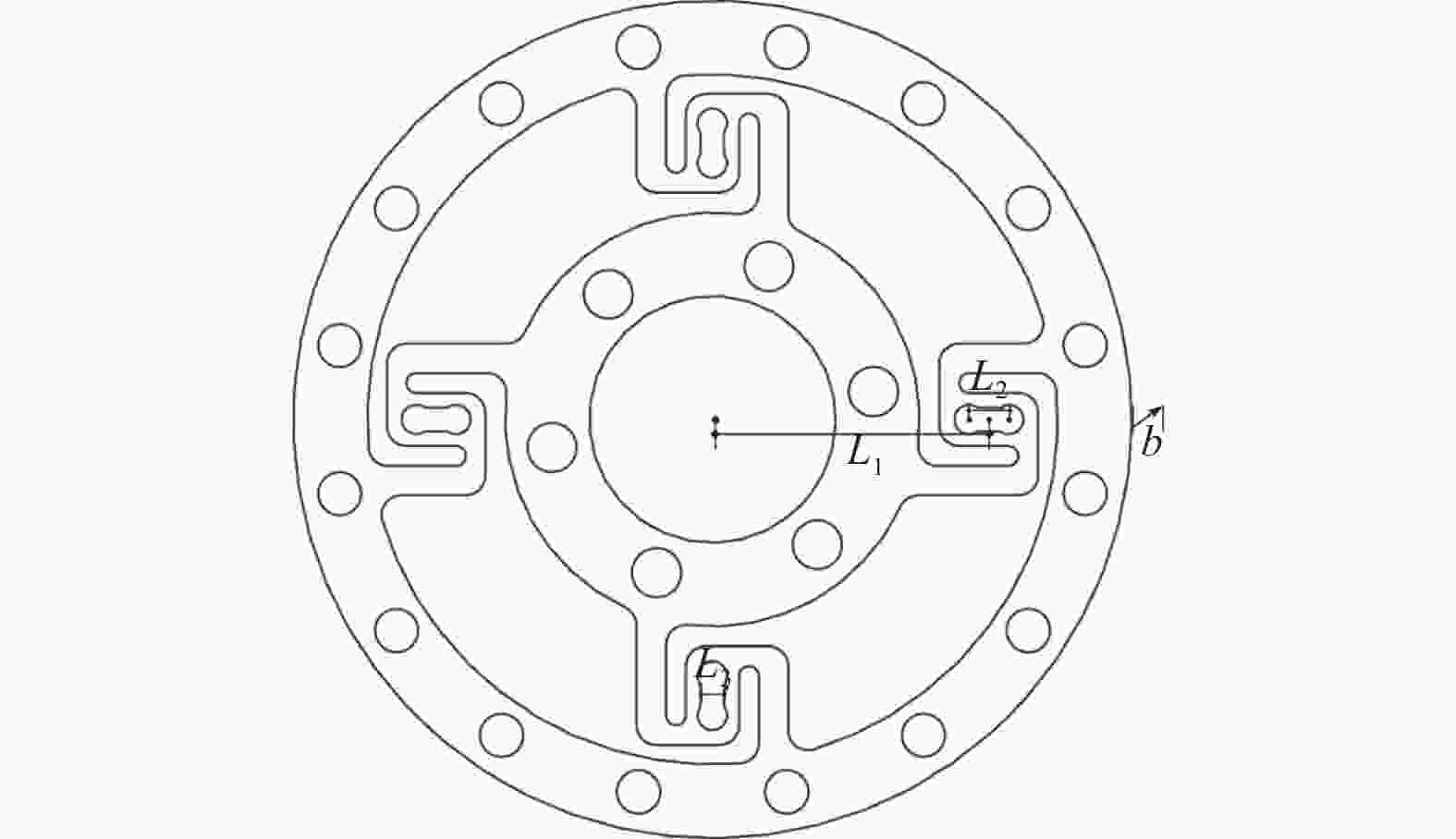
Topology structure design and optimization of a new-type strain torque sensor for robotic joints
-
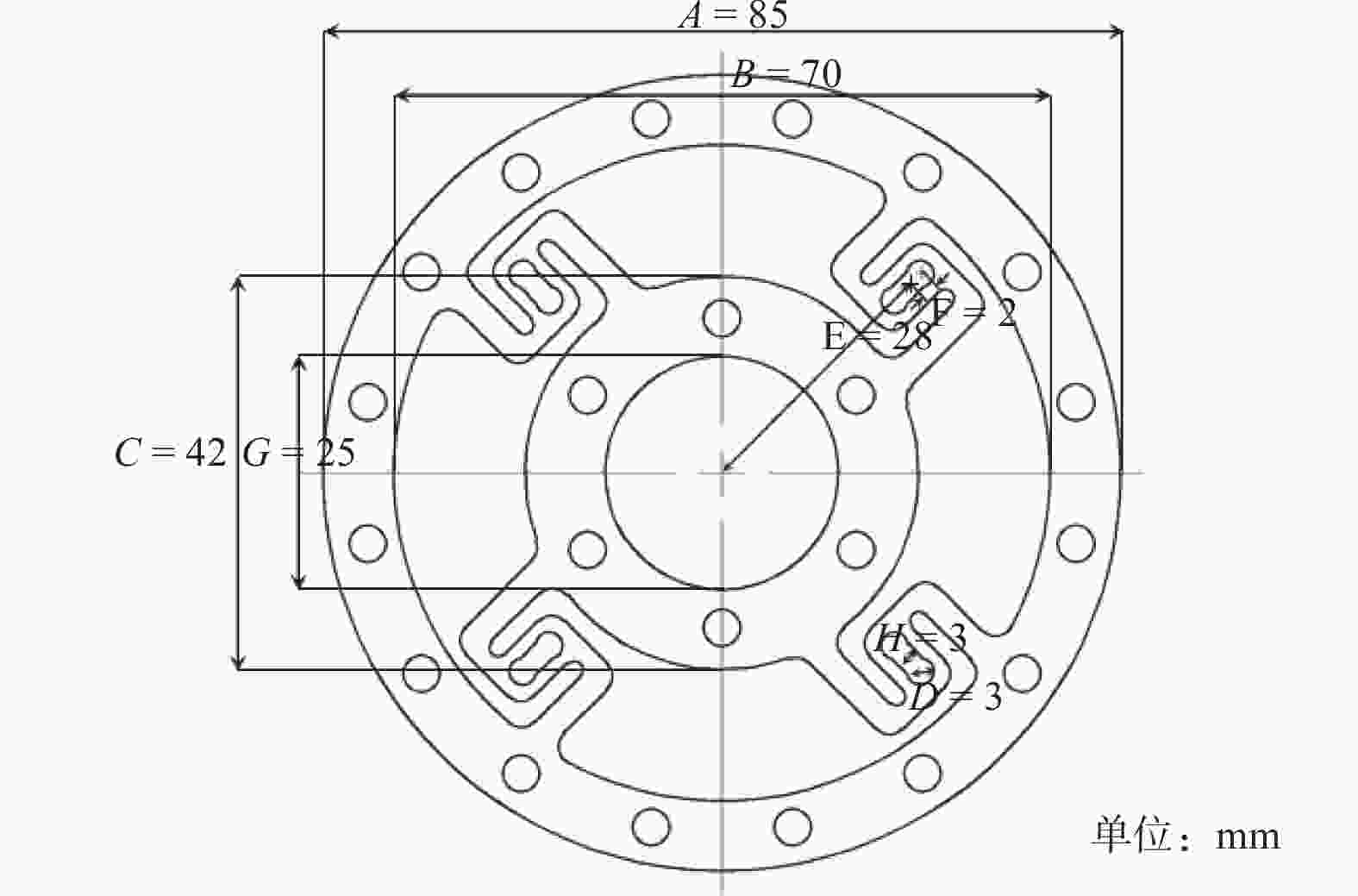
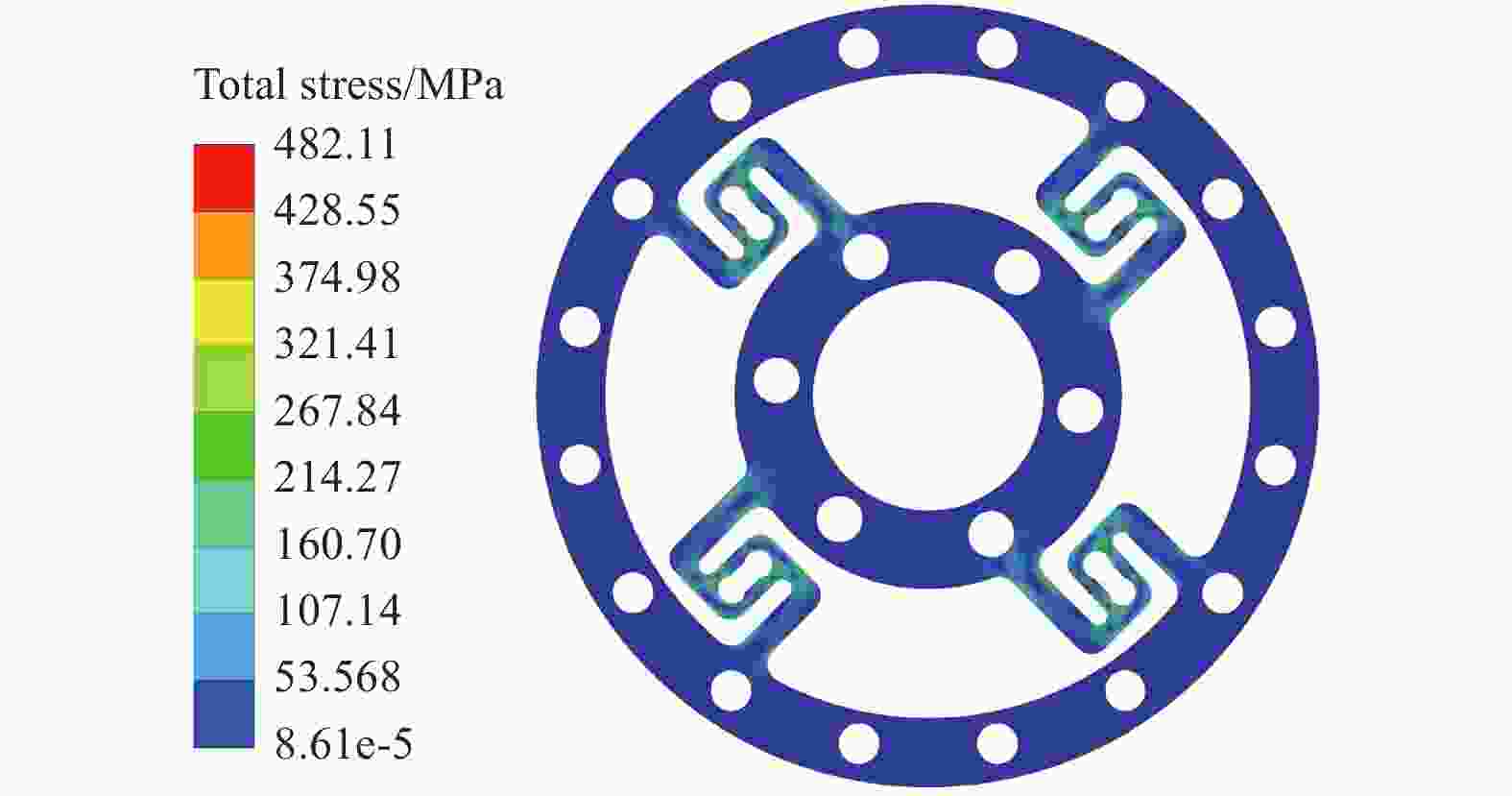
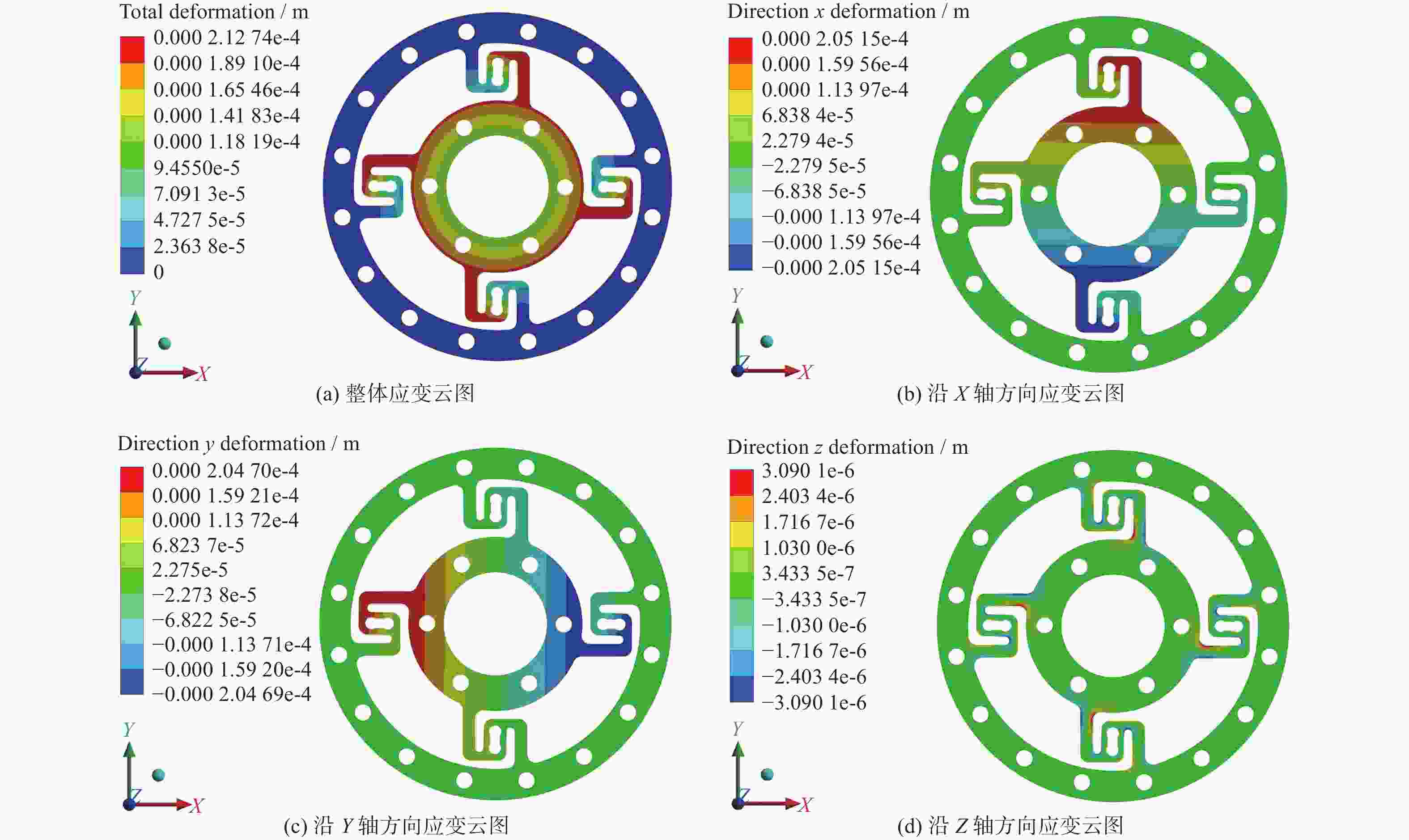
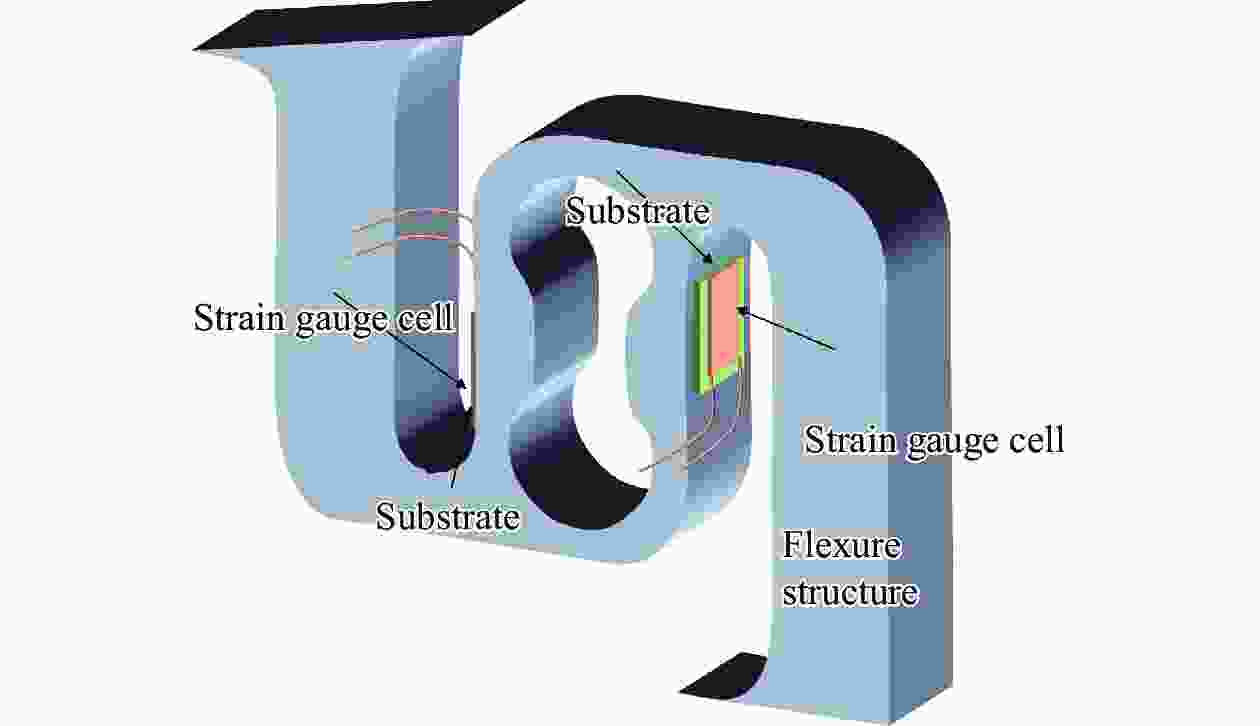
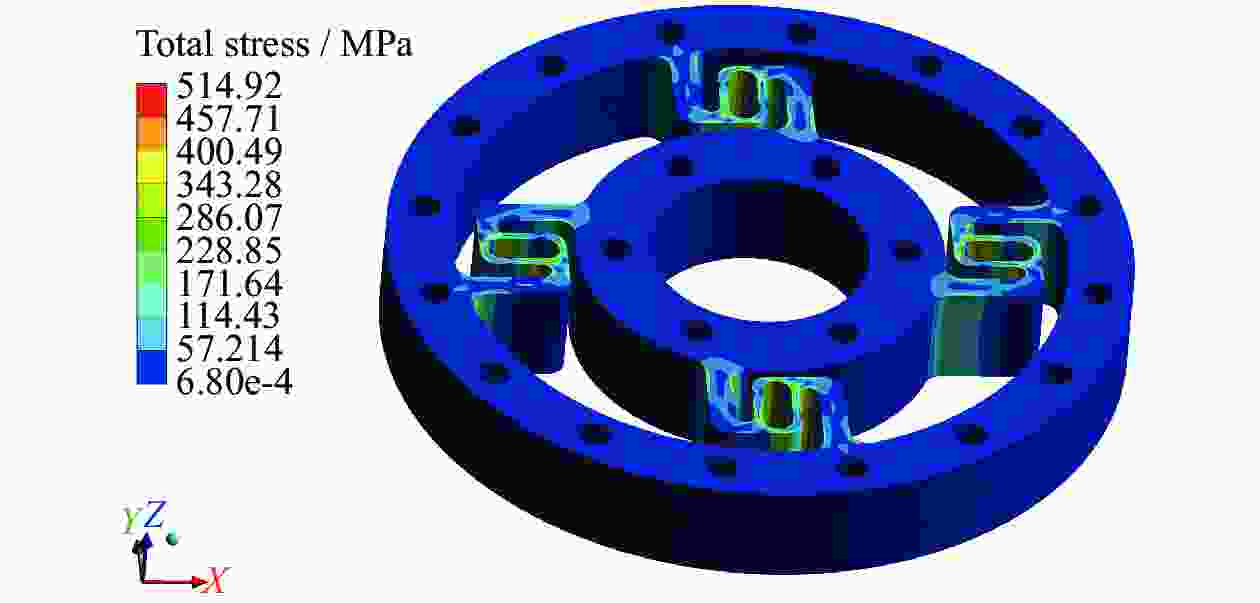
摘要: 协作机器人的柔性控制依赖于关节的力矩感知能力。基于应变式传感器测量原理,提出一种S型双连孔结构的应变式扭矩传感器。首先,依据传感器测量的基本原理,提出基于应变式传感器的构型设计方法。其次,通过传感器整体结构力学仿真试验,验证结构的可靠性。最后,运用中心复合设计(CCD)响应面法对传感器局部尺寸参数进行优化,使传感器表面应变提高93 MPa,从而提高了传感器的灵敏度。Abstract: The flexible control of collaborative robots relies on the torque sensing capability of the joints. Based on the measurement principle of strain sensors, a strain-based torque sensor with an S-shaped double-hole structure was proposed. Firstly, according to the basic principles of sensor measurement, a configuration design method based on strain gauges was proposed. Secondly, the reliability of the structure was verified through mechanical simulation tests of the overall sensor structure. Finally, the central-composite design (CCD) response surface method was ued to optimize the local dimensional parameters of the sensor, which increases the surface strain of the sensor by 93 MPa, thereby enhancing the sensitivity of the sensor.
-
Key words:
- torque sensor /
- resistive strain gauge sensor /
- flexure structure design
-
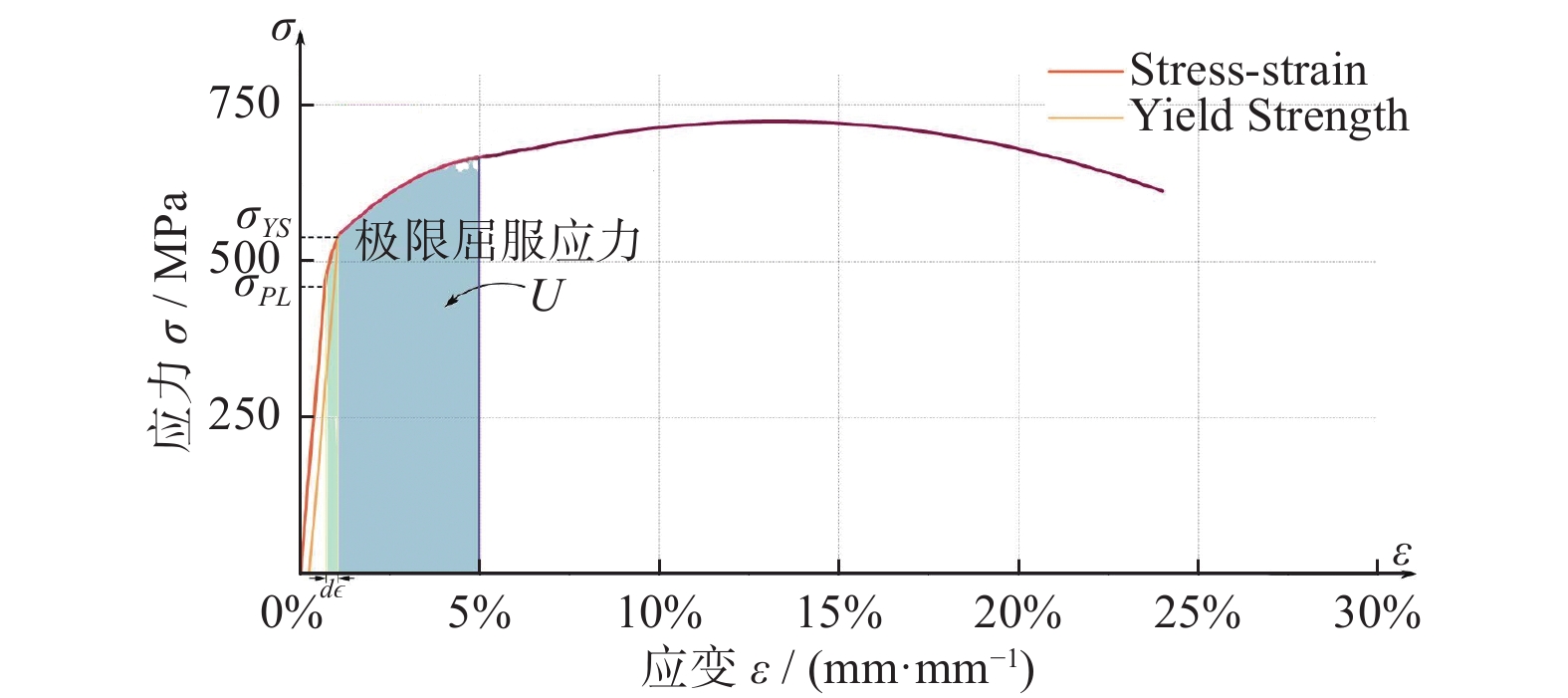
表 1 各种材料应力−应变参数
Table 1. Stress-strain parameters of various materials
参数 45钢 7075-T6 6061-T6 2024-T4 σYS/MPa 530 512 275 320 σY/MPa 481.0 482.1 483.8 483.2 με 1068 3596 3724 3311 表 2 优化模型评价指标
Table 2. Evaluation indicators of optimization model
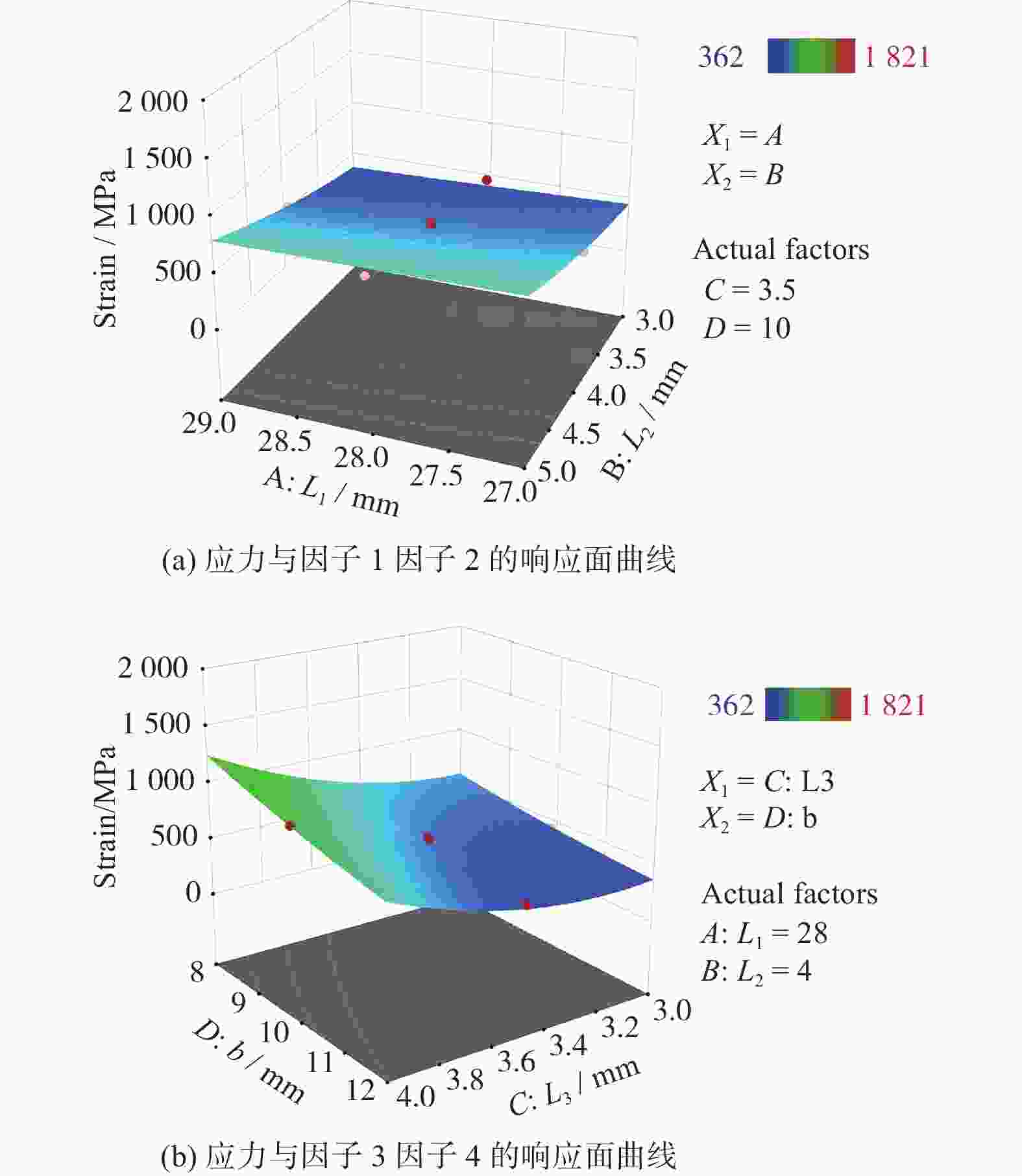
名称 p值 方差 调整方差 信噪比 f1 < 0.000 1 0.988 0.976 9 36.00 f2 < 0.000 1 0.988 0.977 2 40.54 f3 < 0.000 1 0.985 0.971 7 38.29 表 3 优化前后参数对比
Table 3. Parameters comparison before and after optimization
模型优化 L1/mm L2/mm L3/mm b/mm 优化前 28 4 3 10 优化后 27 5 3.25 12 模型优化 f1(x)/MPa f2(x)/(mm·mm−1) f3(x)/(mm·mm−1) 优化前 482 0.012 0.114 优化后 514 0.028 0.148 表 4 构型特点对比
Table 4. Table of configuration comparison and characteristics
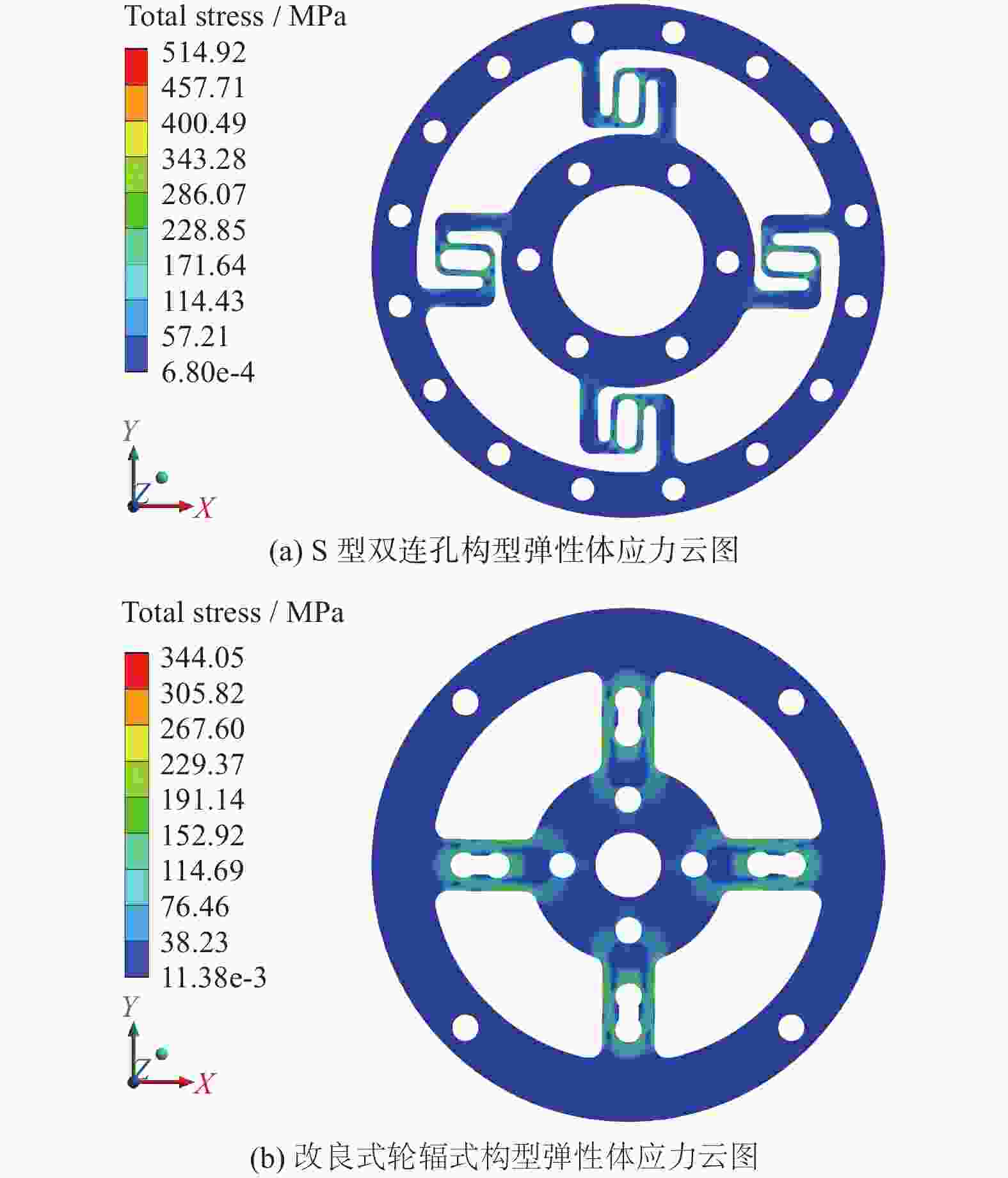
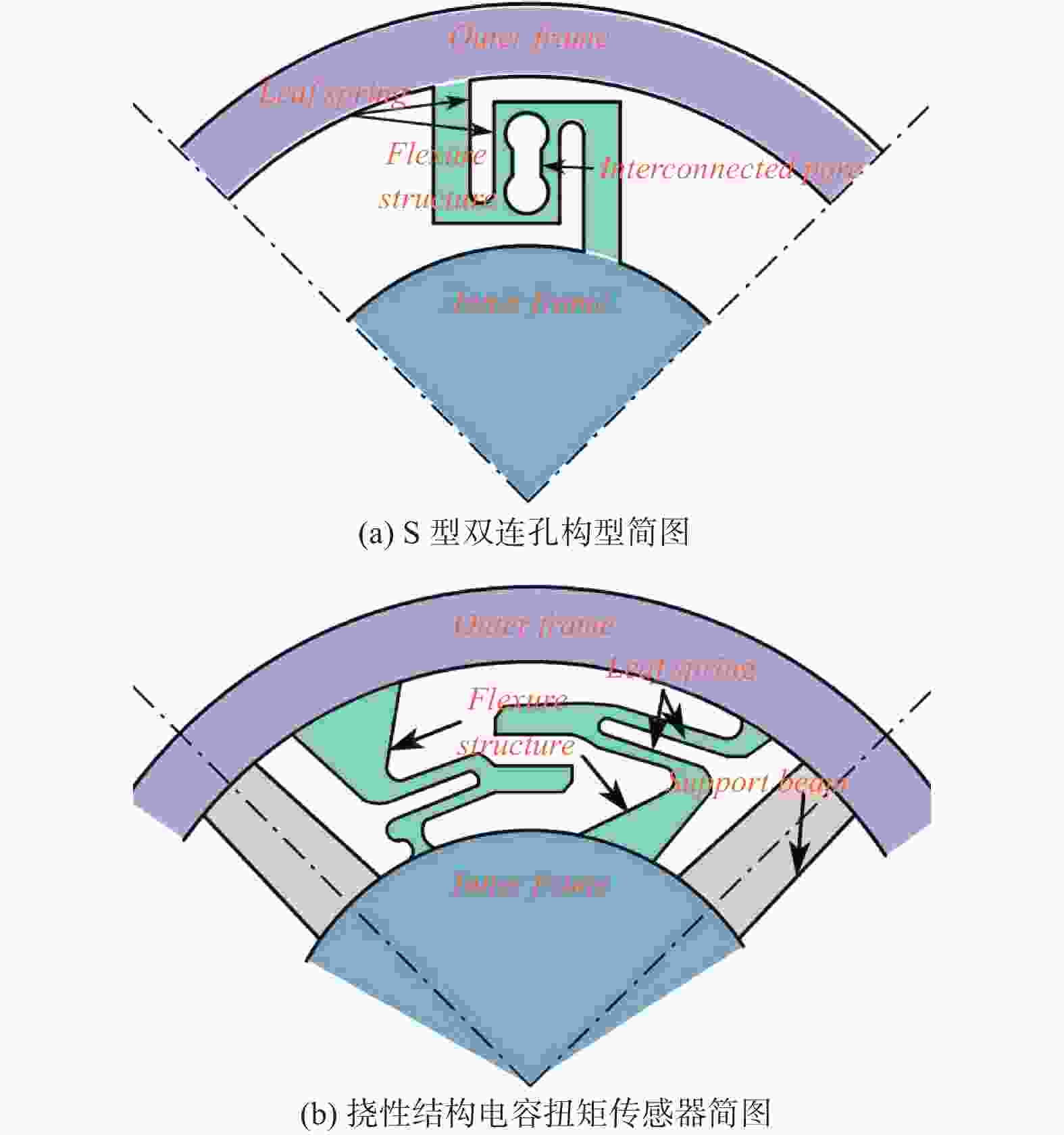
弹性体构型 特点 S型双连孔 应力应变更集中,应变片区域弹性应变好 改进轮辐双连孔 结构简单,应力应变分散不均,易受串扰影响 支撑梁 + 挠性结构 结构复杂,挠性结构不完全对称,制造困难,映射关系不明确 -
[1] HADDADIN S, ELIZABETH C. Physical human–robot interaction[J] . Springer Handbook of Robotics,2016,1(2):1835 − 1874. [2] De STEFANO M.Multi-rate tracking control for a space robot on a controlled satellite: a passivity-based strategy[J] . IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2019,4(2):1319 − 1326. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2895420 [3] LEE S D, SONG J B. Sensorless collision detection based on friction model for a robot manipulator[J] . International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing,2016(17):11 − 17. [4] 王梦含. 基于六维力传感器的机器人力控研究[D] . 太原: 太原理工大学, 2023. [5] OTT C, MUKHERJEE R, Nakamura Y. Unified impedance and admittance control[C] //Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Anchorage: IEEE, 2010: 554 − 561. [6] MADNI A M, VUONG J B, Yang D C H. A differential capacitive torque sensor with optimal kinematic linearity[J] . IEEE Sensors Journal,2007(5):800−807. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2007.894134 [7] LIU J, LI M, QIN L, et al.Active design method for the static characteristics of a piezoelectric six-axis force/torque sensor[J] . Sensors,2014,14:659 − 671. doi: 10.3390/s140100659 [8] TSETSERUKOU D, KAWAKAMI N, TACHI S. Design, control and evaluation of a whole-sensitive robot arm for physical human-robot interaction[J] . International Journal of Humanoid Robotics,2009,6:699 − 725. doi: 10.1142/S0219843609001899 [9] KANG M K, LE S, KIM J H. Shape optimization of a mechanically decoupled six-axis force/torque sensor[J] . Sensors and Actuators A: Physical,2014,209:41 − 51. [10] 朱弟发, 张恩阳, 韩康, 等. 基于协作机器人关节集成扭矩传感器的研究[J] . 仪表技术与传感器,2021,1(10):6 − 9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2021.10.002 [11] 魏家豪. 面向机器人碰撞检测的关节力矩传感器设计与开发[D] . 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. [12] LOU Y J, WEI J H, SONG S. Design and optimization of a joint torque sensor for robot collision detection[J] . IEEE Sensors Journal,2019,19(16):618 − 662. [13] KIM U, MAENG C Y, BAK G, et al. High-stiffness torque sensor with a strain amplification mechanism for cooperative industrial manipulators[J] . IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2021,3(1):3131 − 3141. [14] KIM J I, JEON H S, JEONG Y J, et al. High stiffness capacitive type torque sensor with flexure structure for cooperative industrial robots[C] //Proceedings of 2017 14th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI). Jeju: IEEE, 2017: 433 − 437. -





 下载:
下载: