Combining improved YOLOX and improved second for road vehicle fusion detection
-
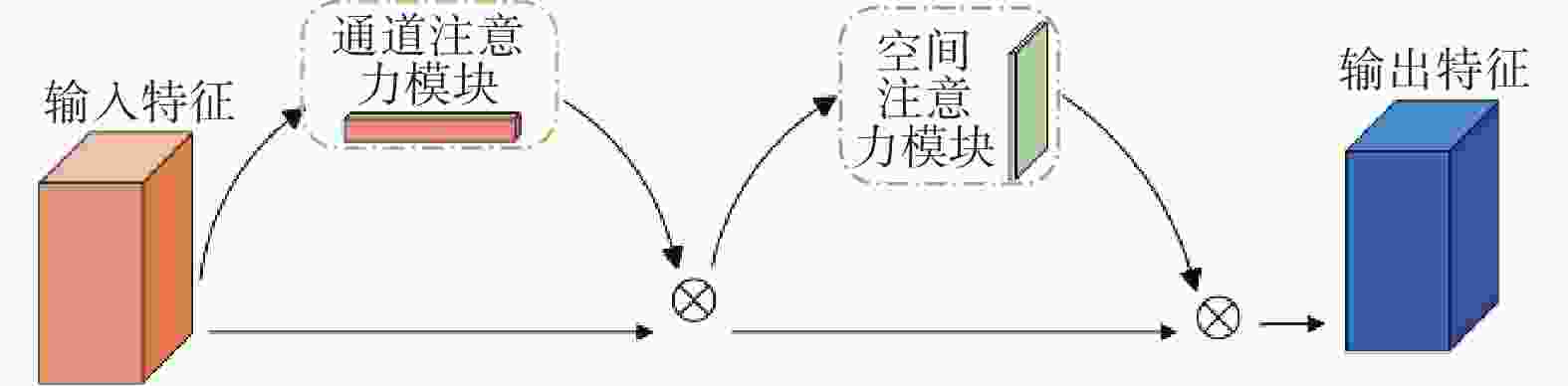
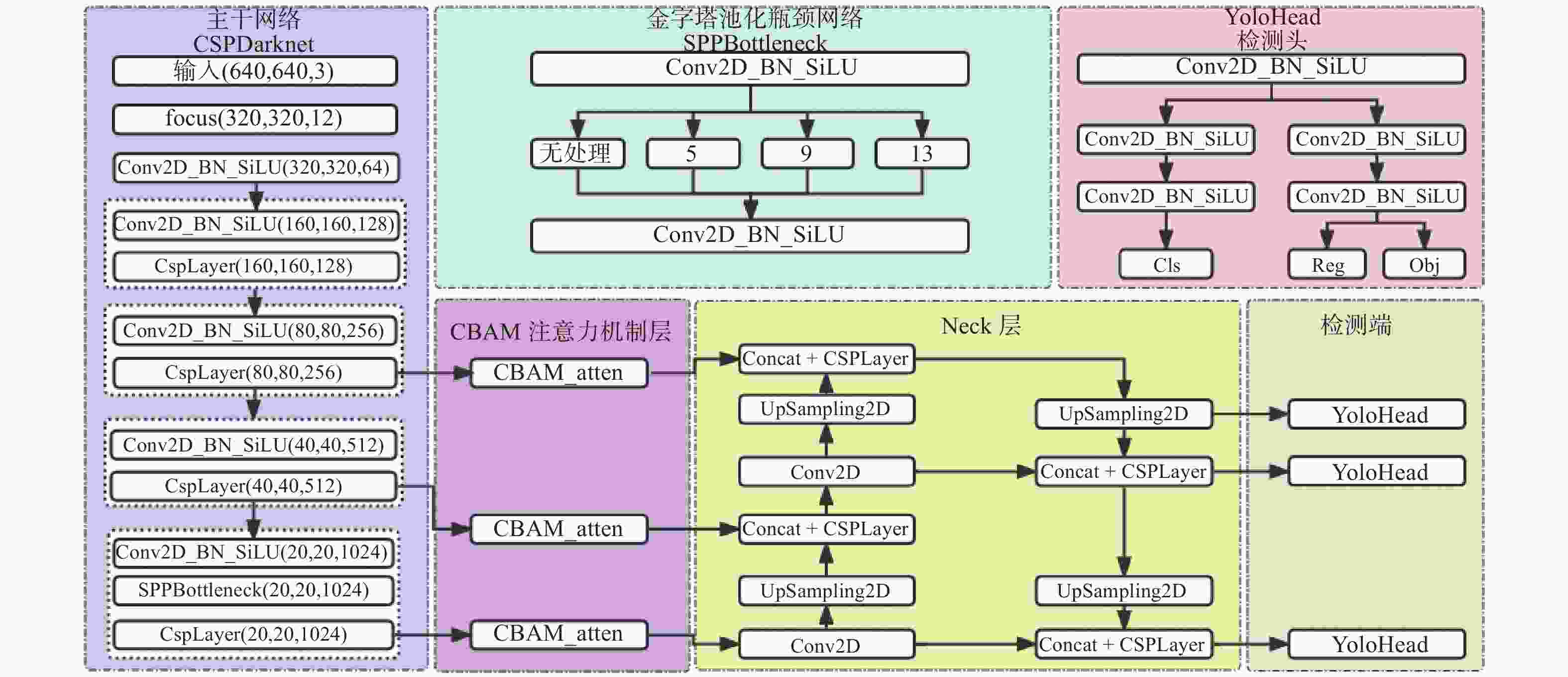
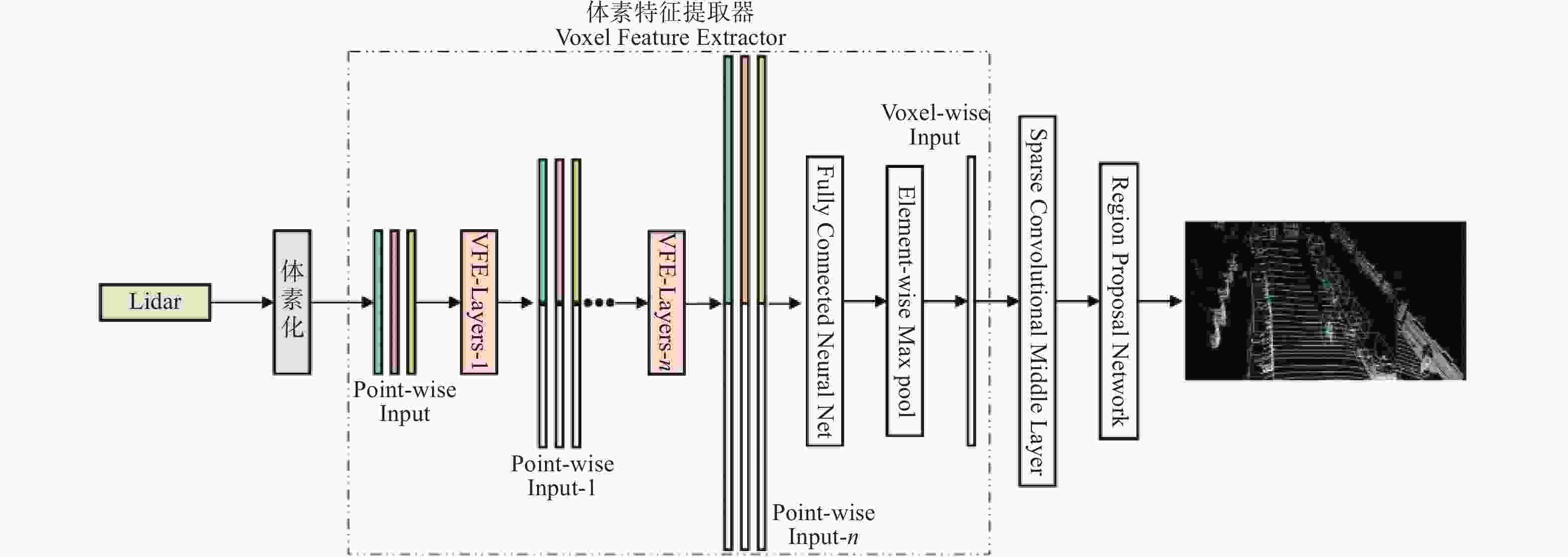
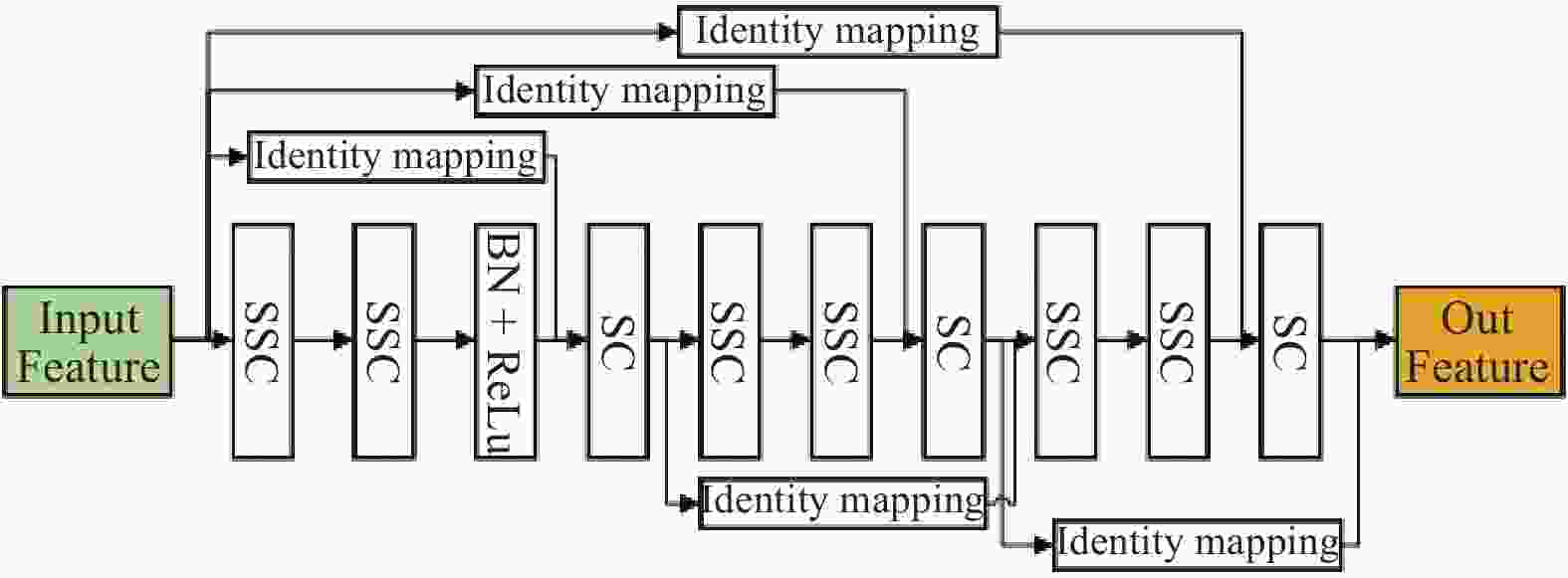
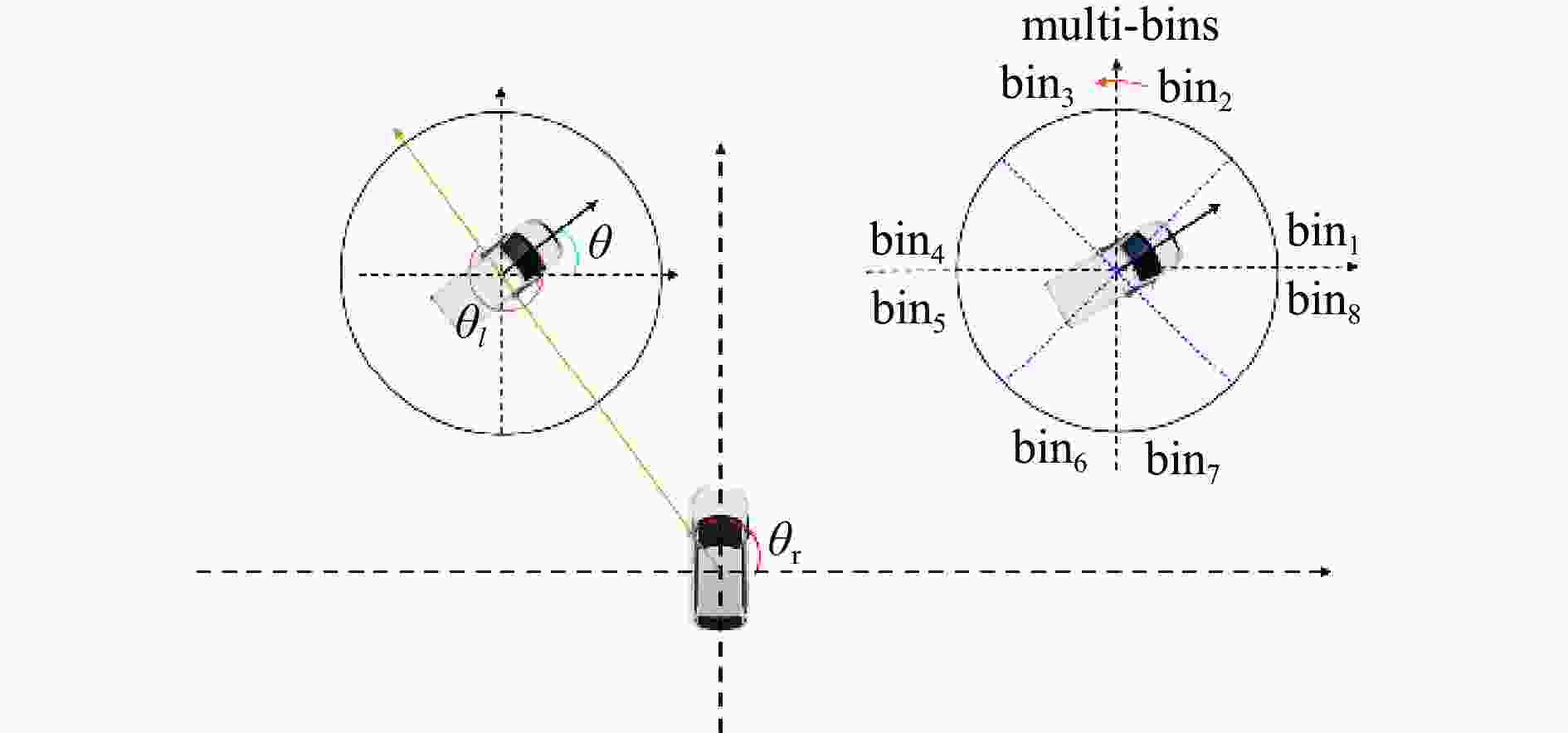
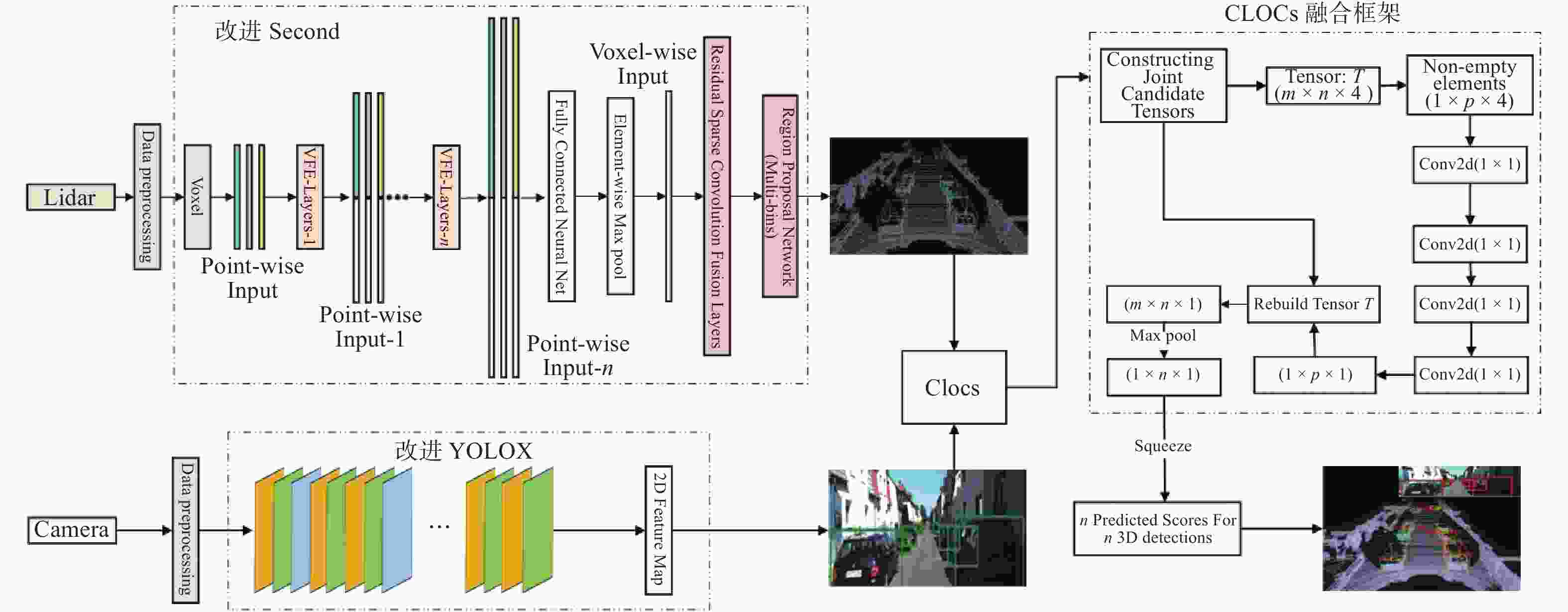
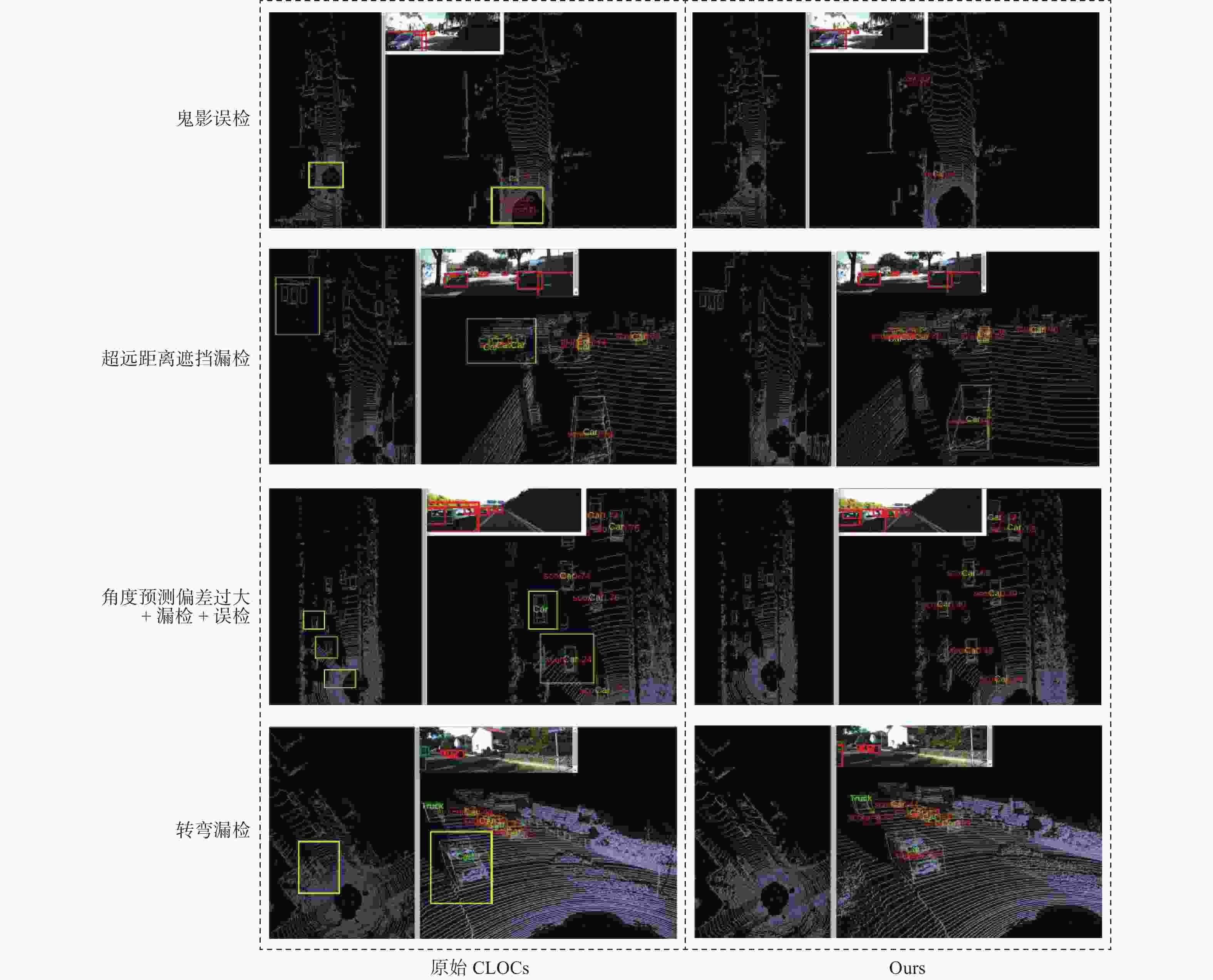
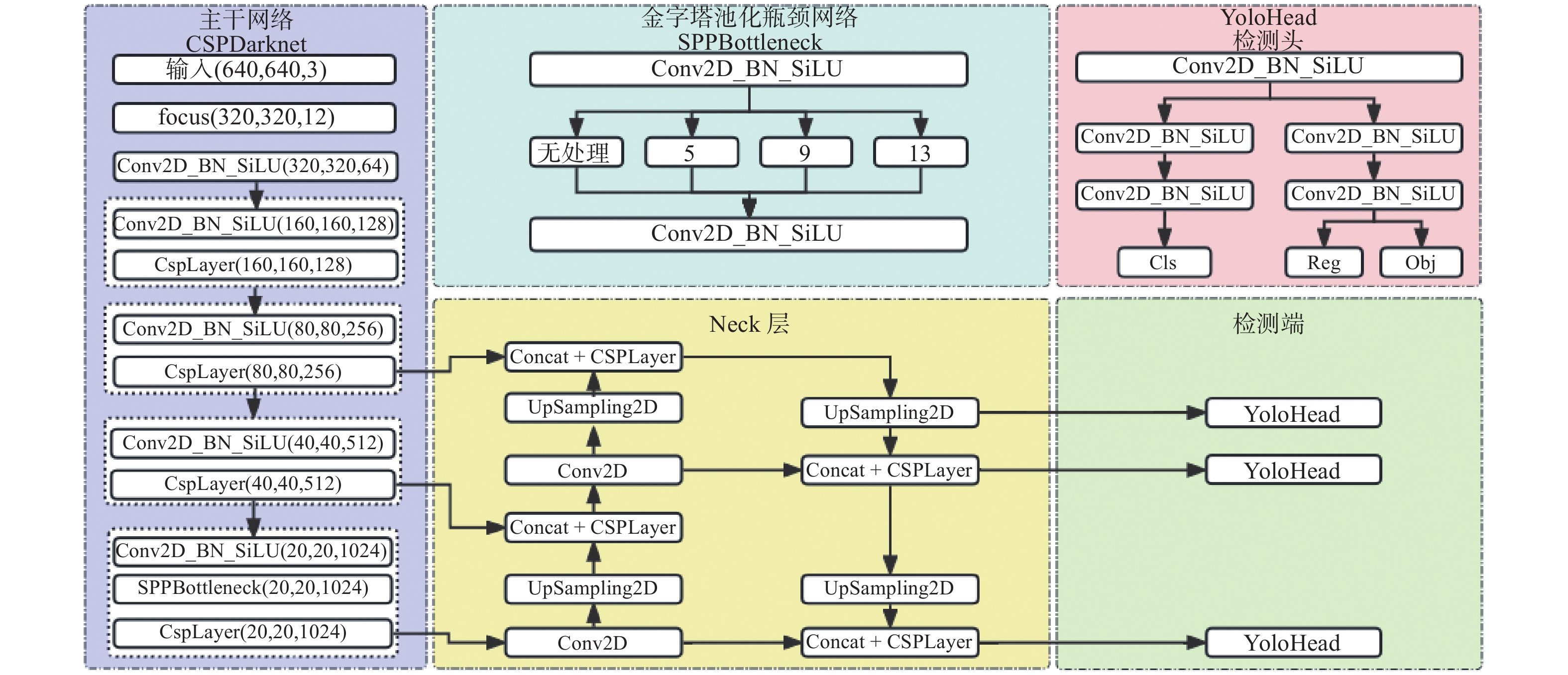
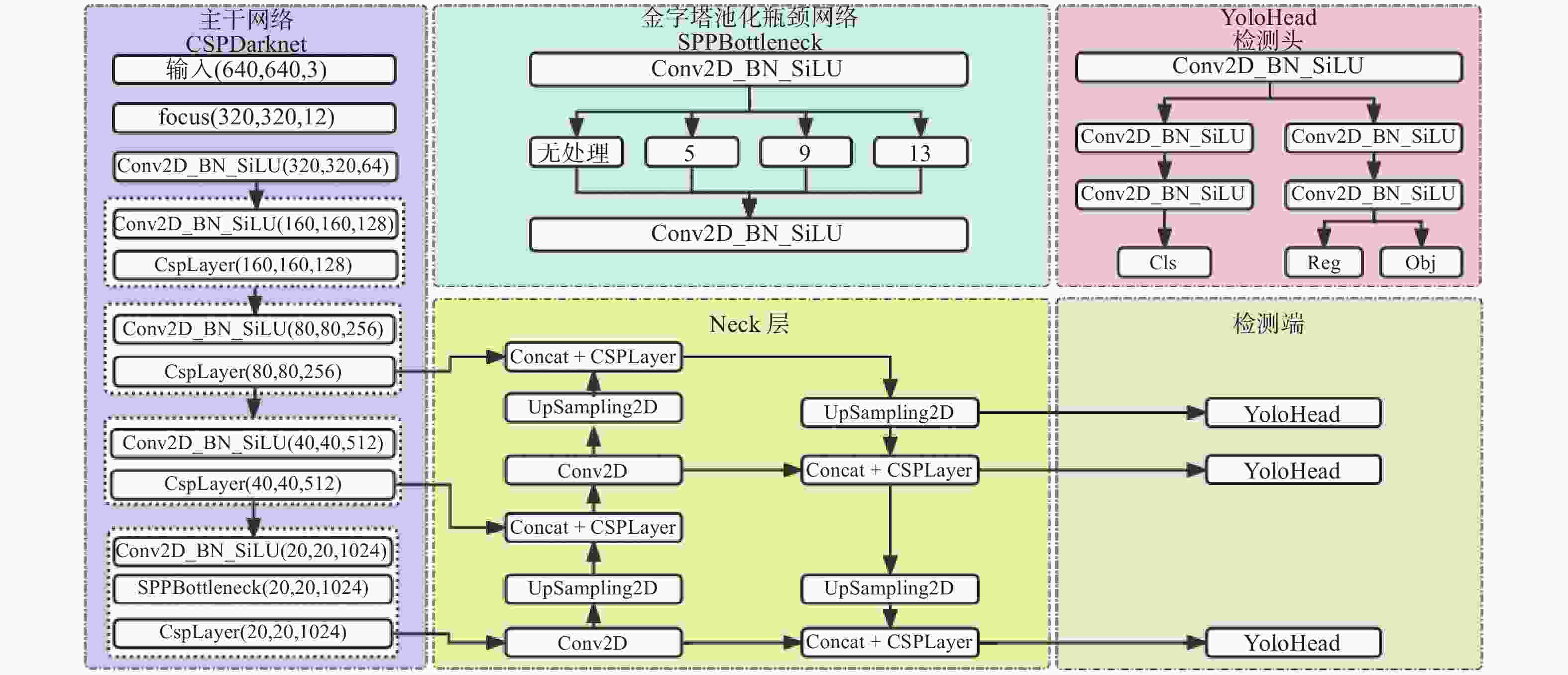
摘要: 针对主流检测算法对于道路车辆易出现漏检、误检、方向角度预测不准情况,设计一种结合改进YOLOX与改进Second的车辆融合检测算法。利用图像和点云的互补优势,采用两个子网络分别进行基于图像与基于点云的车辆检测。在图像检测中,采用基于卷积块的注意力模块、焦点损失和高效交并比损失来提升YOLOX的检测性能;在点云检测中,设计残差式稀疏卷积中间层来增强Second算法的特征表达和上下文信息关联,有效降低了车辆漏检率。构建角度多区域优化车辆角度预测,采用CLOCs的融合框架得到最终的融合检测结果。在KITTI数据集上进行算法实验,结果显示,相比原算法,新算法在简单、中等、困难目标的3D平均精度分别提升1.00%、1.38%、2.66%,检测目标旋转角度准确率得到极大提高。
-
关键词:
- 车辆检测 /
- 残差式稀疏卷积中间层 /
- 角度多区域 /
- 融合检测
Abstract: Common detection algorithms often struggled with missed detections, false positives, and large deviations in predicted orientation angles in road vehicle detection. A fusion detection algorithm combining improved YOLOX and Second was designed. By leveraging images and point clouds, two sub-networks were employed for vehicle detection. For image detection, convolutional block attention module, focal loss, and efficient intersection over union loss function were used to improve the detection performance of existing YOLOX. For point cloud detection, a residual sparse convolutional middle layer was designed to enhance the feature expression and context information association of Second algorithm, effectively reducing the missed detection rate of vehicles. The predictive directional angles was optimized by constructing a multi-bins strategy. Experimental conducted on KITTI dataset show that the algorithm surpassed the original, with improvements of 1.00%, 1.38%, and 2.66% in 3D average precision for easy, moderate, and hard targets, respectively. The accuracy of detecting target rotation angles is also greatly improved. -
表 1 改进YOLOX消融实验
Table 1. Improved YOLOX ablation experiment
方法 CBAM focal loss EIoU mAP50 mAP50:95 YOLOX × × × 0.862 0.753 改进1 √ × × 0.886 0.771 改进2 √ √ × 0.889 0.775 改进3 √ √ √ 0.907 0.793 表 2 图像检测模型对比实验
Table 2. Comparison experiment of image detection models
方法 mAP50 mAP50:95 FPS/(帧·s−1) Faster R-CNN 0.786 0.699 4.9 YOLOV3 0.843 0.731 26.3 YOLOV5 0.854 0.745 36.7 YOLOX 0.862 0.753 36.2 改进YOLOX 0.907 0.793 35.6 表 3 改进Second算法消融实验表
Table 3. Improved Second ablation experiment
方法 RSCML multi-bins 简单/% 中等/% 困难/% 3D mAP aos 3D mAP aos 3D mAP aos Second × × 88.02 94.16 78.19 88.71 77.03 84.92 改进1 √ × 89.22 93.87 80.18 88.67 77.93 84.99 改进2 √ √ 89.57 97.42 80.40 90.17 78.08 89.72 表 4 点云检测模型3D检测精度实验对比
Table 4. Experimental comparison of 3D detection accuracy for point cloud detection models
方法 模态 阶段 简单/% 中等/% 困难/% 3D mAP aos 3D mAP aos 3D mAP aos VoxelNet Lidar Two 81.97 91.94 65.46 80.67 62.85 70.64 TANet[15] Lidar Two 84.39 93.52 75.94 90.11 68.68 84.86 PointPillars Lidar One 85.86 95.13 75.75 91.79 70.65 86.51 Second Lidar One 88.02 94.16 78.19 88.71 77.03 84.92 ACDet[16] Lidar One 88.47 96.07 78.85 92.36 73.86 89.18 改进Second Lidar One 89.57 97.42 80.40 90.17 78.08 89.72 表 5 融合算法精度对比实验
Table 5. Comparison experiment of fusion algorithm accuracy
方法 模态 简单/% 中等/% 困难/% 3D mAP aos 3D mAP aos 3D mAP aos Second Lidar 88.02 94.16 78.19 88.71 77.03 84.92 MV3D Lidar + Camera 86.55 91.32 78.10 86.53 76.67 84.71 F-PointNet Lidar + Camera 88.02 95.85 81.16 92.17 75.33 85.42 AVOD-FPN Lidar + Camera 86.80 94.98 81.79 89.22 77.70 82.14 PFF3D Lidar + Camera 83.11 94.86 80.26 91.06 75.43 86.28 CLOCs Lidar + Camera 91.07 96.77 81.65 93.66 77.97 87.31 Ours(One) Lidar + Camera 91.56 97.00 81.67 93.67 78.65 87.36 Ours(Two) Lidar + Camera 92.07 99.21 83.03 93.53 80.63 92.97 -
[1] BALTRUŠAITIS T, AHUJA C, MORENCY L P. Multimodal machine learning: a survey and taxonomy[J] . IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(2): 423 − 443. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2798607 [2] 刘伟. 基于激光雷达和机器视觉的智能车前方障碍物检测研究[D] . 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学, 2019. [3] 郑少武, 李巍华, 胡坚耀. 基于激光点云与图像信息融合的交通环境车辆检测[J] . 仪器仪表学报, 2022, 40(12): 143 − 151. [4] 陆峰, 徐友春, 李永乐, 等. 基于信息融合的智能车障碍物检测方法[J] . 计算机应用, 2017, 37(S2): 115 − 119. [5] CHEN X Z, MA H M, WAN J, et al. Multi-view 3D object detection network for autonomous driving[C] //Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu: IEEE, 2017: 6526−6534. [6] KU J, MOZIFIAN M, LEE J, et al. Joint 3D proposal generation and object detection from view aggre-gation[C] //Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Madrid: IEEE, 2018: 1−8. [7] YIN T W, ZHOU X Y, KRÄHENBÜHL P. Multimodal virtual point 3D detection[C] //Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. [S. l. ] : Curran Associates Inc. , 2021: 1261. [8] 杨飞, 朱株, 龚小谨, 等. 基于三维激光雷达的动态障碍实时检测与跟踪[J] . 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2012, 46(9): 1565 − 1571. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2012.09.003 [9] GE Z, LIU S T, WANG F, et al. YOLOX: exceeding Yolo series in 2021[EB/OL] . (2021-07-18)[2024-01-22] . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2107.08430. [10] YAN Y, MAO Y X, LI B. SECOND: sparsely embedded convolutional detection[J] . Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3337. doi: 10.3390/s18103337 [11] PANG S, MORRIS D, RADHA H. CLOCs: camera-LiDAR object candidates fusion for 3D object detection[C] //Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Las Vegas: IEEE, 2020: 10386−10393. [12] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[EB/OL] . (2018-04-08)[2024-01-22] . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.02767. [13] 刘凯, 罗素云. 基于改进YOLOX-S的交通标志识别[J] . 电子测量技术, 2023, 46(1): 112 − 119. [14] ZHOU Y, TUZEL O. VoxelNet: end-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection[C] //Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 4490−4499. [15] LIU Z, ZHAO X, HUANG T T, et al. TANet: robust 3D object detection from point clouds with triple attention[C] //Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. New York: AAAI, 2020: 11677−11684. [16] XU J L, WANG G J, ZHANG X, et al. ACDet: attentive cross-view fusion for LiDAR-based 3D object detection[C] //Proceedings of 2022 International Conference on 3D Vision. Prague: IEEE, 2022: 74−83. [17] QI C R, LIU W, WU C X, et al. Frustum pointnets for 3D object detection from RGB-D data[C] //Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 918−927. [18] WEN L H, JO K H. Fast and accurate 3D object detection for lidar-camera-based autonomous vehicles using one shared voxel-based backbone[J] . IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 22080 − 22089. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3055491 -





 下载:
下载: