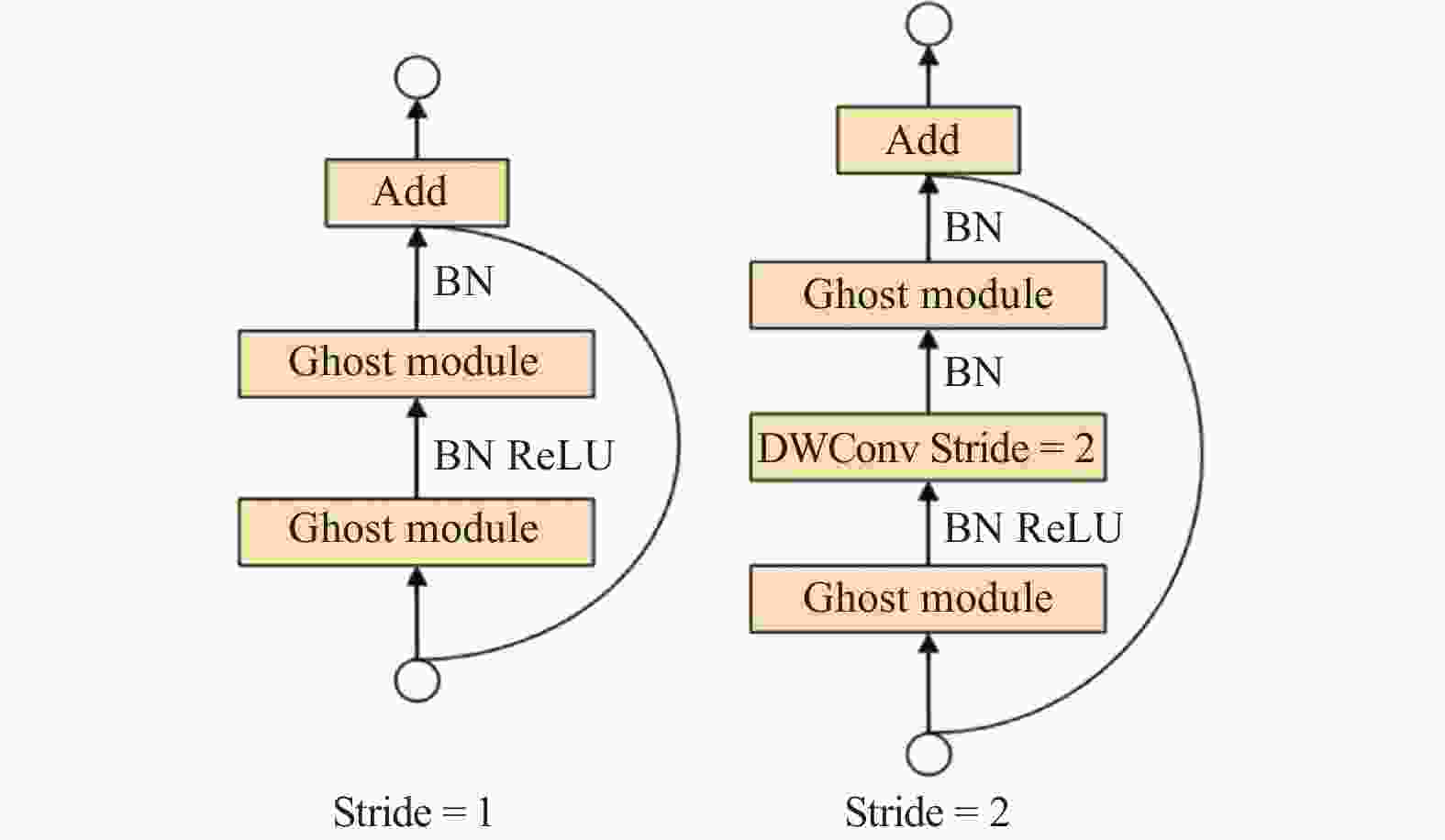
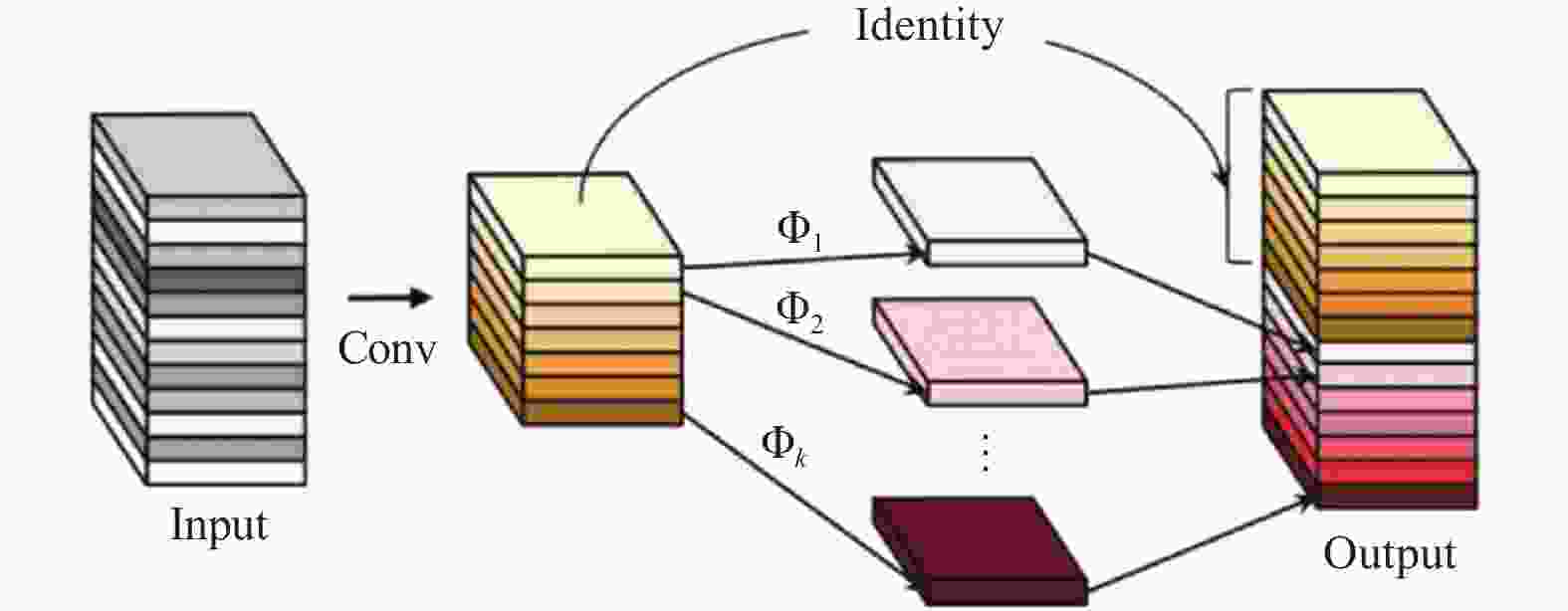
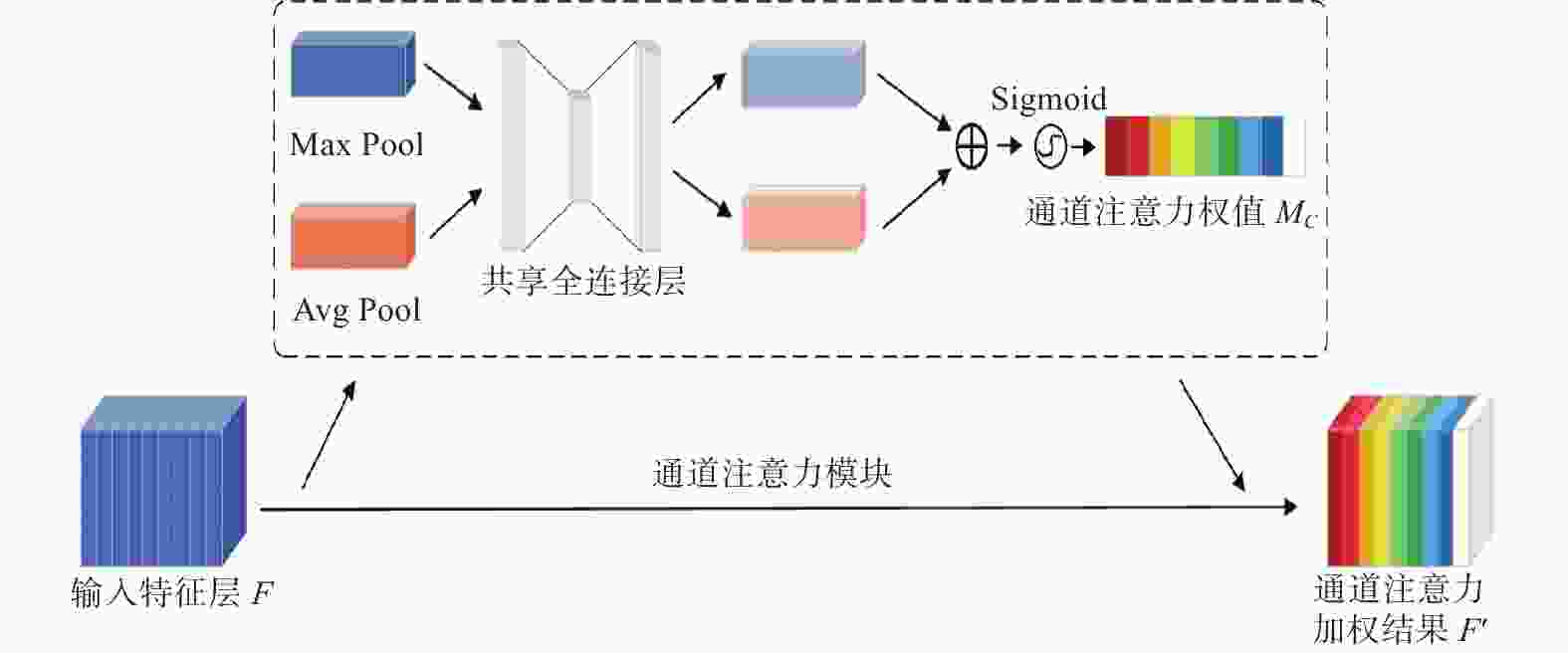
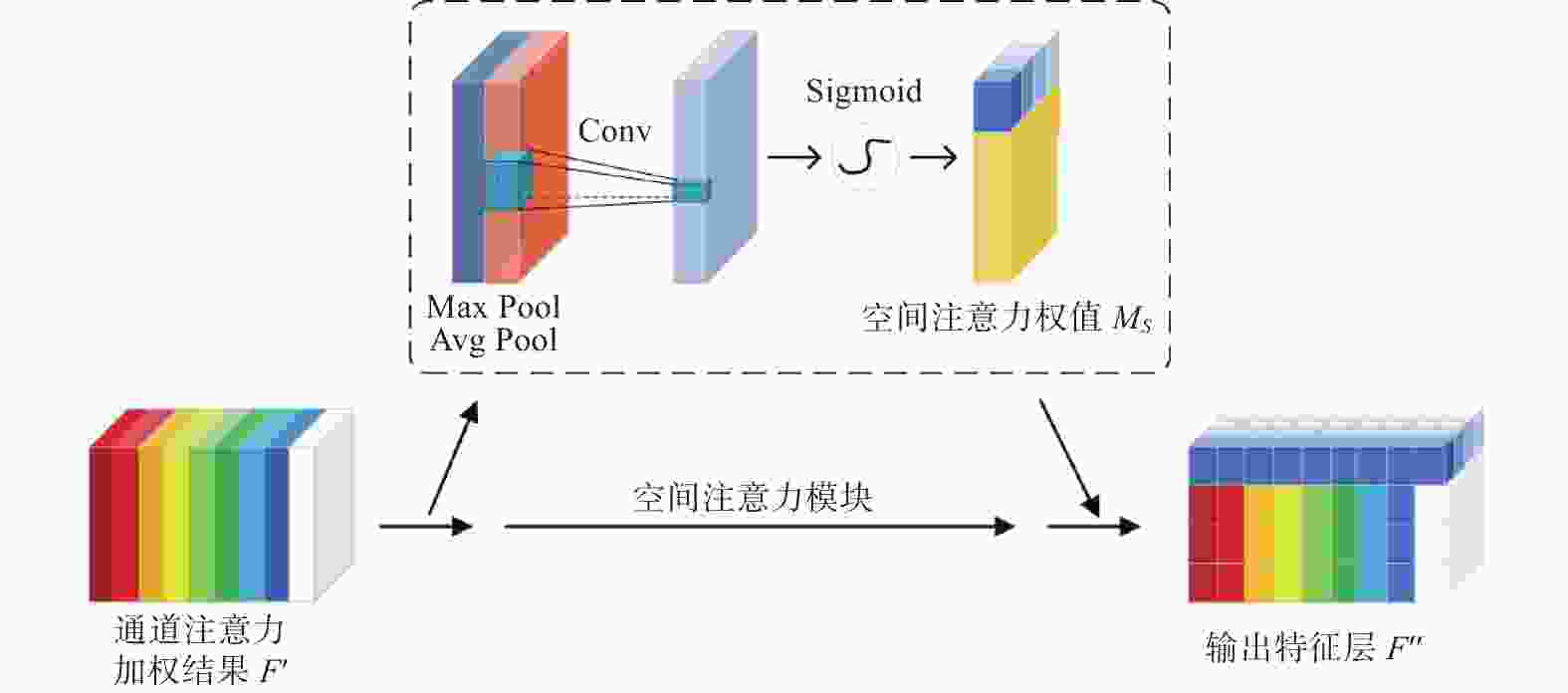
Improved YOLO-based image segmentation method for AEC welding cup profile
-
摘要: 为实现航空电连接器自动化焊接的精准定位,提出一种基于机器学习的航空电连接器焊杯剖面检测与图像分割方法。通过增加小目标检测层、CBAM机制和采用GhostNet网络,提高原始网络模型的特征提取有效性和预测准确率,同时降低改进后的模型参数量和空间大小。实验结果表明,改进YOLOv5s-Seg模型的平均精度均值为84.2%和44.6%。相较于YOLOv5s原模型,平均精度均值分别提升5.5%和1.3%。所提出的检测与分割方法能较好地实现精度与速度的平衡,有利于实际应用和设备部署,为改进基于机器视觉的航空电连接器自动化焊接提供一定的理论基础。Abstract: To achieve the accurate positioning of automated welding of aviation electrical connector (AEC), a method for the detection and segmentation of welding cup profiles was proposed based on machine learning. The effectiveness of feature extraction and prediction accuracy of the original network model were enhanced by incorporating a small target detection layer, the CBAM mechanism, and the GhostNet network. Concurrently, the number of parameters and space size of the improved model were reduced. The experimental results show that the improved YOLOv5s-Seg model achieves mean average precision of 84.2% and 44.6%. Compared with the original YOLOv5s model, this represents improved by 5.5% and 1.3%, respectively. The detection-segmentation method proposed effectively balances precision and speed, facilitating practical application and equipment deployment, and provides a theoretical basis for advancing the automated welding of AEC based on machine vision.
-
表 1 硬件配置
Table 1. Hardware configuration
环境参数 配置 中央处理器 I7-13700KF 显卡型号 GeForce3090 运行内存 64 GB 显卡内存 24 GB 操作系统 Windows10 深度学习框架 Pytorch2.0.1 Cudnn Cudnn11.8 OpenCV 4.8 表 2 训练参数表
Table 2. Training parameters
模型参数 配置 初始学习率 0.01 输入图像大小 640 × 640 优化器 SGD 训练周期 300 批量大小 16 动量 0.937 权重衰减率 0.0005 学习率衰减方式 余弦退火算法 表 3 不同注意力机制模型精度实验结果
Table 3. Experimental results on the accuracy of different attention mechanism models
编号 模型 预测率/% 召回率/% F1/% ${{\mathrm{mAP}}_{50}}$/% ${{\mathrm{mAP}}_{50 - 95}}$/% 0 + CBAM 88.3 75.3 80.7 84.2 44.6 1 + SimAM 90.3 72.5 80.4 80.7 42.7 2 + ECA 91.4 71.4 80.2 81.8 43.5 3 + SE 87.8 72.0 80.2 79.1 43.7 表 4 不同骨干网络模型精度实验结果
Table 4. Experimental results of different backbone network model accuracy
编号 模型 预测率/% 召回率/% F1/% ${{\mathrm{mAP}}_{50}}$/% ${{\mathrm{mAP}}_{50 - 95}}$/% 0 + 4P-CBAM 90.9 72.5 80.7 83.5 44.8 1 + ShuffleNetV2 86.8 67.1 75.7 77.2 40.2 2 + MobileNetV3 87.8 74.5 80.6 79.2 41.7 3 + RepGhost 89.5 72.3 80.0 81.8 42.6 表 5 不同骨干网络模型速度实验结果
Table 5. Experimental results on speed of different backbone network models
编号 模型 层数 参数量 浮点运算量 模型大小/MB FPS 1 + 4P-CBAM 356 7.51×106 54.0×109 15.77 93.5 2 + ShuffleNetV2 340 3.70×106 44.0×109 8.43 94.3 3 + MobileNetV3 356 3.13×106 47.3×109 7.24 83.3 4 + GhostNet 300 5.57×106 48.8×109 12.03 88.5 5 + RepGhost 647 4.02×106 44.4×109 9.17 77.5 表 6 不同模型精度实验结果
Table 6. Experimental results of different model accuracy
编号 模型 预测率/% 召回率/% F1/% ${{\mathrm{mAP}}_{50}}$/% ${{\mathrm{mAP}}_{50 - 95}}$/% 0 YOLOv5s-G 88.3 75.3 81.3 84.2 44.6 1 YOLOv5s-Seg 90.9 71.2 79.8 78.7 43.3 2 YOLOv7s-Seg 93.9 70.7 80.7 78.4 43.3 3 YOLOv8s-Seg 91.8 69.5 79.1 78.3 42.1 表 7 不同模型速度实验结果
Table 7. Experimental results of different model speeds
编号 模型 层数 参数量 浮点运算量 模型大小/MB FPS 0 YOLOv5s -G 300 5.57×106 48.8×109 12.04 88.5 1 YOLOv5s-Seg 165 7.40×106 25.7×109 14.86 90.0 2 YOLOv7s-Seg 325 9.52×106 35.9×109 19.13 130.0 3 YOLOv8s-Seg 261 11.80×106 42.7×109 23.31 151.0 -
[1] 王腾, 郁大照, 朱蒙, 等. 海军某型飞机典型电连接器失效分析[J] . 装备环境工程, 2019, 16(12): 28 − 35. [2] 杨奋为. 电连接器行业基础共性技术展望[J] . 机电元件, 2023, 43(6): 53 − 60,63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6133.2023.06.015 [3] 牛步钊, 唐春燕, 杨存平, 等. 轨道交通装备用电连接器典型失效类型分析[J] . 智慧轨道交通, 2023, 60(3): 67 − 71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0366.2023.03.013 [4] 童宣科. 基于图像处理的航空电连接器识别与焊点定位技术研究[D] . 桂林: 桂林电子科技大学, 2018. [5] 孙逸鹤. 基于机器视觉电连接器自动焊接技术研究[D] . 桂林: 桂林电子科技大学, 2018. [6] 单根立, 董沛森. 基于工业PC和PLC的圆形电连接器与多芯电缆自动焊接设备设计[J] . 机床与液压, 2020, 48(2): 94 − 97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2020.02.021 [7] SONG L M, KANG J W, ZHANG Q L, et al. A weld feature points detection method based on improved YOLO for welding robots in strong noise environment[J] . Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2023, 17(5): 1801 − 1809. doi: 10.1007/s11760-022-02391-0 [8] GAO A, FAN Z X, LI A N, et al. YOLO-Weld: a modified YOLOv5-based weld feature detection network for extreme weld noise[J] . Sensors, 2023, 23(12): 5640. doi: 10.3390/s23125640 [9] LI M, HUANG J, XUE L, et al. A guidance system for robotic welding based on an improved YOLOv5 algorithm with a RealSense depth camera[J] . Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 21299. [10] HAN K, WANG Y H, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C] //Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2020: 1577 − 1586. [11] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C] //Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: Springer, 2018: 3 − 19. [12] YANG L X, ZHANG R Y, LI L D, et al. SimAM: a simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks[C] //Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. [S.l.] : PMLR, 2021: 11863 − 11874. [13] WANG Q L, WU B G, ZHU P F, et al. ECA-Net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C] //Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle: IEEE, 2020: 11531 − 11539. [14] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C] //Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018: 7132 − 7141. [15] MA N N, ZHANG X Y, ZHENG H T, et al. ShuffleNet V2: practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C] //Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: Springer, 2018: 122 − 138. [16] HOWARD A, SANDLER M, CHEN B, et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[C] //Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul: IEEE, 2019: 1314 − 1324. [17] CHEN C P, GUO Z C, ZENG H E, et al. RepGhost: a hardware-efficient ghost module via reparameteri-zation[EB/OL] . (2022-11-11)[2024-01-31] . https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2211.06088. -





 下载:
下载: