Adaptive path planning of surgical robots based on environmental attributes
-
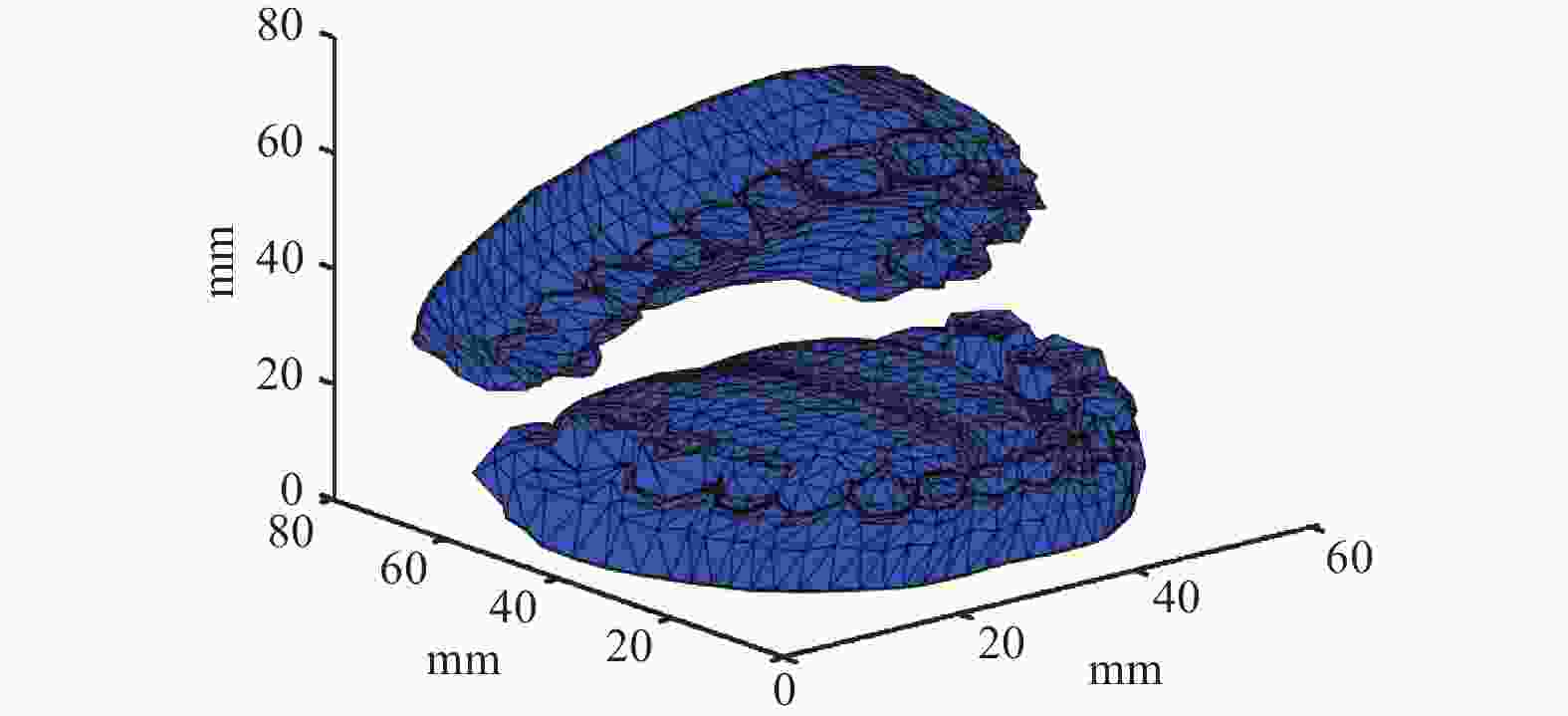
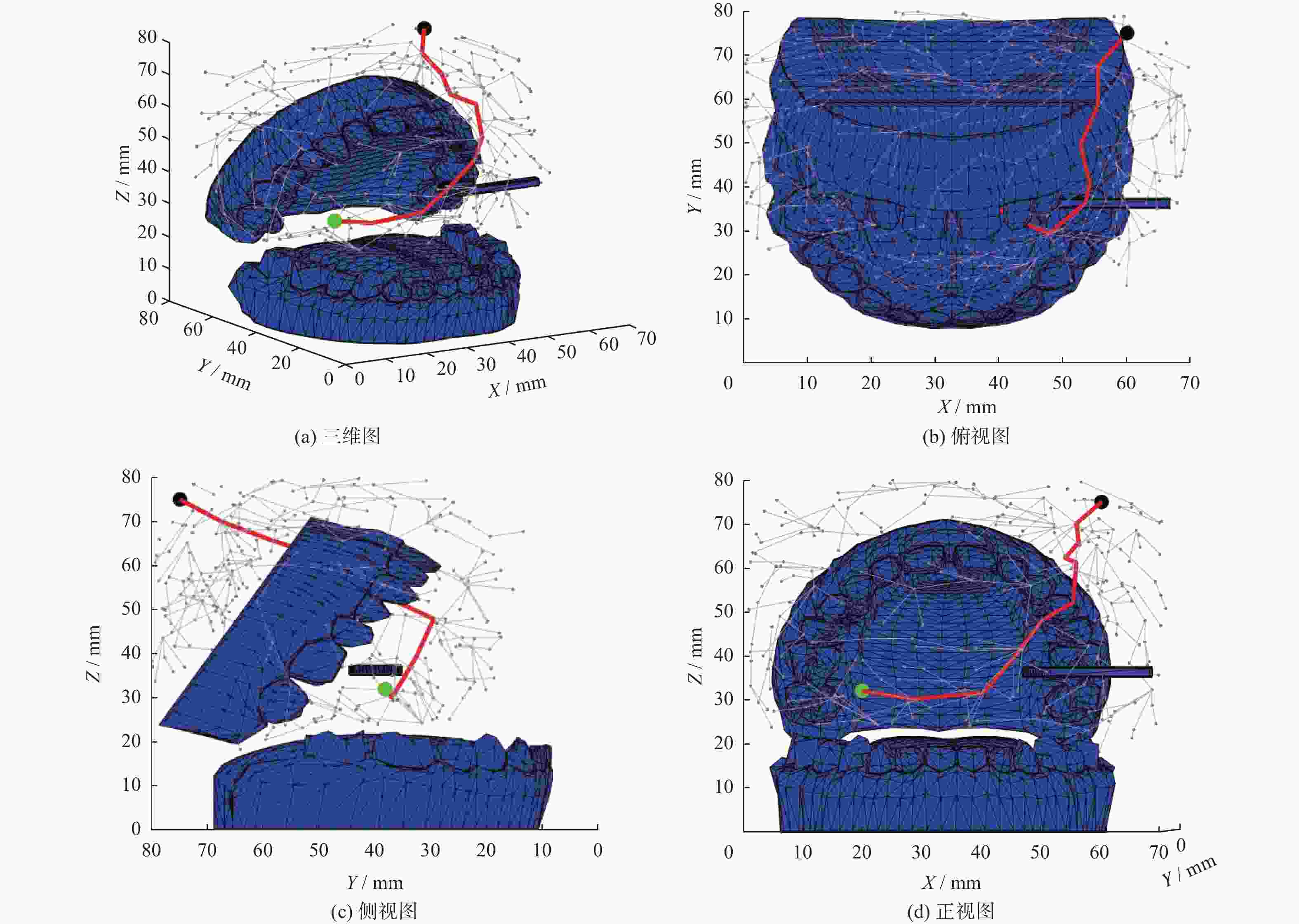
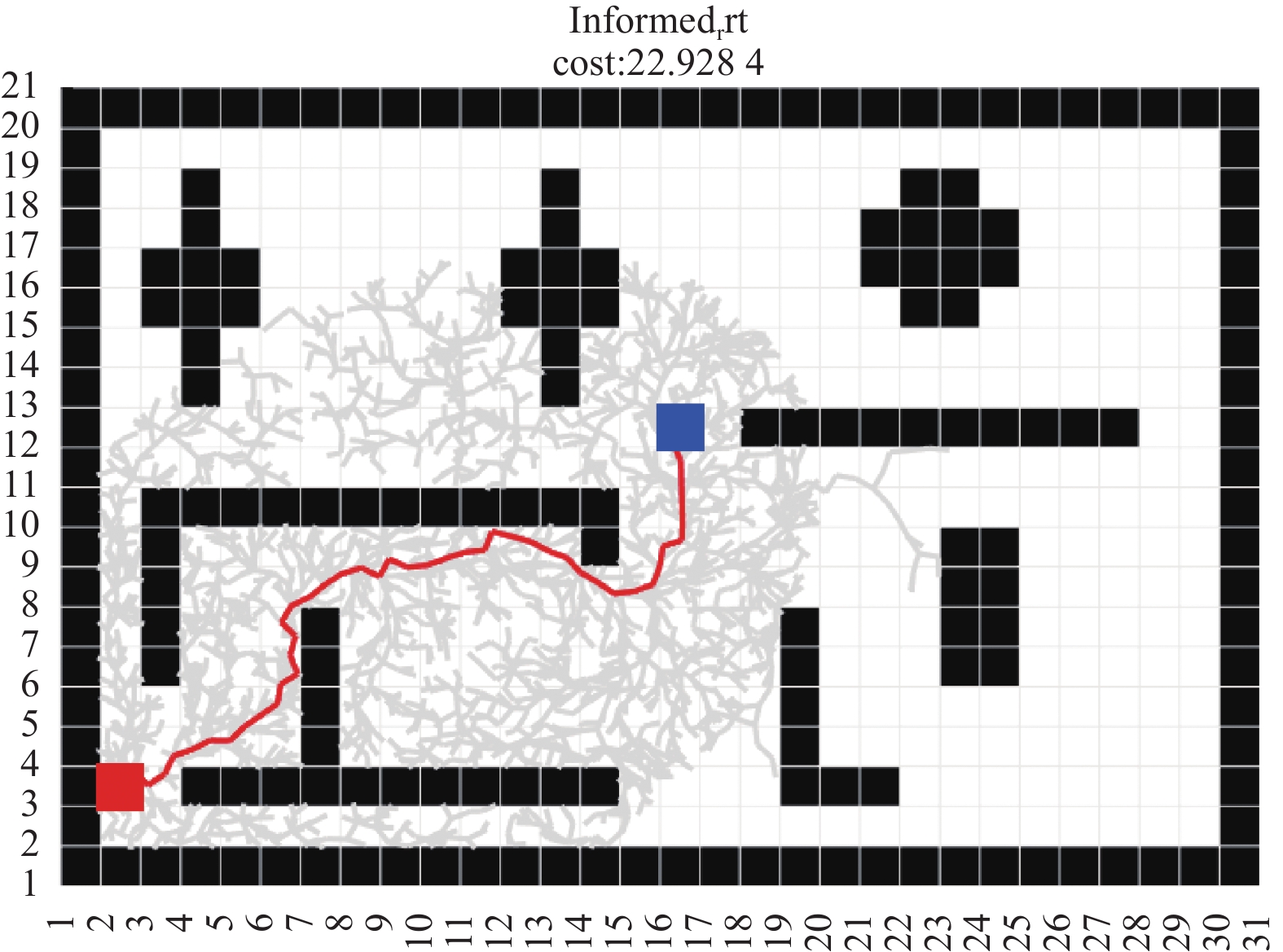
摘要: 在双臂手术机器人环境中,机械臂能否安全、高效地到达目标位置至关重要。提出一种自适应APF-Informed-RRT*路径规划算法,旨在克服传统APF-Informed-RRT*路径规划算法存在的缺乏适应性、路径稳定性不足等问题,以提高机械臂的路径规划质量。该算法根据机器人当前位置与目标位置的欧氏距离及附近区域内障碍物密度对引力项系数、斥力项系数及随机引导项系数进行动态调整,从而适应环境以降低路径规划代价。仿真结果表明,与APF-Informed-RRT*算法相比,该算法在3D口腔仿真环境中路径代价及搜索范围表现出色。这种自适应性使算法在路径规划任务中具备有效的稳定性。Abstract: In a dual-arm surgical robot environment, it is essential for the robotic arms to reach target positions safely and efficiently. An adaptive APF-Informed-RRT* path planning algorithm was proposed to overcome limitation of traditional APF-Informed-RRT* algorithms, such as lack of adaptability and insufficient path stability, thereby improving the quality of path planning for robotic arms. The coefficients of the attraction term, repulsion term, and random guidance term were dynamically adjusted based on the Euclidean distance from the robot's current position to the target, as well as the density of obstacles in the nearby area. This adaptability helps to reduce the path planning cost by adjusting to the environment. Simulation results show that compared to the APF-Informed-RRT* algorithm, the proposed method performs better in terms of path cost and search range in a 3D oral simulation environment. This adaptability endows the algorithm with effective stability in path planning tasks.
-
表 1 RRT*算法
Table 1. RRT* algorithm
输入:起始位置$ {{x}}_{{\mathrm{init}}} $,目标位置$ {{x}}_{{\mathrm{goal}}} $及地图矩阵$ {{\boldsymbol{M}}}_{\mathrm{ap}} $ 输出:树T 1. for $ {i}\leftarrow 1 $ to N do
2. 从状态空间中随机采样点 $ {{x}}_{\rm{rand}} $
3. 在树 T 中找到最近的节点 $ {{x}}_{\rm{nearest}} $,使得 $ {{x}}_{\rm{nearest}} $ 到 $ {{x}}_{\rm{rand}} $ 的连线不与障碍物相交
4. 尝试将 $ {{x}}_{\rm{rand}} $ 连接到 $ {{x}}_{\rm{nearest}} $,生成节点$ {{x}}_{\rm{new}} $
5. 在树 T 中找到 $ {{x}}_{\rm{near}} $ 邻域内的节点,更新节点的父节点为生成的 $ {{x}}_{\rm{new}} $,并重新计算代价
6. 如果新的代价更低,调整树的结构以优化路径
7. return T表 2 参数数据表
Table 2. Parameter data table
指标 μ(len) σ(len) μ(tree) σ(tree) μ(time) σ(time) cost R=5, step=5 109.28 11.14 1180.6 611.32 49.79 59.16 2.42 R=10, step=5 94.66 5.86 700.95 283.06 83.33 45.91 2.97 R=15, step=5 89.91 2.58 864.10 280.23 263.11 145.31 7.90 R=5, step=10 108.22 10.43 418.70 435.02 11.68 16.64 1.00 R=10, step=10 100.26 6.73 220.65 95.56 9.57 5.17 0.98 R=15, step=10 99.32 9.45 228.95 203.81 24.50 44.89 1.77 R=5, step=15 103.50 10.77 124.90 78.03 3.07 1.74 1.56 R=10, step=15 102.65 10.97 116.35 64.02 3.78 2.23 1.57 R=15, step=15 101.43 8.19 103.50 47.22 3.33 1.70 1.24 -
[1] ZHANG X M, YANG F, JIN Q W, et al. Path planning algorithm for dual-arm robot based on depth deterministic gradient strategy algorithm[J] . Mathematics, 2023, 11(20): 4392. doi: 10.3390/math11204392 [2] LIU D X, ZHANG J C, LI Y. Research on master-slave coordinated control method of dual-arm robot[C] //Proceedings of International Conference on Image, Vision and Intelligent Systems 2022 (ICIVIS 2022). Singapore: Springer, 2023: 1037−1047. [3] KARAMAN S, FRAZZOLI E. Sampling-based algorithms for optimal motion planning[J] . The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2011, 30(7): 846 − 894. doi: 10.1177/0278364911406761 [4] KARAMAN S, WALTER M R, PEREZ A, et al. Anytime motion planning using the RRT[C] //Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Shanghai: IEEE, 2011: 1478−1483. [5] GAMMELL J D, SRINIVASA S S, BARFOOT T D. Informed RRT: optimal sampling-based path planning focused via direct sampling of an admissible ellipsoidal heuristic[C] //Proceedings of 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Chicago: IEEE, 2014: 2997−3004. [6] LAVALLE S M, KUFFNER J R. Randomized kinodynamic planning[J] . The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2001, 20(5): 378 − 400. doi: 10.1177/02783640122067453 [7] NADERI K, RAJAMÄKI J, HÄMÄLÄINEN P. RT-RRT*: a real-time path planning algorithm based on RRT[C] //Proceedings of the 8th ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Motion in Games. Paris: ACM, 2015: 113−118. [8] CHEN J G, ZHAO Y, XU X. Improved RRT-connect based path planning algorithm for mobile robots[J] . IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 145988 − 145999. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3123622 [9] TIAN Z Y, GUO C, LIU Y, et al. An improved RRT robot autonomous exploration and SLAM construction method[C] //Proceedings of 2020 5th International Conference on Automation, Control and Robotics Engineering. Dalian: IEEE, 2020: 612−619. [10] ZHAO P L, CHANG Y H, WU W K, et al. Dynamic RRT: fast feasible path planning in randomly distributed obstacle environments[J] . Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2023, 107(4): 48. -





 下载:
下载: