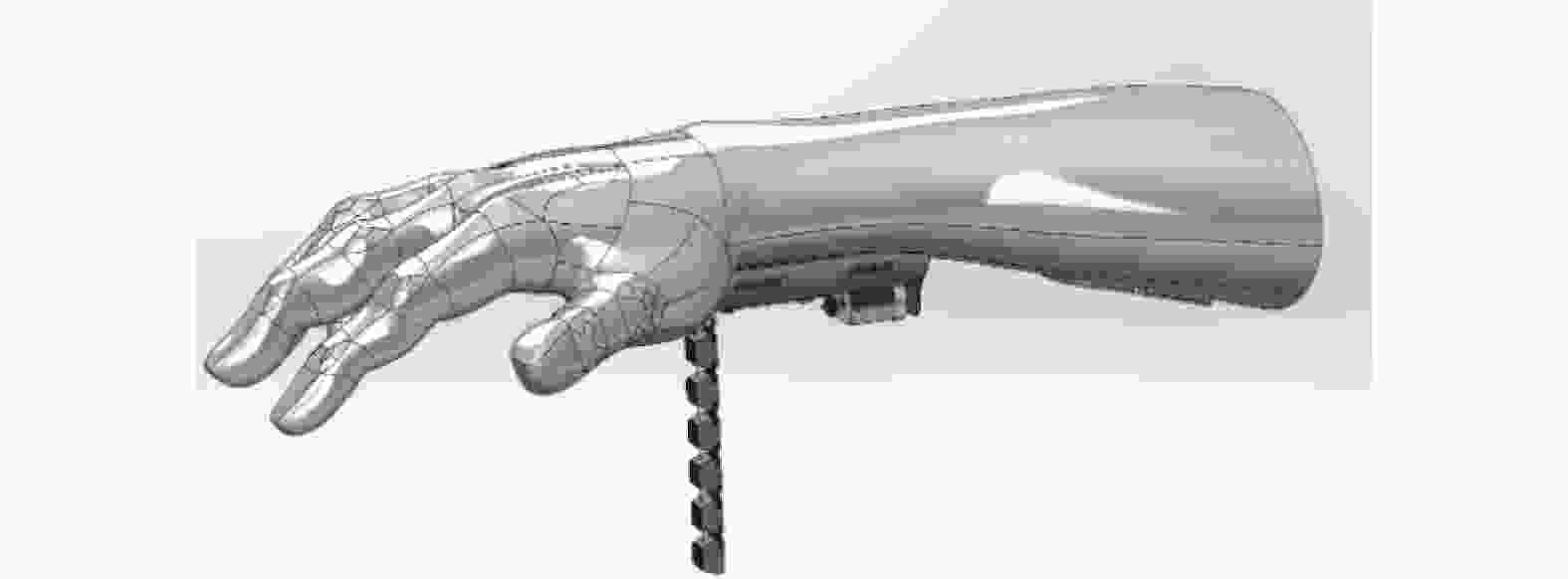
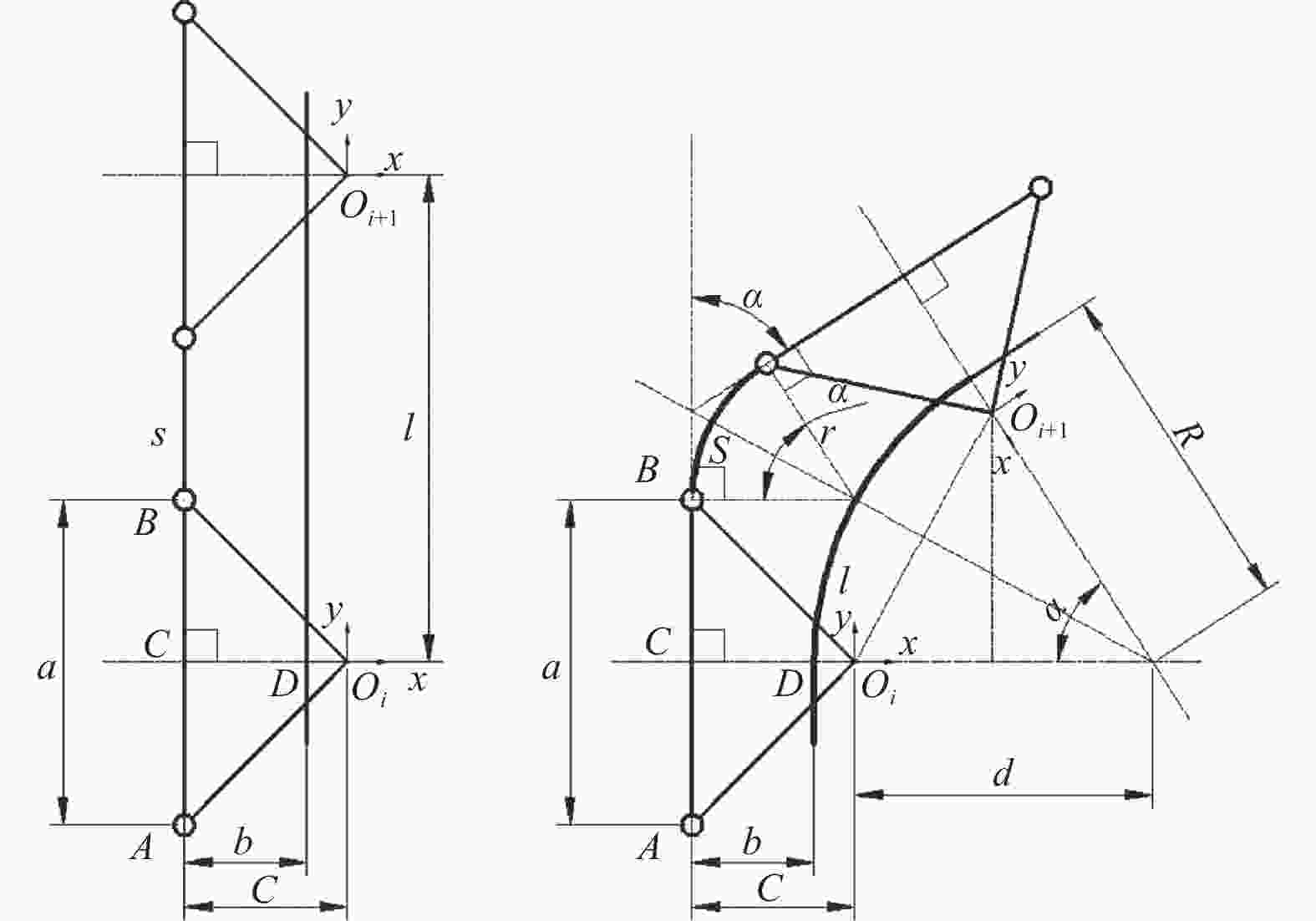
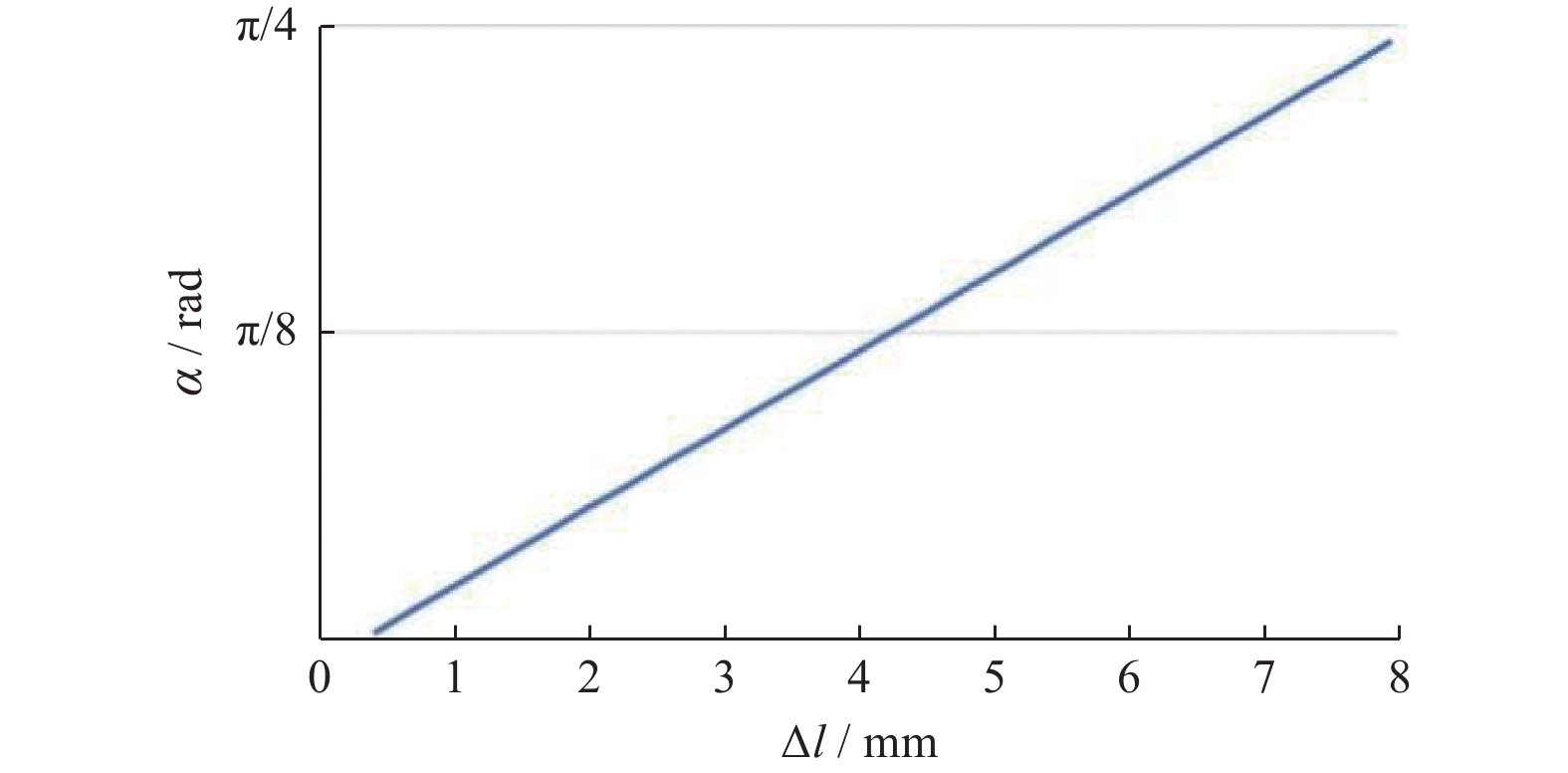
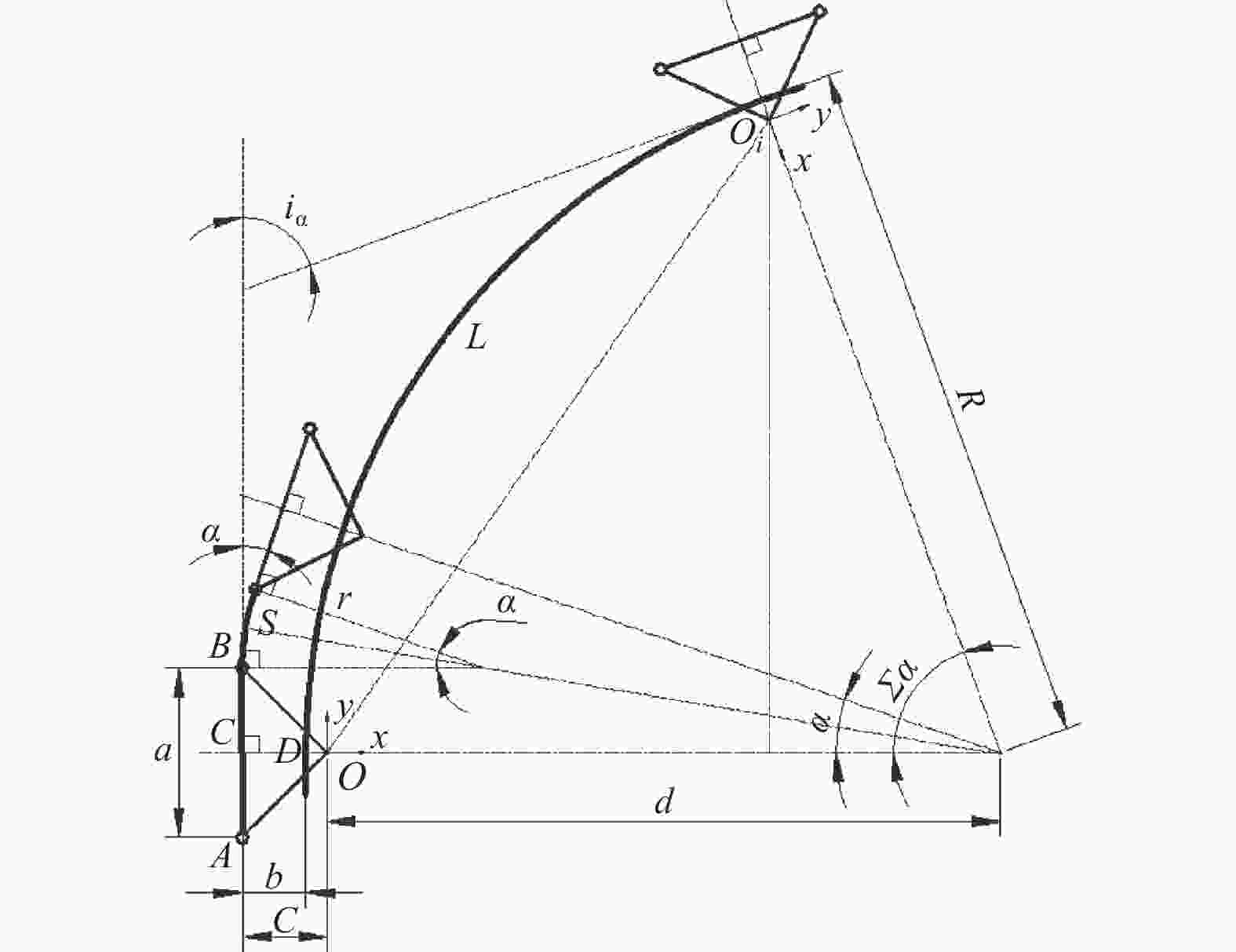
Kinematic modeling and grasp quality analysis and simulation of a supernumerary finger for disabled grasping assistant
-
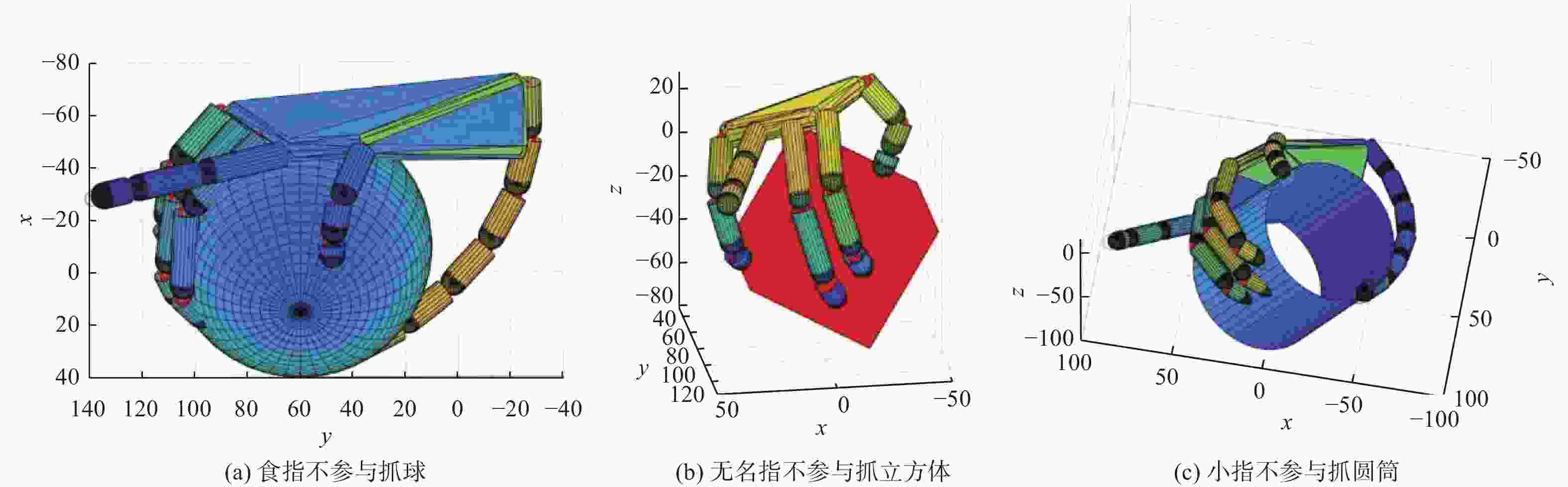
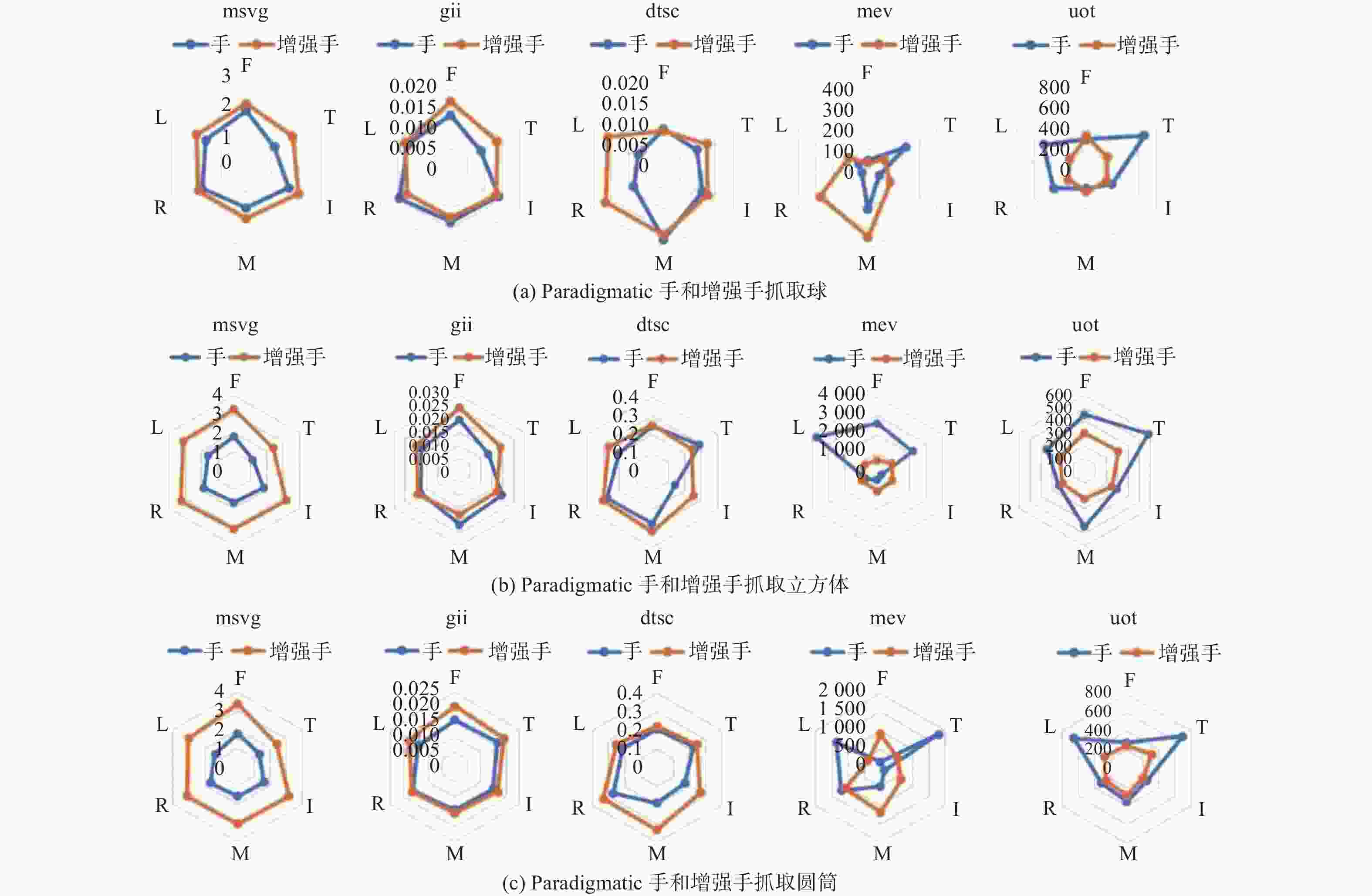
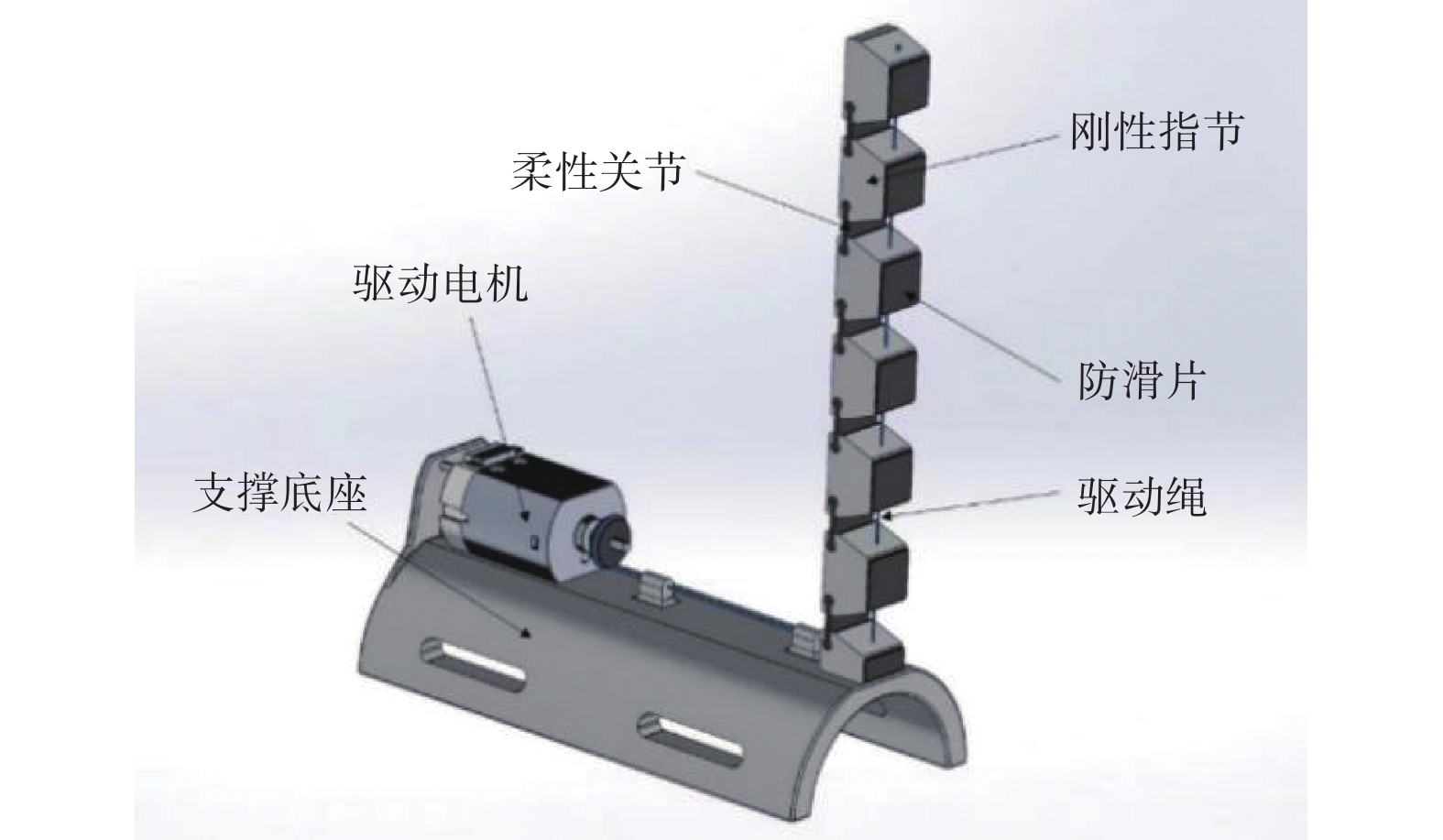
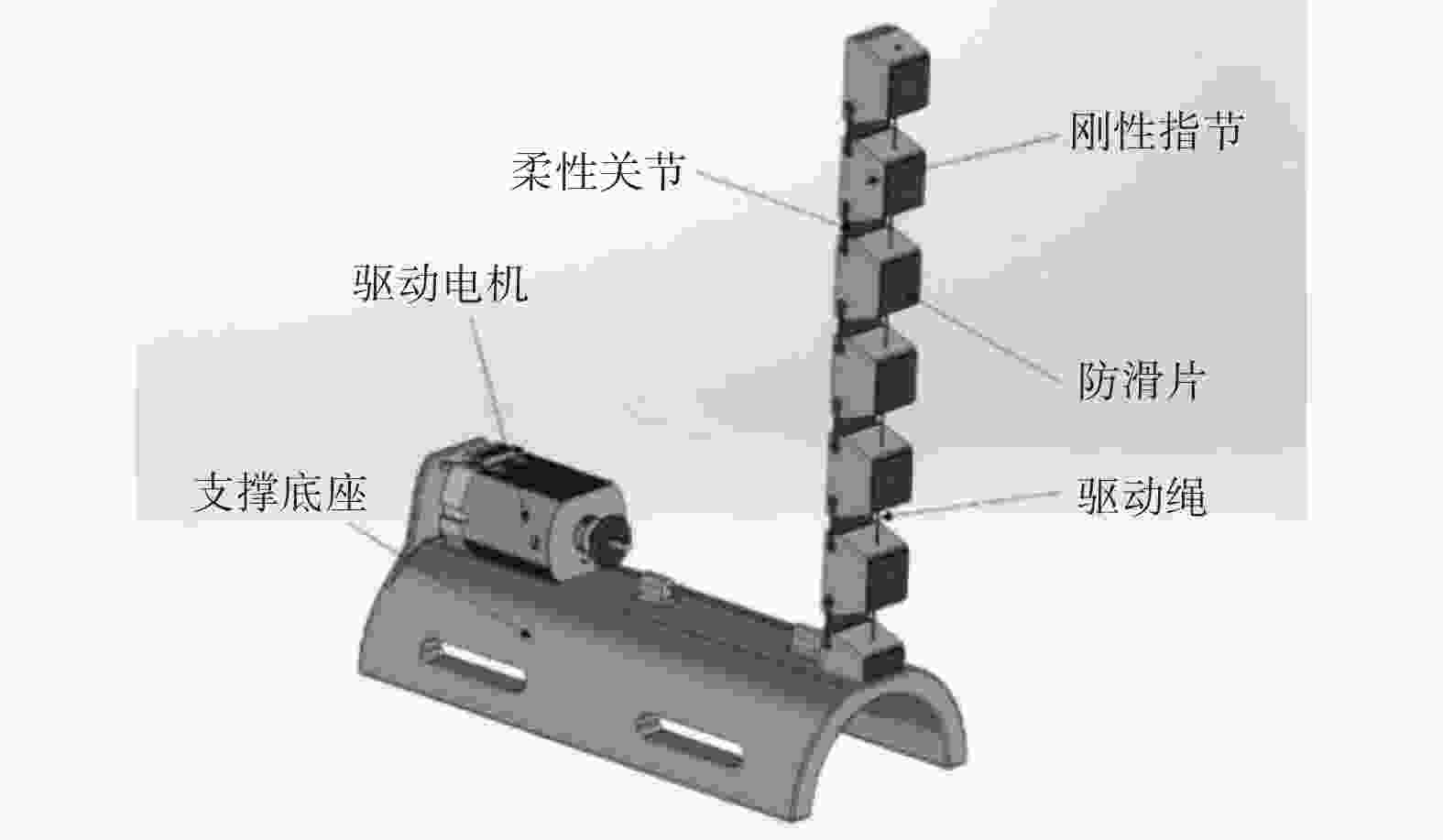
摘要: 提出一种用于助残抓取的外手指机器人。对外手指进行运动学分析,分别给出外手指弯曲单元和外手指整体在驱动空间、关节空间、操作空间之间的映射关系,以抓取系统的准静态分析为基础,列举5种用于评估抓取质量指标。利用Matlab平台的Syngrasp工具箱,建立人手穿戴外手指时的增强手抓取模型,分别进行手和增强手的抓取仿真,比较抓取质量指标。结果表明,穿戴外手指能够提高人手抓取物品时的抓取质量。Abstract: A supernumerary robotic finger for disabled people grasping was proposed. The kinematic analysis of the supernumerary finger was carried out, providing mapping relationships between the bending unit and the overall supernumerary finger across the driving space, joint space and operational space. On the basis of a quasi-static analysis of the grasp system, five indexes for measuring the grasp quality were listed. Using the Syngrasp toolbox based on Matlab platform, a grasp model of augmented hand which contained human hand wearing a supernumerary finger was established, grasp simulations of the natural hand and the augmented hand were performed, and the grasp quality indexes were compared. The result demonstrates that wearing the supernumerary finger can improve the quality of grasping objects with the human hand.
-
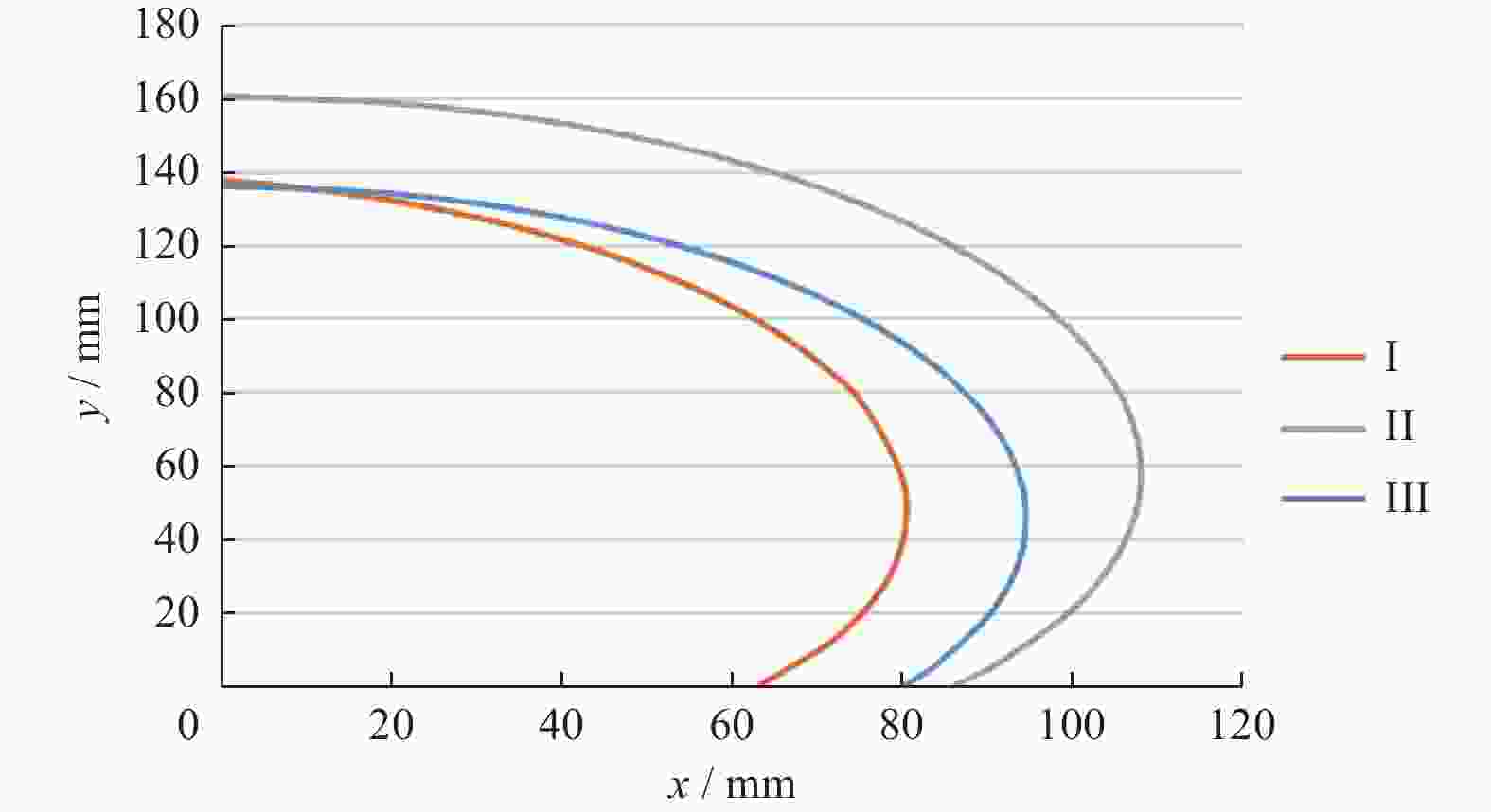
表 1 弯曲单元参数取值
Table 1. Geometric parameters of bending unit
单位:mm 指节长度a 驱动绳定位b 指节厚度c 关节长度s 10 10 12 13 -
[1] 刘德斌, 王旦, 陈柏, 等. 外肢体机器人研究综述[J] . 浙江大学学报(工学版),2021,55(2):251 − 258. [2] PRATTICHIZZO D, MALVEZZI M, HUSSAIN I, et al. The sixth-finger: a modular extra-finger to enhance human hand capabilities[C] //Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Robot & Human Interactive Communication. Edinburgh: IEEE, 2014: 993−998. [3] TIZIANI L, HART A, CAHOON T, et al. Empirical characterization of modular variable stiffness inflatable structures for supernumerary grasp-assist devices[J] . The International Journal of Robotics Research,2017,36(13/14):1391 − 1413. doi: 10.1177/0278364917714062 [4] CUNNINGHAM J. The supernumerary robotic 3rd thumb for skilled music tasks[C] //Proceedings of 2018 7th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (Biorob). Enschede: IEEE, 2018. [5] KIELIBA P, CLODE D, MAIMON-MOR R, et al. Robotic hand augmentation drives changes in neural body representation[J] . Science Robotics,2021,6(54): 7935. [6] MALVEZZI M, GIOIOSO G, SALVIETTI G, et al. SynGrasp: a Matlab toolbox for grasp analysis of human and robotic hands[C] //Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Karlsruhe: IEEE, 2013. [7] 彭登靖. 基于动作学习与模仿的助老助残智能机器人系统研究与设计[D] . 昆明: 云南大学, 2019. [8] LIU C, SUN F, BAN X. An effective method for grasp planning on objects with complex geometry combining human experience and analytical approach[J] . Science China(Information Sciences),2016,59(11):170 − 181. [9] 洪峥. 基于神经网络算法的搬运机器人动力学性能控制[D] . 芜湖: 安徽工程大学, 2016. [10] 姜启源. 大学数学实验[M] . 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015: 113. [11] ROA M, SUÁREZ R. Grasp quality measures: review and performance[J] . Autonomous Robots,2015,38(1):65 − 88. [12] MALVEZZI M, GIOIOSO G, SALVIETTI G, et al. SynGrasp: a Matlab toolbox for underactuated and compliant hands[EB /OL] . (2015-09-24)[2022-05-13] . http://SynGrasp.dii.unisi.it. -





 下载:
下载: