Study on effect of diesel injection strategy on performance of ammonia-diesel dual-fuel engine
-
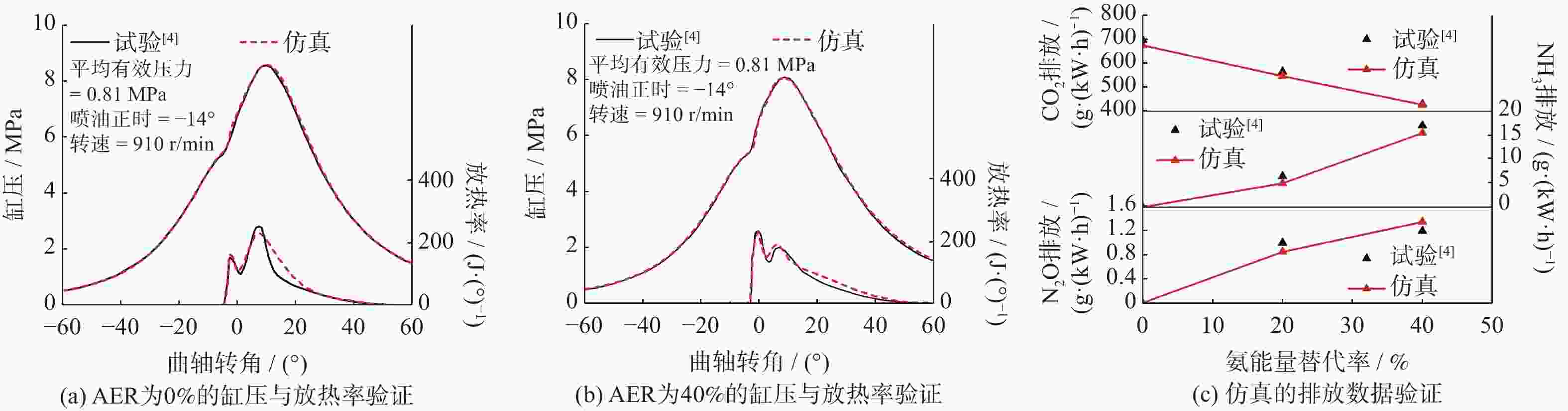
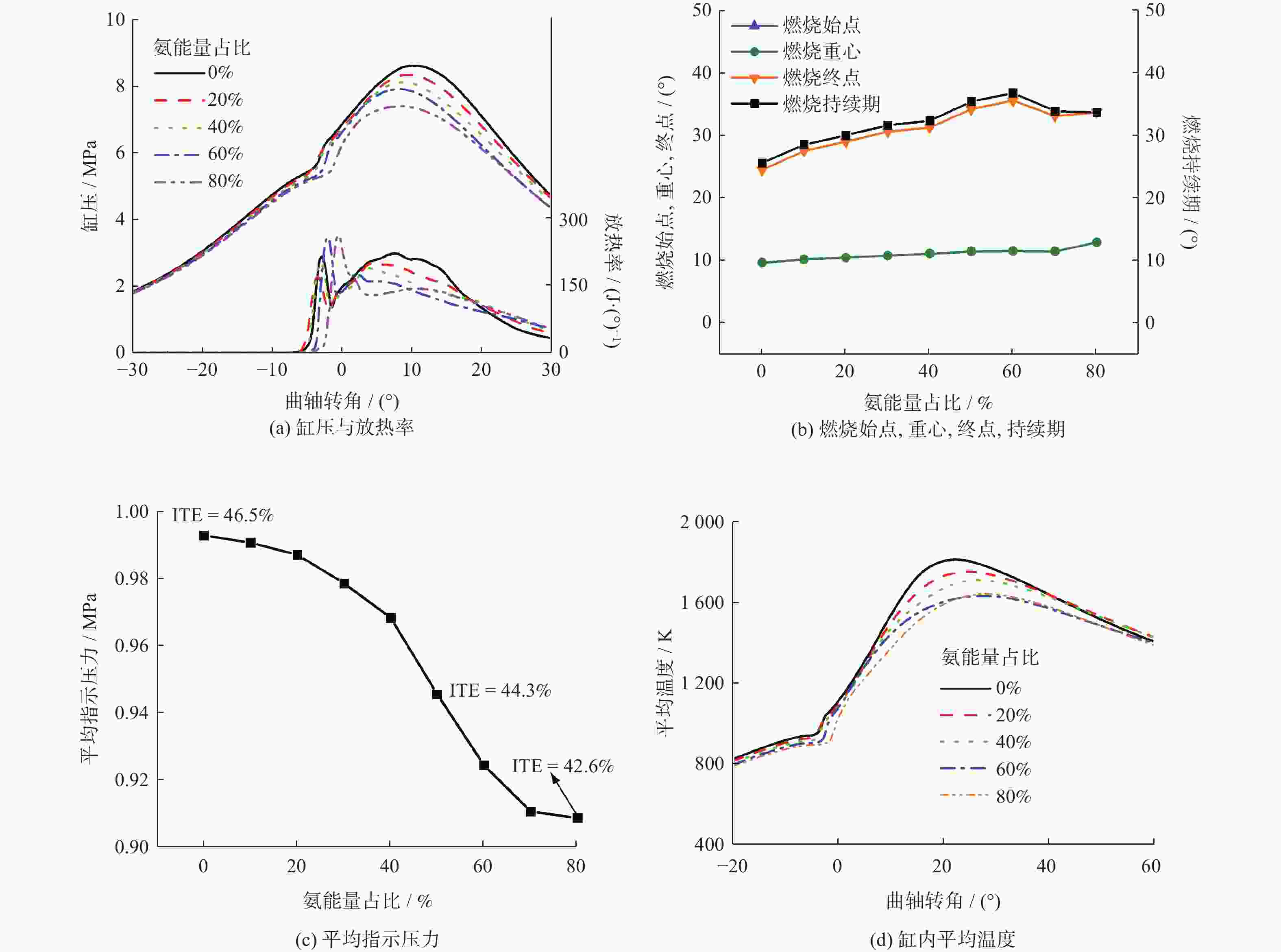
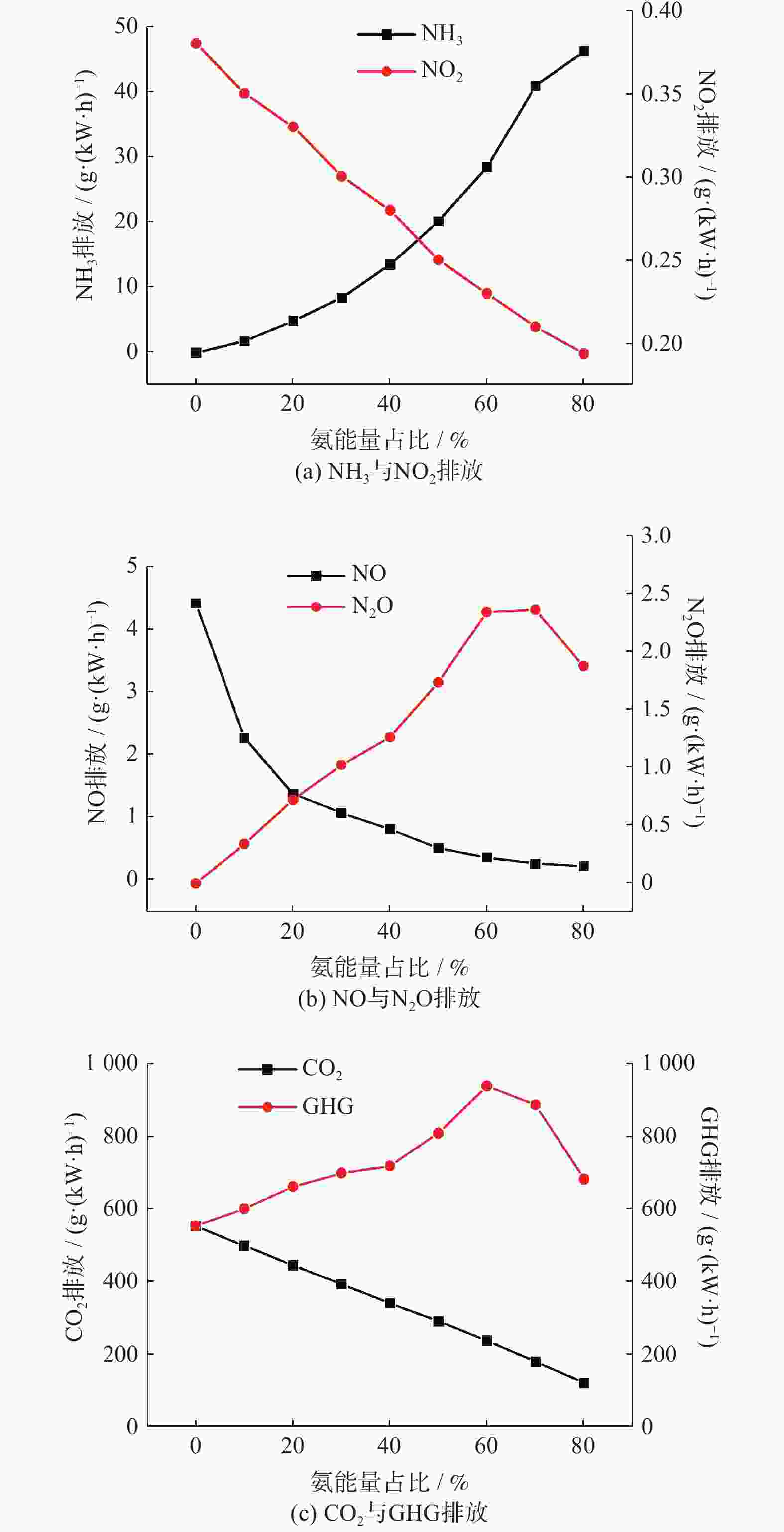
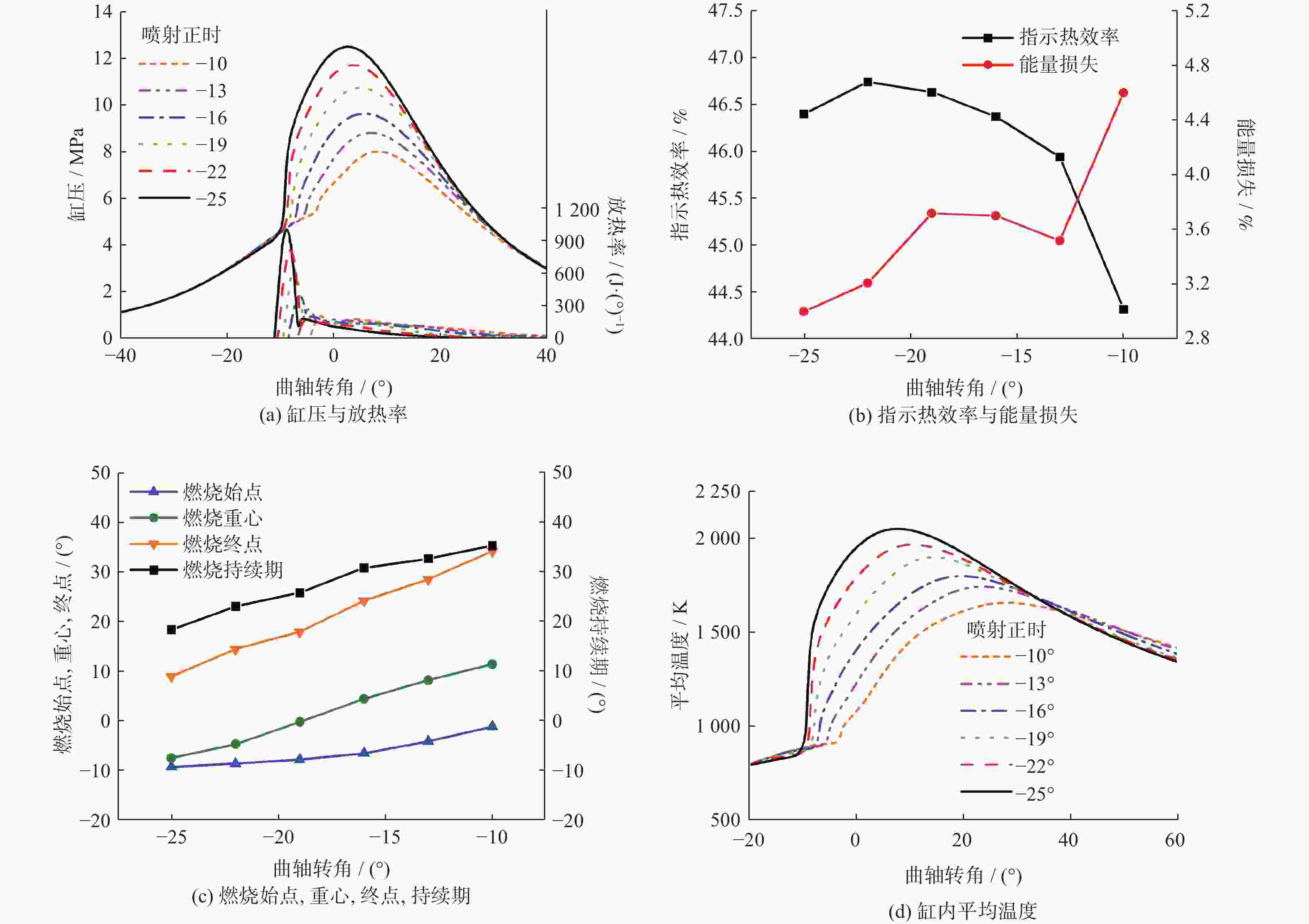
摘要: 基于某重型柴油机,利用CONVERGE软件研究不同氨能量占比(AER)及柴油喷射策略对氨柴油双燃料发动机燃烧性能的影响,通过调整柴油喷射策略来实现发动机指示热效率的最佳值。研究表明,氨能量占比从0%增至80%,指示热效率随之下降,反应产物N2O的增加导致温室气体排放大于原柴油机的柴油燃烧模式。氨能量占比恒定为50%,在柴油单次喷射正时最佳点,指示热效率可与原柴油燃烧模式相当,同时温室气体(greenhouse gas, GHG)排放量下降19.7%,NO排放量上升41.6%。在柴油二次喷射的预、主喷正时最佳点,相对于原柴油燃烧模式,指示热效率上升1.6%,GHG排放量下降40.4%,NO排放量上升31.8%,延迟柴油二次喷射的主喷正时可有效降低NO排放量。Abstract: Based on a heavy-duty diesel engine, the effects of different ammonia energy ratio (AER) and diesel injection strategies on the combustion performance of ammonia-diesel dual-fuel engine were investigated by using CONVERGE software, the indicated thermal efficiency (ITE) of the engine was optimized by adjusting the diesel injection strategy. The results of the study show that the AER increases from 0% to 80% with a consequent decrease in the ITE, the increase in the reaction product N2O resulted in greater greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions than in the original diesel-only combustion mode of the diesel engine. The AER is constant at 50%. At the optimum point of diesel single injection timing, the ITE is comparable to that of the original diesel combustion mode, while GHG emissions decreases by 19.7% and NO emissions increases by 41.6%. At the optimum point of pre- and main injection timing for diesel split injection, the ITE increases by 1.6%, GHG emission decreases by 40.4%, and NO emission increased by 31.8% compared with the original diesel combustion mode, delaying the main injection timing of diesel split injection can effectively reduce NO emissions.
-
表 1 发动机参数
Table 1. Engine parameters
项目 参数 发动机模型 Caterpillar3401 缸径/mm 137.2 行程/mm 165.1 连杆长度/mm 261.6 排量/L 2.44 压缩比 16.25 进气门开启时刻/(°) −358.3 进气门关闭时刻/(°) −169.7 排气门开启时刻/(°) 145.3 排气门关闭时刻/(°) 348.3 表 2 仿真初始边界条件
Table 2. Simulation initial boundary conditions
项目 参数 进气门关时刻压力/MPa 0.13 进气门关时刻温度/K 340 活塞温度/K 500 缸壁温度/K 420 缸盖温度/K 480 涡流比 0.5 柴油喷射压力/MPa 52.5 柴油喷射角度/(°) 65 转速/(r·min−1) 910 表 3 氨能量占比的参数设置
Table 3. Parameter settings for different AERs
氨能量占比 /% 柴油每循环量/mg 氨每循环量/mg 过量空气系数 0 120 0 1.72 10 108 28 1.70 20 96 56 1.69 30 84 84 1.68 40 72 112 1.66 50 60 140 1.65 60 48 168 1.64 70 36 196 1.63 80 24 224 1.62 表 4 柴油喷射策略参数设置
Table 4. Parameters setting of diesel injection strategies
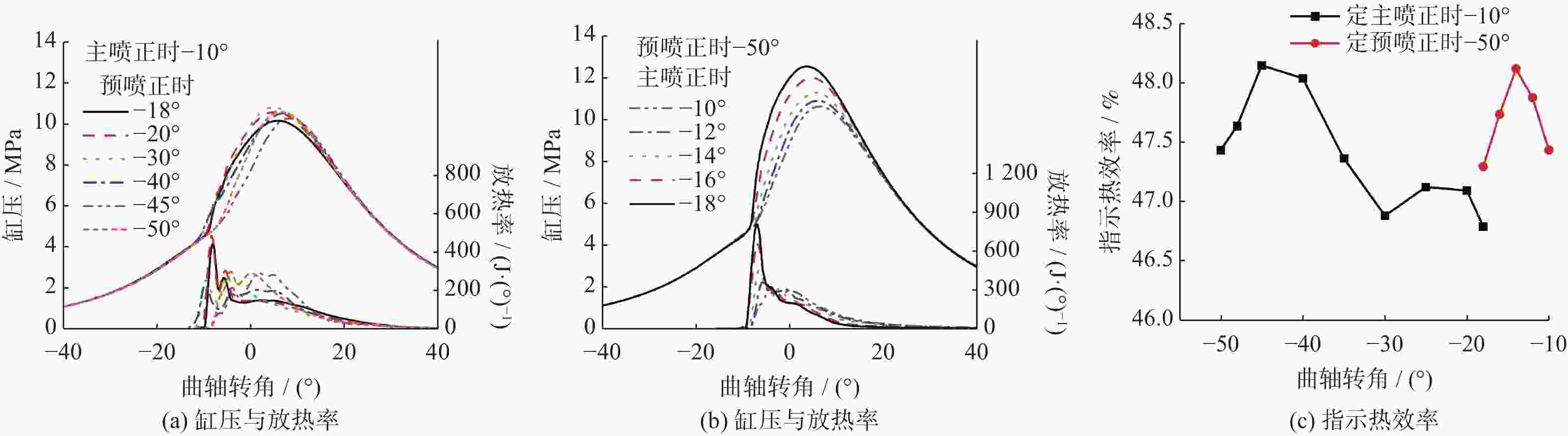
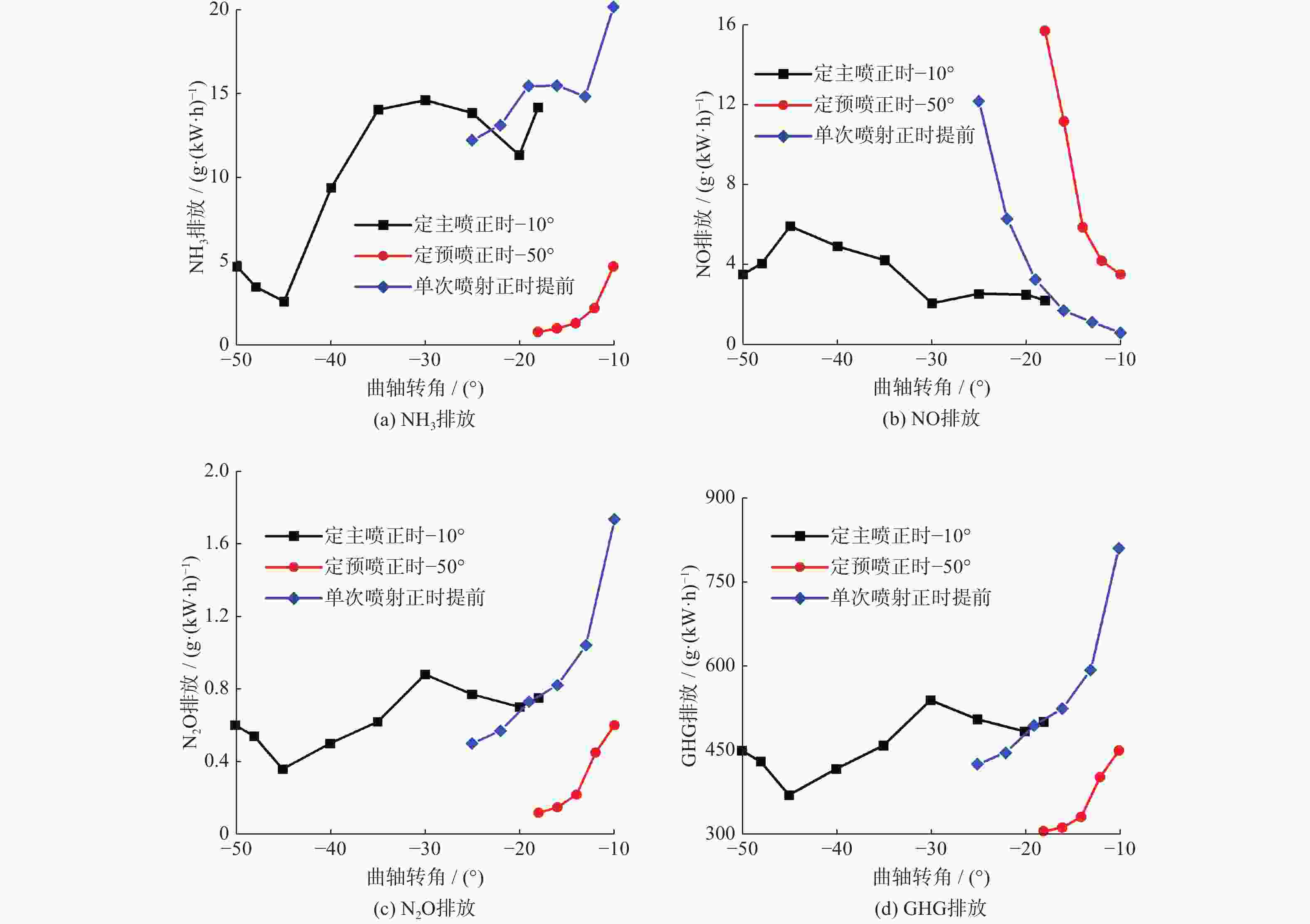
策略模式 预喷量占比/% 预喷正时/(°) 主喷正时/(°) 单次喷射 0 −10、−13、−16、−19、−22、−25 二次喷射 40 −18、−20、−25、−30、−35、−40、−45、−48、−50 −10 二次喷射 40 −50 −10、−12、−14、−16 、−18 -
[1] KURIEN C, MITTAL M. Review on the production and utilization of green ammonia as an alternate fuel in dual-fuel compression ignition engines[J] . Energy Conversion and Management,2022,251:114990. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2021.114990 [2] REITER A J, KONG S C. Combustion and emissions characteristics of compression-ignition engine using dual ammonia-diesel fuel[J] . Fuel,2011,90(1):87 − 97. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2010.07.055 [3] NIKI Y, NITTA Y, SEKIGUCHI H, et al. Diesel fuel multiple injection effects on emission characteristics of diesel engine mixed ammonia gas into intake air[J] . Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power: Transactions of the ASME,2019,141(6). DOI: 10.1115/1.4042507. [4] YOUSEFI A, GUO H S, DEV S, et al. Effects of ammonia energy fraction and diesel injection timing on combustion and emissions of an ammonia/diesel dual-fuel engine[J] . Fuel,2022,314:122723. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.122723 [5] YOUSEFI A, GUO H, DEV S, et al. A study on split diesel injection on thermal efficiency and emissions of an ammonia/diesel dual-fuel engine[J] . Fuel,2022,316:123412. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.123412 [6] LI T, ZHOU X, WANG N, et al. A comparison between low- and high-pressure injection dual-fuel modes of diesel-pilot-ignition ammonia combustion engines[J] . Journal of the Energy Institute,2022,102:362 − 373. doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2022.04.009 [7] WANG B, YANG C, WANG H, et al. Effect of Diesel-Ignited Ammonia/Hydrogen mixture fuel combustion on engine combustion and emission performance[J] . Fuel,2023,331:125865. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2022.125865 [8] 刘海峰, 宋腾达, 黄志雄, 等. 氨/柴油燃烧模型构建及低速机性能优化[J] . 内燃机学报,2023,41(5):395 − 403. [9] 崔磊, 王怀印. 船用氨燃料低速机缸内燃烧的数值模拟研究[J] . 工程热物理学报,2023,44(11):3151 − 3159. [10] FRASSOLDATI A, D'ERRICO G, LUCCHINI T, et al. Reduced kinetic mechanisms of diesel fuel surrogate for engine CFD simulations[J] . Combustion and Flame,2015,162(10):3991 − 4007. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2015.07.039 [11] OTOMO J, KOSHI M, MITSUMORI T, et al. Chemical kinetic modeling of ammonia oxidation with improved reaction mechanism for ammonia/air and ammonia/hydrogen/air combustion[J] . International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2018,43(5):3004 − 3014. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.12.066 [12] HAN Z, REITZ R D. Turbulence modeling of internal combustion engines using RNG κ-ε models[J] . Combustion Science and Technology, 1995, 106(4/5/6): 267 − 295. doi: 10.1080/00102209508907782 [13] AMSDEN A A, O'ROURKE P J, BUTLER T. D. A computer program for chemically reactive flows with sprays[J] . NASA STI/Recon Technical Report N, 1989, 89: 27975. [14] BEALE J C, REITZ R D. Modeling spray atomization with the Kelvin-Helmholtz/Rayleigh-Taylor hybrid model [J] . Atomization and Sprays, 1999, 9(6): 623−650. [15] SCHMIDT D P, RUTLAND C J. A new droplet collision algorithm[J] . Journal of Computational Physics,2000,164(1):62 − 80. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2000.6568 [16] O'ROURKE P J, AMSDEN A A. A Spray/Wall Interaction Submodel for the KIVA-3 Wall Film Model[J] . SAE Transactions,2000,109:281 − 298. [17] JIN S, WU B, ZI Z, et al. Effects of fuel injection strategy and ammonia energy ratio on combustion and emissions of ammonia-diesel dual-fuel engine[J] . Fuel,2023,341:127668. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127668 [18] HAN X L, LUBRANO L M, KONNOV A A. An experimental and kinetic modeling study on the laminar burning velocity of NH3 + N2O + air flames[J] . Combustion and Flame,2021,228:13 − 28. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2021.01.027 -





 下载:
下载: