Offline reinforcement learning dynamic obstacles avoidance navigation algorithm
-
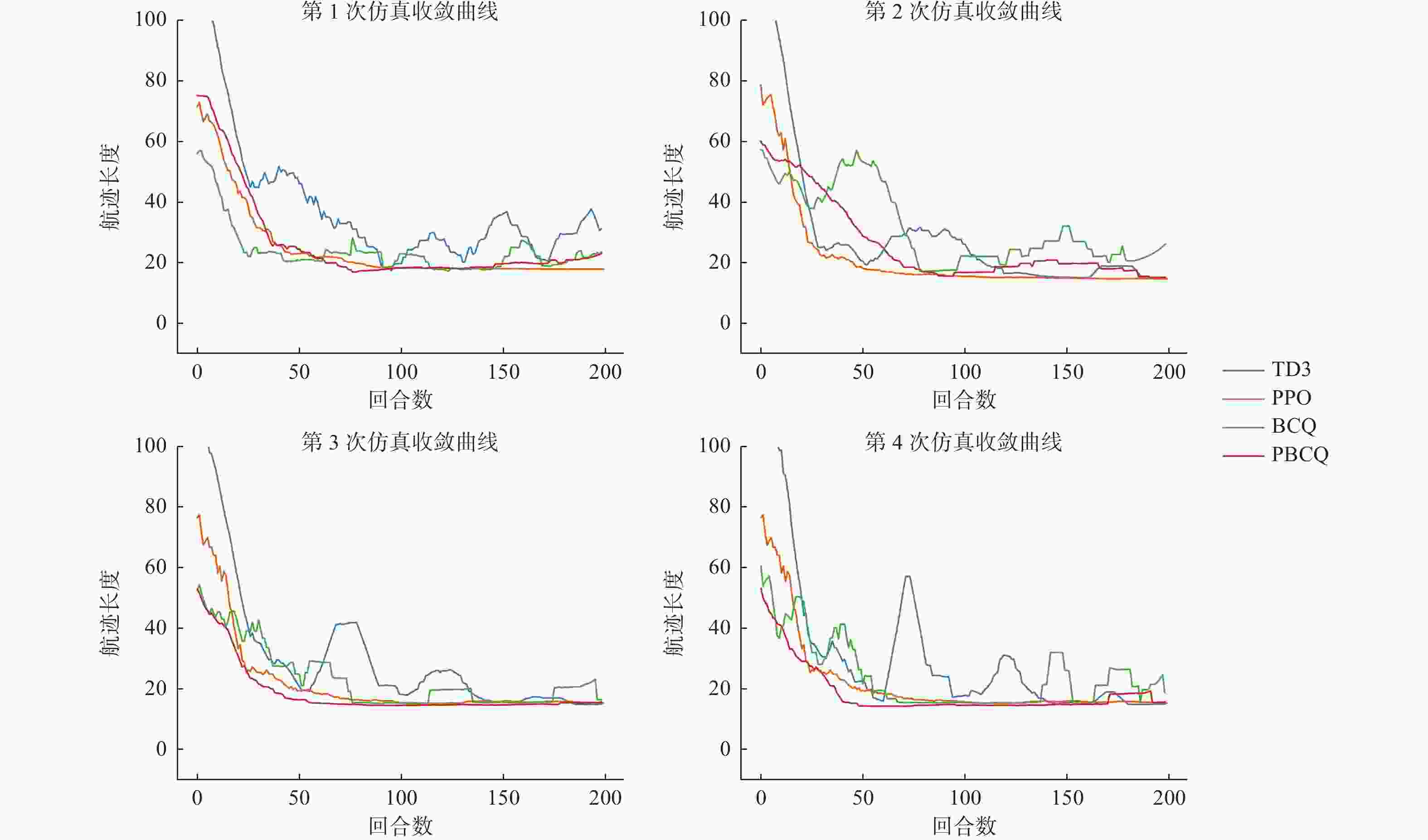
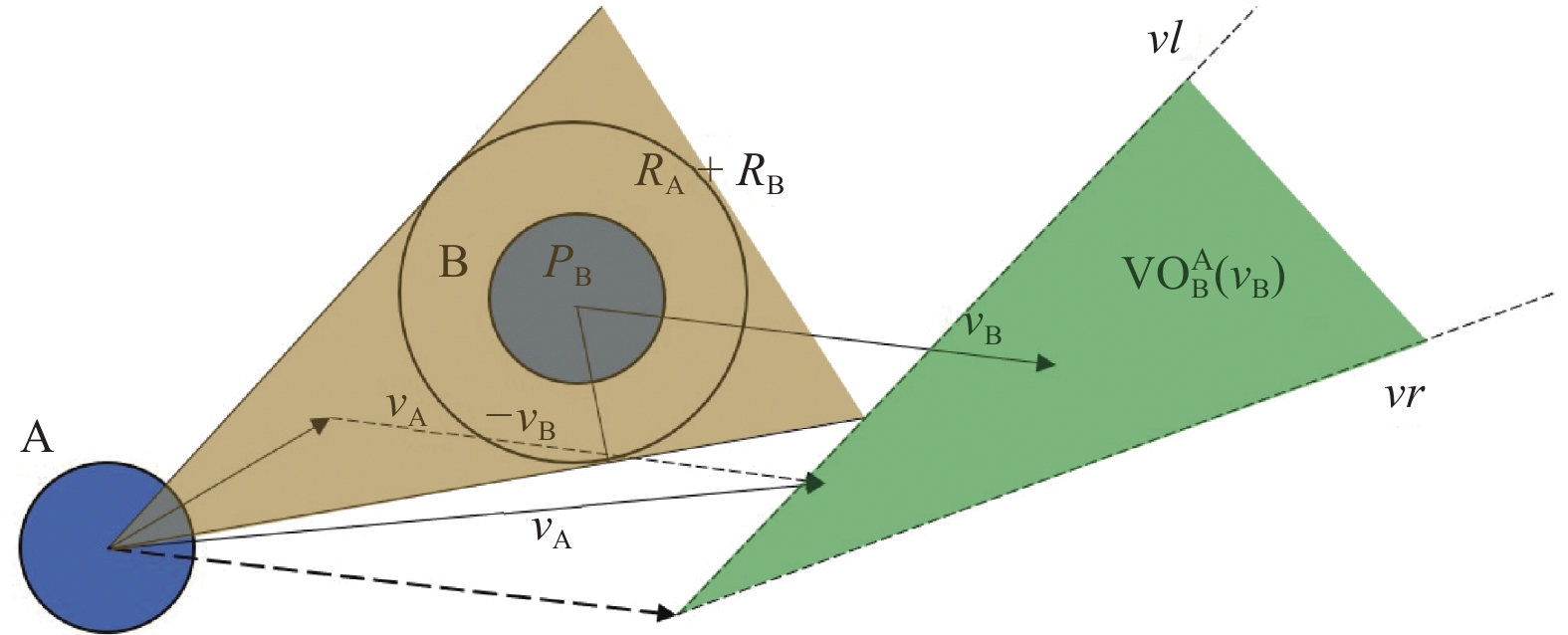
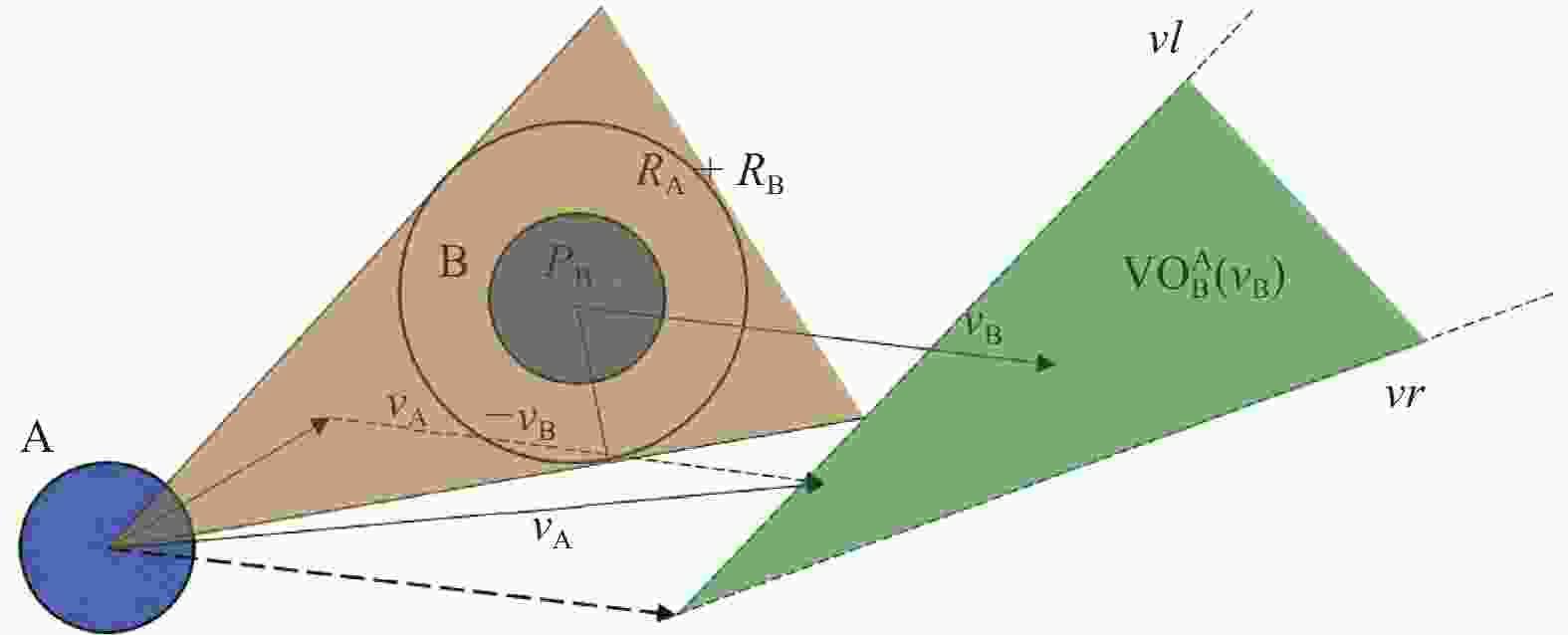
摘要: 需要实时采样更新数据供无人机(unmanned aerial vehicle, UAV)优化避障策略是深度强化学习(deep reinforcement learning, DRL)应用于防撞领域亟需解决的问题。针对此,提出一种基于离线DRL的动态避障导航算法。将离线DRL算法与速度障碍(velocity obstacle, VO)法结合,改善在线深度强化学习算法需要高实时性交互数据的问题。通过对策略更新进行约束,提升离线DRL算法的性能。开发一个基于VO的奖励函数,使无人机在躲避动态障物的同时考虑耗时和路径最短问题。在三维避障导航环境中仿真进一步验证该方法在路径长度、飞行耗时以及避障成功率等方面均优于在线深度强化学习避障算法,有效改善了DRL需要不断输入在线数据才能有效更新策略的问题。Abstract: Real-time sampling and updating of data to optimize obstacle avoidance strategies for unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is an urgent issue in applying deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to collision prevention. In response to this problem, a dynamic obstacle avoidance navigation algorithm based on offline DRL was proposed. The combination of an offline DRL algorithm and velocity obstacle (VO) algorithm was introduced to address the issue of the high real-time interaction data required by online DRL algorithms. Performance enhancement of the offline DRL algorithm was achieved by imposing constraints on policy updates. A reward function based on VO was developed, which could enable the UAV to consider both time consumption and the shortest path while avoiding dynamic obstacles. Simulation verification in a three-dimensional obstacle navigation environment show that this method can surpass online deep reinforcement learning obstacle avoidance algorithms in terms of path length, flight time, and obstacle avoidance success rate. It will effectively address the problem of DRL requiring continuous input of online data for efficient policy updates
-
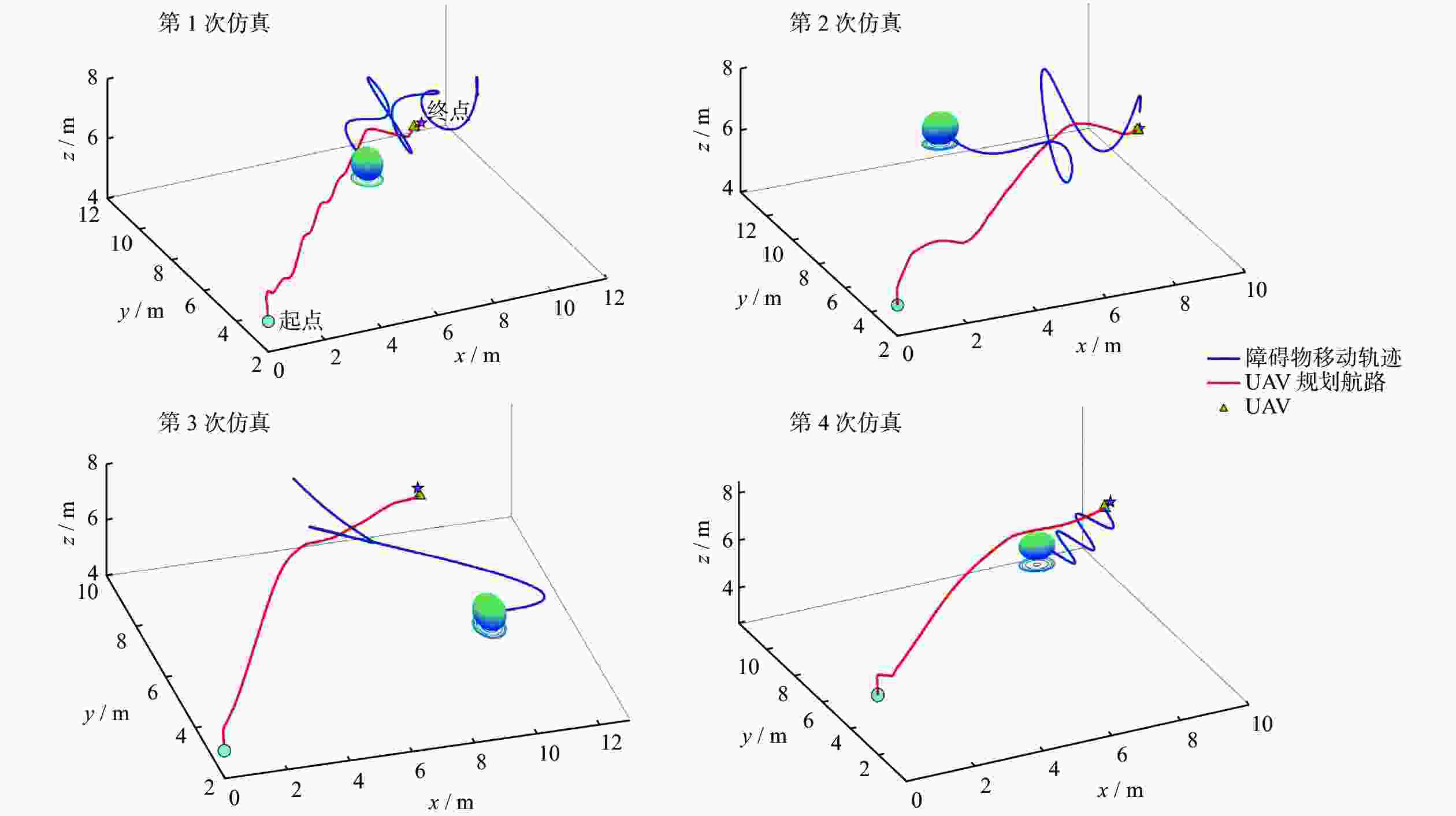
表 1 单动态障碍物环境下算法的避障导航指标模拟
Table 1. Simulations of obstacle avoidance and navigation indexes of algorithms in single dynamic obstacle environment
环境 路径长度 飞行耗时 避障成功率 TD3 PPO BCQ PBCQ TD3 PPO BCQ PBCQ TD3 PPO BCQ PBCQ 1 66.1 14.9 15.2 14.7 42.0 15.0 11.5 11.3 0.98 0.99 0.85 0.95 2 29.1 15.3 17.4 17.2 20.6 14.3 12.7 12.4 1 0.99 0.97 1 3 20.5 15.3 16.1 15.3 21.0 12.7 12.4 12.2 0.87 0.99 0.99 0.99 4 17.9 15.6 14.5 14.2 20.6 13.2 12.5 11.5 0.92 0.98 0.97 0.99 表 2 多动态障碍物环境下算法的避障导航指标模拟
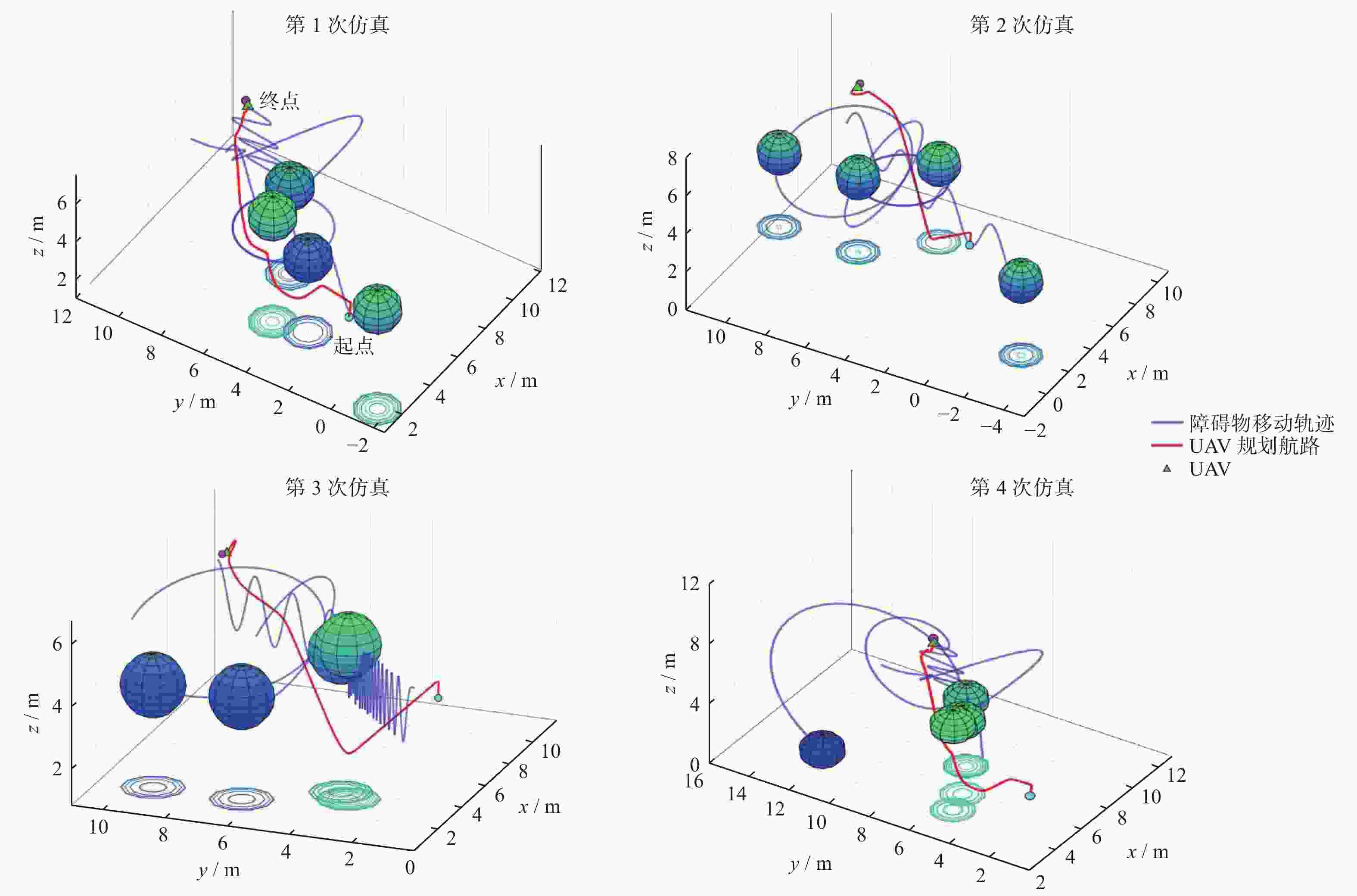
Table 2. Simulations of obstacle avoidance and navigation indexes of algorithms in multi-dynamic obstacle environment
环境 路径长度 飞行耗时 避障成功率 TD3 PPO BCQ PBCQ TD3 PPO BCQ PBCQ TD3 PPO BCQ PBCQ 1 28.3 17.2 21.0 19.8 23.1 18.8 20.2 17.9 0.97 0.98 0.77 0.96 2 16.8 16.0 22.4 17.0 12.2 17.1 19.3 16.7 1 0.91 0.99 0.99 3 18.5 15.6 17.6 15.0 15.4 15.5 17.2 15.4 0.93 0.87 0.85 0.94 4 18.6 15.9 19.9 15.7 15.3 15.7 19.8 16.3 0.93 0.87 0.99 0.99 -
[1] NEX F, REMONDINO F. UAV for 3D mapping applications: a review[J] . Applied Geomatics,2014,6(1):1 − 15. doi: 10.1007/s12518-013-0120-x [2] RADOGLOU-GRAMMATIKIS P, SARIGIANNIDISP, LAGKAS T, et al. A compilation of UAV applications for precision agriculture[J] . Computer Networks,2020,172:107148. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107148 [3] ALZAHRANI B, OUBBATI O S, BARNAWI A, et al. UAV assistance paradigm: State-of-the-art in applications and challenges[J] . Journal of Network and Computer Applications,2020,166:102706. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102706 [4] 多南讯, 吕强, 林辉灿, 等. 迈进高维连续空间: 深度强化学习在机器人领域中的应用[J] . 机器人,2019,41(2):276 − 288. [5] 王怿, 祝小平, 周洲, 等. 3维动态环境下的无人机路径跟踪算法[J] . 机器人,2014,36(1):83 − 91. [6] 陈海, 何开锋, 钱炜祺. 多无人机协同覆盖路径规划[J] . 航空学报,2016,37(3):928 − 935. [7] 贾永楠, 田似营, 李擎. 无人机集群研究进展综述[J] . 航空学报,2020,41(S1):4 − 14. [8] 赵晓, 王铮, 黄程侃, 等. 基于改进A算法的移动机器人路径规划[J] . 机器人,2018,40(6):903 − 910. [9] 徐飞. 基于改进人工势场法的机器人避障及路径规划研究[J] . 计算机科学,2016,43(12):293 − 296. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2016.12.054 [10] GAMMELL J D, SRINIVASA S S, BARFOOT T D. Informed RRT*: Optimal sampling-based path planning focused via direct sampling of an admissible ellipsoidal heuristic[C] //Proceedings of 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Macao: IEEE, 2014: 2997 − 3004. [11] YANG H, QI J, MIAO Y, et al. A new robot navigation algorithm based on a double-layer ant algorithm and trajectory optimization[J] . IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2018,66(11):8557 − 8566. [12] FOX D, BURGARD W, THRUN S. The dynamic window approach to collision avoidance[J] . IEEE Robotics & Automation Magazine,1997,4(1):23 − 33. [13] CHEN Y F, LIU M, EVERETT M, et al. Decentralized non-communicating multiagent collision avoidance with deep reinforcement learning[C] //Proceedings of 2017 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA). Singapore: IEEE, 2017: 285 − 292 [14] EVERETT M, CHEN Y F, HOW J P. Motion planning among dynamic, decision-making agents with deep reinforcement learning[C] //Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 3052 − 3059. [15] FIORINI P, SHILLER Z. Motion planning in dynamic environments using velocity obstacles[J] . The International Journal of Robotics Research,1998,17(7):760 − 772. doi: 10.1177/027836499801700706 [16] VAN DEN BERG J, LIN M, MANOCHA D. Reciprocal velocity obstacles for real-time multi-agent navigation[C] //Proceedings of 2008 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation. Pasadena: IEEE, 2008: 1928 − 1935. [17] ALONSO-MORA J, BREITENMOSER A, RUFLI M, et al. Optimal reciprocal collision avoidance for multiple non-holonomic robots[M] . Berlin: Springer, 2013: 203 − 216. [18] HAN R, CHEN S, WANG S, et al. Reinforcement learned distributed multi-robot navigation with reciprocal velocity obstacle shaped rewards[J] . IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2022,7(3):5896 − 5903. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3161699 [19] SUTTON R S, BARTO A G. Reinforcement learning: An introduction[M] . London: MIT press, 2018. [20] SCHULMAN J, WOLSKI F, DHARIWAL P, et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithms[EB/OL] . (2017−08−28)[2023−03−13] . https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.06347. [21] FUJIMOTO S, VAN HOOF H, MEGER D. Addressing function approximation error in actor-critic methods[EB/OL] . (2018−10−22)[2023−05−11] . https://arxiv.org/pdf/1802.09477. [22] FUJIMOTO S, MEGER D, PRECUP D. Off-policy deep reinforcement learning without exploration[EB/OL] . (2019−01−29)[2023−07−03] . https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329525481. [23] KUMAR A, FU J, SOH M, et al. Stabilizing off-policy Q-learning via bootstrapping error reduction[C] //Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: Curran Associates Inc., 2019. [24] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J] . Nature,2015,518:529 − 533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 -





 下载:
下载: