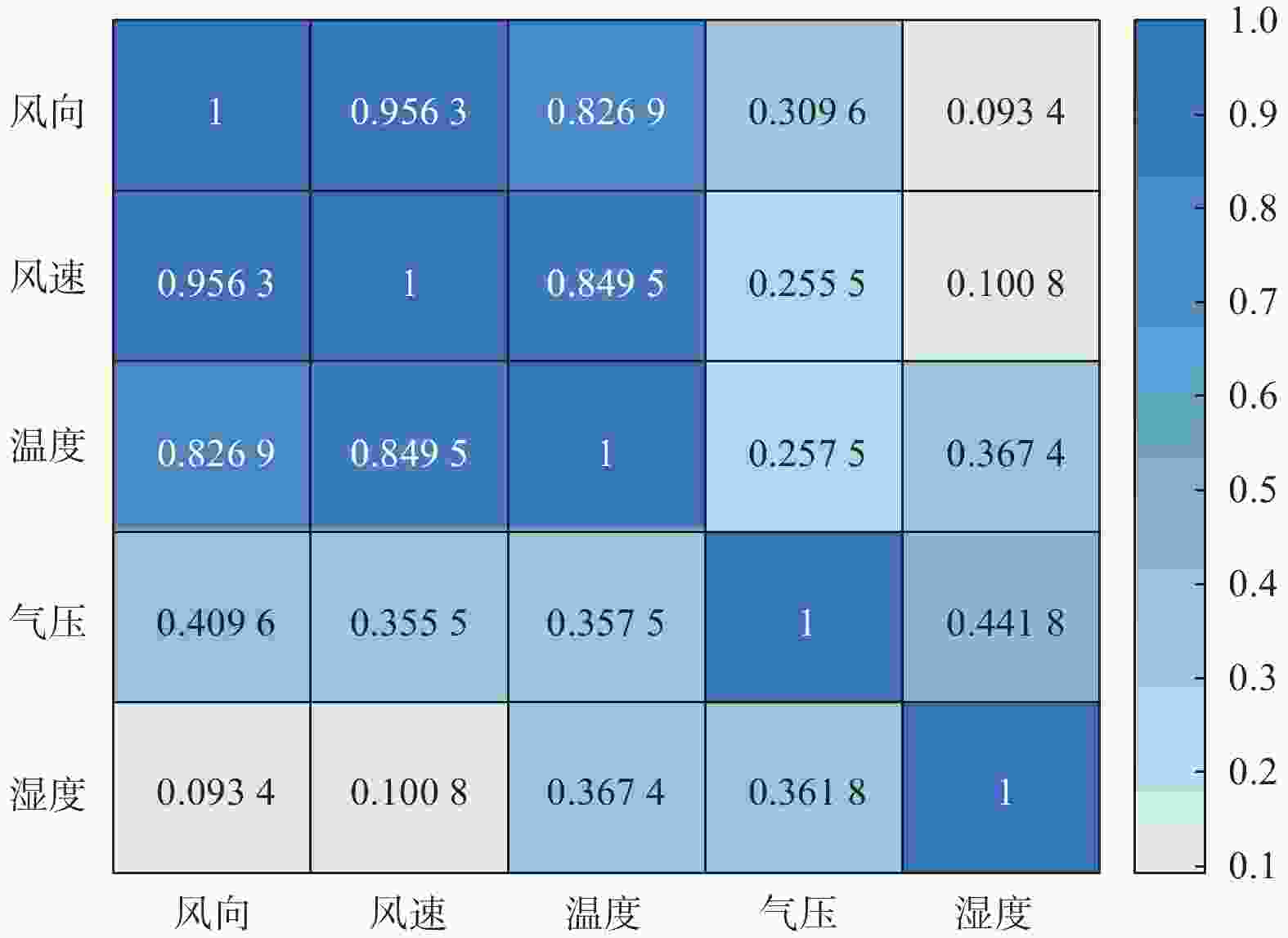
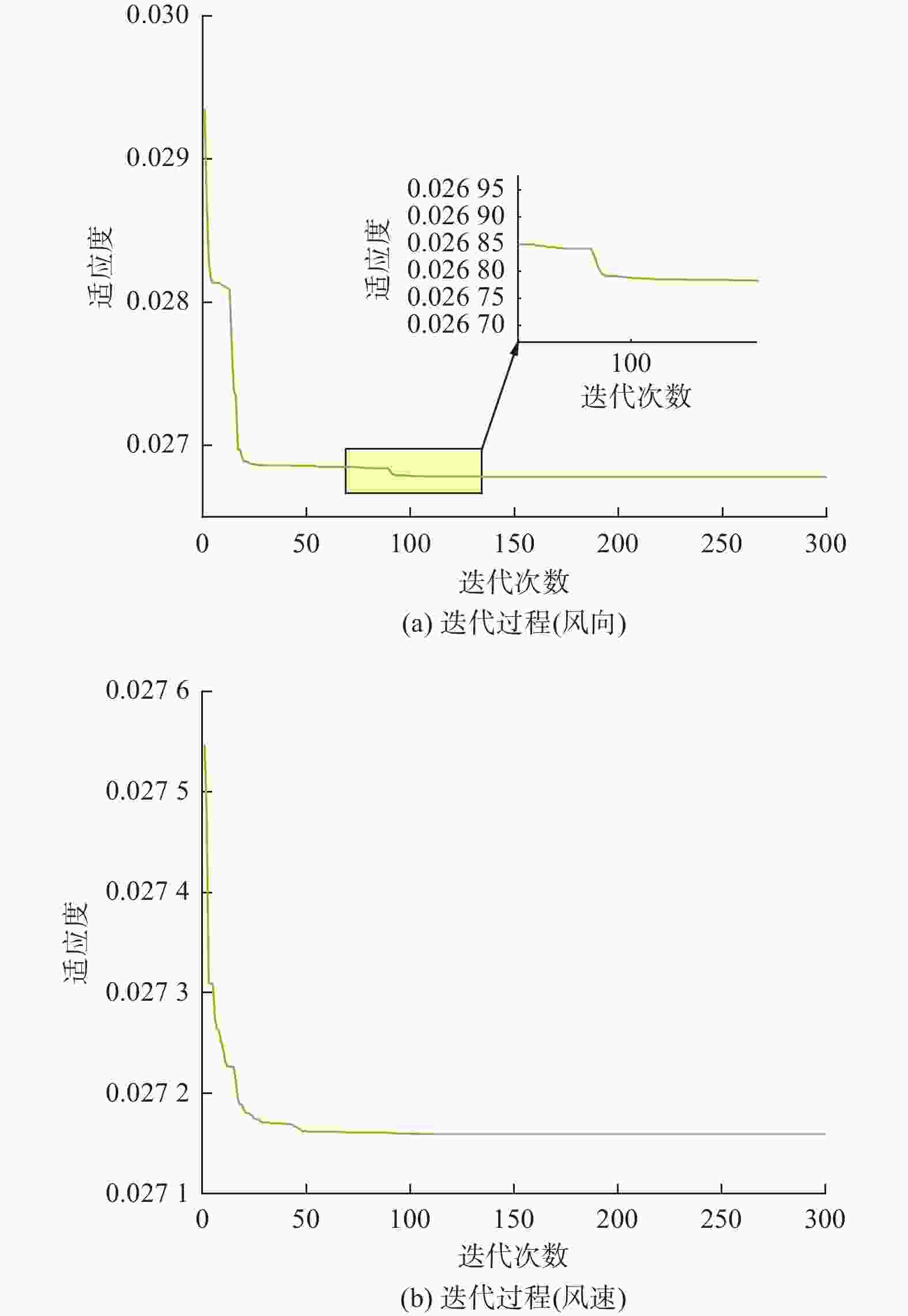
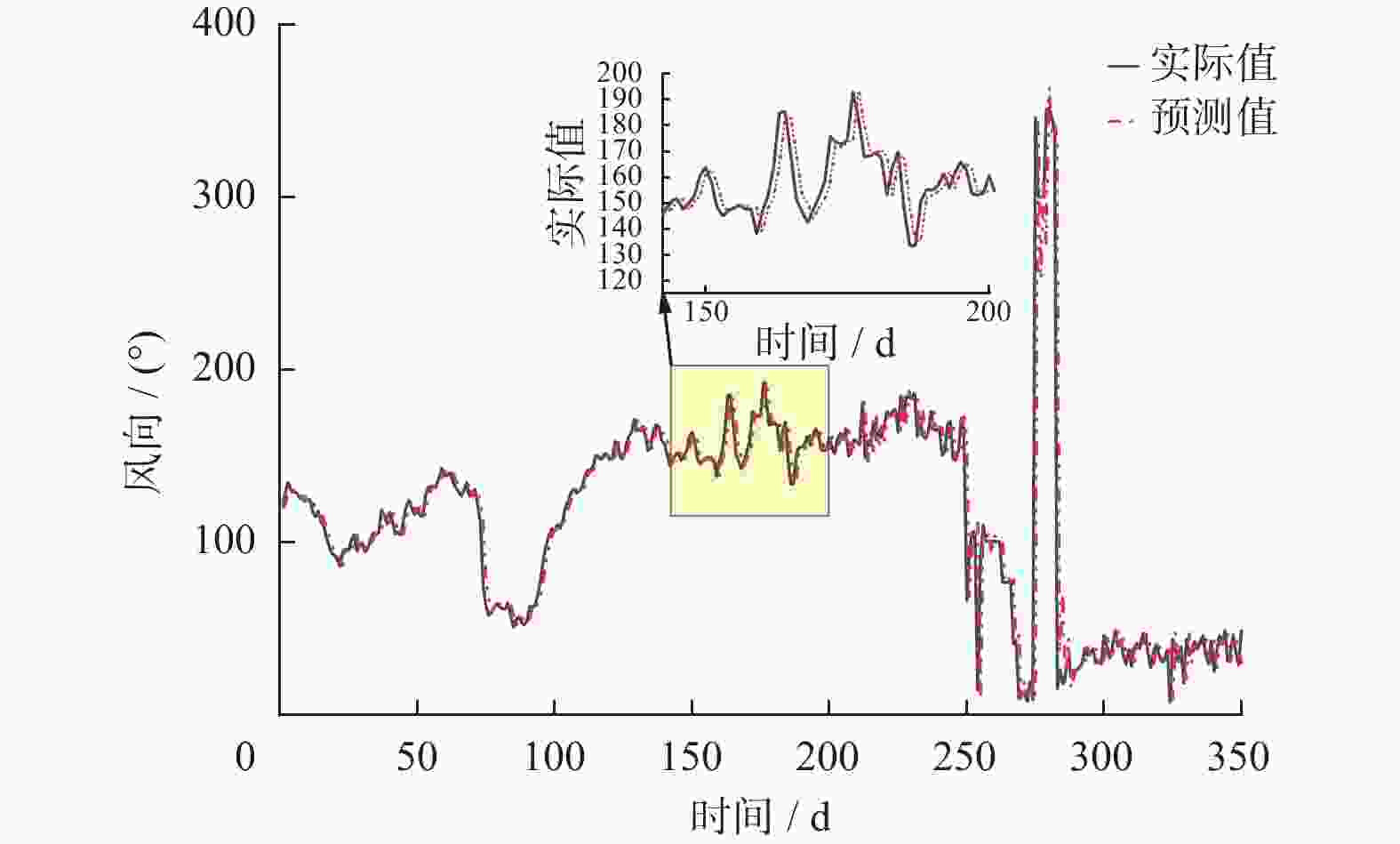
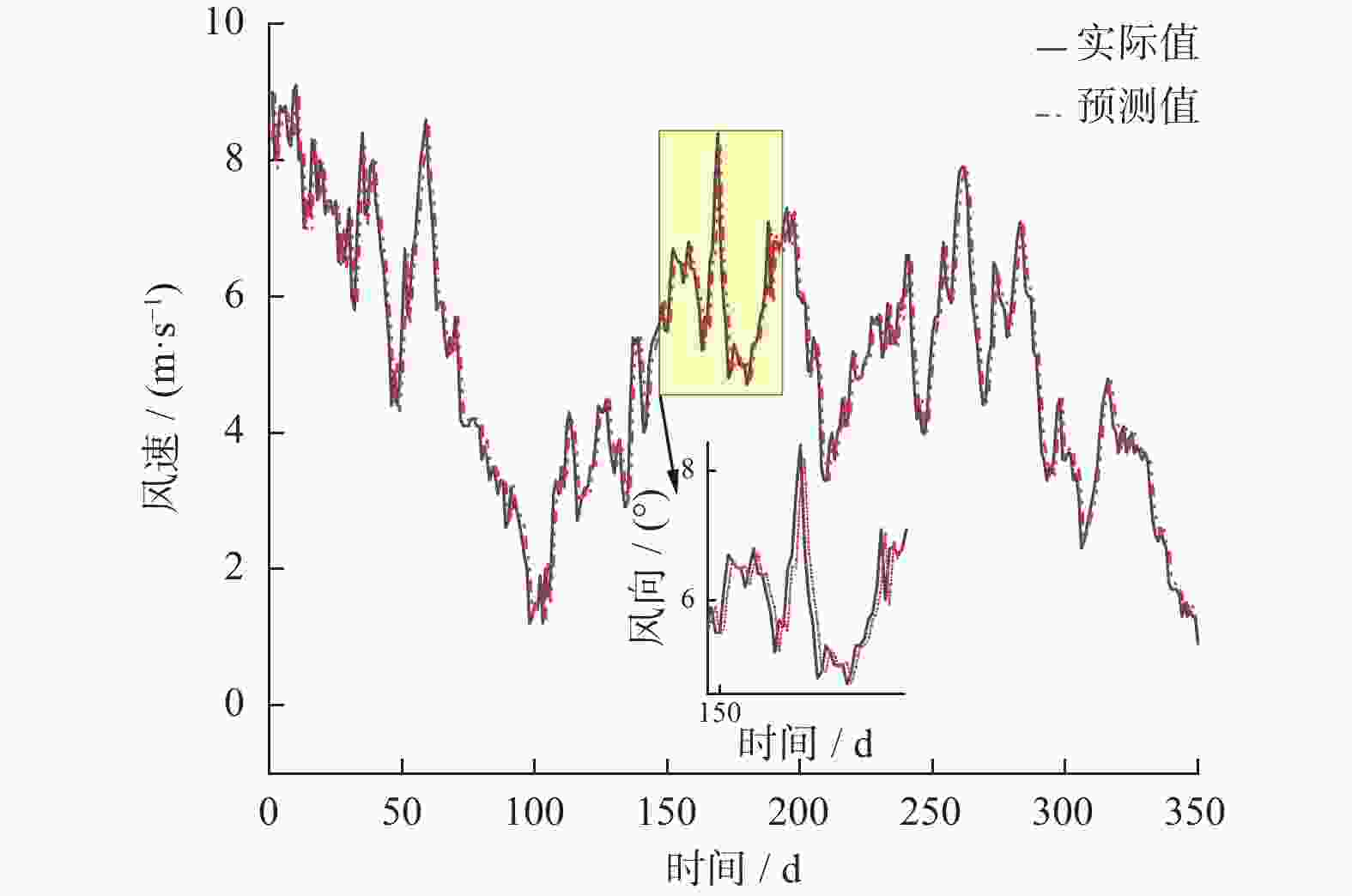
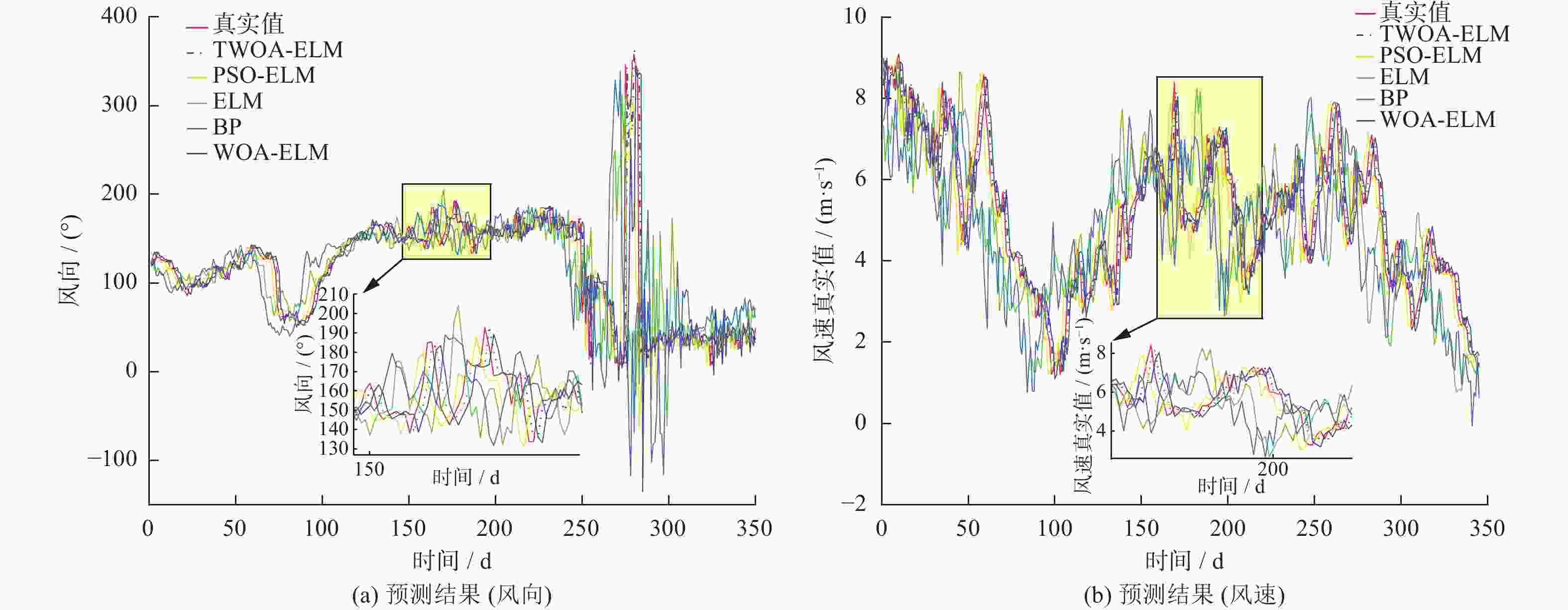
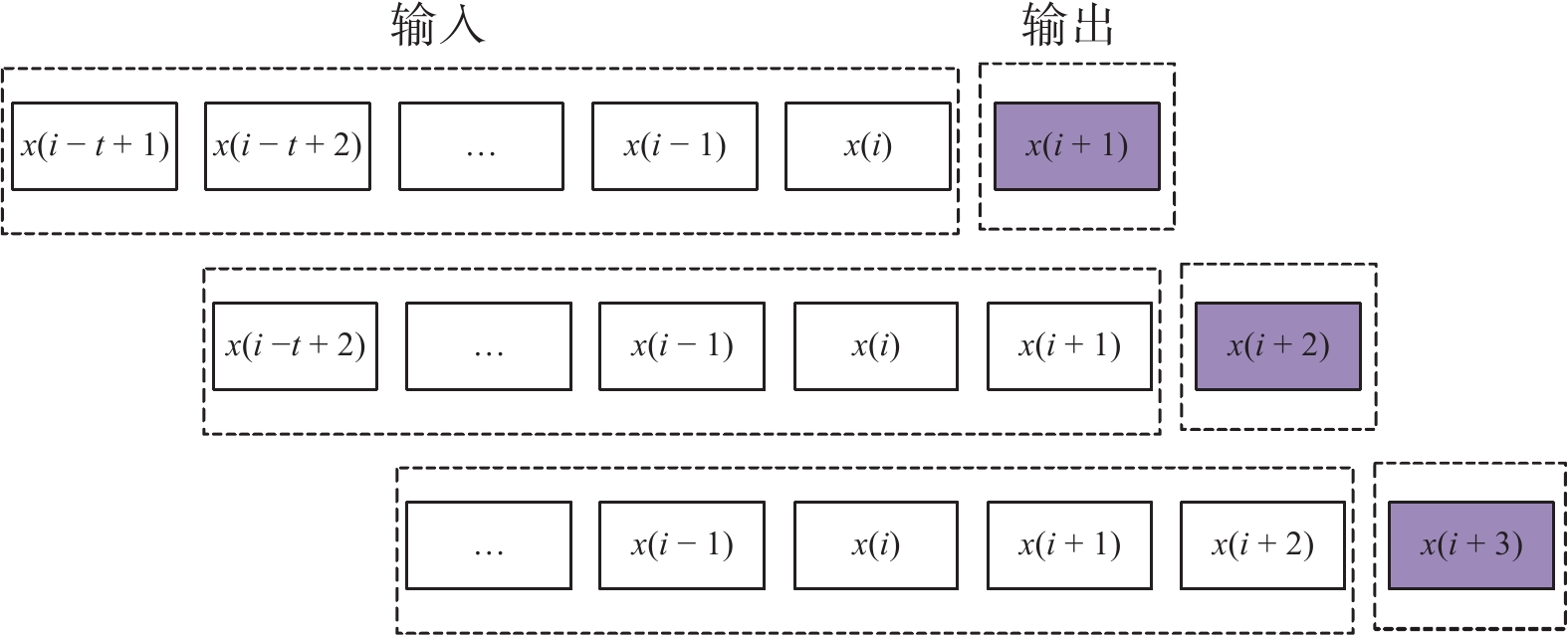
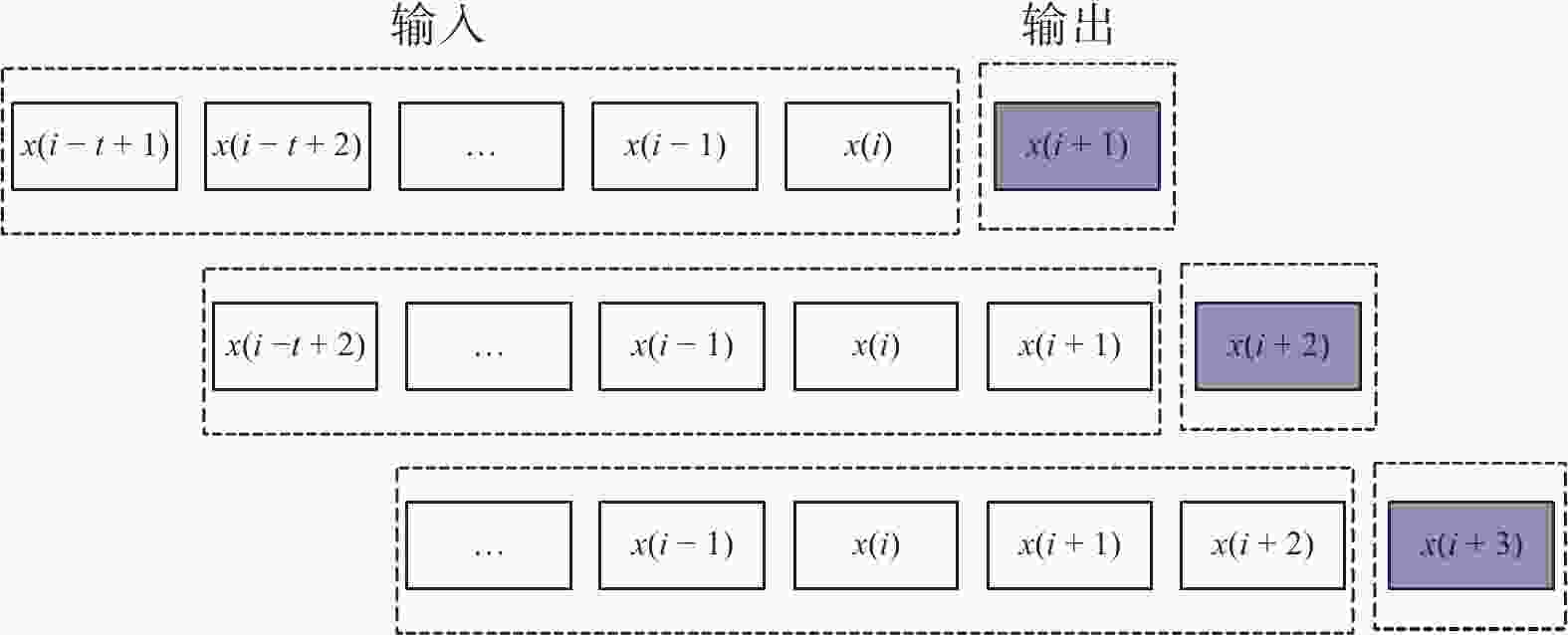
摘要: 在风力储能微电网中,提前精确地对风电场的实际输出功率进行预测,能够有效提高并网调节的稳定性。针对现有模型对风功率特征参量预测精度不高,提出一种基于IWOA-ELM(improved whale optimization algorithm of extreme learning machine, IWOA-ELM)的风功率特征参量预测方法。通过改进鲸鱼算法优化极限学习机的参数,建立基于时间序列的IWOA-ELM风功率特征参量预测模型,预测未来时刻风功率的特征参量;采用均方根误差、平均绝对误差等指标综合评估模型的预测性能。试验结果表明,提出的预测方法在风速上的均方根误差和平均绝对误差为5.488、3.72%,在风向上的均方根误差和平均绝对误差为19.354、12.46%。预测精度明显高于WOA-ELM、PSO-ELM、BP、ELM等风功率预测模型。Abstract: In wind energy storage microgrids, accurately predicting the actual output power of wind farms in advance can effectively improve the stability of grid integration regulation. To address the low prediction accuracy of existing models for wind power characteristic parameters, a wind power characteristic parameter prediction method based on improved whale optimization algorithm of extreme learning machine (IWOA-ELM) was proposed. By optimizing the parameters of the extreme learning machine using an improved whale optimization algorithm, a IWOA-ELM wind power characteristic parameter prediction model based on time series was established to predict the characteristic parameters of future wind power. Model performance was evaluated using metrics such as root mean square error and mean absolute error. Experimental results show that the proposed prediction method has a root mean square error of 5.488% and a mean absolute error of 3.72% for wind speed prediction, and a root mean square error of 19.354% and a mean absolute error of 12.46% for wind direction prediction. The prediction accuracy is significantly higher than that of other wind power prediction models such as WOA-ELM, PSO-ELM, BP, and ELM.
-
表 1 不同模型的误差指标对比
Table 1. Comparison of error indicators of different models
对比模型 风速 风向 RMSE MAPE/% R2 RMSE MAPE/% R2 BP 9.496 7.66 0.66 24.316 18.61 0.354 ELM 10.395 7.96 0.620 25.747 17.82 0.374 PSO-ELM 6.345 5.71 0.853 21.178 15.91 0.573 WOA-ELM 6.120 4.77 0.856 21.072 14.70 0.671 IWOA-ELM 5.488 3.72 0.893 19.354 12.46 0.732 -
[1] 吴慧军, 郭超雨, 苏承国, 等. 基于EEMD-GRU-MC的短期风功率组合预测方法[J] . 南方电网技术,2023,17(2):66 − 73. [2] 杨雷, 张宝峰, 朱均超, 等. 基于PCA-PSO-LSSVM的温室大棚温度预测方法[J] . 传感器与微系统,2018,37(7):52 − 55. [3] 程启明, 陈路, 程尹曼, 等. 基于EEMD和LS-SVM模型的风电功率短期预测方法[J] . 电力自动化设备,2018,38(5):27 − 35. [4] 曹天行, 刘三明, 王致杰, 等. 基于集合经验模态和深浅层学习组合的风电场功率短期预测研究[J] . 电测与仪表,2018,55(13):84 − 88. [5] 杨茂, 董骏城, 刘铁, 等. 两种基于自适应神经模糊推理系统的风功率预测方法[J] . 电测与仪表,2016,53(19):22 − 26. [6] 张景杨, 王维庆, 王海云, 等. 基于CEEMDAN-SAFA-LSSVM的短期风功率预测[J] . 计算机仿真,2021,38(8):134 − 138. [7] 胡健伟, 周玉良, 金菊良. BP神经网络洪水预报模型在洪水预报系统中的应用[J] . 水文,2015,35(1):20 − 25. [8] 孔俊, 李士进, 朱跃龙. 集成极限学习机的中小河流洪水预报方法研究[J] . 水文,2018,38(1):67 − 72. [9] 耿读艳, 赵杰, 王晨旭, 等. 基于归一化最小均方差联合集合经验模态分解的运动状态下心率提取算法研究[J] . 生物医学工程学杂志,2020,37(1):71 − 79. [10] 袁冬芳, 曹富军, 李德荣. 主成分分析结合极限学习机的高炉炉温预测模型[J] . 内蒙古科技大学学报,2017,36(4):327 − 332. [11] 刘栋, 魏霞, 王维庆, 等. 基于SSA-ELM的短期风电功率预测[J] . 智慧电力,2021,49(6):53 − 59, 123. [12] 陈真, 马细霞, 张晓蕾. 基于PCA和AHP的小流域山洪灾害风险评价[J] . 水电能源科学,2018,36(11):56 − 59. [13] 孟宪猛, 蔡翠翠. 基于改进鲸鱼优化算法的阵列单元失效校正[J] . 探测与控制学报,2020,42(6):72 − 76. [14] 王珂珂, 牛东晓, 甄皓, 等. 基于WOA-ELM模型的中国碳排放预测研究[J] . 生态经济,2020,36(8):20 − 27. [15] 韩永亮, 李胜, 杨宏伟, 等. 基于LMD-BA-ELM的边坡变形时序非线性预测模型研究[J] . 中国安全科学学报,2015,25(9):59 − 65. [16] 董东林, 陈昱吟, 倪林根, 等. 基于WOA-ELM算法的矿井突水水源快速判别模型[J] . 煤炭学报,2021,46(3):984 − 993. -





 下载:
下载: