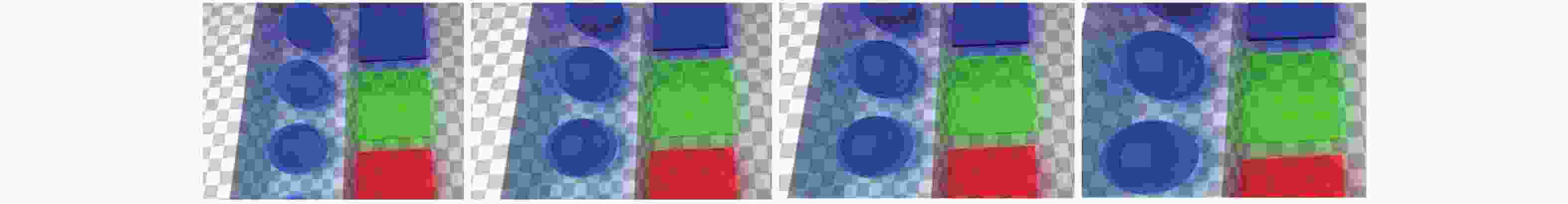
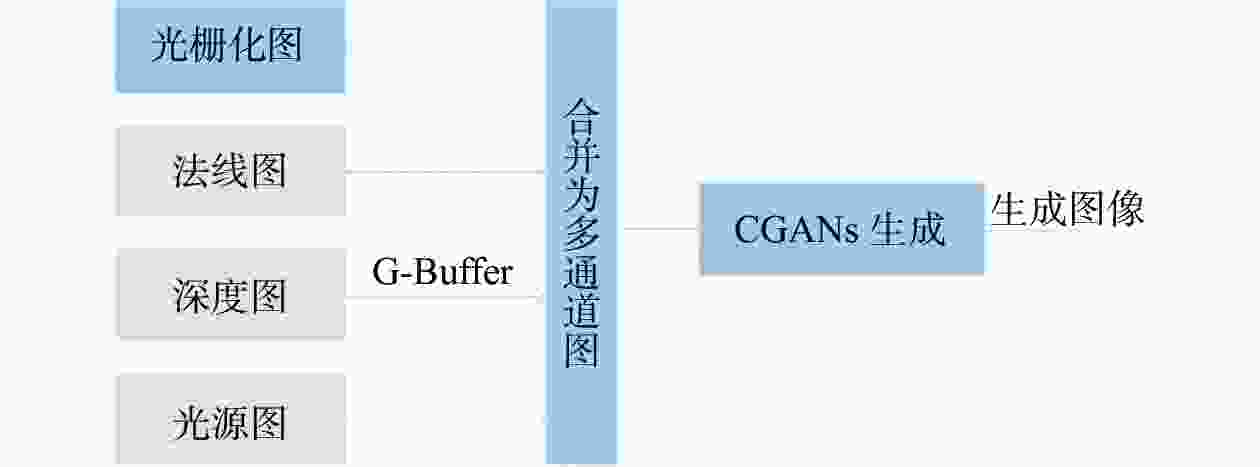
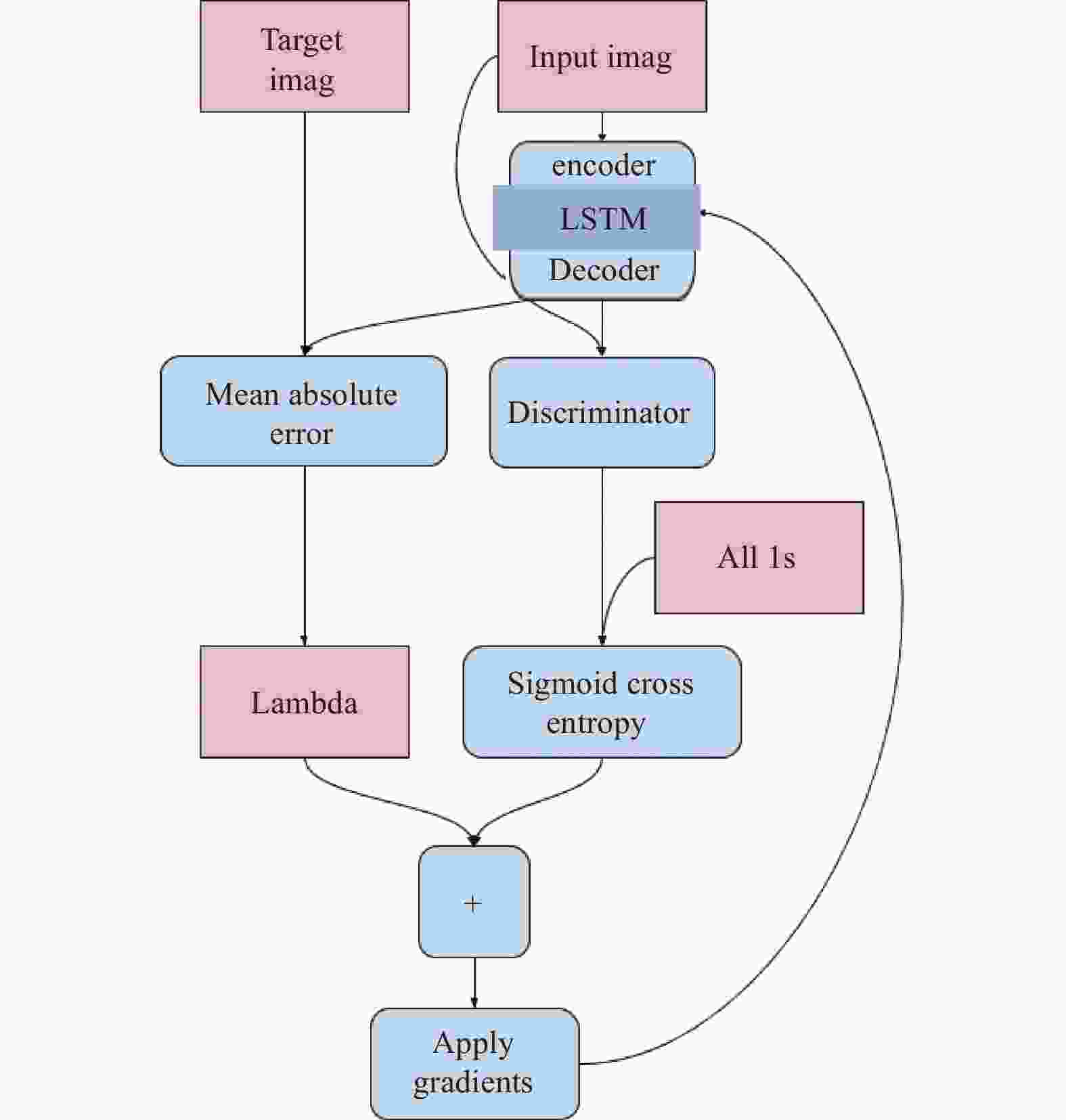
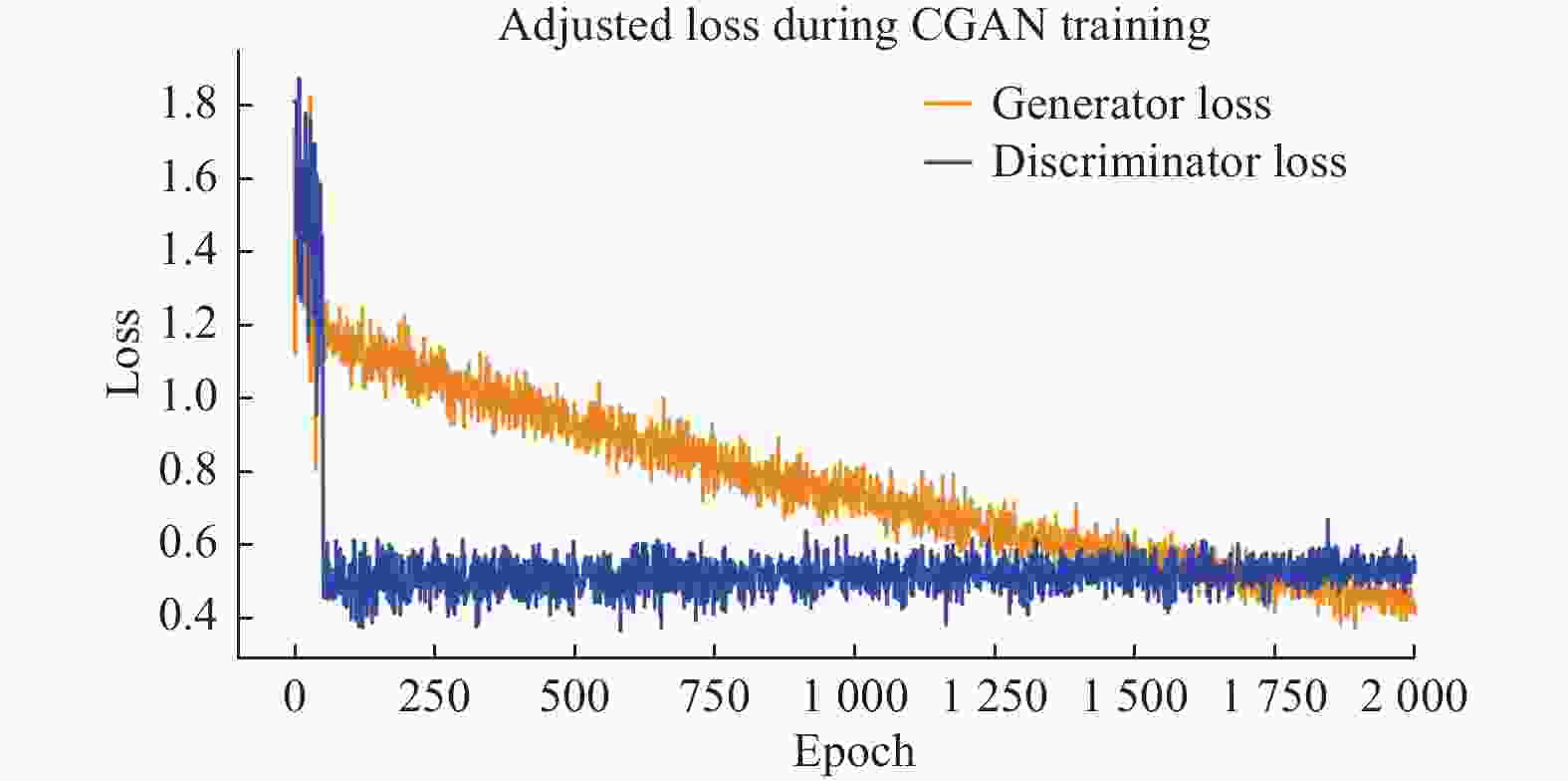
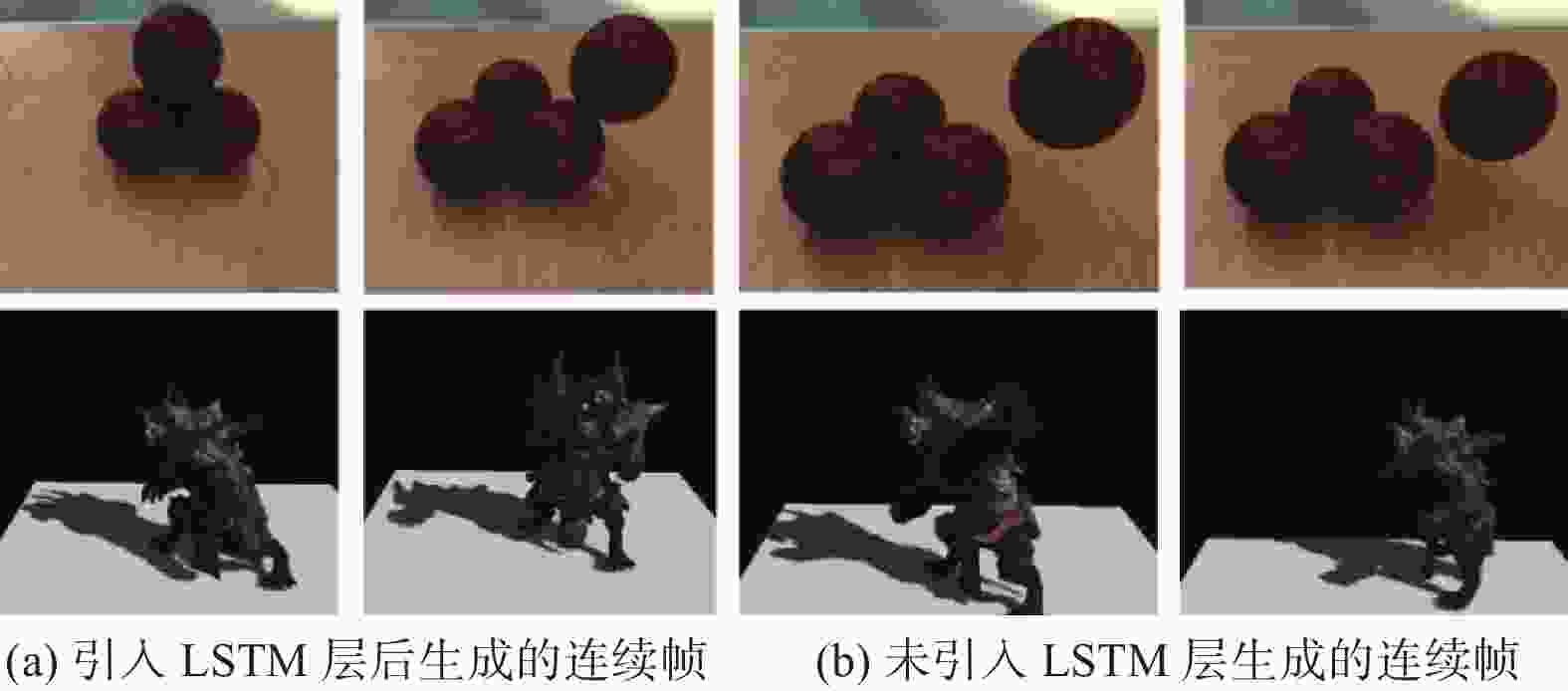
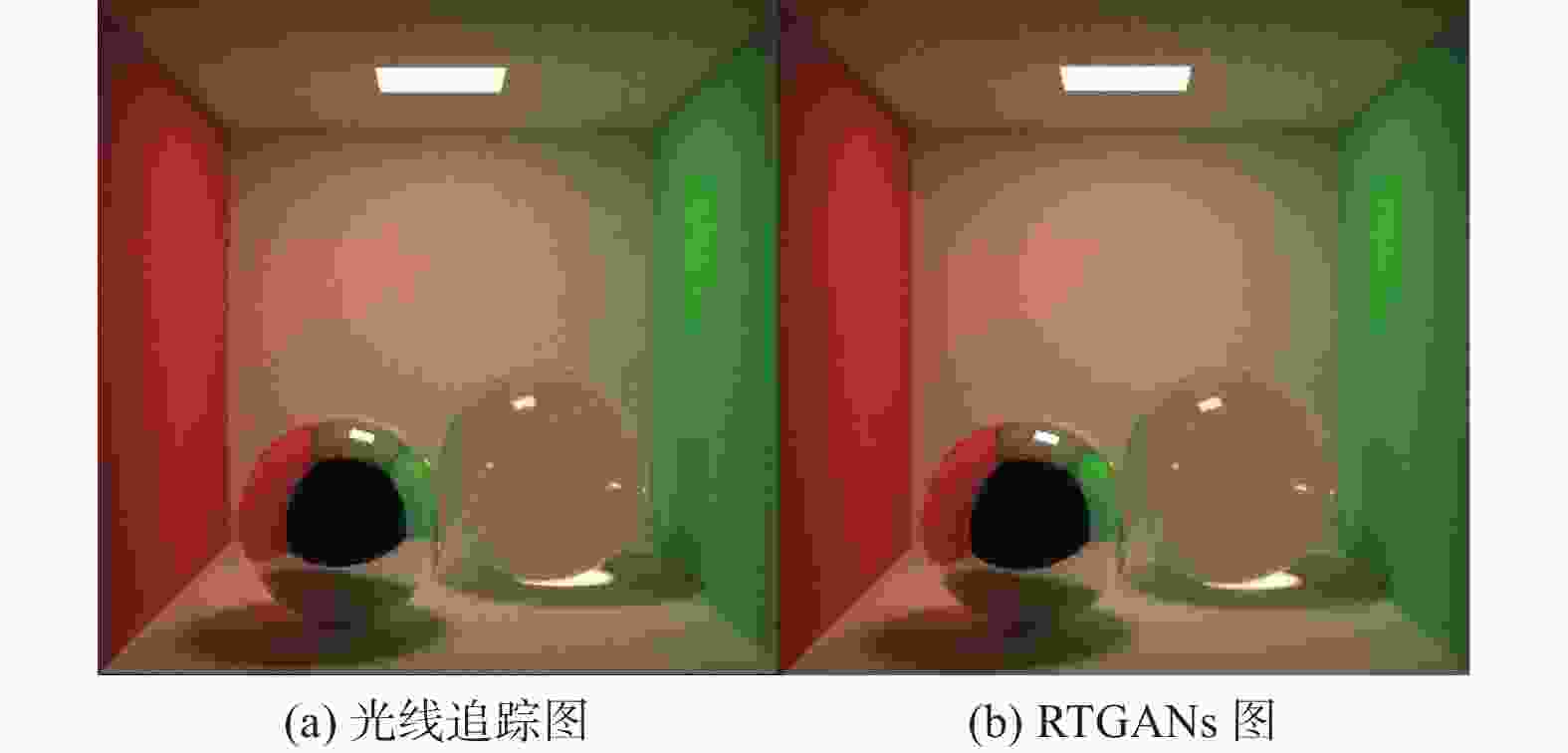
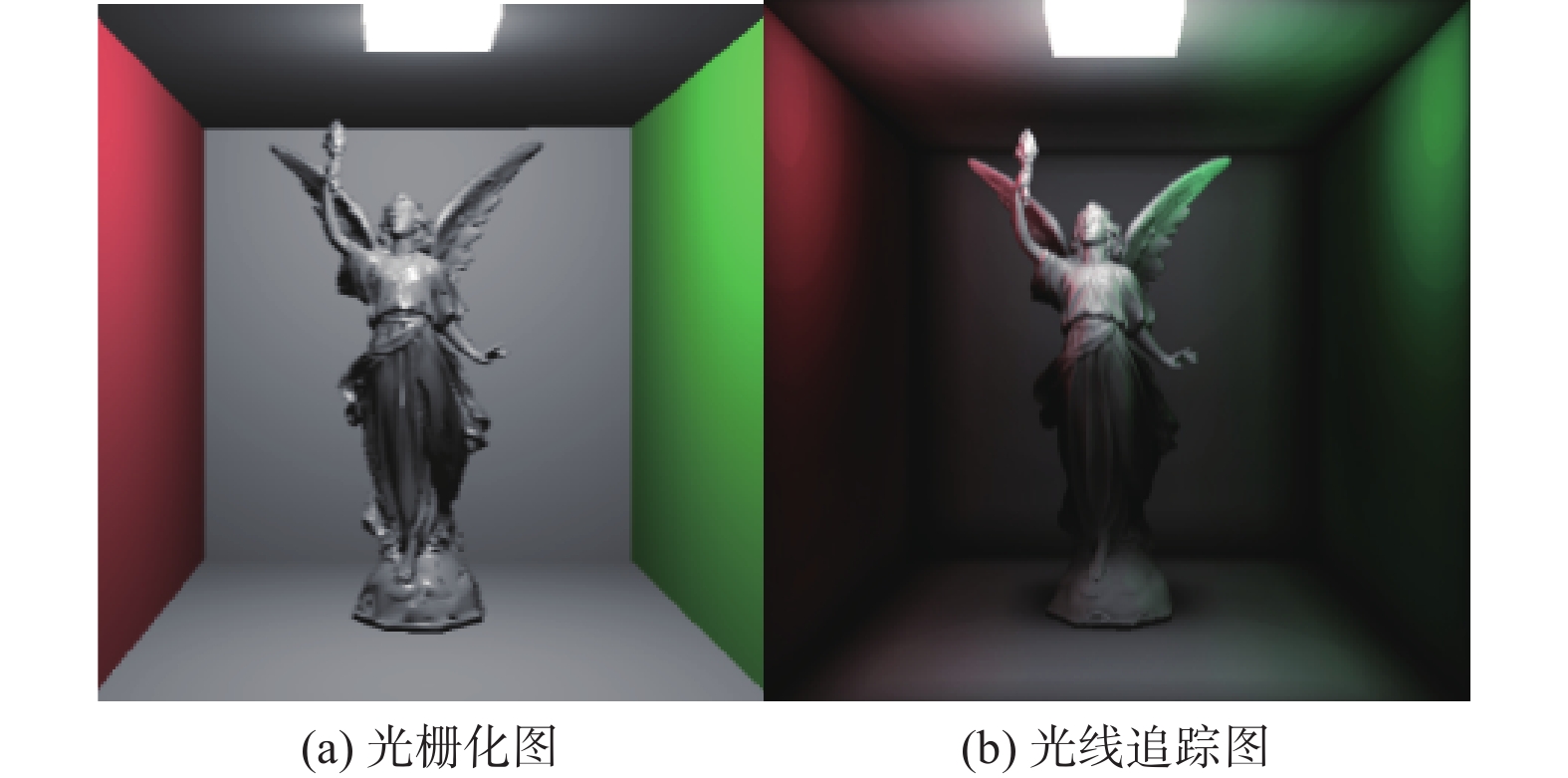
High-quality dynamic real-time rendering method based on conditional generative adversarial networks
-
摘要: 聚焦计算机图形学中的实时渲染挑战,通过结合光栅化技术和优化后的条件生成式对抗网络(conditional generative adversarial networks, CGANs),实现实时生成近似光线追踪图像,解决现有研究中生成的帧与帧之间不连贯的问题,实现实时性、真实感和视觉连贯性之间的优化平衡。基于Pix2PixGAN架构,对CGANs进行结构、数据输入和损失函数方面的改进,并利用Unity和Blender构建一套训练渲染数据集。结果表明,本研究提出的渲染方法在关键性能指标上优于传统方法,显著提升了图像生成的质量以及帧与帧之间的连贯性。Abstract: Focusing on the challenge of real-time rendering in computer graphics, integrating rasterization techniques with optimized conditional generative adversarial networks (CGANs), real-time generation of approximate ray-traced images was achieved, the issue of discontinuity between frames in existing research was effectively addressed, and optimized balances among real-time performance, realism, and visual coherence were achieved. Based on Pix2PixGAN architecture, the structure, data input and loss functions of CGANs were improved, a training rendering dataset using by Unity and Blender was constructed. Experimental results demonstrate that our rendering method can surpass traditional approaches in key performance metrics, enhance the quality of image generation and the coherence between frames.
-
表 1 帧间差异度量指标
Table 1. Frame-to-frame difference metric
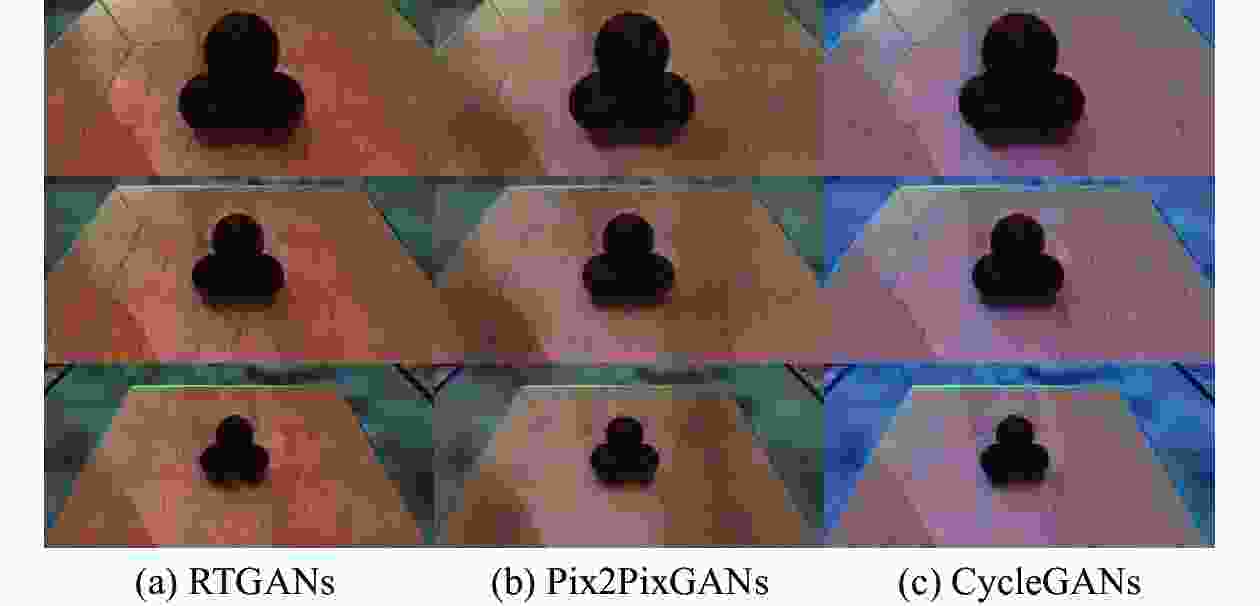
方法 SSIM 光流误差 MSE RTGANs 0.96 0.02 5 Pix2PixGANs 0.90 0.08 11 CycleGANs 0.84 0.20 30 表 2 渲染质量评估结果
Table 2. Rendering quality assessment results
渲染方法 渲染时间/s L1 L2 SSIM FID VIF 光栅化 0.04 0.15 0.06 0.85 45 0.70 光线追踪 5.20 0 0 1.00 0 1.00 RTGANs 0.08 0.10 0.04 0.93 25 0.85 屏幕空间技术 0.15 0.13 0.05 0.88 35 0.75 -
[1] GOODFELLOW I, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J] . Communications of the ACM,2020,63(11):139 − 144. doi: 10.1145/3422622 [2] VASILAKIS A A, VARDIS K, PAPAIOANNOU G. A survey of multifragment rendering[J] . Computer Graphics Forum, 2020, 39(2): 623−642. DOI: 10.1111/cgf.14019. [3] TAN P. Phong reflectance model[C] //IKEUCHI K. Computer vision. Boston: Springer, 2020: 1−3. [4] WANG Z J. Implementation of shading techniques based on OpenGL[J] . Applied Mechanics and Materials,2014,577:1038 − 1042. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.577.1038 [5] LAURITZEN A. Deferred rendering for current and future rendering pipelines[EB/OL] . https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/deferred-rendering-for-current-and-future-rendering-pipelines. [6] BEUG A P. Screen space reflection techniques[D] . Regina: Faculty of Graduate Studies and Research, University of Regina, 2020. [7] DONG Y Z, PENG C. Multi-GPU multi-display rendering of extremely large 3D environments[J] . The Visual Computer,2023,39(12):6473 − 6489. doi: 10.1007/s00371-022-02740-7 [8] DUTRÉ P, BALA K, BEKAERT P, et al. Advanced global illumination[M] . Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2018. [9] MÜLLER T, ROUSSELLE F, NOVÁK J, et al. Real-time neural radiance caching for path tracing[J] . ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG),2021,40(4):1 − 16. [10] HU J, YIP M K , ALONSO G E, et al. Efficient real-time dynamic diffuse global illumination using signed distance fields[J] . The Visual Computer,2021,37:2539 − 2551. doi: 10.1007/s00371-021-02197-0 [11] OUYANG Y, LIU S Q, KETTUNEN M, et al. ReSTIR GI: Path resampling for real-time path tracing[J] . Computer Graphics Forum, 2021,40(8): 17−29. [12] XIE F, MISHCHUK P, HUNT W, et al. Real time cluster path tracing[C] //Proceedings of SIGGRAPH Asia 2021 Technical Communications. Tokyo: SIGGRAPH, 2021: 1−4. [13] IGLESIAS GUITIÁN J A, MANE P S, MOON B, et al. Real-time denoising of volumetric path tracing for direct volume rendering[J] . IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics,2022,28(7):1 − 15. [14] HUO Y, YOON S E. A survey on deep learning-based Monte Carlo denoising[J] . Computational Visual Media,2021,7(2):169 − 185. doi: 10.1007/s41095-021-0209-9 [15] MARA M, MCGUIRE M, NOWROUZEZAHRAI D, et al. Deep G-buffers for stable global illumination approximation[J] . IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics,2017,24(4):1408 − 1421. [16] ABBAS F, MALAH M, BABAHENINI M C. Approximating global illumination with ambient occlusion and environment light via generative adversarial networks[J] . Pattern Recognition Letters,2023,166:209 − 217. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2022.12.007 [17] WANG Q, ZHONG Z Z, HUO Y C, et al. State of the art on deep learning-enhanced rendering methods[J] . Machine Intelligence Research,2023,20(6):799 − 821. doi: 10.1007/s11633-022-1400-x [18] GOMES T, ESTEVAO L, DE TOLEDO R, et al. A survey of glsl examples[C] //Proceedings of the 25th SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images Tutorials. Ouro Preto: IEEE, 2012: 60−73. [19] RATH A, GRITTMANN P, HERHOLZ S, et al. EARS: Efficiency-aware Russian roulette and splitting[J] . ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG),2022,41(4):1 − 14. [20] TANG H, XU D, YAN Y, et al. Multi-channel attention selection gans for guided image-to-image translation[J] . IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2022,45(5):6055 − 6071. [21] ISOLA P, ZHU J Y, ZHOU T H, et al. Pix2Pix gan for image-to-image translation[EB/OL] . (2016-11-21)[2023-12-15] . https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.07004. [22] STAUDEMEYER R C, MORRIS E R. Understanding LSTM: A tutorial into long short-term memory recurrent neural networks[J] . arXiv, 2019. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1909.09586. [23] PAN Z, YU W J, WANG B S, et al. Loss functions of generative adversarial networks (GANs): Opportunities and challenges[J] . IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence,2020,4(4):500 − 522. doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2020.2991774 [24] LI M, HSU W, XIE X D, et al. SACNN: Self-attention convolutional neural network for low-dose CT denoising with self-supervised perceptual loss network[J] . IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging,2020,39(7):2289 − 2301. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.2968472 [25] XU J, LI Z, DU B, et al. Reluplex made more practical: Leaky ReLU[C] //Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC). Rennes: IEEE, 2020: 1−7. [26] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C] //Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego: ICLR, 2014. DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.1412.6980. -





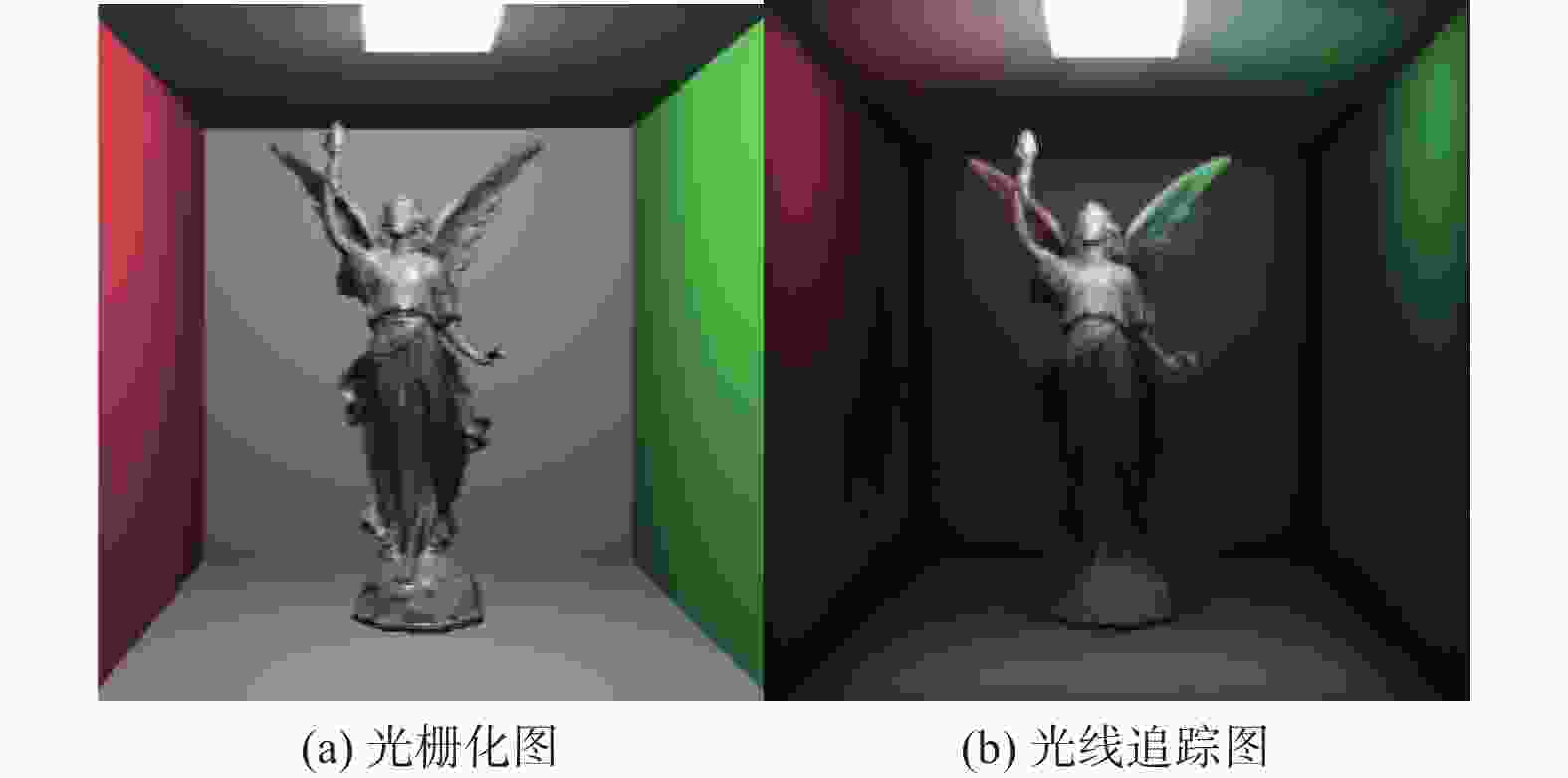
 下载:
下载: