Identification of key cognitive ability factors for metro train drivers based on VTS data mining
-
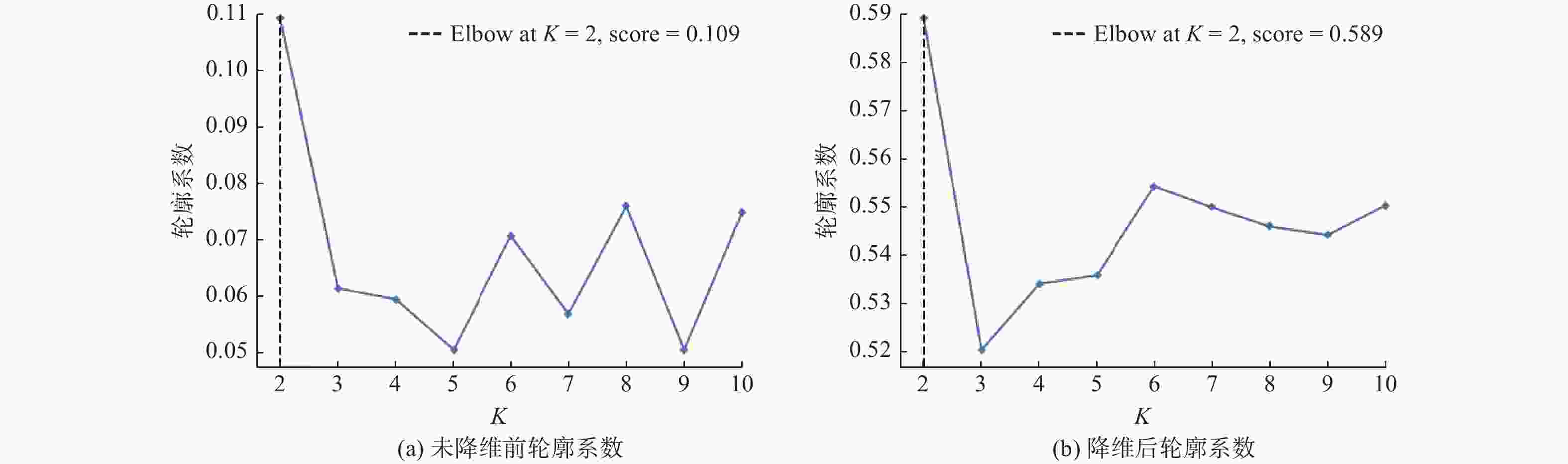
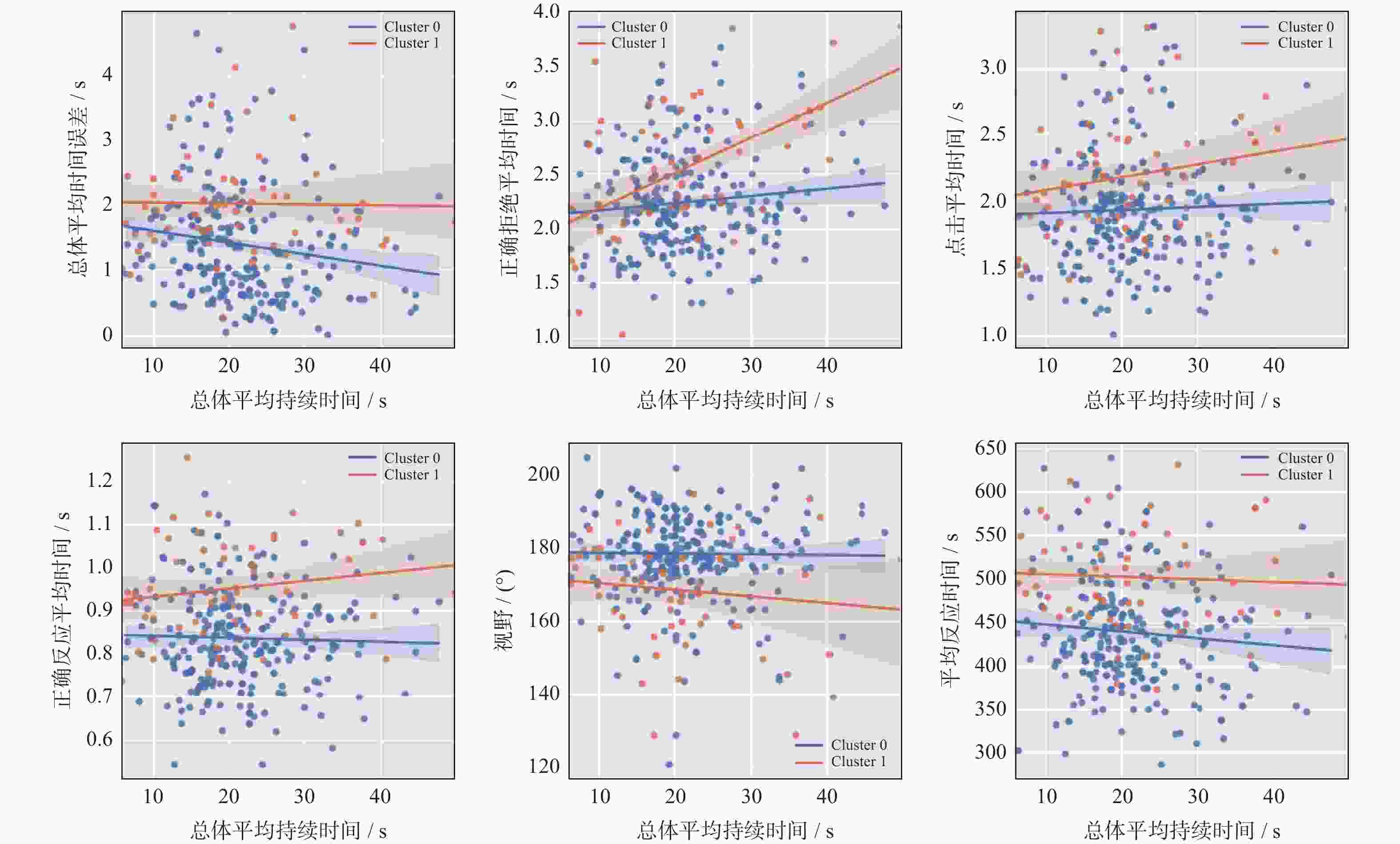
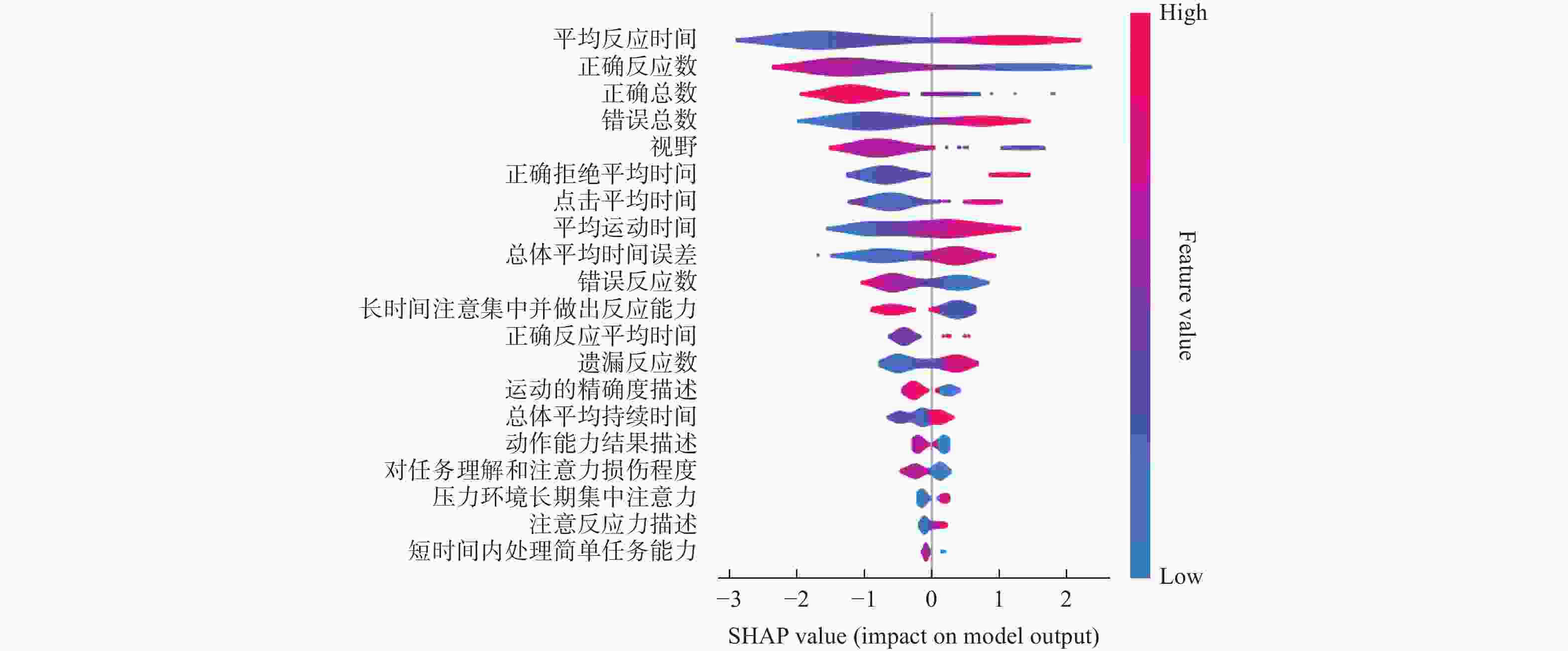
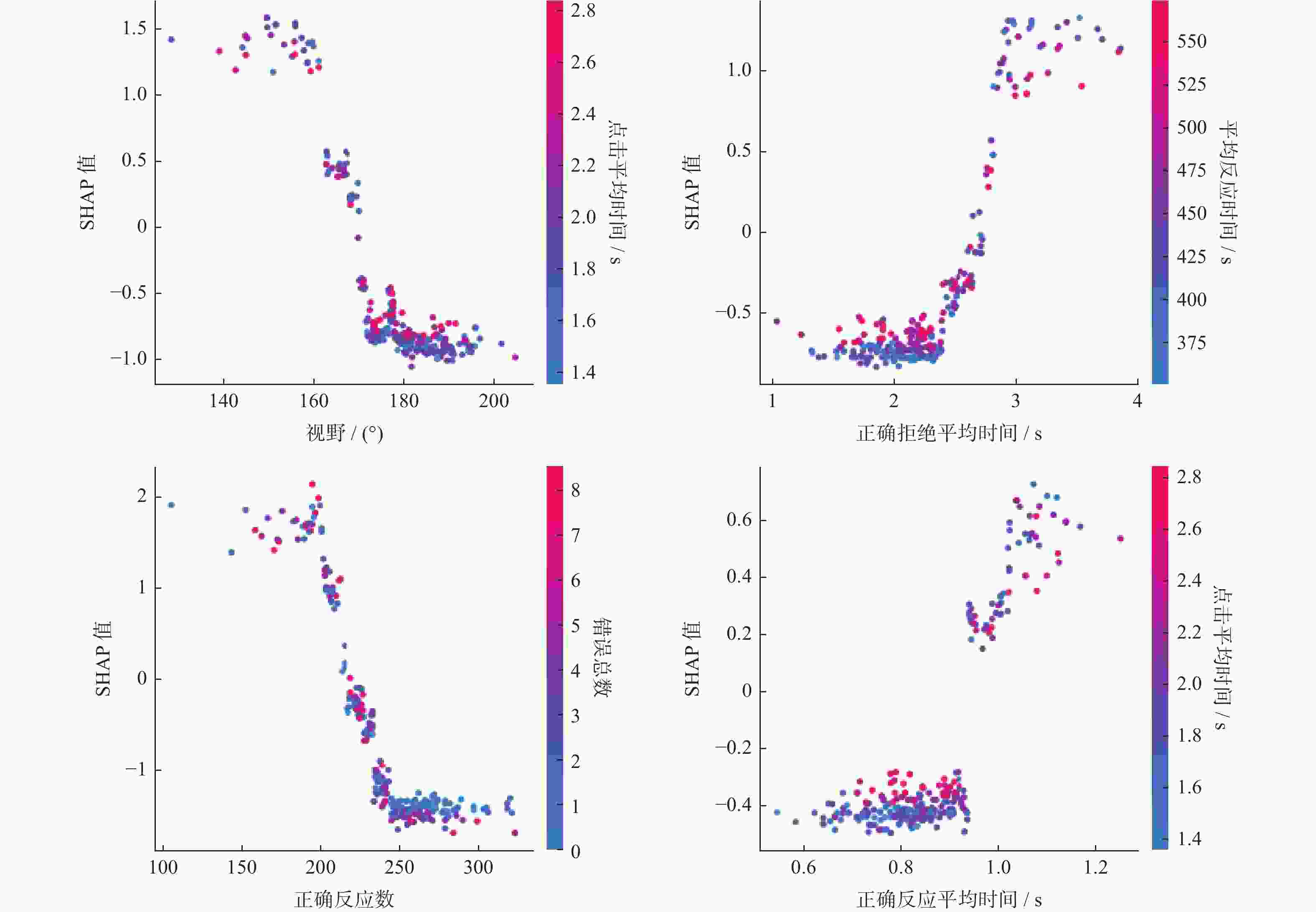
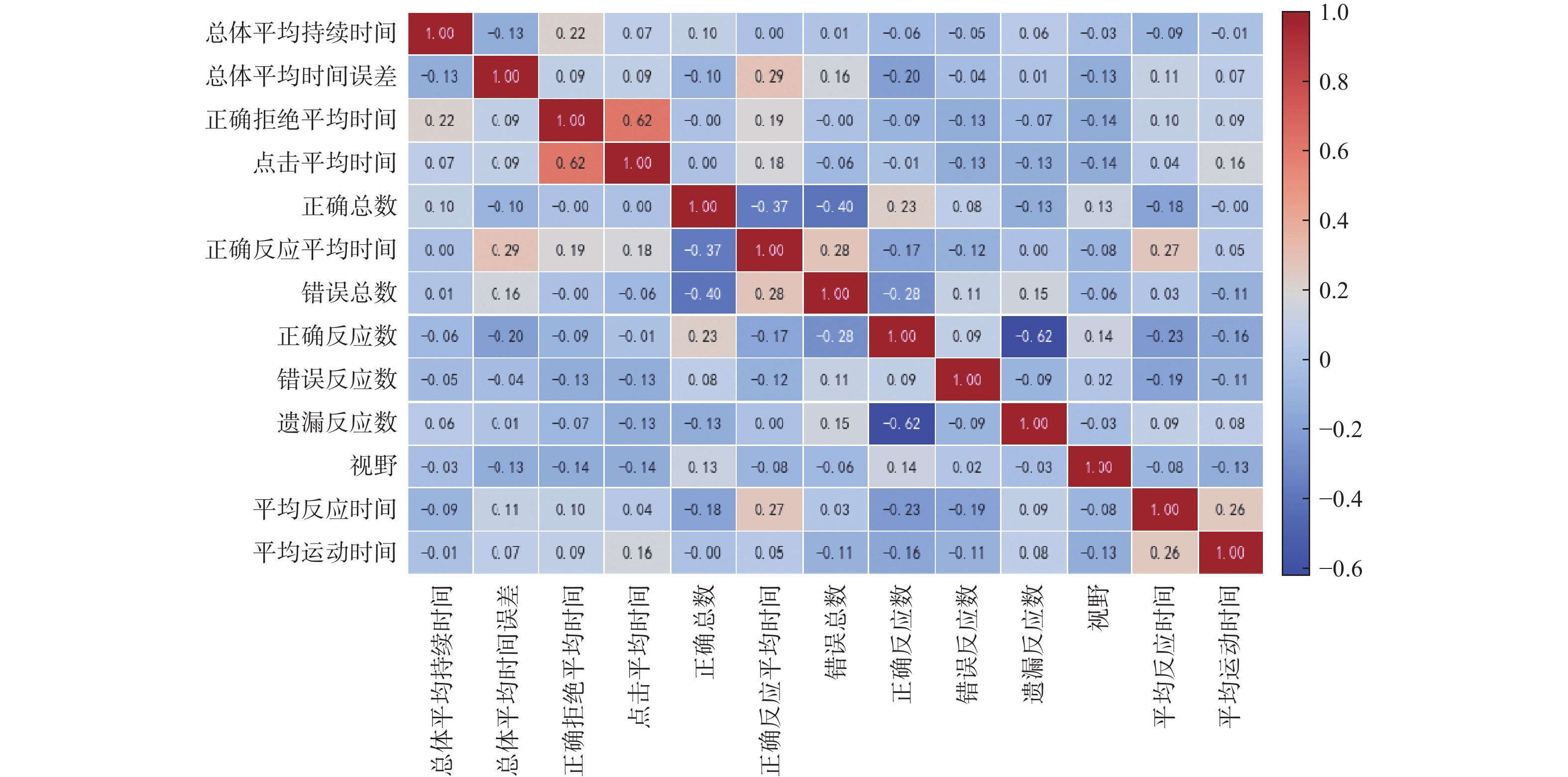
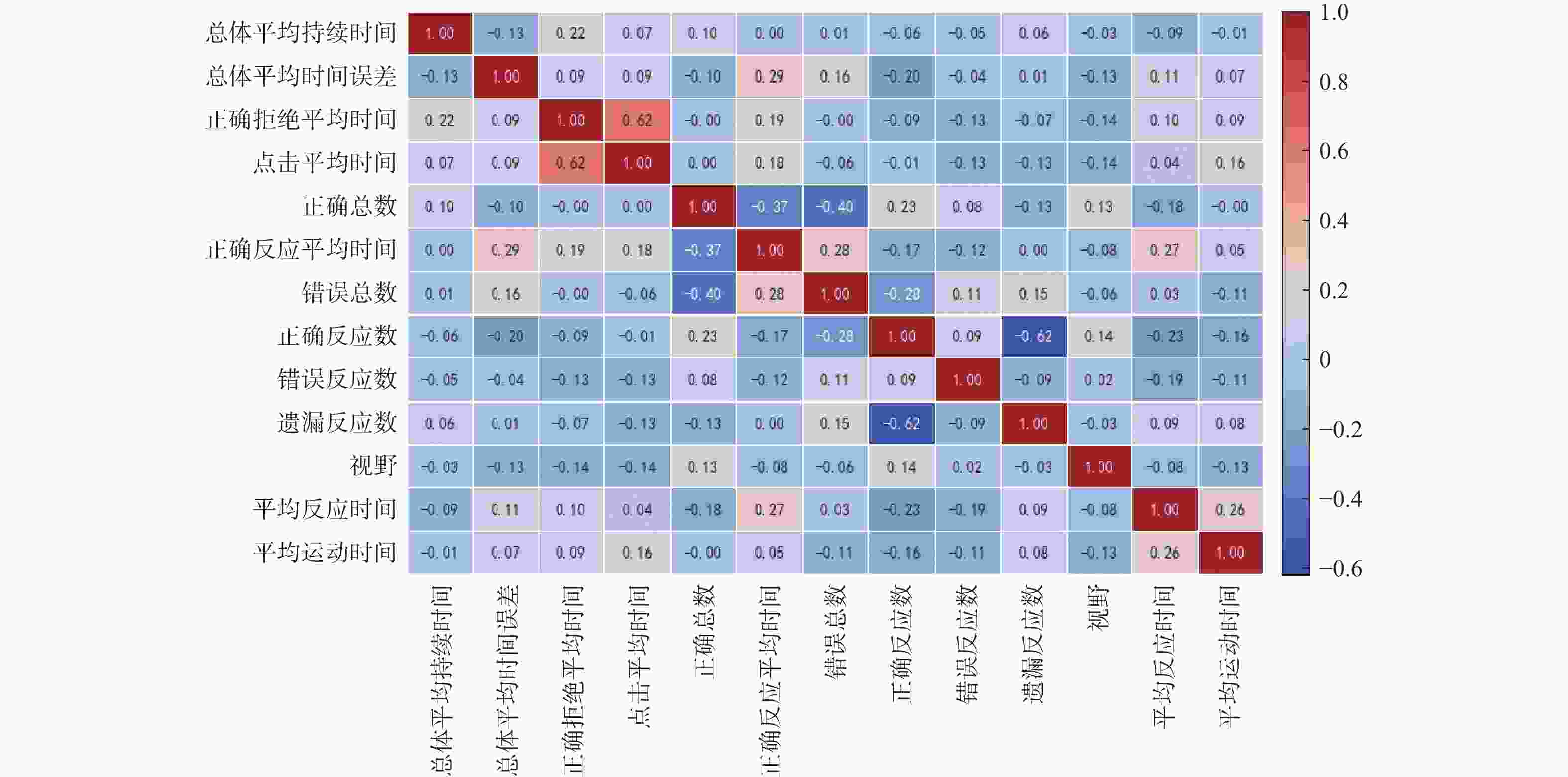
摘要: 运用维也纳测试系统(Vienna test system, VTS)对354名地铁司机的认知能力进行测评,通过K-means聚类算法对VTS数据进行无监督学习建模,得到司机认知能力分类模型。以Recall值最大为目标函数,对认知能力分类模型进行XGBoost训练和优化,采用SHAP算法对模型中各项认知能力特征指标的重要度进行分析,识别出平均反应时间、正确总数和视野范围三项关键因素以及它们之间的交互作用。研究结果用于认知与应急能力领域,可为地铁司机的遴选、在岗测评和培训提供一种更精确的工具。Abstract: Cognitive abilities of 354 metro train drivers were assessed by using the Vienna test system (VTS). An unsupervised learning model was developed through K-means clustering algorithm on the VTS data to establish a cognitive ability classification model. With the maximum Recall value as the objective function, XGBoost training and optimization were performed on the classification model. SHAP algorithm was employed to analyze the importance of various cognitive ability feature indicators in the model, and three key factors that mean reaction time, total correct responses, visual field range, as well as their interactions were identified. The research results can provide a more precise tool for the selection, on-the-job assessment, and training of metro train drivers when applied to the field of cognition and emergency capabilities.
-
表 1 混淆矩阵
Table 1. Confusion matrix
真实状态 预测状态 0类司机 1类司机 0类司机 TP FN 1类司机 FP TN -
[1] 周晓勤. 中国城市轨道交通发展战略与“十四五”发展思路[J] . 城市轨道交通,2020(11):16 − 21. [2] 宋俊福. 铁路车站值班员应急处置能力评价体系构建[J] . 铁道运输与经济,2022,44(1):112 − 119, 133. [3] 潘雨帆, 史磊, 周宏宇等. 基于LSTM-Attention的高速铁路司机警觉度预测[J] . 铁道学报,2023,45(11):29 − 37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2023.11.004 [4] 何静, 丁晨辉, 刘伟. 地铁列车司机压力知觉的潜在剖面及影响因素[J] . 中国健康心理学杂志,2023,31(9):1359 − 1364. [5] 郑刚, 俎兆飞, 孔祚. 基于驾驶员反应时间的自动紧急制动避撞策略[J] . 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学),2020,34(12):45 − 52. [6] GUO M, HU L, YE L. Cognition and driving safety: How does the high-speed railway drivers’s cognitive ability affect safety performance[J] . Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour,2019,65:10 − 22. doi: 10.1016/j.trf.2019.07.006 [7] ASCHENBRENNER A J, MURPHY S A, DOHERTY J M, et al. Neuropsychological correlates of changes in driving behavior among clinically healthy older adults[J] . The Journals of Gerontology: Series B,2022,77(10):1769 − 1778. doi: 10.1093/geronb/gbac101 [8] LI G, LAI W, SUI X, et al. Influence of traffic congestion on driver behavior in post-congestion driving[J] . Accident Analysis & Prevention,2020,141:105508. [9] LE A S, SUZUKI T, AOKI H. Evaluating driver cognitive distraction by eye tracking: From simulator to driving[J] . Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives,2020,4:100087. doi: 10.1016/j.trip.2019.100087 [10] 王清源, 黄远春, 刘志钢. 基于VTS测评的轨道交通驾驶员职业素质能力与大五人格特质的相关性分析[J] . 物流科技,2022,45(3):77 − 80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3100.2022.03.019 [11] 刘海江, 吴雨林. 基于PCA-SVM的DCT汽车驾驶员起步意图识别[J] . 汽车工程学报,2021,11(5):369 − 378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1469.2021.05.08 [12] HASAN B M S, ABDULAZEEZ A M. A review of principal component analysis algorithm for dimensionality reduction[J] . Journal of Soft Computing and Data Mining,2021,2(1):20 − 30. [13] 王丽芳, 刘泽, 何科毅, 等. 基于主成分分析和聚类分析的再造烟叶综合品质评价[J] . 品牌与标准化,2023(1):121 − 123. [14] CHEN T, GUESTRIN C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system[C] //Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: IEEE, 2016: 785−794. [15] XU J, ZHANG Y, MIAO D. Three-way confusion matrix for classification: A measure driven view[J] . Information Sciences,2020,507:772 − 794. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.06.064 [16] YACOUBY R, AXMAN D. Probabilistic extension of precision, recall, and f1 score for more thorough evaluation of classification models[C] //Proceedings of the First Workshop on Evaluation and Comparison of NLP Systems. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020: 79−91. [17] LUNDBERG S , LEE S I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions[C] //Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach: NIPS, 2017. [18] 聂小虎, 吴东平, 安静仪, 等. 基于LightGBM和SHAP的地铁短时进站客流预测及影响因素分析[J] . 铁道经济研究,2023(5):50 − 55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9746.2023.05.010 -





 下载:
下载: