Short-term wind prediction based on mRMR and SVMD-TPA-BiSTM
-
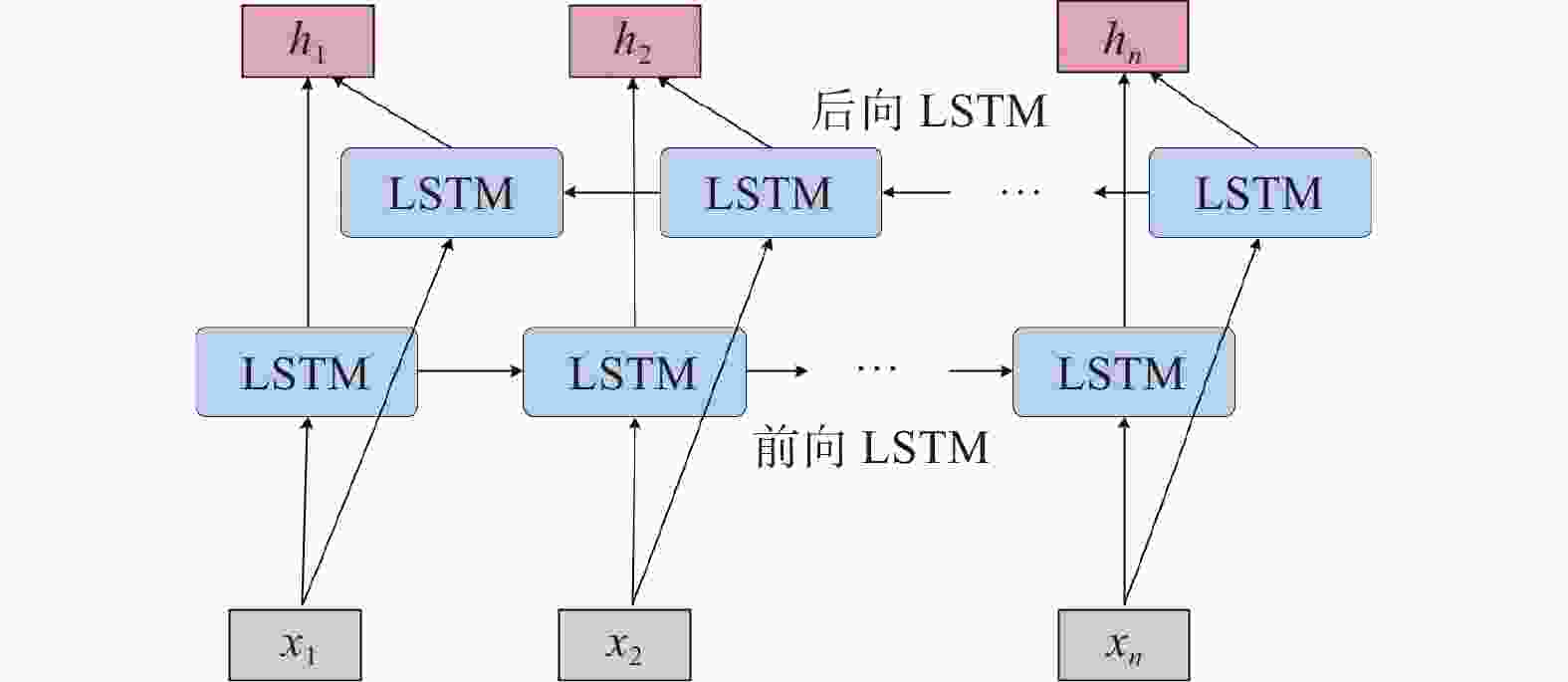
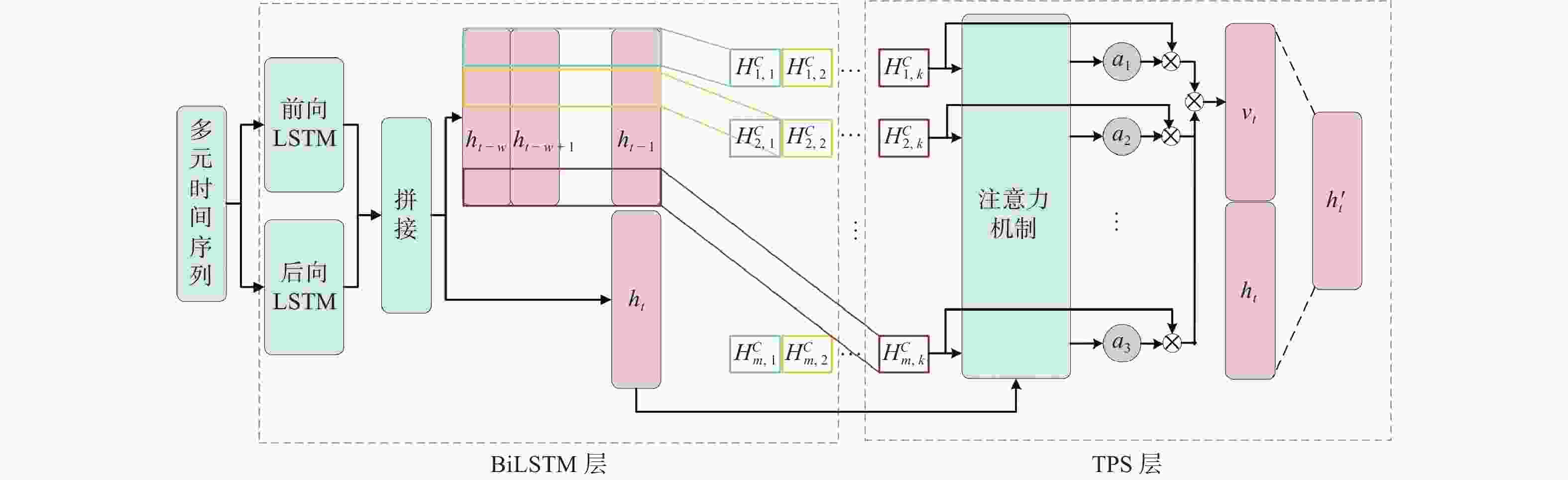
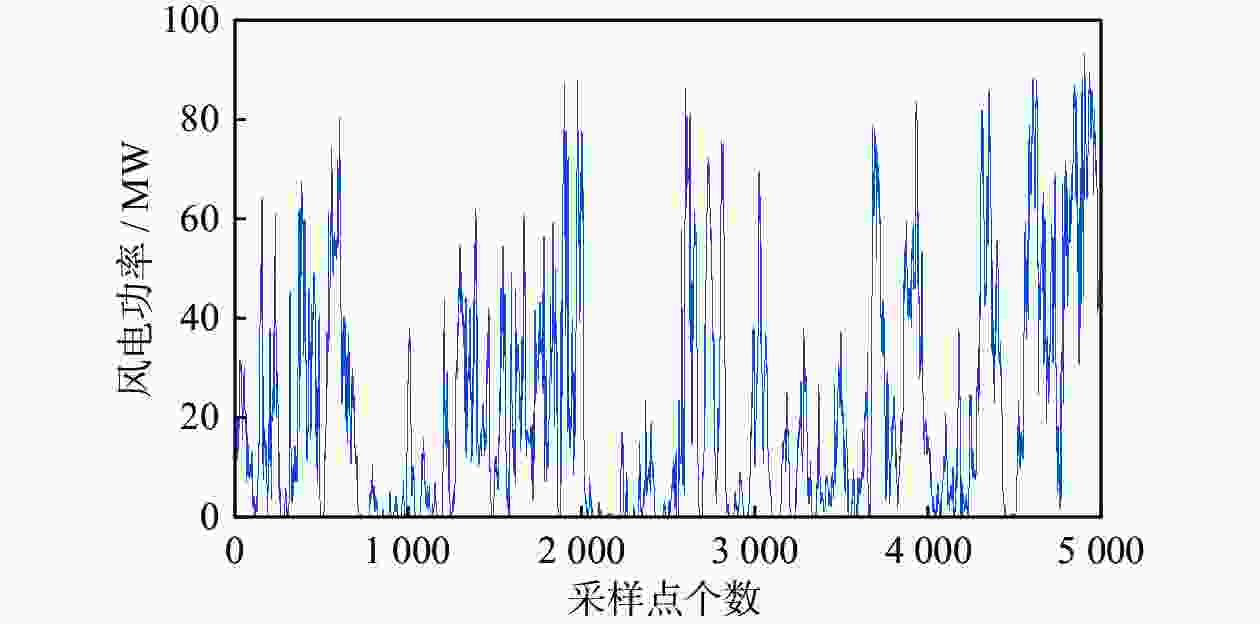
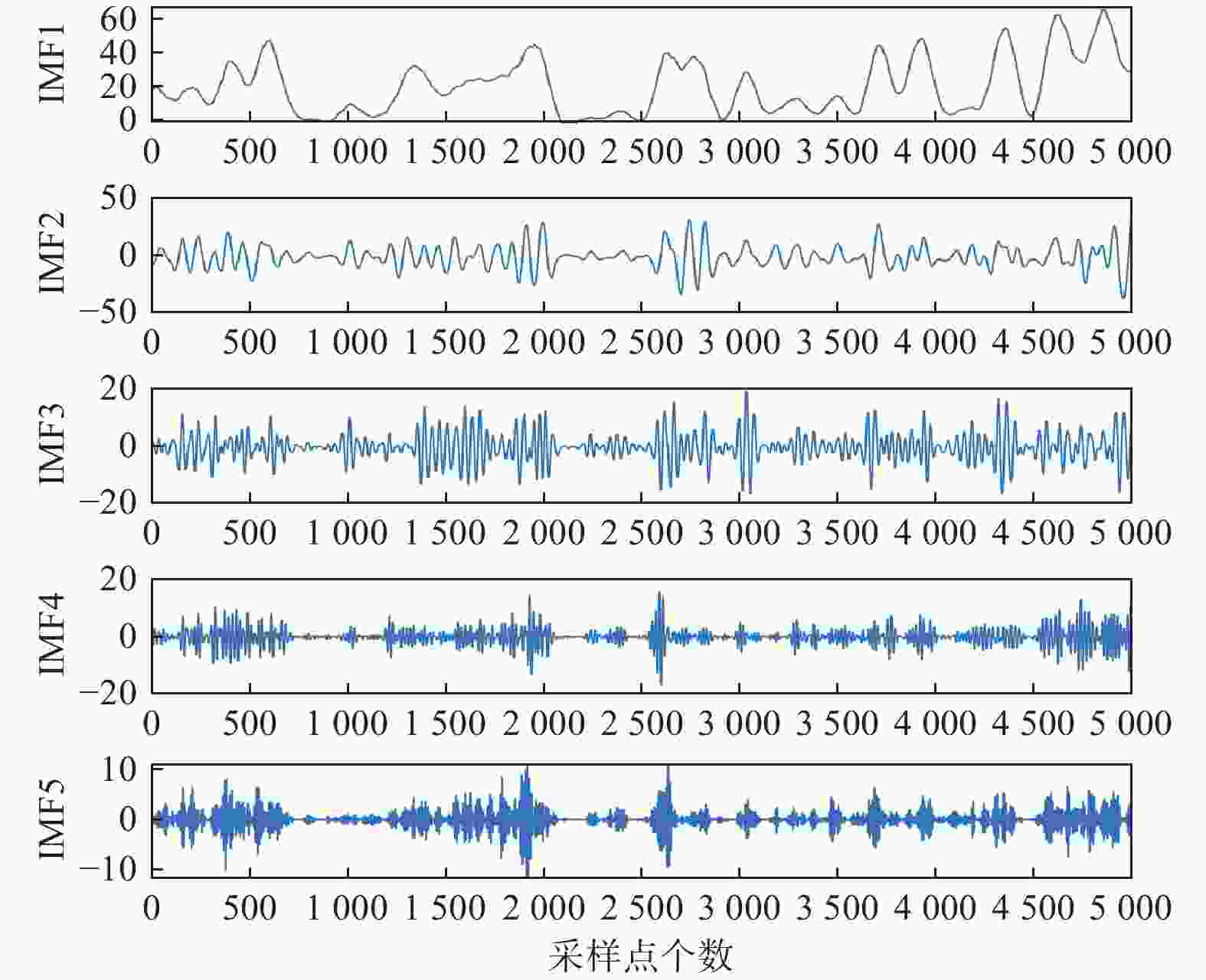
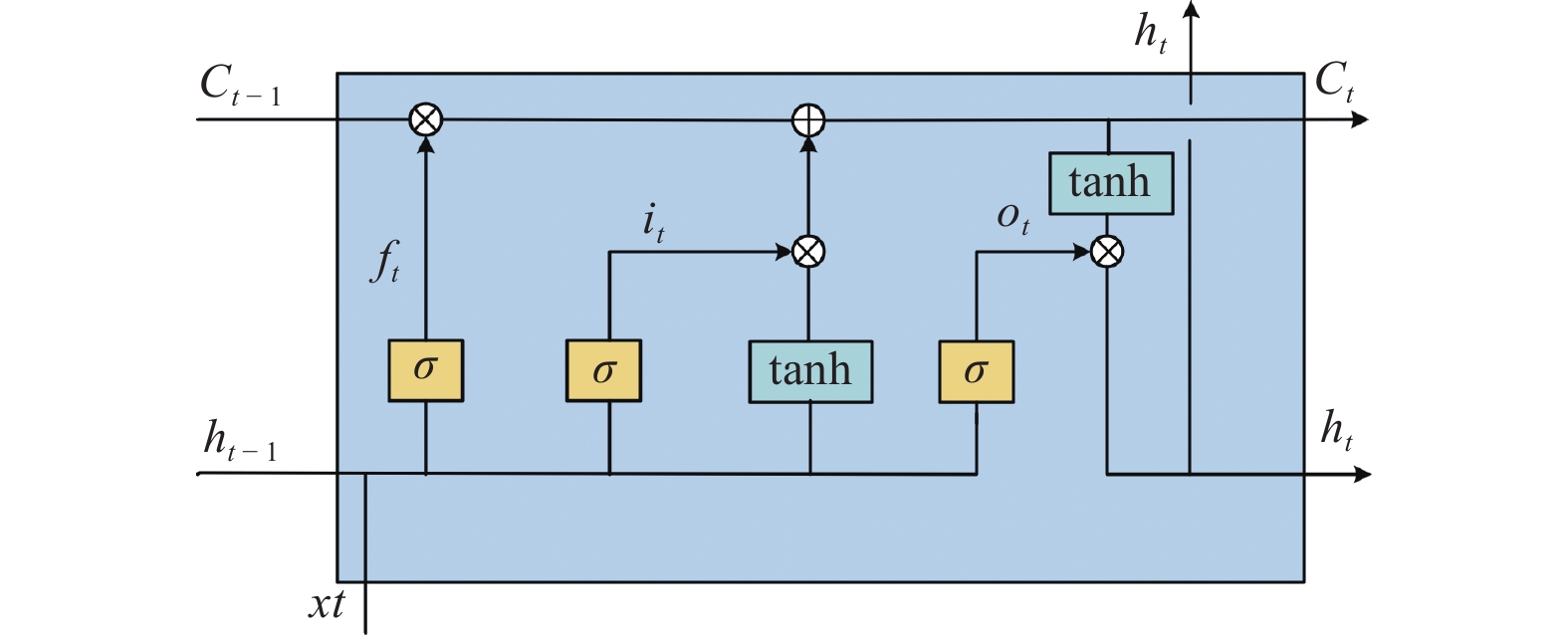
摘要: 提出一种基于mRMR和SVMD-TPA-BiLSTM的短期风电功率预测方法。首先,通过逐次变分模态分解(SVMD)对风电功率序列进行降维处理,得到风电功率子序列,与最大相关−最小冗余(mRMR)筛选出的关键气象特征数据结合构成训练集。其次,建立基于时间模式注意力机制(TPA)改进双向长短时记忆(BiLSTM)神经网络的组合模型,利用TPA机制抓取不同时序数据的关联性。最后,将预测分量结果叠加得到最终预测结果。以某风电场的数据集为例,对不同模型进行单步和多步预测试验对比精度,试验表明预测方法能有效刻画风电的分量特性,提高风电功率预测的准确率。
-
关键词:
- 短期风电功率预测 /
- 气象特征筛选 /
- 逐次变分模态分解 /
- 时间模式注意力机制 /
- 双向长短时记忆神经网络
Abstract: A short-term wind power prediction method based on mRMR and SVMD-TPA-BiLSTM was proposed. Firstly, successive variational modal decomposition (SVMD) was adopted to reduce the dimensionality of wind power sequences, and the decomposed subsequences were combined with the key meteorological feature data selected maximum correlation minimum redundancy (mRMR) to form a training set. Secondly, a combined model based on the temporal pattern attention (TPA) mechanism to improve the Bi-directional long short-term memory neural network (BiLSTM) was established, and TPA mechanism was used to capture the correlation of different time sequence data. Finally, the prediction component results were superimposed to obtain the final prediction results. Taking the dataset of a certain wind farm as an example, different models were subjected to single step and multi-step prediction experiments to compare the accuracy, and it was proved that the prediction method can effectively portray the component characteristics of wind power and improve the prediction accuracy of wind power. -
表 1 气象特征名称及含义
Table 1. Name and meaning of meteorological features
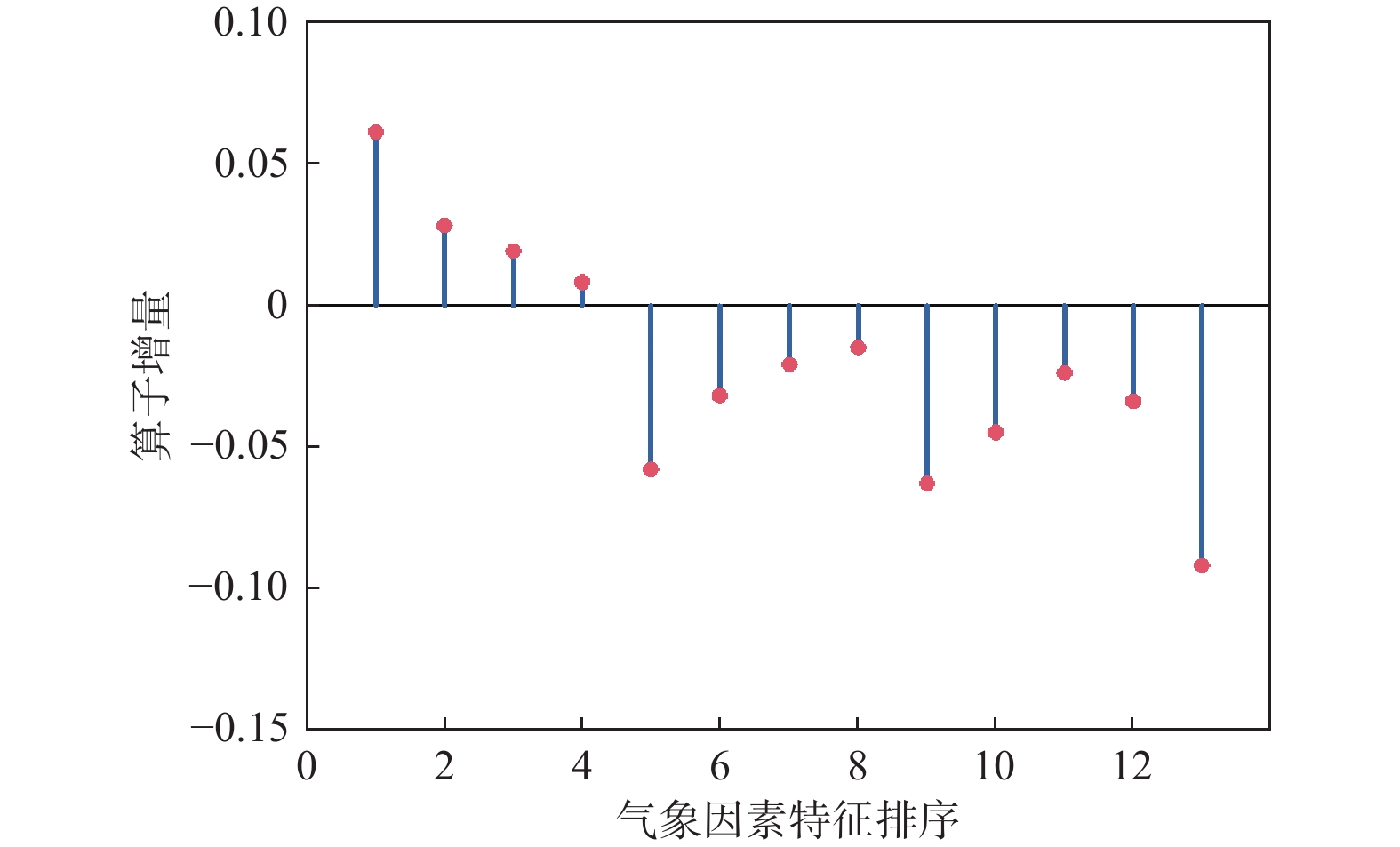
序号 名称 含义 1~4 $ v_{70}、v_{50}、v_{30}、v_{10} $ 70、50、30、10 m高风向 5~8 $ D_{70}、D_{50}、D_{30}、D_{10} $ 70、50、30、10 m高风向 9 $ P $ 气压 10 $ R_{{\mathrm{h}}} $ 相对湿度 11 $ c_{{\mathrm{f}}} $ 云量百分比 12 $ T $ 温度 13 $ P_{n} $ 降水量 表 2 多步预测试验结果
Table 2. Multi-step prediction of experimental results
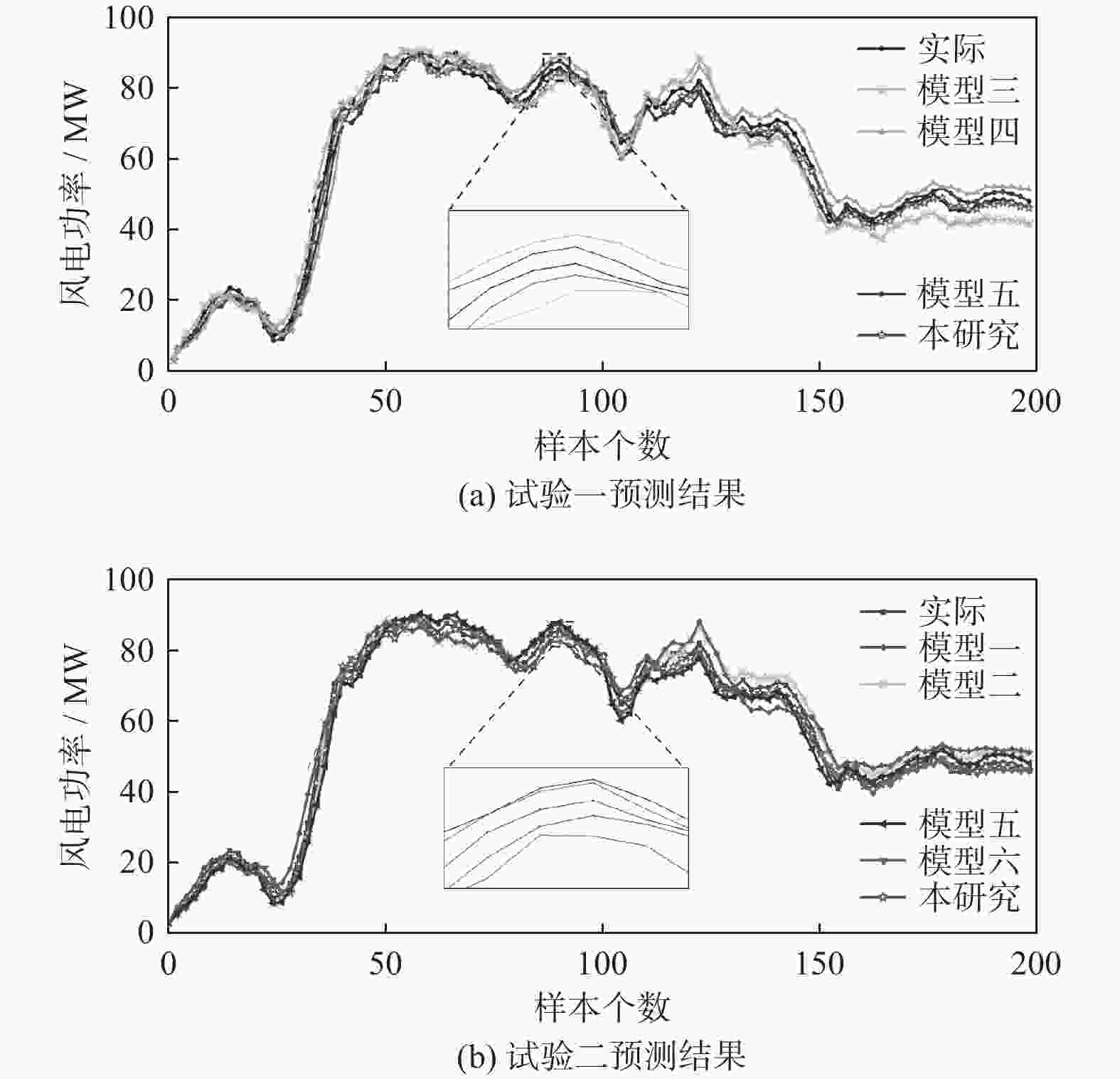
模型 MAPE/% RMSE/MW 1步 2步 3步 1步 2步 3步 SVMD-LSTM(模型一) 4.127 4.587 5.436 4.541 4.952 6.014 SVMD-BiLSTM(模型二) 3.645 4.142 4.923 4.169 4.582 5.473 TPA-BiLSTM(模型三) 3.854 4.451 5.257 4.327 4.971 5.842 EMD-TPA-BiLSTM(模型四) 3.113 3.667 4.261 3.586 4.125 4.782 SVMD-TPA-BiLSTM(模型五) 2.542 3.176 3.717 2.946 3.481 4.259 mRMR-SVMD-AM-BiLSTM(模型六) 2.254 2.698 3.191 2.665 3.146 3.629 mRMR-SVMD-TPA-BiLSTM(本研究) 1.947 2.405 2.884 2.378 2.854 3.321 -
[1] GANG ZHANG, BENBEN XU, HONGCHI LIU, et al. Wind power prediction based on variational mode decomposition and feature selection[J] . Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy,2021,9(6):1520 − 1529. doi: 10.35833/MPCE.2020.000205 [2] 黄玲玲, 符杨, 任浩瀚, 等. 基于状态信息的风电机组维护研究综述[J] . 中国电机工程学报,2020,40(21):7065 − 7078. [3] 王依宁, 解大, 王西田, 等. 基于PCA- LSTM模型的风电机网相互作用预测[J] . 中国电机工程学报,2019,39(14):4070 − 4081. [4] 符杨, 郑紫宸, 时帅, 等. 考虑气象相似性与数值天气预报修正的海上风功率预测[J] . 电网技术,2019,43(4):1253 − 1260. [5] WANG JIANZHOU, SONG YILIAO, LIU FENG, et al. Analysis and application of forecasting models in wind power integration: a review of multi-step-ahead wind speed forecasting models[J] . Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 60:960 − 981. [6] 赵腾, 王林童, 张焰, 等. 采用互信息与随机森林算法的用户用电关联因素辨识及用电量预测方法[J] . 中国电机工程学报,2016,36(3):604 − 614. [7] 李燕青, 袁燕舞, 郭通. 基于AMD-ICSA-SVM的超短期风电功率组合预测[J] . 电力系统保护与控制,2017,45(14):113 − 120. doi: 10.7667/PSPC161082 [8] 田壁源, 刘琪, 张新燕, 等. 基于APSO-GSA和相关向量机的短期风电功率预测[J] . 电力系统保护与控制,2020,48(2):107 − 114. [9] 史加荣, 赵丹梦, 王琳华, 等. 基于RR-VMD-LSTM的短期风电功率预测[J] . 电力系统保护与控制,2021,49(21):63 − 70. [10] 张淑清, 李君, 姜安琦, 等. 基于FPA-VMD和BiLSTM神经网络的新型两阶段短期电力负荷预测[J] . 电网技术,2022,46(8):3269 − 3279. [11] 任建吉, 位慧慧, 邹卓霖, 等. 基于CNN-BiLSTM-Attention的超短期电力负荷预测[J] . 电力系统保护与控制,2022,50(8):108 − 116. [12] 杨晶显, 张帅, 刘继春, 等. 基于VMD和双重注意力机制LSTM的短期光伏功率预测[J] . 电力系统自动化,2021,45(3):174 − 182 . [13] GANG ZHANG, HONGCHI LIU, JIANGBIN ZHANG, et al. Wind power prediction based on variational mode decomposition multi-frequency combinations[J] . Journal of Modern Power Systems and Clean Energy,2019,7(2):281 − 288. doi: 10.1007/s40565-018-0471-8 [14] 商立群, 李洪波, 侯亚东, 等. 基于VMD-ISSA-KELM的短期光伏发电功率预测[J] . 电力系统保护与控制,2022,50(1):138 − 148. [15] 范磊, 卫志农, 李慧杰, 等. 基于变分模态分解和蝙蝠算法-相关向量机的短期风速区间预测[J] . 电力自动化设备,2017,37(1):93 − 100. [16] 吴浩天, 孙荣富, 廖思阳, 等. 基于改进气象聚类分型的短期风电功率概率预测方法[J] . 电力系统自动化,2022,46(15):56 − 65. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20210914003 [17] 白冰青, 刘江涛, 王旭, 等. 基于MRMR和双重注意力机制的城市能源多元负荷短期预测[J] . 电力系统自动化,2022,46(17):44 − 55. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20211209006 [18] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. LSTM can solve hard long time lag problems[J] . Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,1997,9:473 − 479. [19] SIAMI-NAMINI S, TAVAKOLI N, NAMIN A. A comparative analysis of forecasting financial time series using ARIMA, LSTM, and BILSTM[EB/OL] . (2019-11-21) [2021-07-23] . https://export.arxiv.org/pdf/1911.09512v1.pdf -





 下载:
下载: