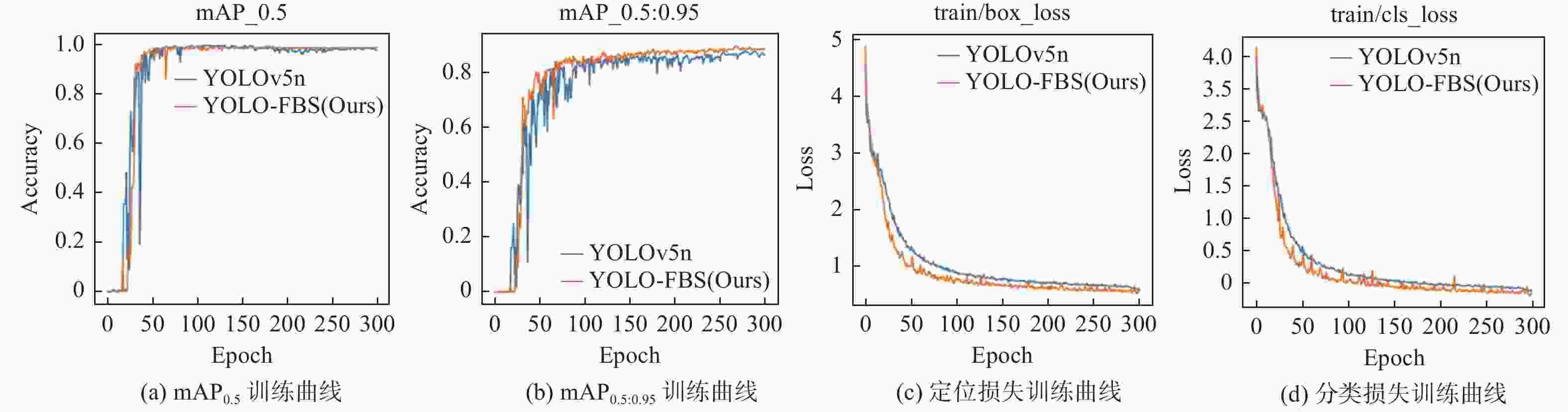
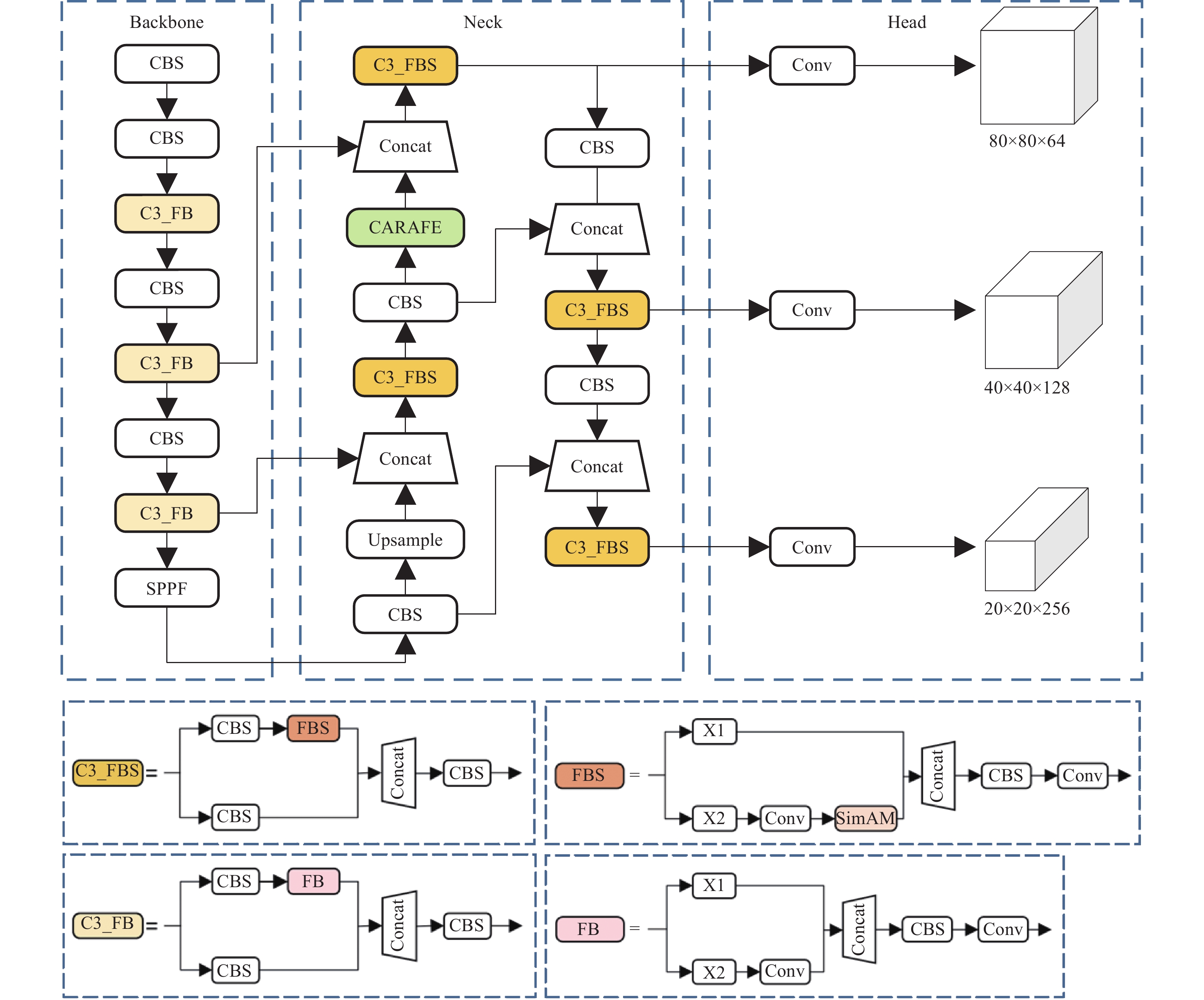
Research on lightweight rail fastener inspection model based on YOLOv5
-
摘要: 针对轨道扣件检测算法在模型参数量、检测精度和效率等方面的问题,提出一种基于YOLOv5n的轻量化网络模型YOLO-FBS。该模型嵌入了Faster Block模块,实现了网络参数轻量化的改进,引入SimAM无参数特征选择模块和CAFARE轻量级上采样模块,提升了模型的检测精度,最后采用基于LAMP分数的剪枝方式裁剪掉权重较小的通道,得到网络参数仅为0.28×106的YOLO-FBS模型,其检测精度达到89.2%,检测速度达到190.2 帧/s。该网络模型具有低参数量和高检测速度的优势,同时保证了较高的检测精度。Abstract: Aiming at the issues of model parameter size, detection accuracy, and efficiency in rail fastener detection algorithms, a lightweight network model named YOLO-FBS based on YOLOv5n was proposed. The model embeds the Faster Block module to achieve a reduction in network parameters, introduces the SimAM parameter-free feature selection module and the CAFARE lightweight upsampling module to improve detection accuracy, and finally employs LAMP score-based pruning to remove channels with lower weights. The resulting YOLO-FBS model has only 0.28×106 parameters, achieves a detection accuracy of 89.2%, and reaches a detection speed of 190.2 frames/s. This network model offers the advantages of low parameter count and high detection speed while maintaining high detection accuracy.
-
Key words:
- YOLOv5 /
- lightweight /
- SimAM /
- pruning /
- fastener detection
-
表 1 轻量化网络改进对比
Table 1. Lightweight network improvement comparison
网络 参数 FLOPs fps mAP0.5:0.95 MobileNet 2.21×106 6.3×109 138.8 0.867 GhostNet 1.98×106 5.8×109 135.3 0.876 C3_FB 2.19×106 6.3×109 161.5 0.870 表 2 各特征选择模块消融实验数据对比
Table 2. Comparison of experimental data for each feature selection module
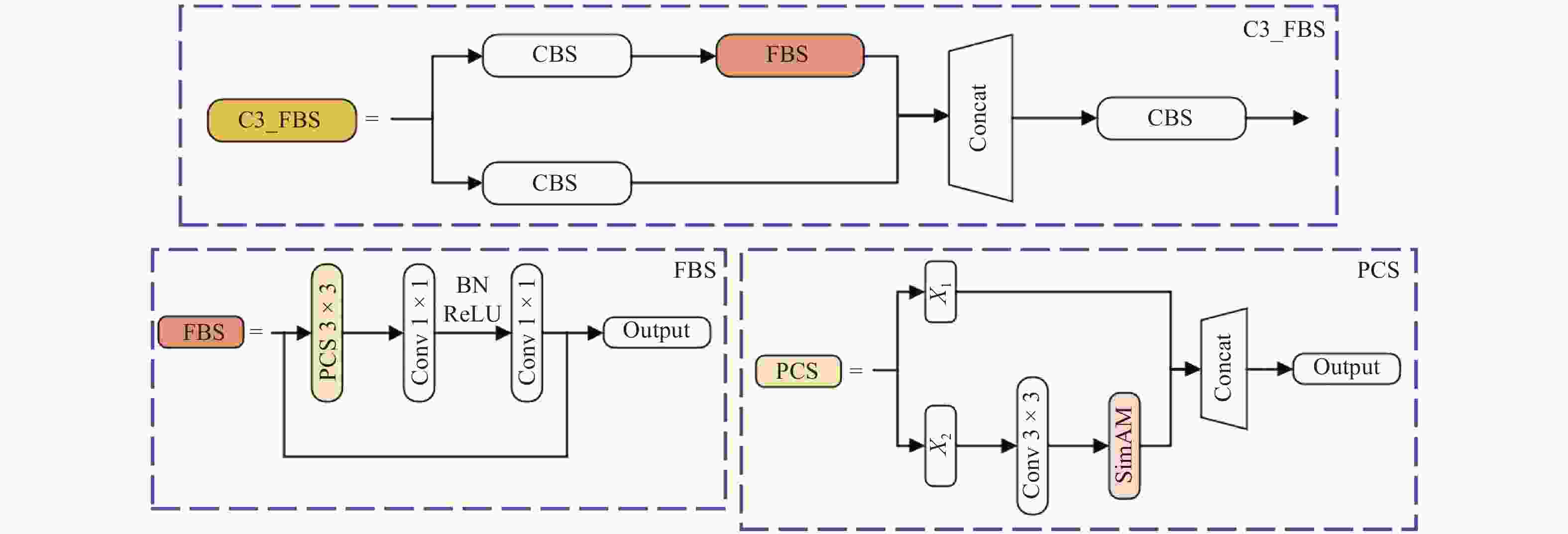
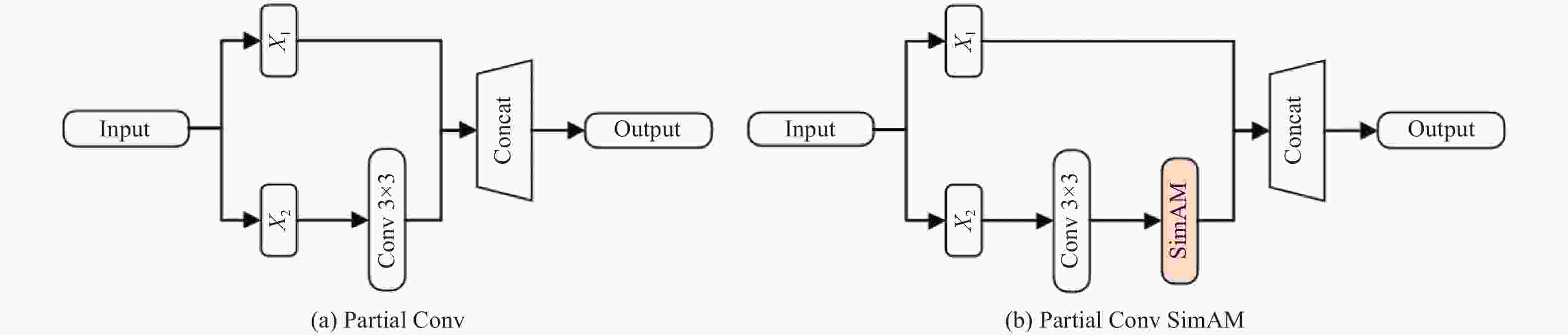
网络 修改 参数 fps mAP0.5:0.95 C3_FBNet 2.19×106 161.5 0.870 + SE 2.20×106 122.0 0.867 + CBAM 2.21×106 62.8 0.852 + CA 2.21×106 95.5 0.859 + ECA 2.21×106 62.0 0.852 + EMA 2.20×106 83.9 0.868 + SimAM 2.19×106 143.1 0.890 表 3 C3_FBS不同位置的实验数据对比
Table 3. Comparison of experimental data for different locations of C3_FBS
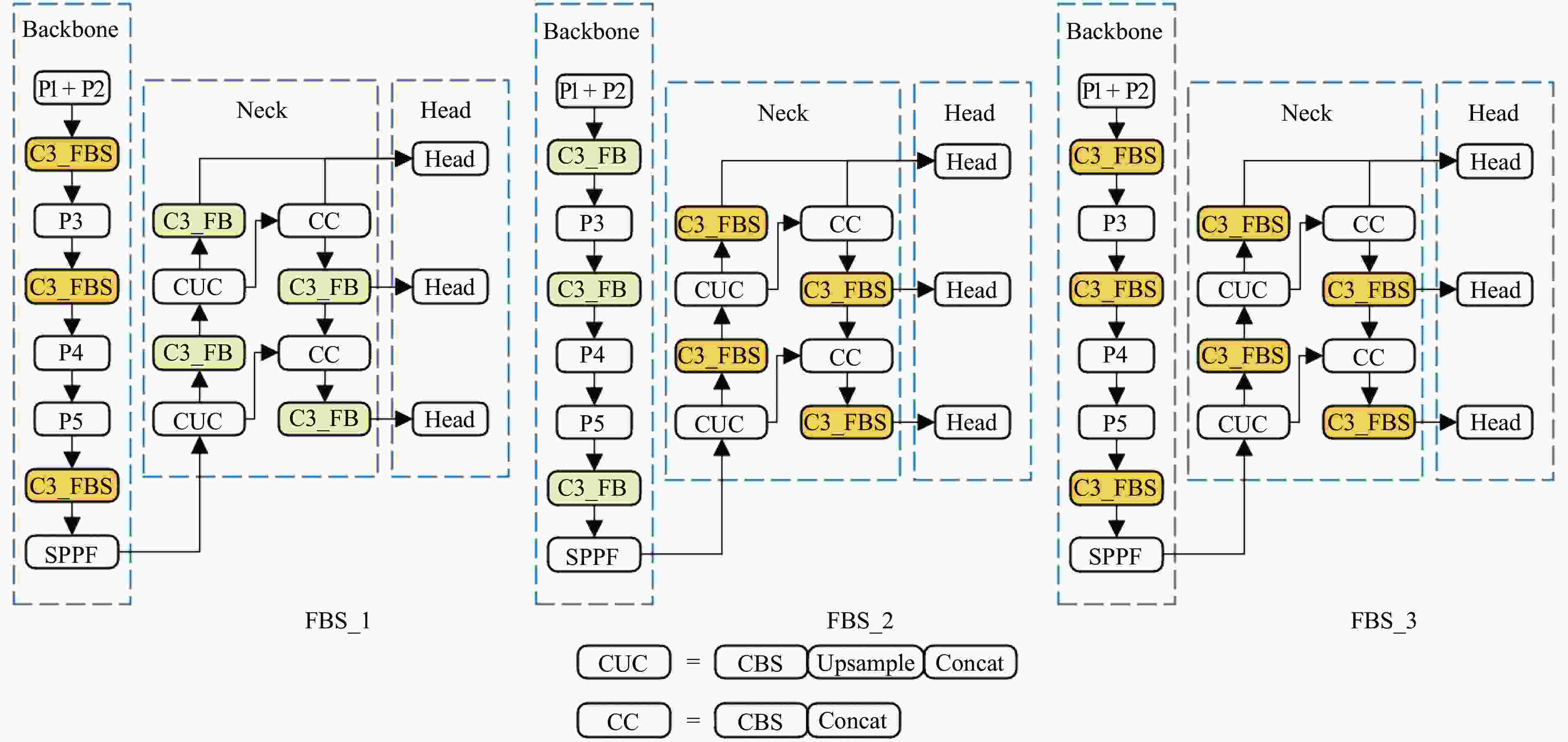
网络 参数 FLOPs fps mAP0.5:0.95 C3_FBNet 2.19×106 6.3×109 161.5 0.870 FBS_1 2.19×106 6.3×109 131.1 0.882 FBS_2 2.19×106 6.3×109 143.2 0.890 FBS_3 2.19×106 6.3×109 137.7 0.879 表 4 LAMP不同加速比剪枝效果
Table 4. Effect of pruning with different speedup ratios in LAMP
Speed-up 参数 FLOPs fps mAP0.5:0.95 1 2.19×106 6.3×109 146.1 0.892 1.5 0.86×106 4.2×109 156.5 0.900 2 0.59×106 3.1×109 162.3 0.896 2.5 0.44×106 2.5×109 164.0 0.891 3(Ours) 0.35×106 2.1×109 184.2 0.891 3.5 0.28×106 1.8×109 190.2 0.892 4 0.23×106 1.5×109 202 0.880 表 5 消融实验各模型数据对比
Table 5. Comparison of data across models for ablation experiments
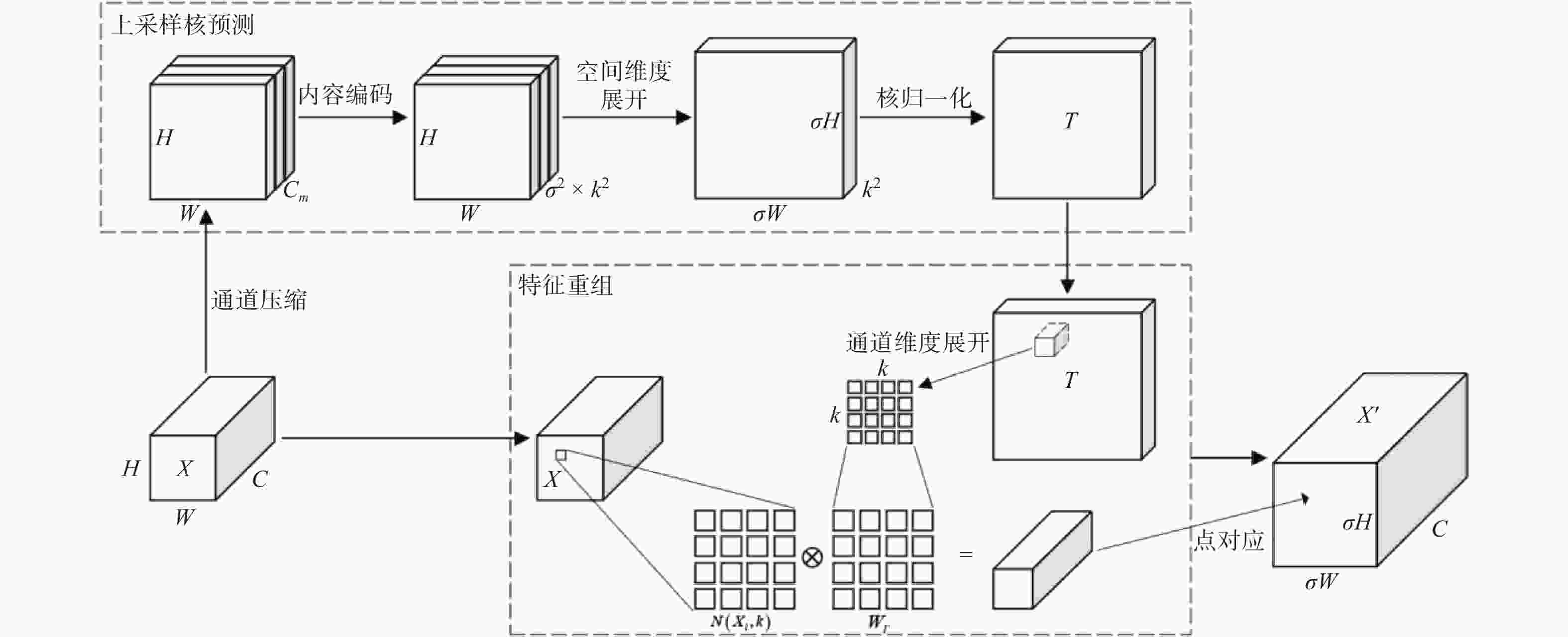
优化方式 FB SimA M CARAFE LAMP 参数 FLOPs fps mAP0.5:0.95 YOLOv5n 2.51×106 7.1×109 176.7 0.881 FB √ 2.19×106 6.3×109 161.5 0.870 SimAM √ √ 2.19×106 6.3×109 137.7 0.890 CARAFE √ √ √ 2.25×106 6.5×109 146.1 0.892 LAMP √ √ √ √ 0.28×106 1.8×109 190.2 0.892 -
[1] 李海锋, 许玉德. 计算机编制铁路轨道养护维修计划的方法[J] . 同济大学学报, 2004, 32(4): 480 − 484. [2] 张曦. 浅析超声波探伤技术在钢轨探伤中的应用[J] . 中国设备工程, 2023(5): 130 − 132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0711.2023.05.054 [3] 叶杭璐, 王超, 吴杨娜, 等. 轨道交通涡流探伤仪的设计与实现[J] . 浙江树人大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 16(3): 7 − 11. [4] 韦若禹, 李舒婷, 吴松荣, 等. 基于改进YOLO V3算法的轨道扣件缺陷检测[J] . 铁道标准设计, 2020, 64(12): 30 − 36. [5] 邹文武, 许贵阳, 白堂博. 基于EfficientDet的轨道扣件识别与检测[J] . 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2024, 57(7): 1006 − 1012. [6] HOWARD A G, ZHU M L, CHEN B, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL] . (2017-04-17)[2021-01-12] . https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861. [7] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M L, et al. MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C] //Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 4510-4520. [8] ZHANG X Y, ZHOU X Y, LIN M X, et al. ShuffleNet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C] //Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 6848−6856. [9] HAN K, WANG Y H, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C] //Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2020: 1577−1586. [10] CHEN J R, KAO S H, HE H, et al. Run, don't walk: chasing higher FLOPS for faster neural networks[C] //Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Vancouver: IEEE, 2023: 12021−12031. [11] YANG L X, ZHANG R Y, LI L D, et al. SimAM: a simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks[J] . PMLR, 2021, 139: 11863−11874. [12] WANG J Q, CHEN K, XU R, et al. CARAFE: content-aware ReAssembly of FEatures[C] //IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul: IEEE, 2019: 3007−3016. [13] LEE J, PARK S, MO S, et al. Layer-adaptive sparsity for the magnitude-based pruning[EB/OL] . (2020-10-15)[2024-01-15] . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2010.07611. [14] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C] //IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 7132−7141. [15] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C] //Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: Springer, 2018: 3−19. -





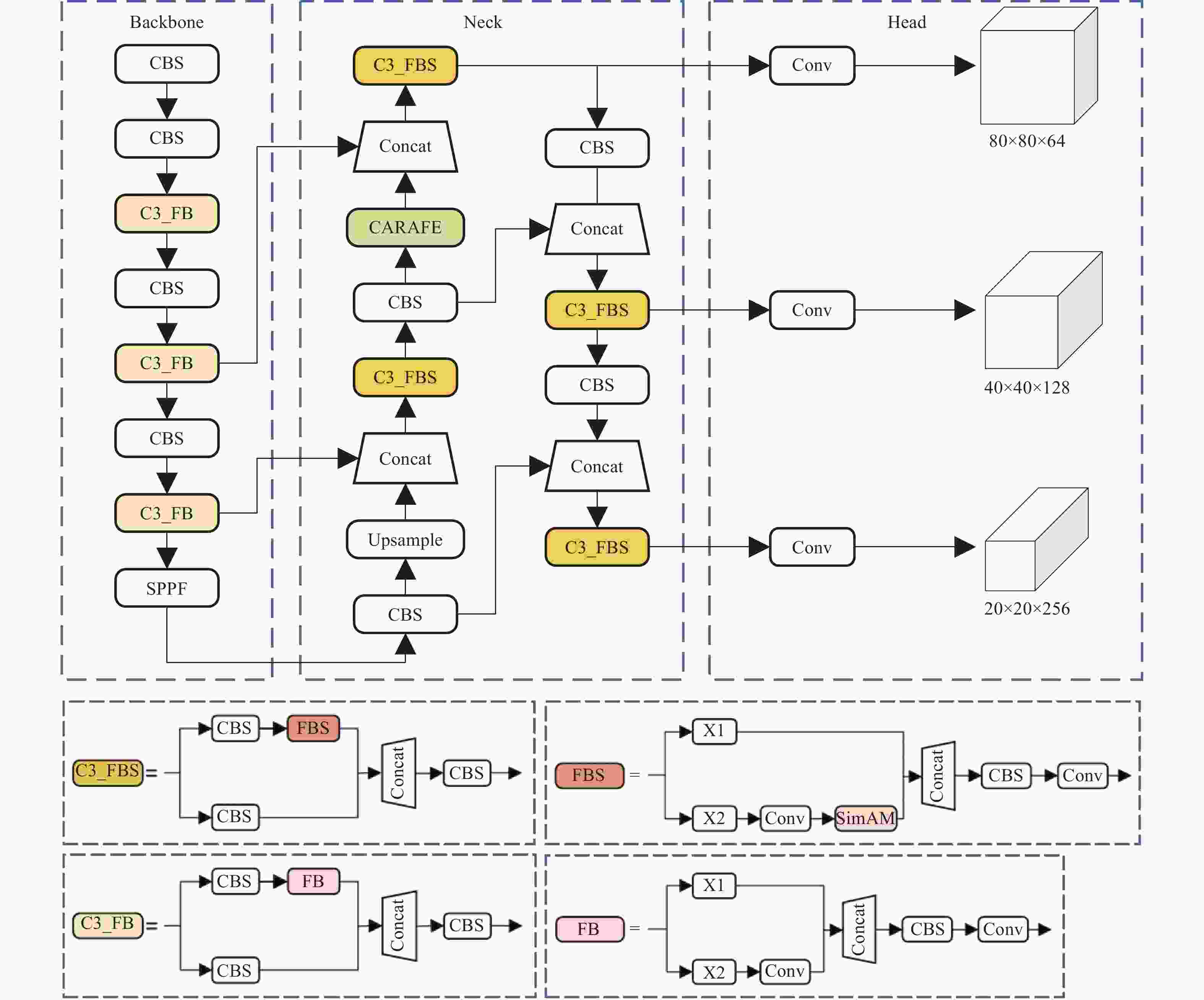
 下载:
下载: