Study on flow field and heat transfer mechanism of nanofluid minimal quantity lubrication machining for Ti6Al4V
-
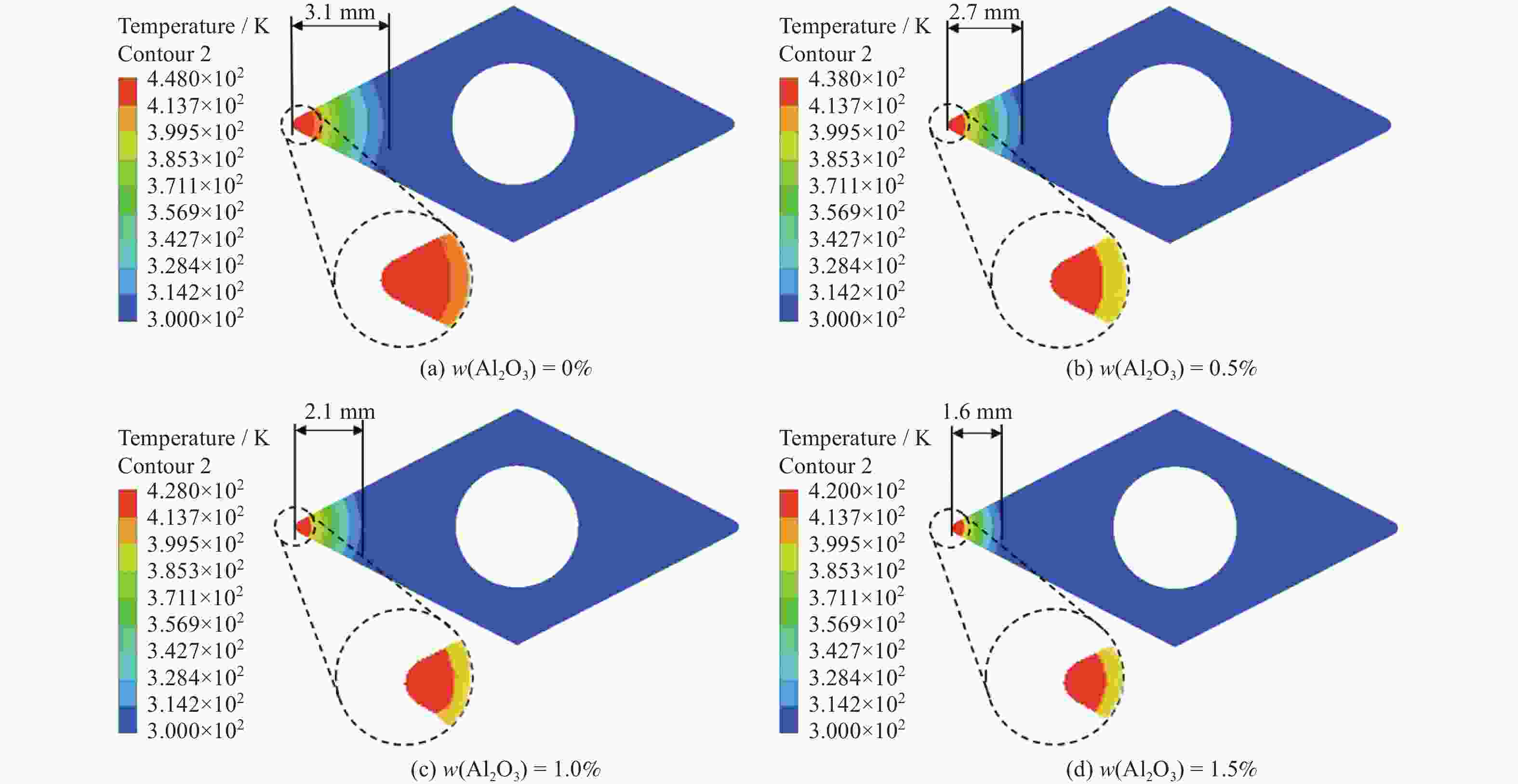
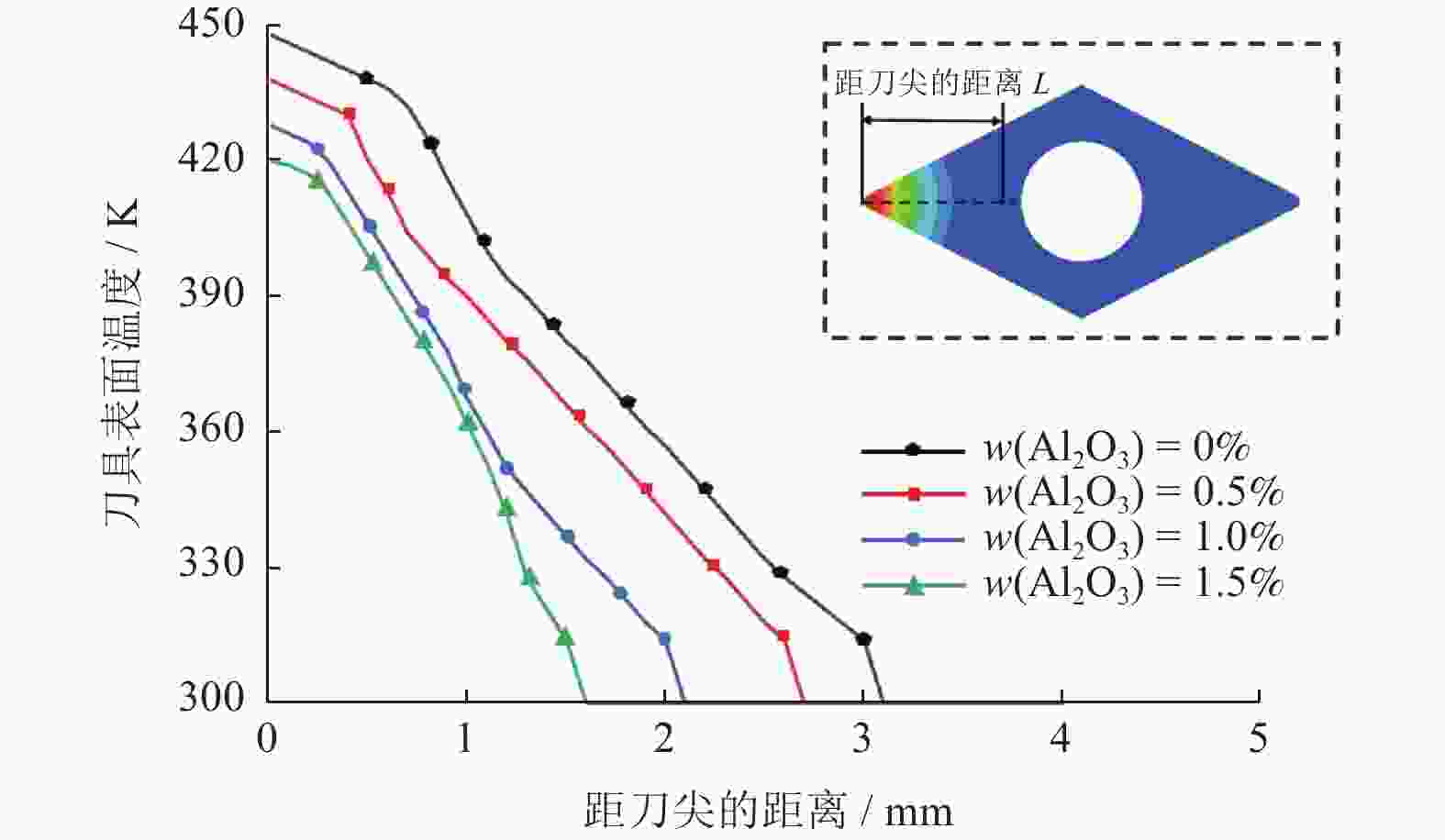
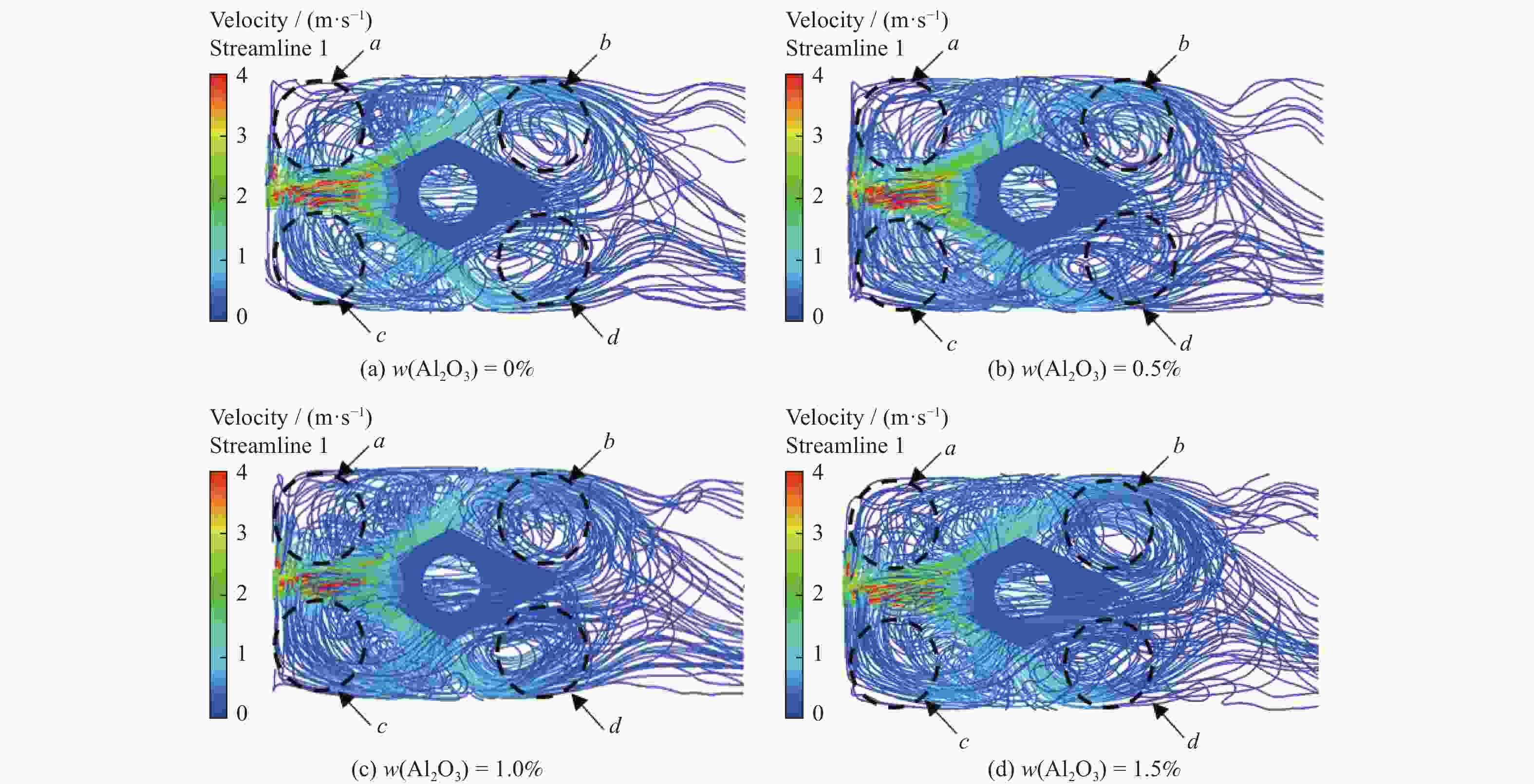
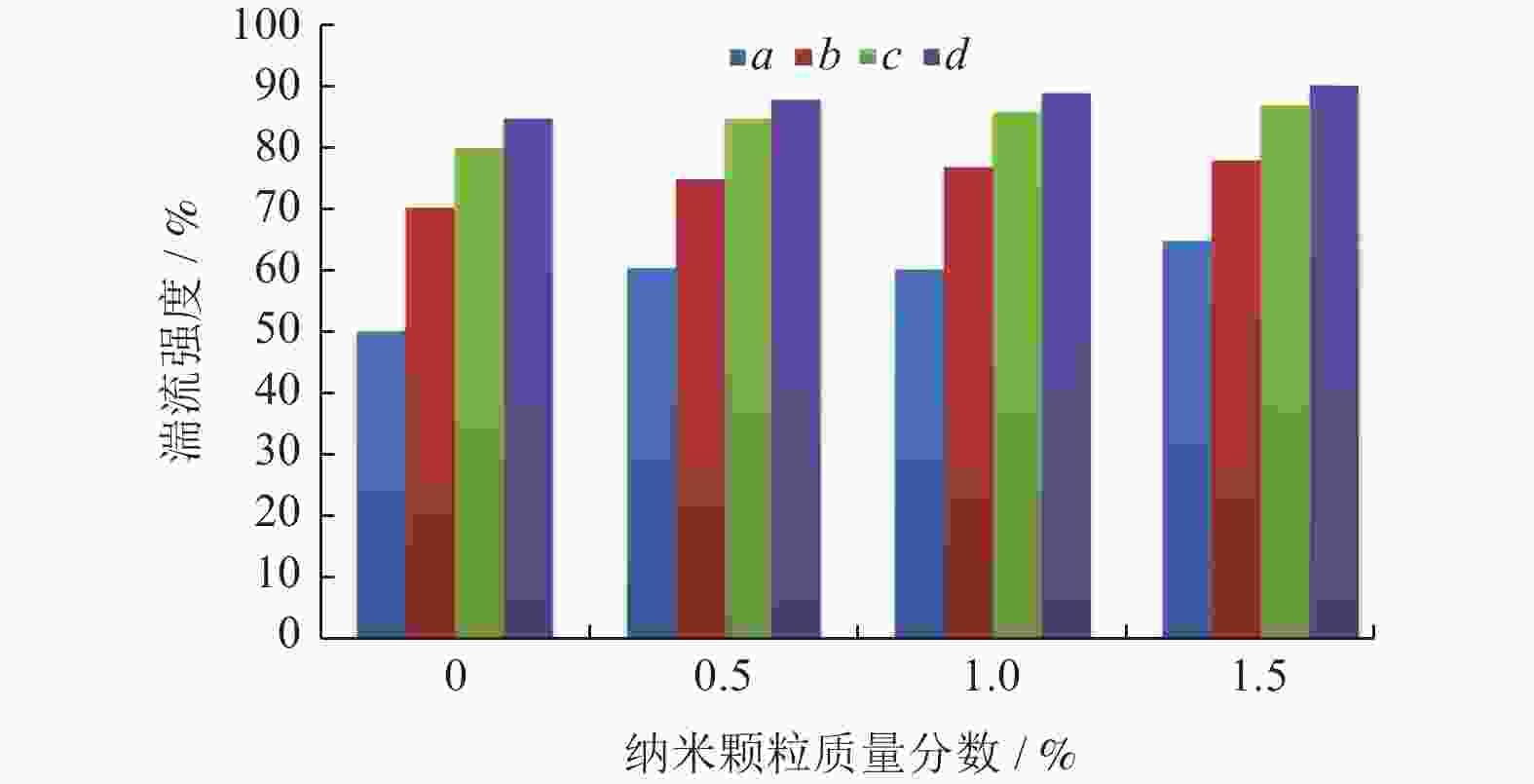
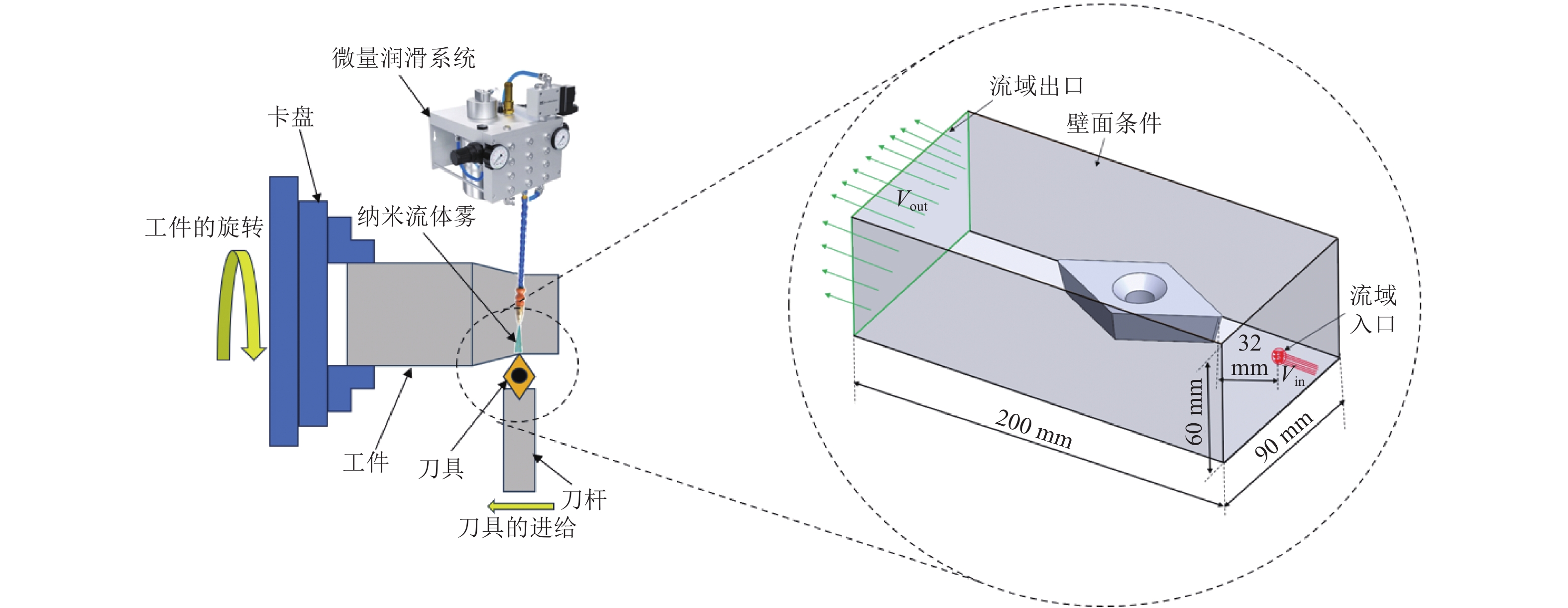
摘要: 在微量润滑(MQL)基础油中添加氧化铝(Al2O3)纳米颗粒形成纳米流体微量润滑(NMQL),采用NMQL加工可以进一步改善摩擦学状态,提高工件加工表面质量。建立三维计算流体动力学(CFD)模型并进行模拟分析,开展NMQL加工Ti6Al4V过程中的流场和传热机理研究。对CFD模型开展不同流量和入口压力等参数交叉分析,探讨不同冷却条件下NMQL对切削热的影响规律及最佳工艺参数的选择原则。进行湍流两相流和传热的有限元分析,总结在MQL基础油中添加 Al2O3)纳米颗粒对刀具表面温度分布的影响规律。研究结果表明,刀具的平均温度随着Al2O3纳米粒子质量分数的增加呈现降低趋势,刀尖附近最高温度平均降幅约为6%,有效改善了切削区域的温度分布状态。在纳米流体微量润滑加工Ti6Al4V的流场和传热方面进行探索,可为Ti6Al4V等难加工材料的加工方式和加工机理研究提供借鉴。Abstract: The addition of aluminum oxide (Al2O3) nanoparticle to minimal quantity lubrication (MQL) base oils forms nanofluid minimal quantity lubrication (NMQL). Using NMQL machining can further enhance the tribological state and improve the surface quality of workpiece. A three-dimensional computational fluid dynamic (CFD) model was developed and simulated to investigate the flow field and heat transfer mechanism during NMQL machining of Ti6Al4V. Through the CFD model, a parametric cross-analysis of different flow rates and inlet pressures was conducted to explore the effects of NMQL on cutting heat under various cooling conditions and the selection principles of optimal process parameters. Finite element analysis of turbulent two-phase flow and heat transfer was performed to sumrize the effect of adding Al2O3 nanoparticle to MQL base oil on the temperature distribution across the tool surface. The results show that the average tool temperature decreases with increasing Al2O3 nanoparticle concentration, and the maximum temperature near the tool tip decreases by about 6% on average, thus effectively improving the temperature distribution in the cutting area. The exploration of the flow field and heat transfer during NMQL machining of Ti6Al4V can provide valuable references for studying machining modes and mechanisms of difficult-to-process materials such as Ti6Al4V, offering both theoretical significance and application value.
-
表 1 基础油的性质参数
Table 1. MQL base oil properties
ρbf/
(kg·m−3)Cbf/
(J·(kg·K)−1)Kbf/
(W·(m·K)−1)μbf/
(kg·ms−1)920 1670 0.58 0.066 表 2 Al2O3纳米粒子的性质参数
Table 2. Al2O3 nanoparticle properties
ρp/(kg·m−3) Cp/(J·(kg·K)−1) Kp/(W·(m·K)−1) 3800 800 30 表 3 纳米流体雾的性质参数
Table 3. Properties of nanofluids’ mist
参数 w(Al2O3)=0.5% w(Al2O3)=1% w(Al2O3)=1.5% ρmist /(kg·m−3) 414.14 418.70 421.33 µmist/((N·s)·m−2) 0.0318 0.0325 0.0343 Kmist/(W·(m·K)−1) 0.5645 0.5774 0.5902 Cmist/(J·(kg·K)−1) 1441.32 1570.18 1703.21 -
[1] 陈德雄 , 佘青青 , 李哲 , 等. 钛合金超声振动辅助切削研究进展[J] . 精密成形工程,2020,12(5):151 − 158. [2] YANG S C, HE C S, ZHENG M L. A prediction model for titanium alloy surface roughness when milling with micro-textured ball-end cutters at different workpiece inclination angles[J] . The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2019,100(5/6/7/8):2115 − 2122. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2852-6 [3] 李宝栋, 唐林虎, 易湘斌, 等. 基于响应面分析法的Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo钛合金切削温度仿真研究[J] . 化工机械,2019,46(3):300 − 303. [4] 黎宇嘉, 黄兵, 鲁娟, 等. 基于有限元模拟的Ti6Al4V铣削过程参数多目标优化[J] . 中国机械工程,2021,32(13):1555 − 1561. [5] 王大中, 吴淑晶, 林靖朋, 等. 基于MQL 的超声椭圆振动微切削Inconel718 的机理研究[J] . 机械工程学报,2021,57(9):264 − 272. [6] WU W T, LI C H, YANG M, et al. Specific energy and G ratio of grinding cemented carbide under different cooling and lubrication conditions[J] . The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2019,105(1/2/3/4):67 − 82. [7] YANG M, LI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Research on microscale skull grinding temperature field under different cooling conditions[J] . Applied Thermal Engineering,2017,126:525 − 537. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.183 [8] 王晓铭, 李长河, 张彦彬, 等. 微量润滑赋能雾化与供给系统关键技术研究进展[J] . 表面技术,2022,51(9):1 − 14. [9] 杨简彰, 王成勇, 袁尧辉, 等. 微量润滑复合增效技术及其应用研究进展[J] . 中国机械工程,2022,33(5):506 − 528. [10] 宋宇翔, 许芝令, 李长河, 等. 纳米生物润滑剂微量润滑磨削性能研究进展[J] . 表面技术,2023,52(12):1 − 19. [11] KHANNA N, SHAH P, SARIKAYA M, et al. Energy consumption and ecological analysis of sustainable and conventional cutting fluid strategies in machining 15-5 PHSS[J] . Sustainable Materials and Technologies,2022,32:e00416. doi: 10.1016/j.susmat.2022.e00416 [12] JAMIL M, HE N, GUPTA M K, et al. Tool wear mechanisms and its influence on machining tribology of face milled titanium alloy under sustainable hybrid lubri-cooling[J] . Tribology International,2022,170:107497. doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2022.107497 [13] AN Q, LIU Z, JIANG L, et al. Experimental and numerical research on the effects of minimum quantity lubrication in thread turning of free-cutting steel AISI 1215[J] . Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B: Journal of Engineering Manufacture,2015,229(5):878 − 885. doi: 10.1177/0954405414534429 [14] 隋孟华, 张乃庆, 李长河, 等. 纳米流体微量润滑磨削硬质合金温度场模型与实验验证[J] . 制造技术与机床,2020,3:85 − 91. [15] NAJIHA M S, RAHMAN M M. A computational fluid dynamics analysis of single and three nozzles minimum quantity lubricant flow for milling[J] . International Journal of Automotive and Mechanical Engineering,2014,10:1891 − 1900. doi: 10.15282/ijame.10.2014.6.0157 [16] VAZQUEZ E, KEMMOKU D T, NORITOMI P Y, et al. Computer fluid dynamics analysis for efficient cooling and lubrication conditions in micromilling of Ti6Al4V alloy[J] . Materials and Manufacturing Processes,2014,29(11/12):1494 − 1501. doi: 10.1080/10426914.2014.941864 [17] KIM S H, LEE S W, HAN S, et al. Numerical investigation of thermal characteristics of spray cooling with minimum quantity lubrication in milling process[J] . Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2019, 65: 137−147. [18] ZHU G, YUAN S, CHEN B. Numerical and experimental optimizations of nozzle distance in minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) milling process[J] . The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2019,101:565 − 578. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2928-3 [19] PENG R, ZHAO L F, TANG X, et al. Heat transfer performance assessment of abrasive phyllotaxy arrangement in internal cooling grinding[J] . International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2022, 197: 123317. [20] DOE J, SMITH A, JOHNSON M, et al. Numerical CFD-FEM model for machining titanium Ti-6Al-4V with nano minimum quantity lubrication: a step towards digital twin[J] . Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 66: 123−145. [21] 文华. 基于CFD的柴油机喷雾混合过程的多维数值模拟[D] . 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2004. [22] KLEINSTREUER C, FENG Y. Experimental and theoretical studies of nanofluid thermal conductivity enhancement: a review[J] . Nanoscale Research Letters,2011,6:1 − 13. [23] PAK B C, CHO Y I. Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles[J] . Experimental Heat Transfer an International Journal,1998,11(2):151 − 170. doi: 10.1080/08916159808946559 -





 下载:
下载: