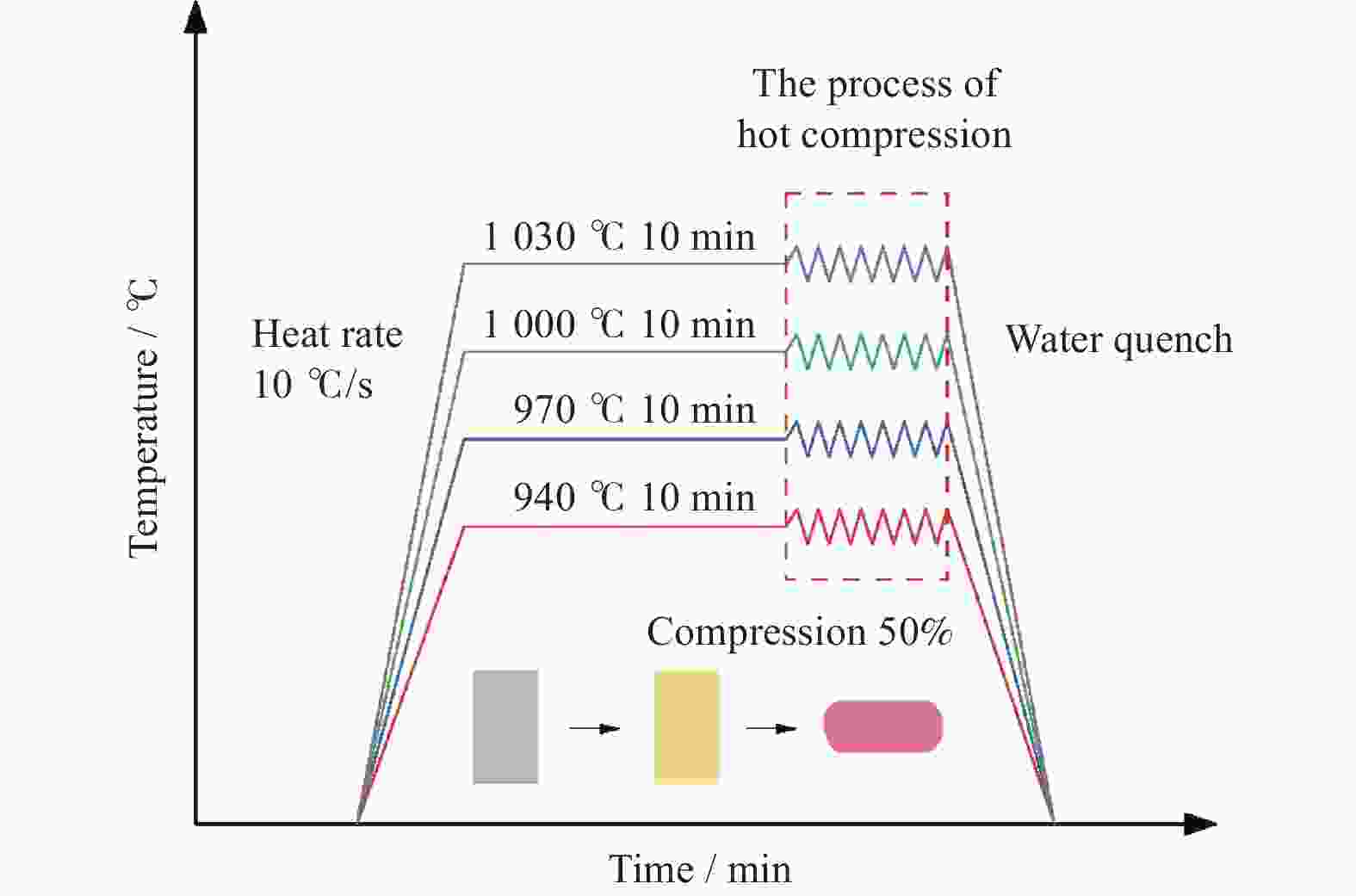
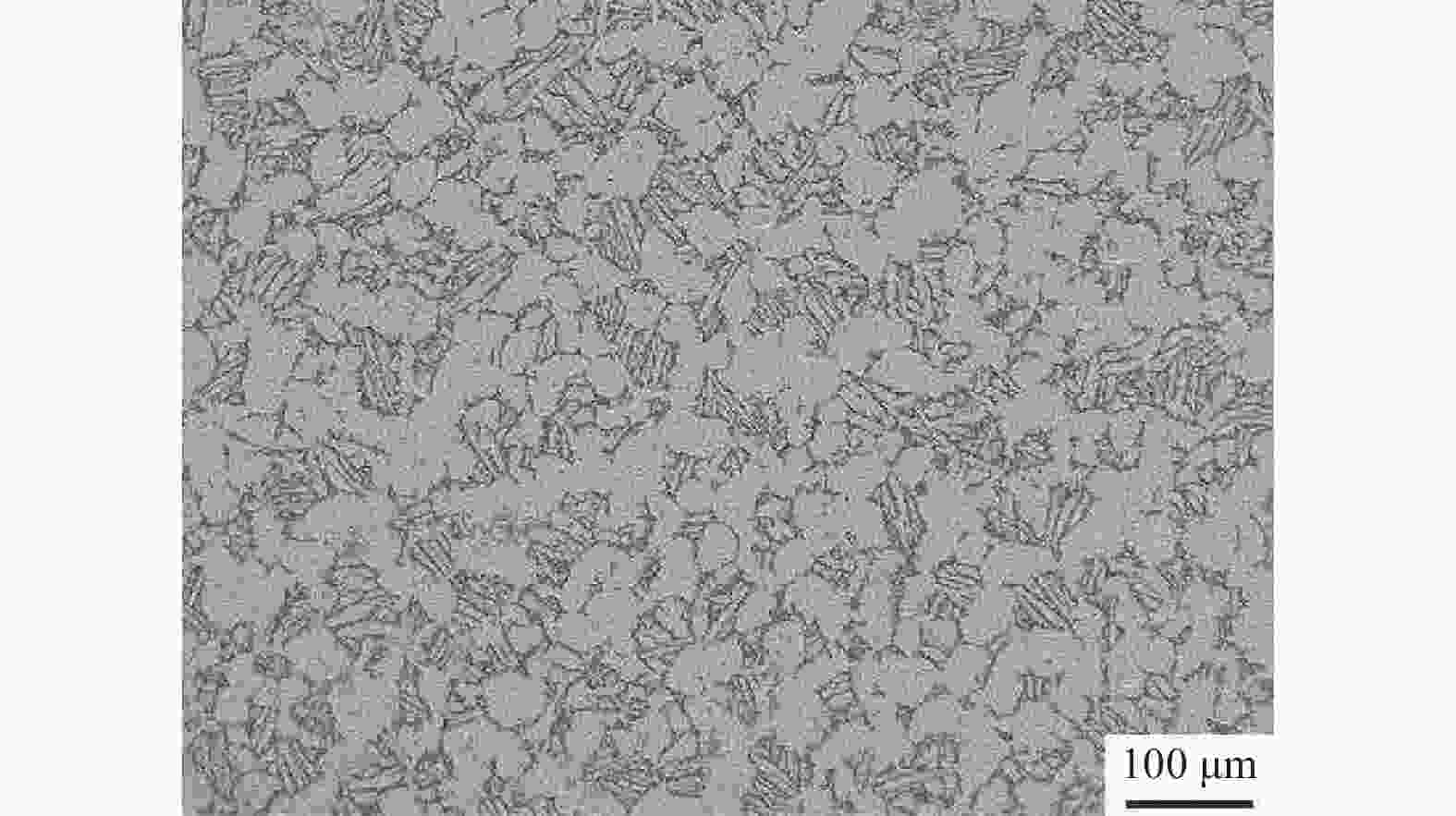
Microstructure evolution during hot deformation and dynamic transformation of Ti-5Al-3.3Sn-3.7Zr-0.6Ta-0.5W alloy in α + β two-phase region
-
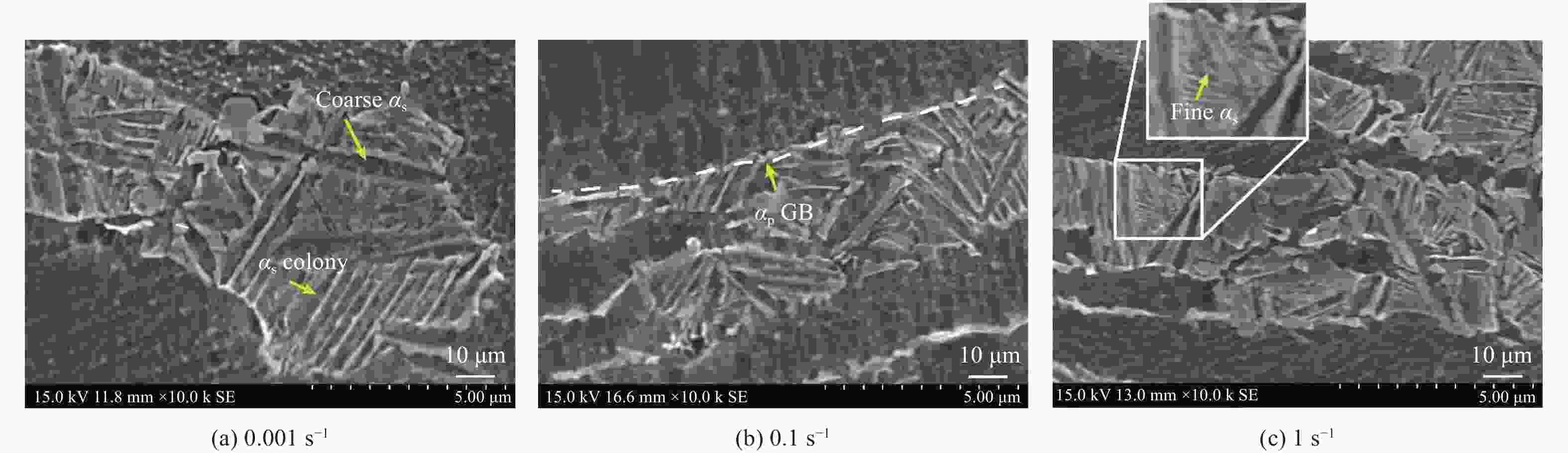
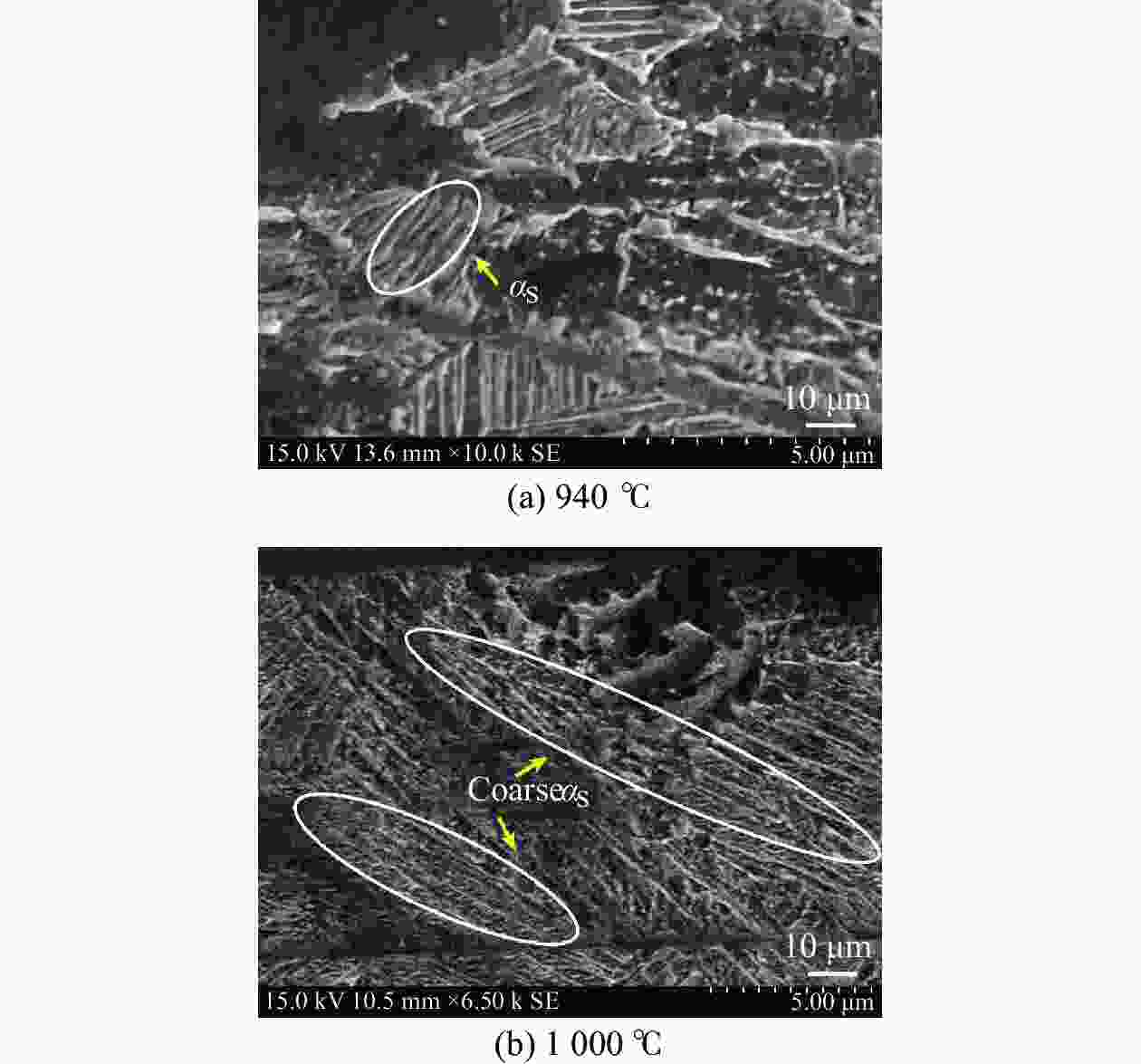
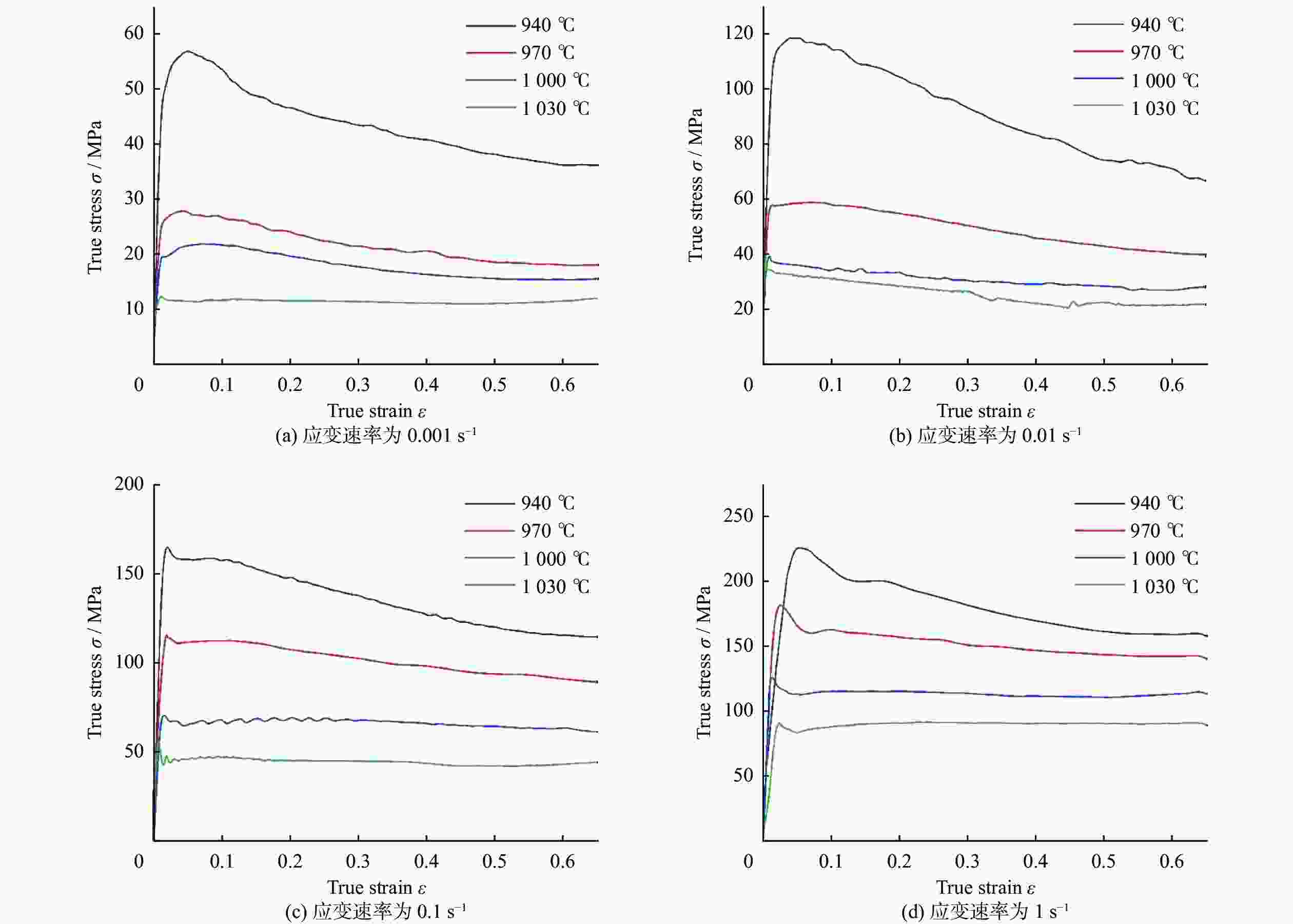
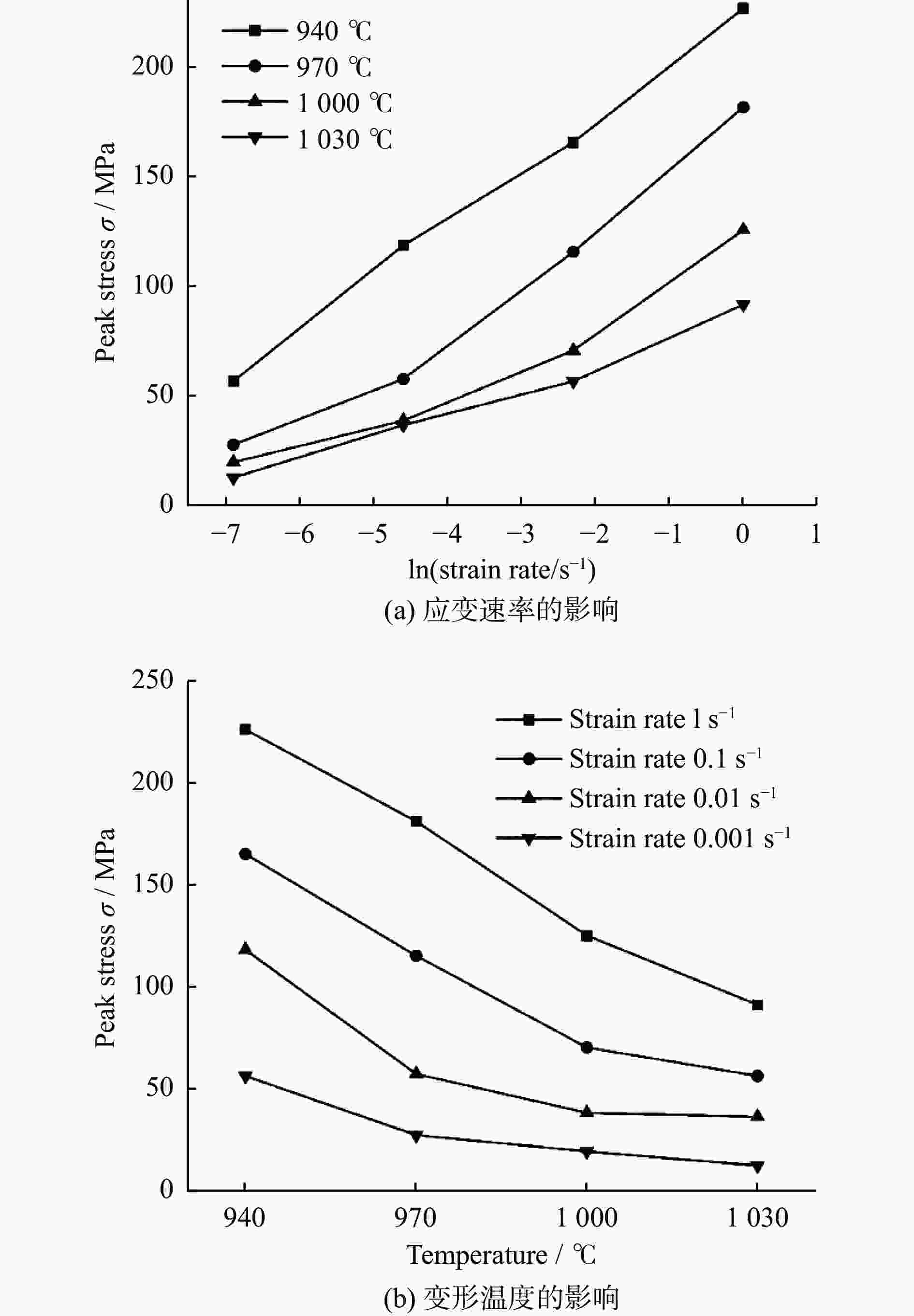
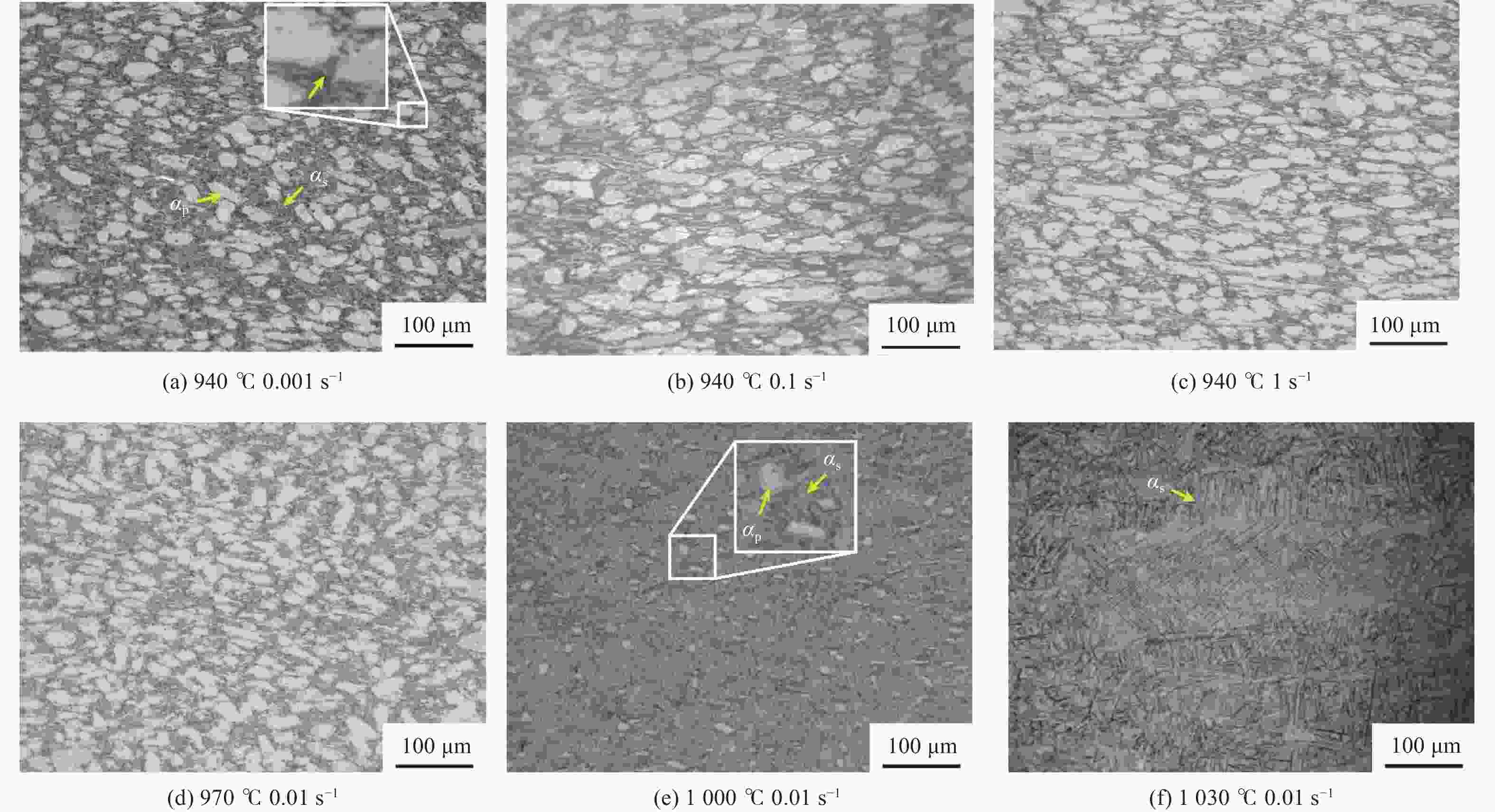
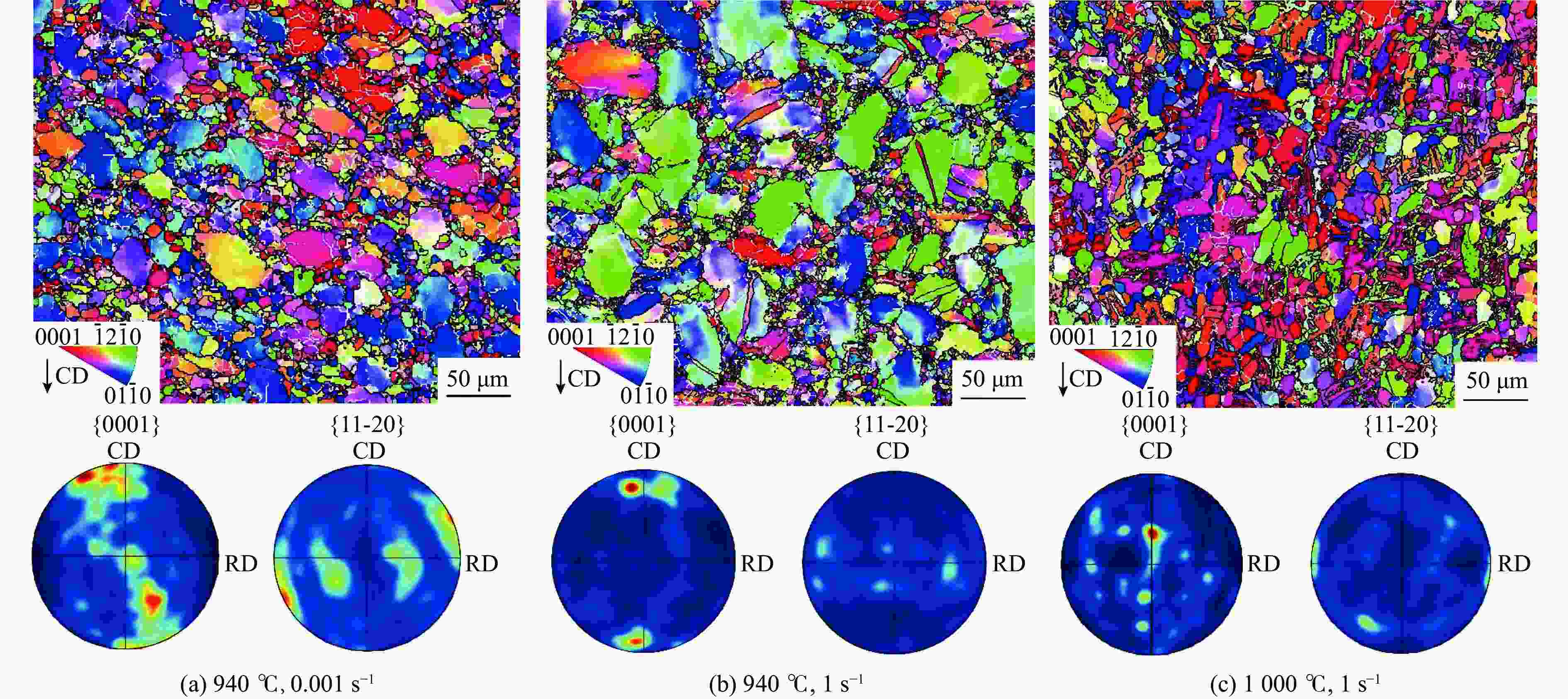
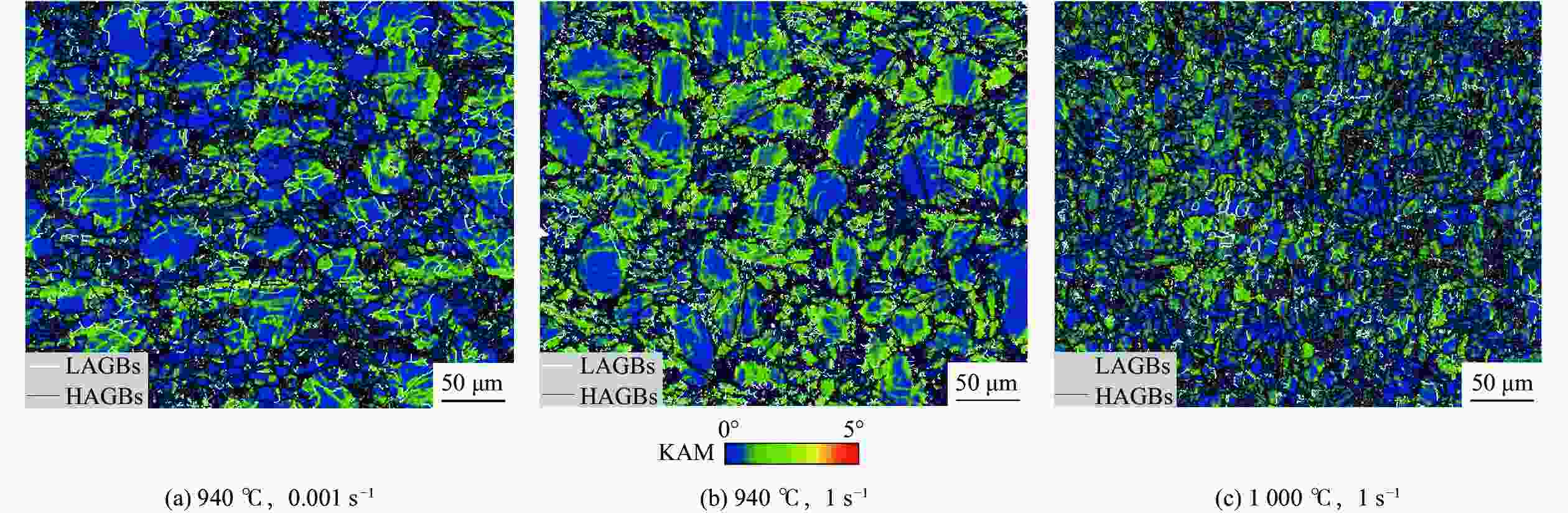
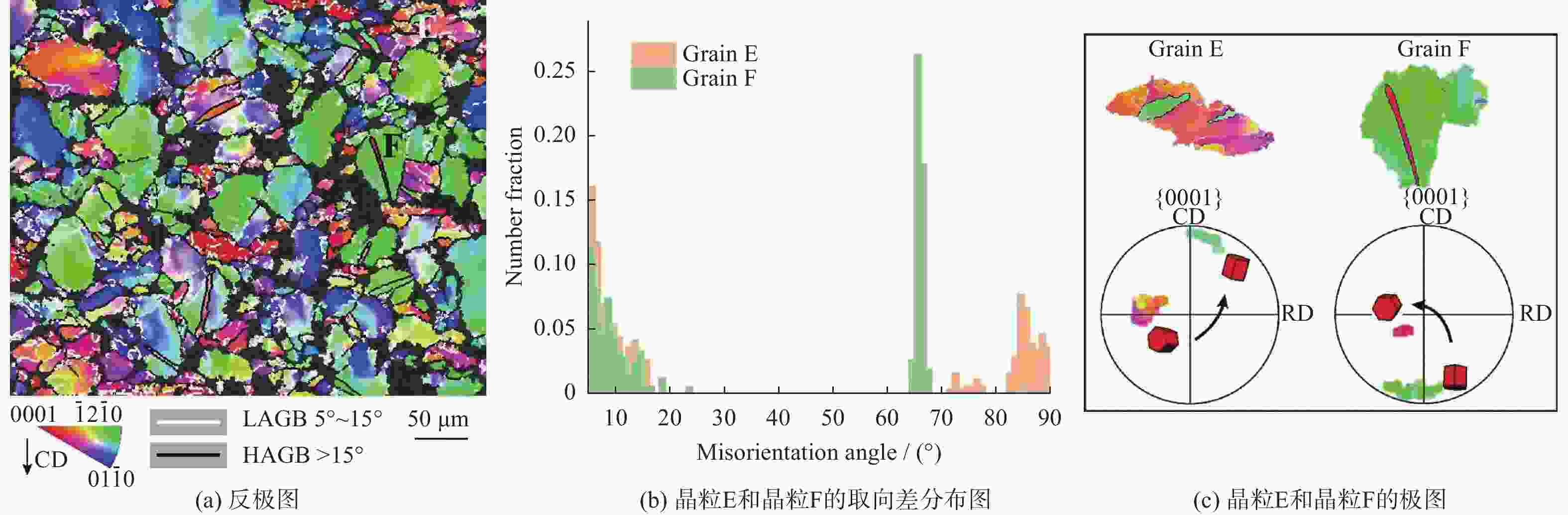
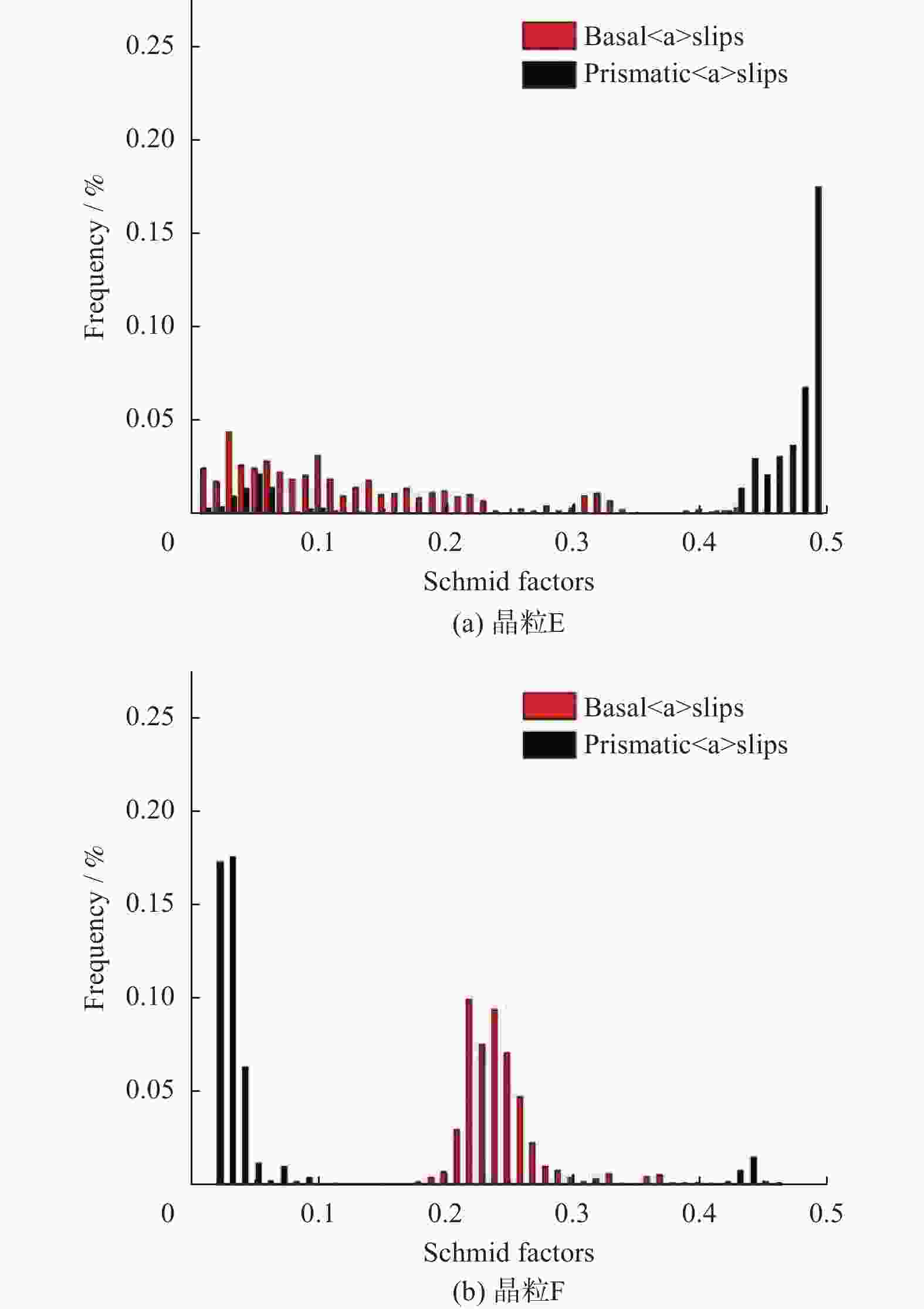
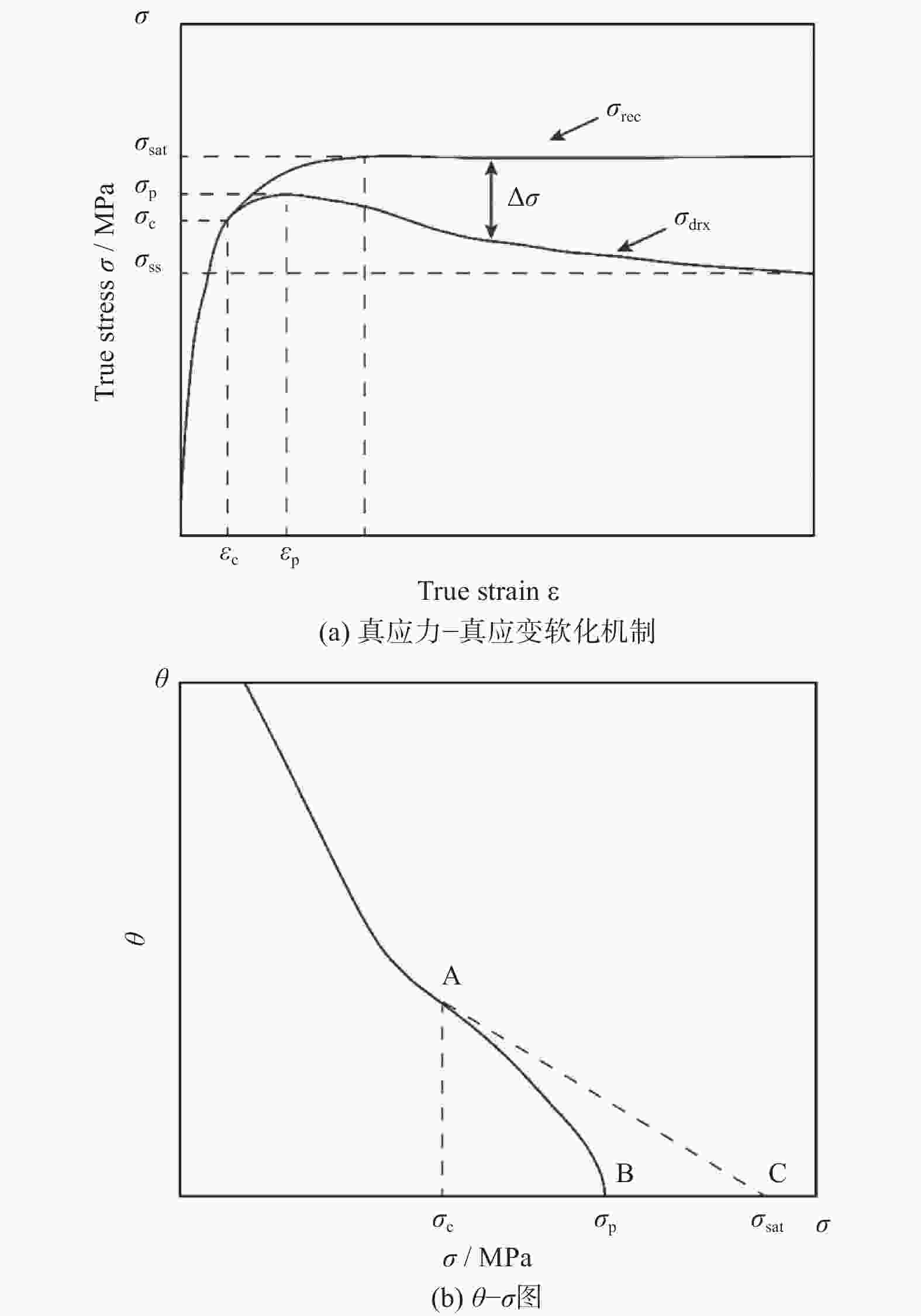
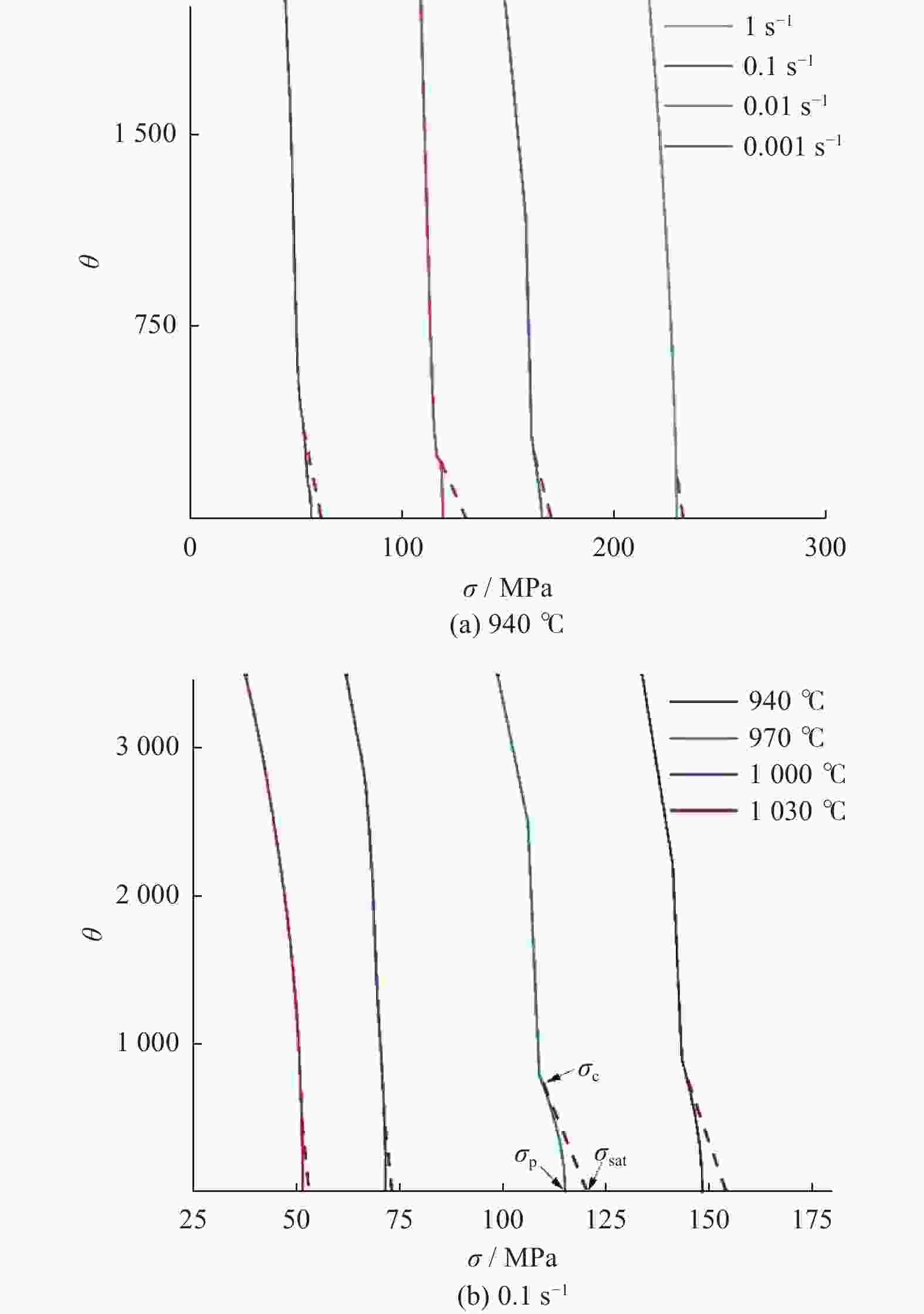
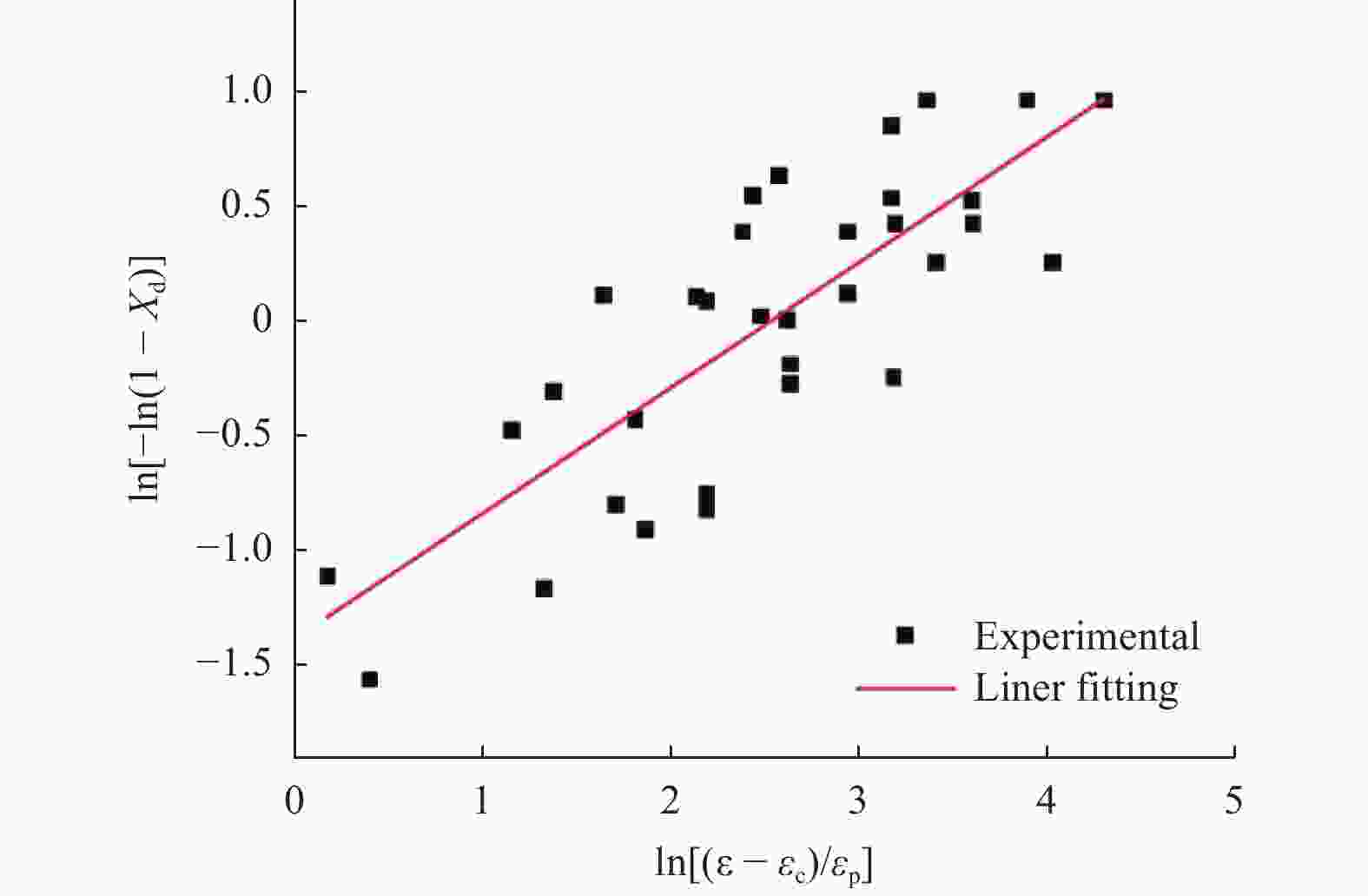
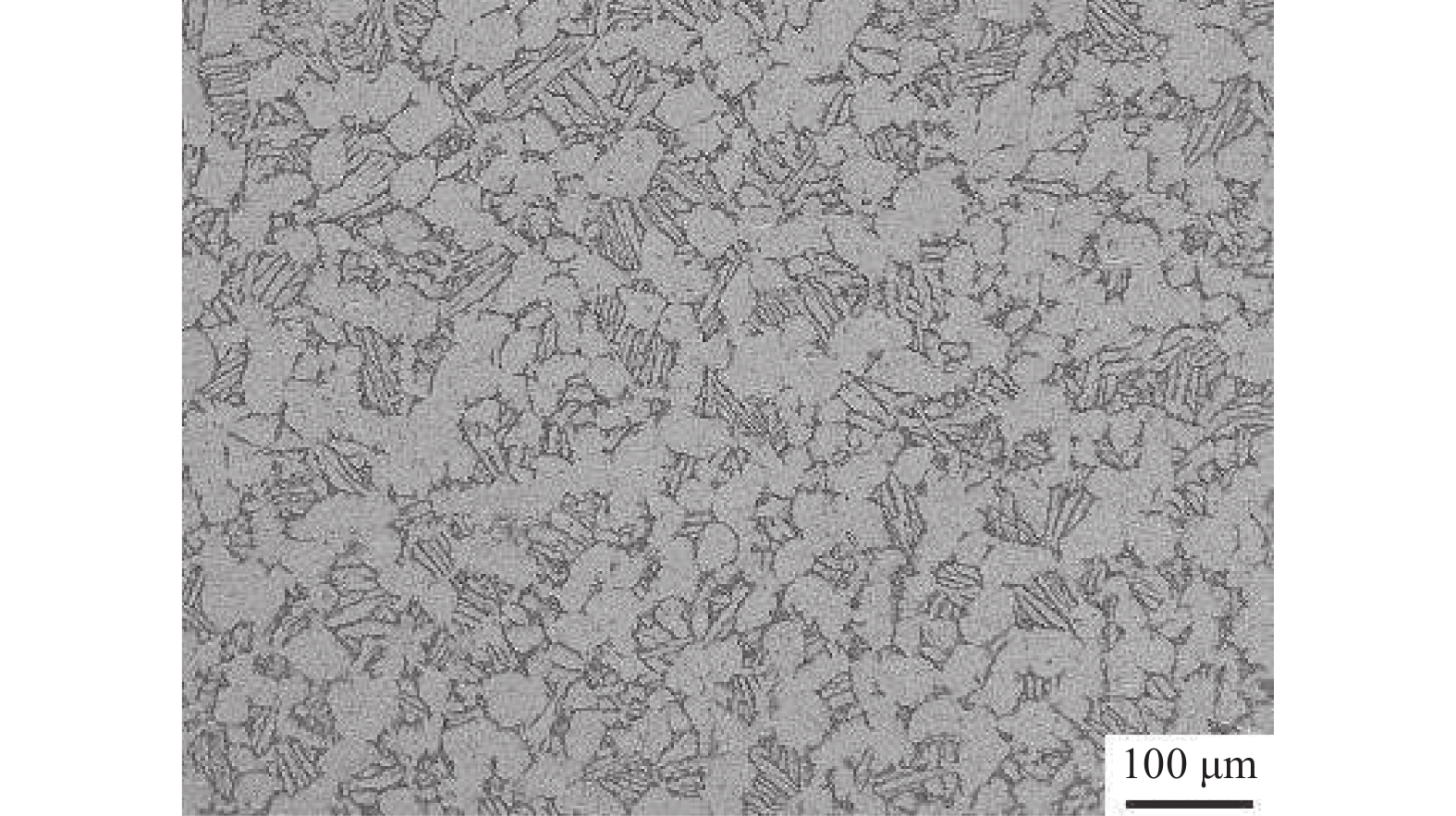
摘要: 采用热压缩试验和微观组织表征试验相结合的方法,探究一种新型近α型钛合金在不同变形条件下的流变行为和微观组织演变。研究发现,真实应力−应变曲线显示出峰值后应力整体下降并趋于稳定的特点,并且在高应变速率下,峰值应力较高且迅速下降。这是硬取向的α相向软取向的β相的转变导致了流变应力的快速下降,以及动态再结晶细化晶粒和动态回复对于亚晶组织中位错的排布。基于这些发现建立了动态再结晶体积分数模型。Abstract: The rheological behavior and microstructure evolution of the new near-α titanium alloy under different deformation conditions were investigated by thermal compression tests and microstructure characterization experiments. The results show that the real stress-strain curve displays characteristics of stress decrease and tendency to stabilize after the peak. At high strain rates, the peak stress is high and decreases rapidly. The transformation of the hard-oriented α phase to the soft-oriented β phase leads to a rapid decrease in the flow stress, with dynamic recrystallization (DRX) refining grains and dynamic recovery (DRV) rearranging dislocations within subgrains. Based on these findings, a dynamic recrystallization volume fraction model was established.
-
表 1 Ti-5Al-3.3Sn-3.7Zr-0.6Ta-0.5W合金化学成分
Table 1. Main chemical composition of Ti-5Al-3.3Sn-3.7Zr-0.6Ta-0.5W alloy
元素 Al Zr Sn Ta W Ti 质量分数/% 5.0 3.7 3.3 0.6 0.5 Bal. -
[1] ZHAO H, YE L Y, CHENG Q S, et al. Constitutive model and processing maps of 7055 aluminum alloy used for fasteners[J] . Materials Today Communications, 2022, 33: 104996. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104996 [2] WHITTAKER J T, HESS D P. Ductility of titanium alloy and stainless steel aerospace fasteners[J] . Journal of Failure Analysis and Prevention, 2015, 15(5): 571−575. doi: 10.1007/s11668-015-0007-8 [3] BAI Q, LIN J G, DEAN T A, et al. Modelling of dominant softening mechanisms for Ti-6Al-4V in steady state hot forming conditions[J] . Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013, 559: 352 − 358. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.08.110 [4] PARADKAR A, KAMAT S V, GOGIA A K, et al. Effect of Al and Nb on the trigger stress for stress-induced martensitic transformation during tensile loading in Ti–Al–Nb alloys[J] . Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2008, 487(1/2): 14 − 19. [5] JIANG Y Q, LIN Y C, JIANG X Y, et al. Hot tensile properties, microstructure evolution and fracture mechanisms of Ti-6Al-4V alloy with initial coarse equiaxed phases[J] . Materials Characterization, 2020, 163: 110272. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110272 [6] 蔡贇, 孙朝阳, 万李, 等. AZ80镁合金动态再结晶软化行为研究[J] . 金属学报, 2016, 52(9): 1123−1132. [7] LI A B, HUANG L J, MENG Q Y, et al. Hot working of Ti–6Al–3Mo–2Zr–0.3Si alloy with lamellar α + β starting structure using processing map[J] . Materials & Design, 2009, 30(5): 1625 − 1631. [8] ZHAO Z L, LIU N, XU W X, et al. Rapid dynamic transformation in the initial stage of hot deformation of a near alpha titanium alloy[J] . Materials Letters, 2021, 305: 130837. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130837 [9] JONAS J J, ARANAS C, FALL A, et al. Transformation softening in three titanium alloys[J] . Materials & Design, 2017, 113: 305 − 310. [10] JI X K, GUO B Q, JIANG F L, et al. Accelerated flow softening and dynamic transformation of Ti-6Al-4V alloy in two-phase region during hot deformation via coarsening α grain[J] . Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2020, 36: 160 − 166. [11] GHOSH C, ARANAS C, JONAS J J. Dynamic transformation of deformed austenite at temperatures above the Ae3[J] . Progress in Materials Science, 2016, 82: 151 − 233. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2016.04.004 [12] LIU H J, XUE Y, ZHANG Z M, et al. Effect of multi-pass hot deformation on flow stress and microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy prepared by hot isostatic pressing[J] . Procedia Manufacturing, 2020, 50: 652 − 657. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.08.117 [13] ZHAO Z L, LI H, FU M W, et al. Effect of the initial microstructure on the deformation behavior of Ti60 titanium alloy at high temperature processing[J] . Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 617: 525 − 533. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.08.092 [14] PIAO R X, YANG S L, ZHU Y L, et al. Hot deformation behavior of near-α titanium alloy Ti-1100 prepared by TiH2-based powder metallurgy[J] . Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020, 49(10): 3314 − 3324. [15] WARCHOMICKA F, POLETTI C, STOCKINGER M. Study of the hot deformation behaviour in Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–3Cr–1Zr[J] . Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528(28): 8277 − 8285. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.07.068 [16] ZHAO E T, SUN S C, YU J R, et al. Dynamic recrystallization and silicide precipitation behavior of titanium matrix composites under different strains[J] . Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2021, 31(11): 3416 − 3427. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(21)65739-4 [17] KANG X D, DU Z X, WANG Z, et al. Efficient access to ultrafine crystalline metastable-β titanium alloy via dual-phase recrystallization competition[J] . Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 29: 335−343. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.01.101 [18] GUO Y H, NIU J Z, CAO J X, et al. Relative strength of β phase stabilization by transition metals in titanium alloys: the Mo equivalent from a first principles study[J] . Materials Today Communications, 2023, 35: 106123. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.106123 [19] XU S, ZHANG H M, XIAO N M, et al. Mechanisms of macrozone elimination and grain refinement of near α Ti alloy via the spheroidization of the Widmannstätten structure[J] . Acta Materialia, 2023, 260: 119339. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2023.119339 [20] BALASUNDAR I, RAGHU T, KASHYAP B P. Hot working and geometric dynamic recrystallisation behaviour of a near-α titanium alloy with acicular microstructure[J] . Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2014, 600: 135 − 144. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.01.088 -





 下载:
下载: