Energy management strategy for piezoelectric passive sensing nodes in rail vehicle vibration
-
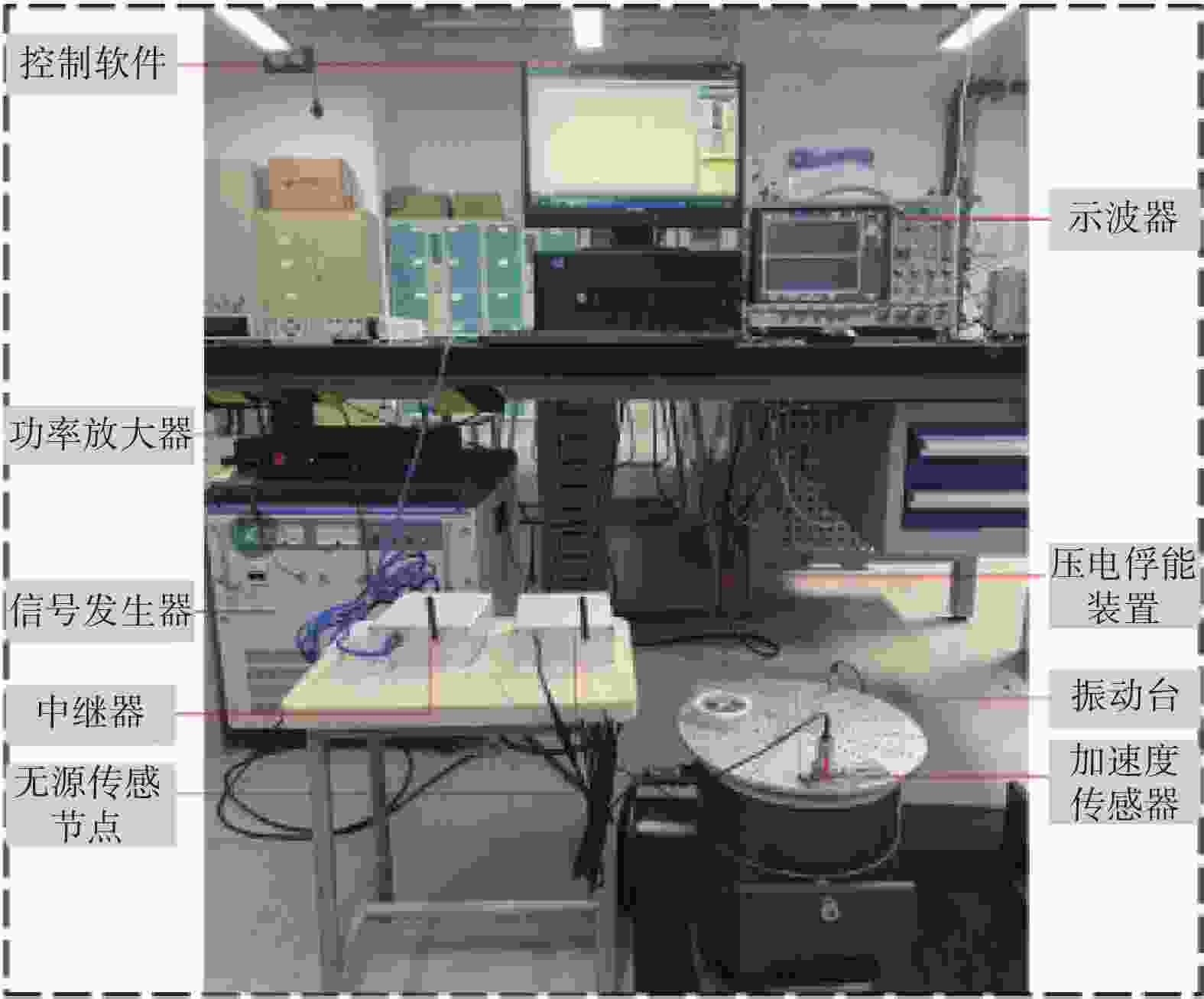
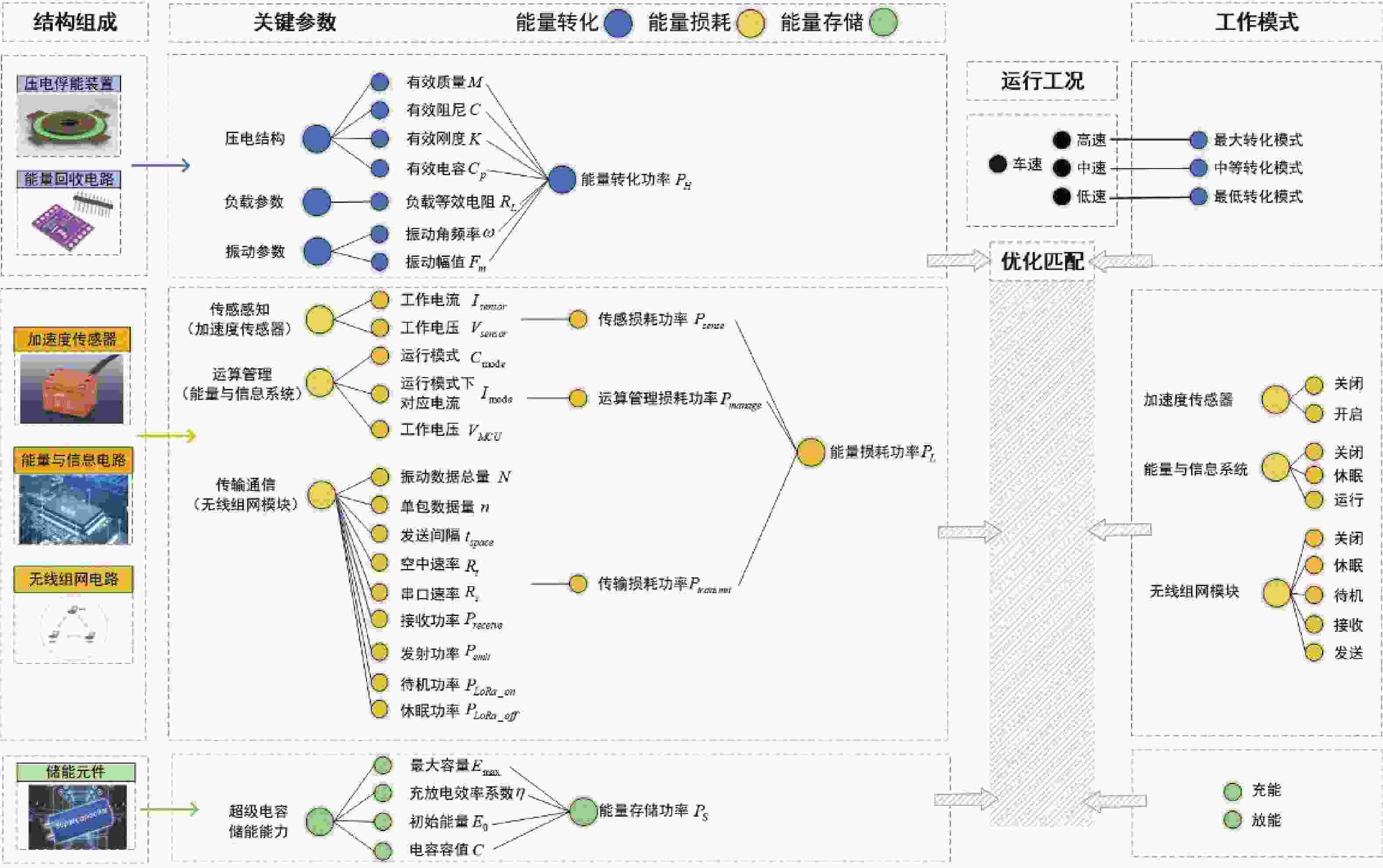
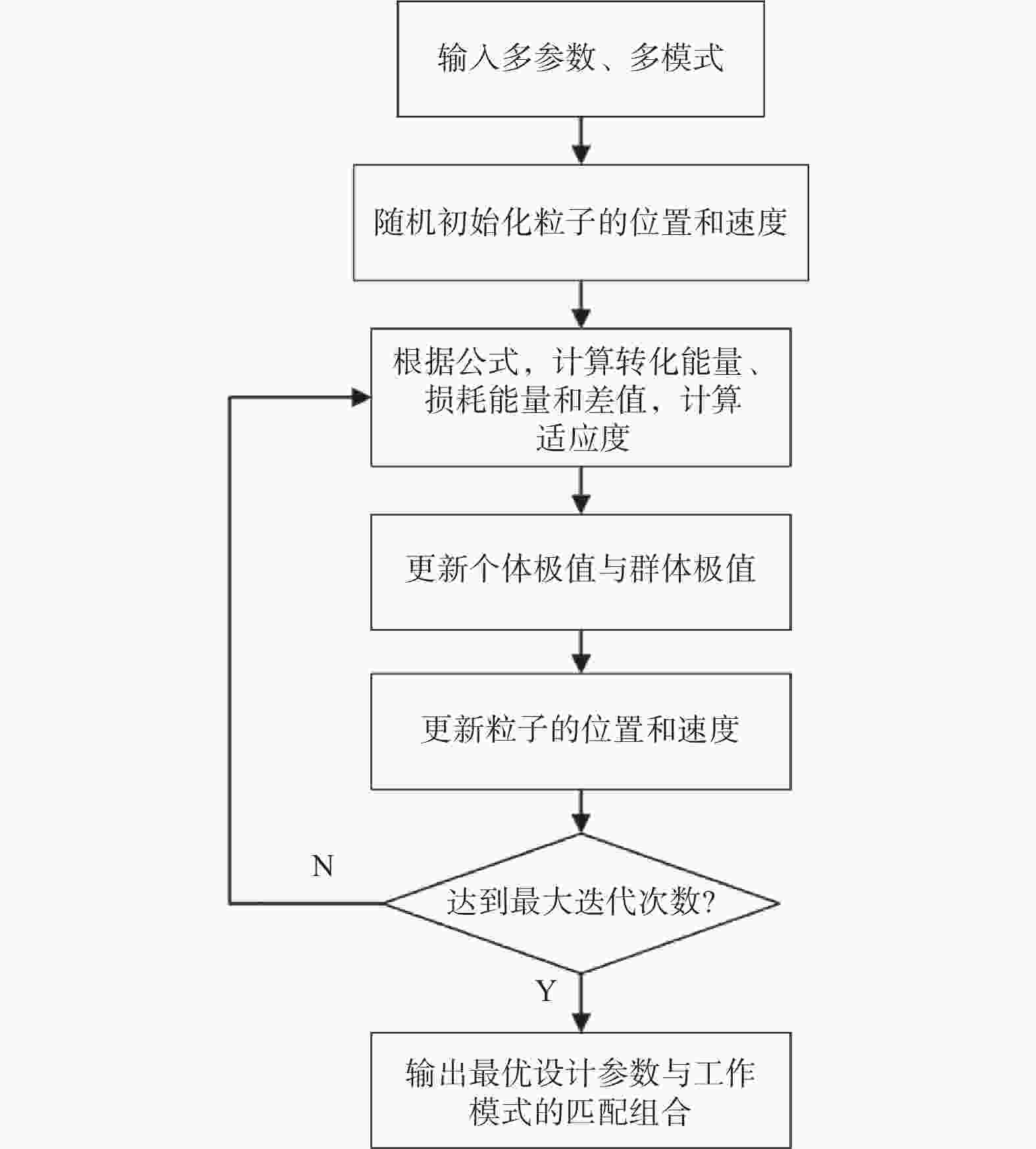
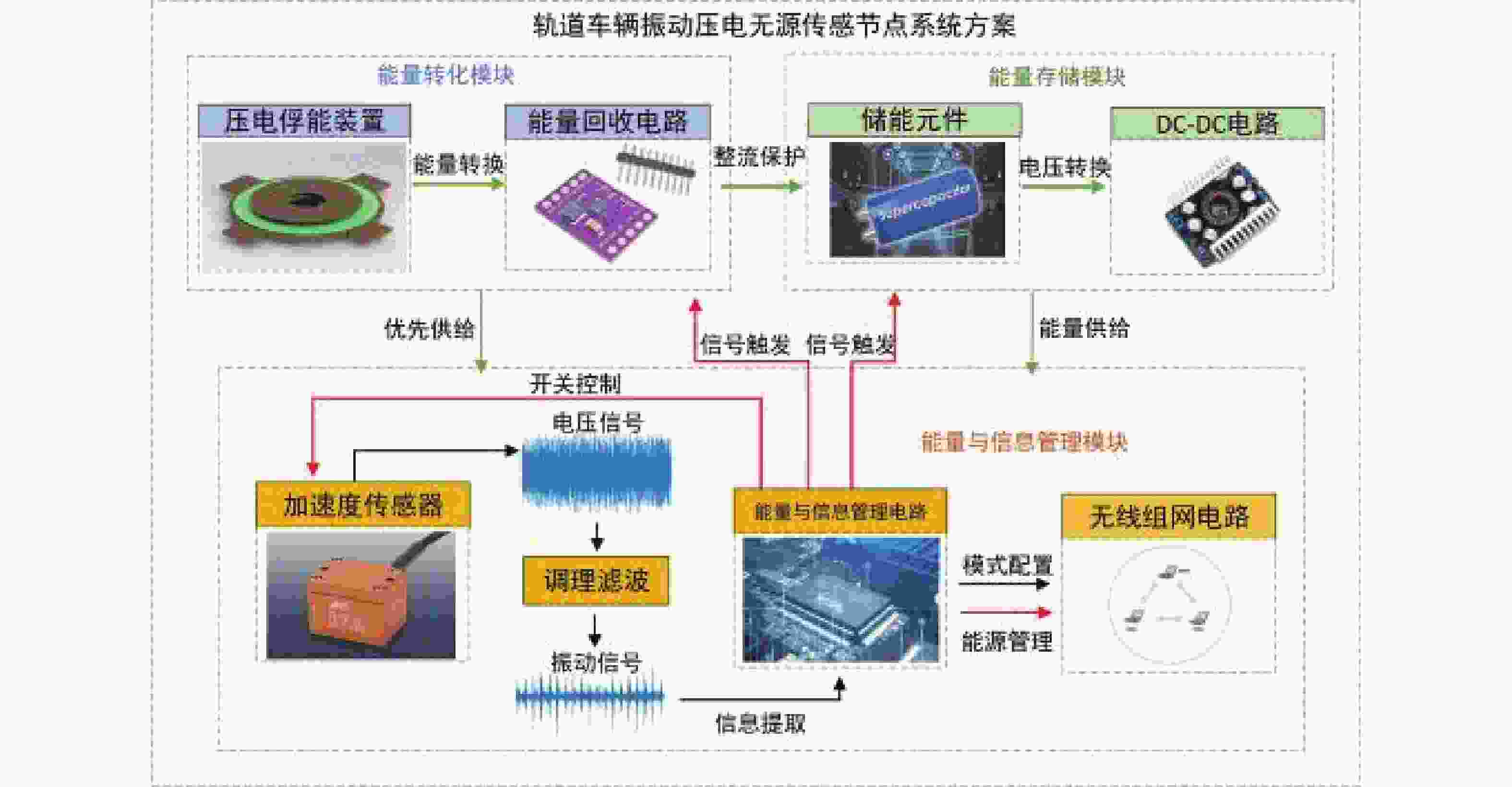
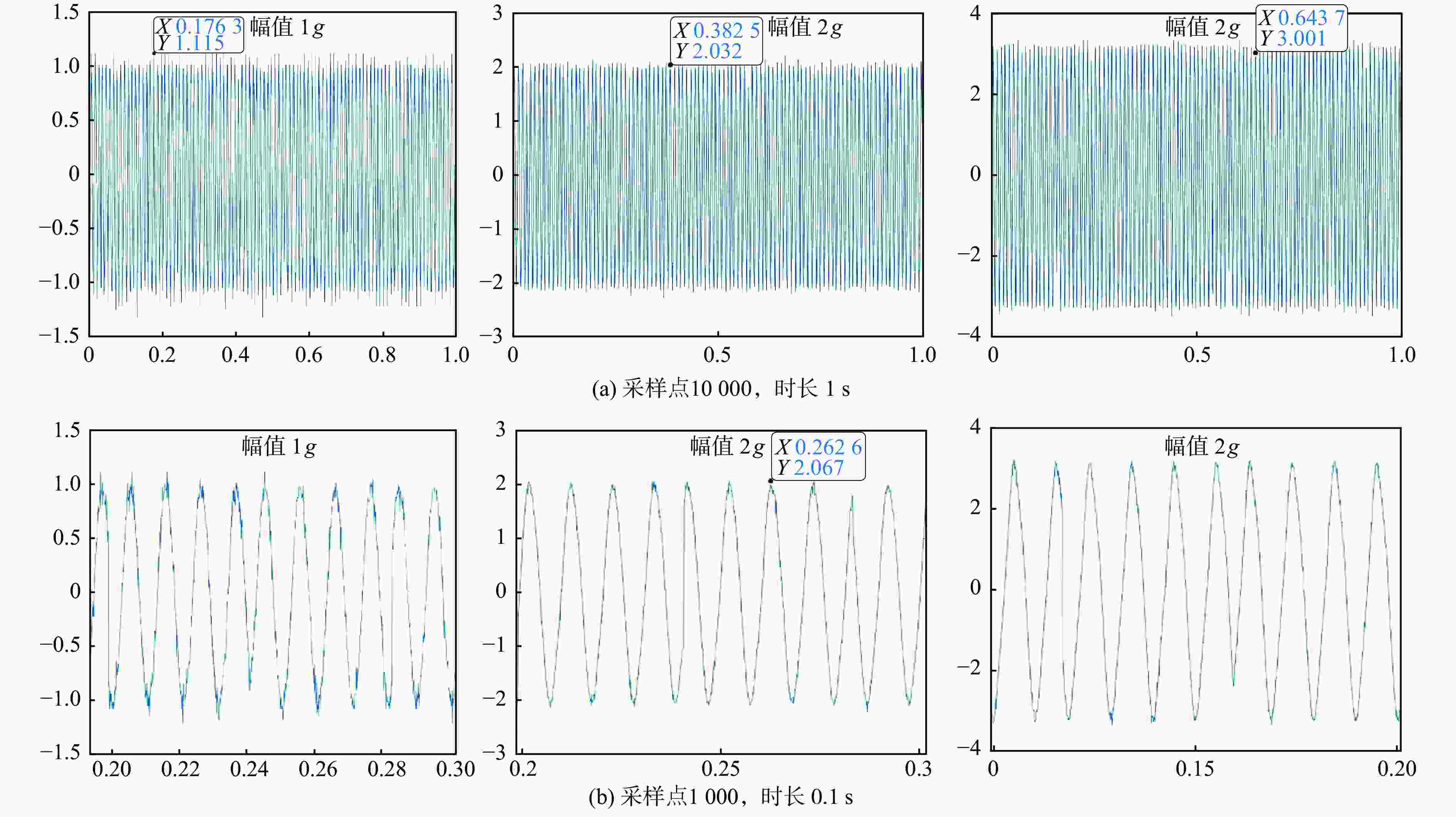
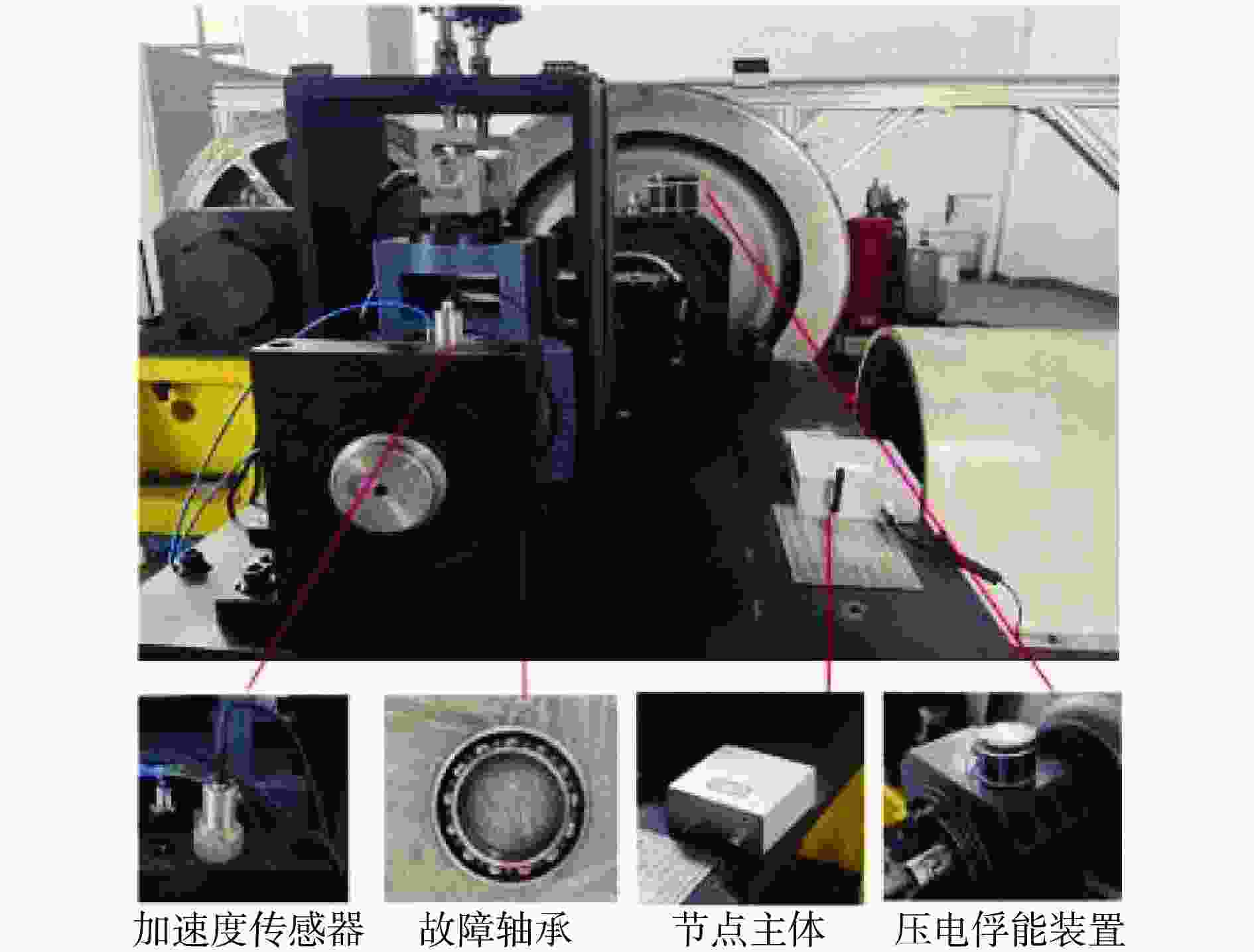
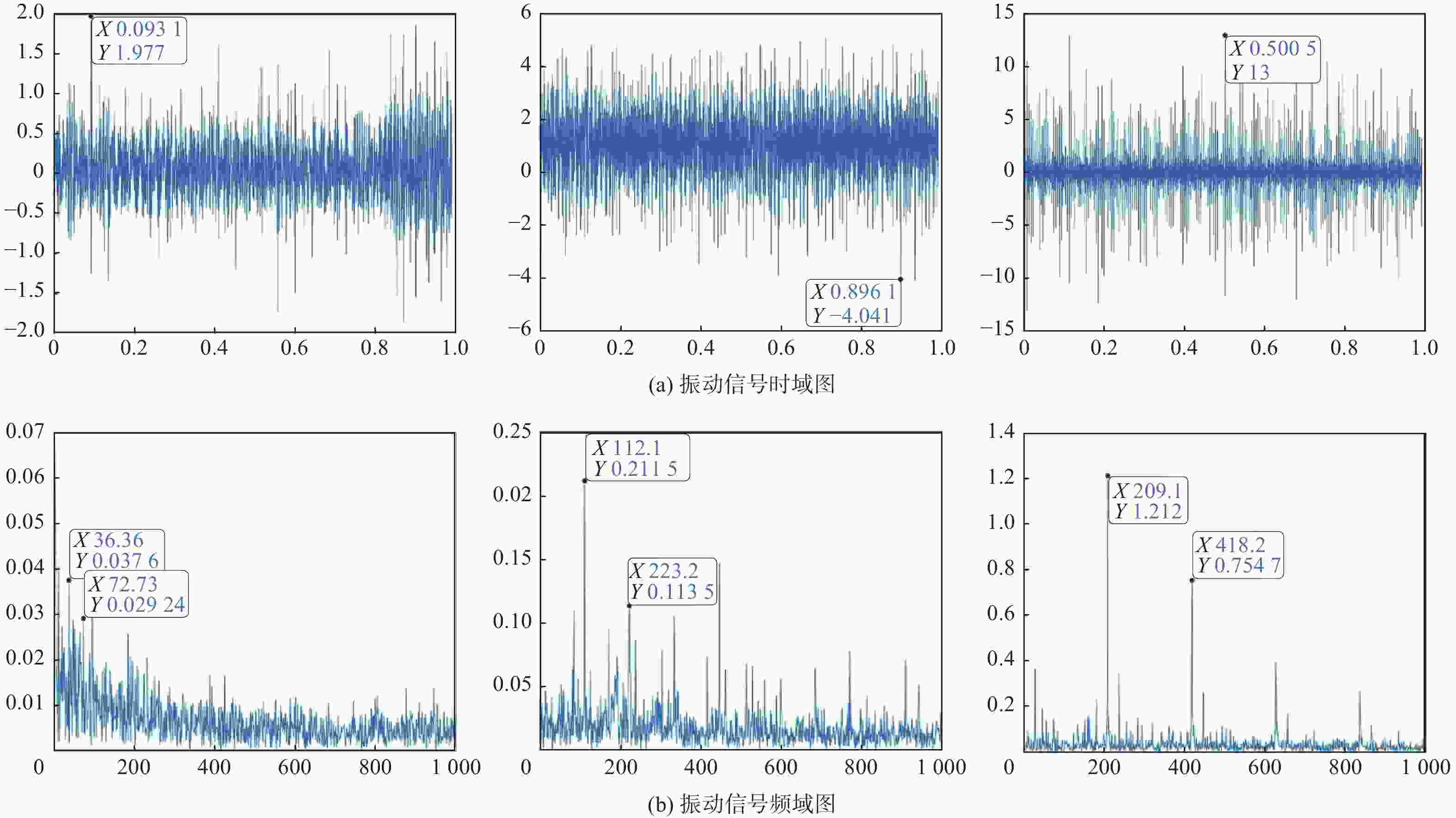
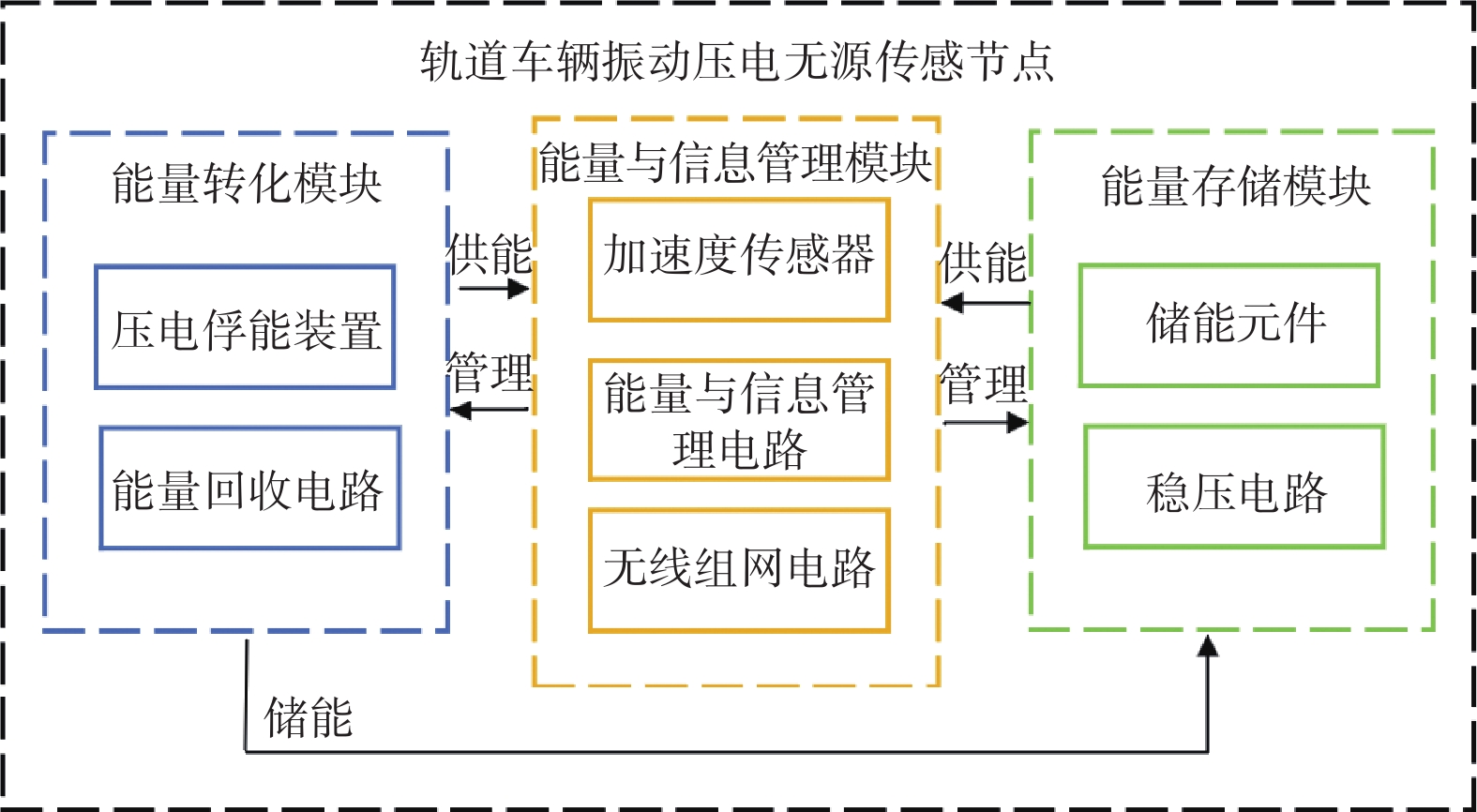
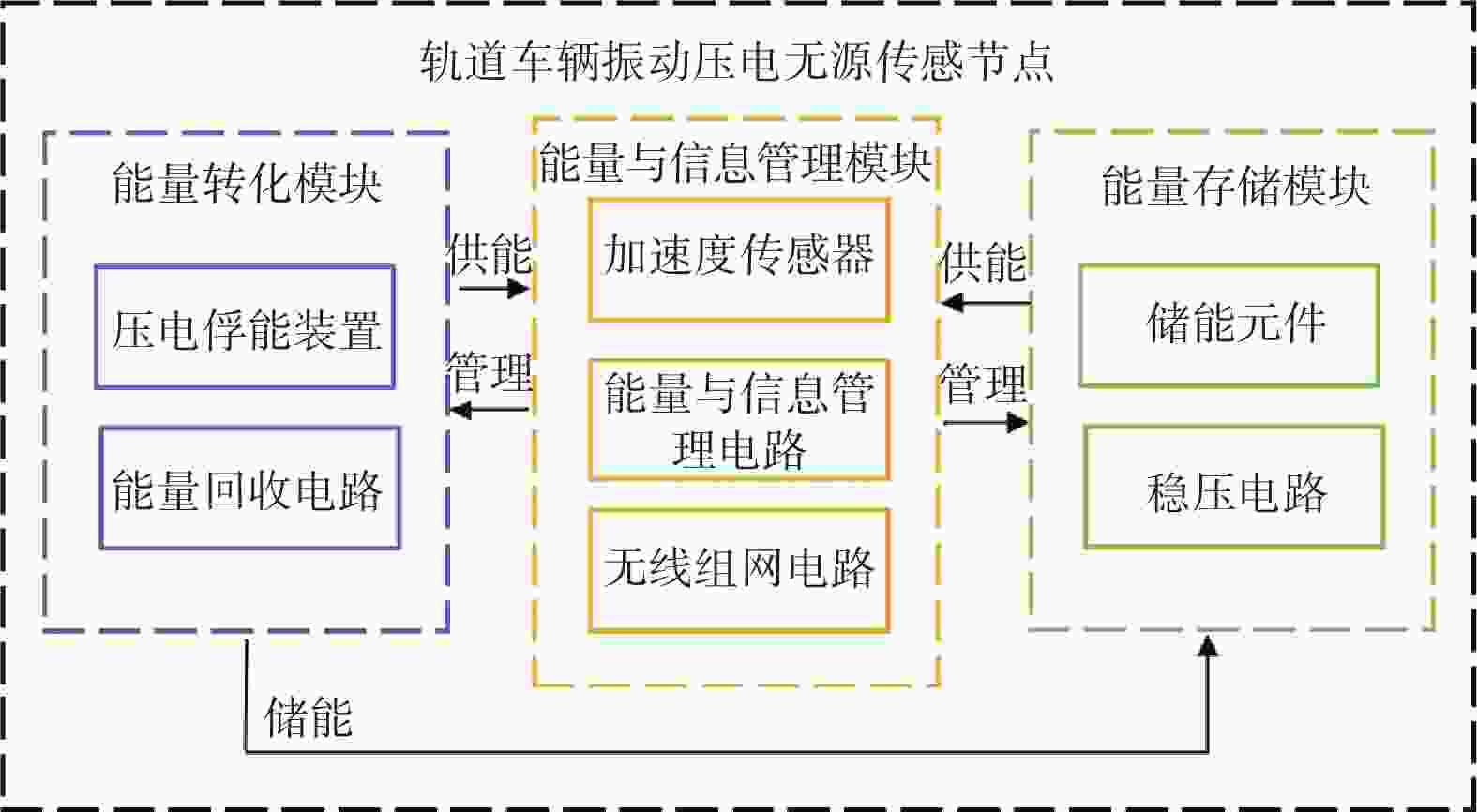
摘要: 针对轨道车辆振动压电无源传感节点的振动能量来源与供电需求不匹配而导致的系统工作异常,提出节点层级的能源管理策略。通过分析结构组成、相关参数和工作模式,构建能量策略模型,并利用粒子群优化(PSO)算法优化匹配设计参数与工作模式,最终设计了系统方案并搭建了样机。结果表明,节点的最低待机功耗为8 mW,可准确采集牵引电机振动数据,并从中提取轴承故障特征频率,验证了所提出能源管理策略的有效性。Abstract: In response to the system operational anomalies caused by the mismatch between the vibration energy source and power supply requirements in piezoelectric passive sensing nodes for rail vehicle vibration, a node-level energy management strategy was proposed. By analyzing the structural composition, relevant parameters, and operational modes, an energy management strategy model was constructed. The particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm was then utilized to optimize and match the design parameters and operational modes, resulting in the design of a system solution and the development of a prototype. The results demonstrate that the node achieves a minimum standby power consumption of 8 mW, accurately collects traction motor vibration data, and extracts bearing fault characteristic frequencies from the data, validating the effectiveness of the proposed energy management strategy.
-
表 1 能量转化的工作模式分类
Table 1. Classification of working modes of energy conversion
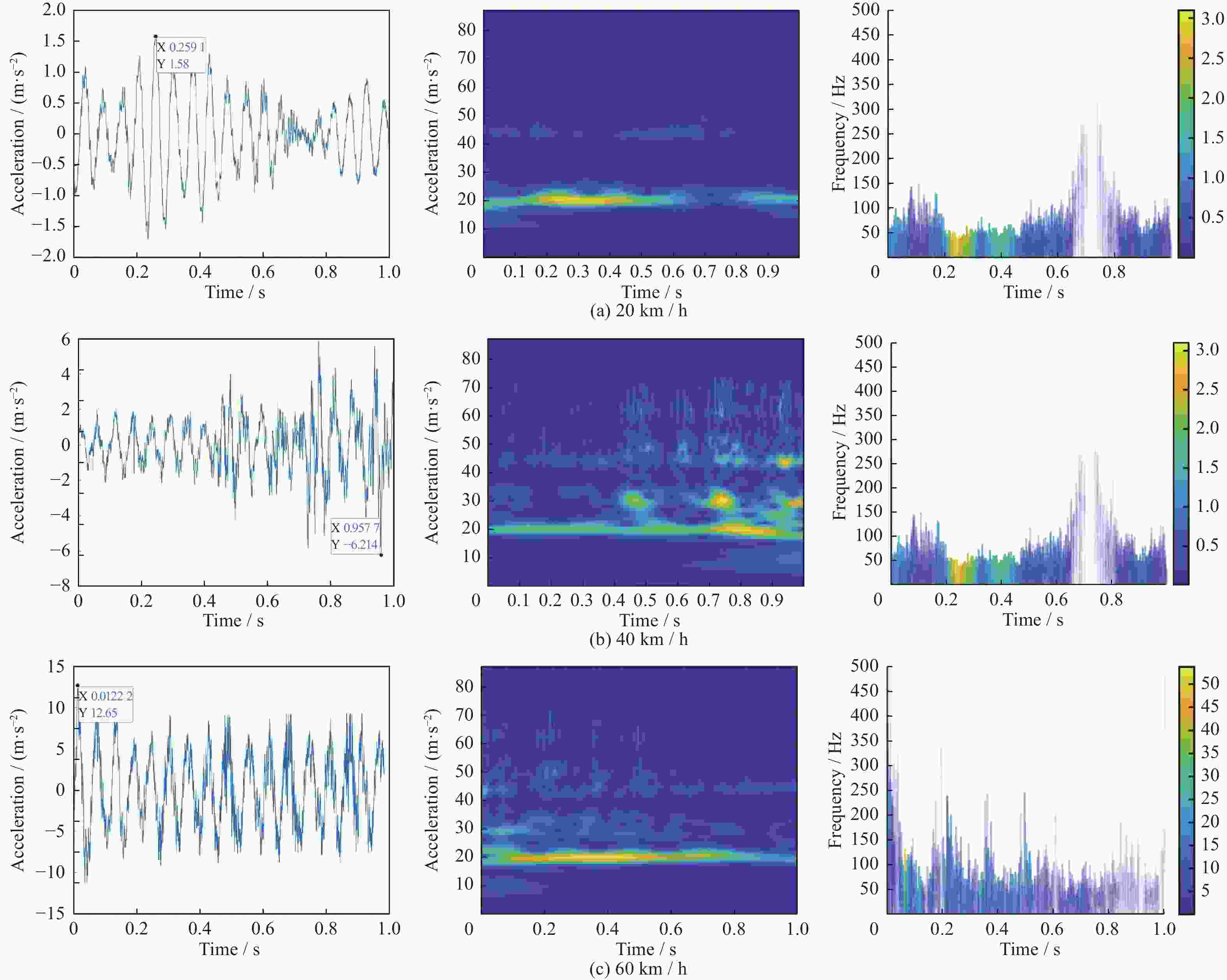
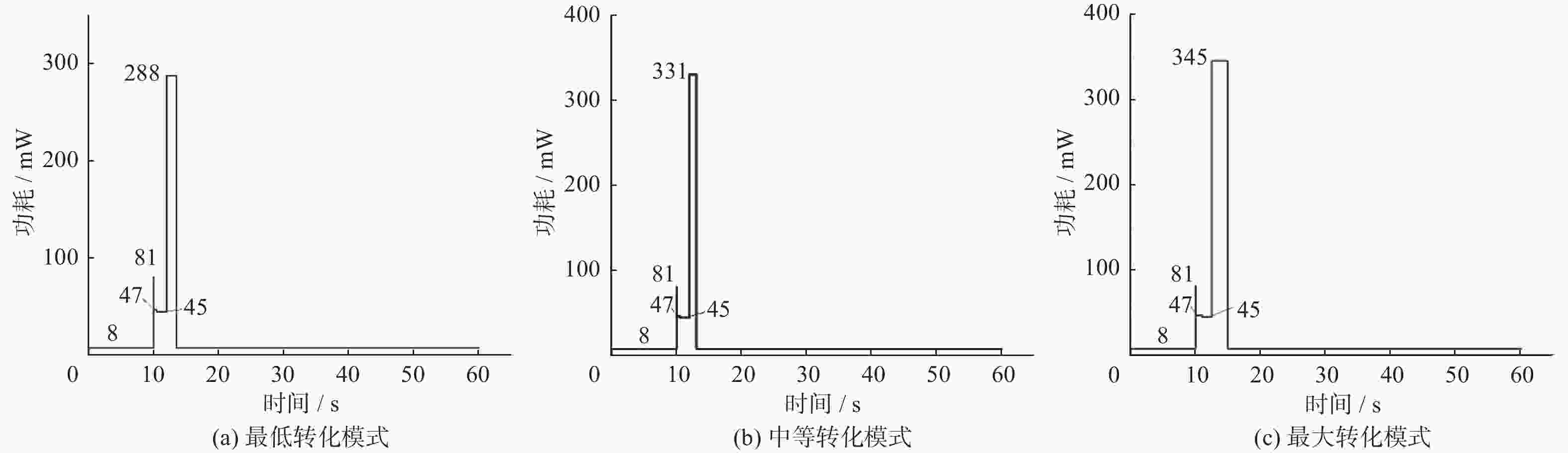
列车运行时速/(km·h−1) 能量转化模式 20 最低转化模式 40 中等转化模式 60 最大转化模式 表 2 最大转化模式的优化匹配结果
Table 2. Optimization and matching results of maximum conversion pattern
参数 工作模式 工作时间 振动数据总量 8192 加速度传感器 开启时间 1.0 s 单包数据量512 关闭时间59.0 s 发送间隔140 ms 能量与信息
管理电路关闭时间0 s 空中速率40 KB/s 休眠时间54.99 s 串口速率 38400 运行时间5.01 s 接收功率52.8 mW 无线组网电路 关闭时间0 s 发射功率100 mW 休眠时间54.99 s — 待机时间2.5 s — 接收时间10 ms — 发送时间2.5 s 表 3 中等转化模式的优化匹配结果
Table 3. Optimization and matching results of medium conversion pattern
参数 工作模式 工作时间 振动数据总量 4096 加速度传感器 开启时间 0.5 s 单包数据量512 关闭时间59.5 s 发送间隔140 ms 能量与信息
管理电路关闭时间0 s 空中速率40 KB/s 休眠时间56.99 s 串口速率 38400 运行时间3.01 s 接收功率52.8 mW 无线组网电路 关闭时间0 s 发射功率86 mW 休眠时间56.99 s — 待机时间2 s — 接收时间10 ms — 发送时间1.1 s 表 4 最低转化模式优化匹配结果
Table 4. Optimization and matching results of minimum conversion pattern
参数 工作模式 工作时间 振动数据总量 4096 加速度传感器 开启时间 0.5 s 单包数据量512 关闭时间59.5 s 发送间隔140 ms 能量与信息
管理电路关闭时间0 s 空中速率10 KB/s 休眠时间55.99 s 串口速率 9800 运行时间4.01 s 接收功率52.8 无线组网电路 关闭时间0 s 发射功率86 mW 休眠时间55.99 s — 待机时间2.0 s — 接收时间10 ms — 发送时间1.5 s 表 5 加速度传感器关键参数表
Table 5. Key parameters of acceleration sensor
参数 数值 功耗/mW 1.3 灵敏度/(mV·g−1) 12.45 频率范围/Hz DC-7000 加速度/(m·s−2) ± 100g 安装谐振频率/kHz >30 最大加速度/(m·s−2) 3000 g温度范围/ ℃ −50~150 体积大小/(mm×mm) ϕ19× 24 质量/g 45 -
[1] 崔恩放, 张宏科, 杨冬. 无源无线传感网在轨道交通车辆健康监测中的应用[J] . 北京交通大学学报, 2018, 42(5): 20 − 27. doi: 10.11860/j.issn.1673-0291.2018.05.003 [2] 王鹏. 压电材料在轨道振动能量收集与存储中的应用[J] . 电子技术, 2022, 51(9): 218 − 219. [3] 李春龙, 黄辉, 梁云, 等. 面向电力传感器的环境能量收集技术发展趋势及面临的挑战[J] . 中国电力, 2021, 54(2): 27 − 35. [4] LI S F, LU L, HUSSAIN M J, et al. Sentinel: breaking the bottleneck of energy utilization efficiency in RF-powered devices[J] . IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(1): 705 − 717. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2854374 [5] 翟成瑞, 翟聪, 王柳明. 一体式无线无源振动传感器设计[J] . 电子器件, 2020, 43(1): 34 − 38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9490.2020.01.008 [6] CAMMARANO A, PETRIOLI C, SPENZA D. Online energy harvesting prediction in environmentally powered wireless sensor networks[J] . IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(17): 6793 − 6804. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2016.2587220 [7] 魏双会. 压电陶瓷发电特性及其应用研究[D] . 大连: 大连理工大学, 2008. [8] OTTMAN G K, HOFMANN H F, LESIEUTRE G A. Optimized piezoelectric energy harvesting circuit using step-down converter in discontinuous conduction mode[J] . IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2003, 18(2): 696 − 703. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2003.809379 [9] 陈蕾. 无线传感网络节点锂离子电池能量状态预估研究[D] . 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2023. [10] KENNEDY J, EBERHART R. Particle swarm optimization[C] //Proceeding of ICNN’95-IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. Perth: IEEE, 1995: 1942 − 1948. [11] KANSAL A, HSU J, ZAHEDI S, et al. Power management in energy harvesting sensor networks[J] . ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems (TECS), 2007, 6(4). DOI: 10.1145/1274858.1274870. -





 下载:
下载: