Performance research of MnOx/Co3O4 composites within nanosheets for catalytic soot combustion
-
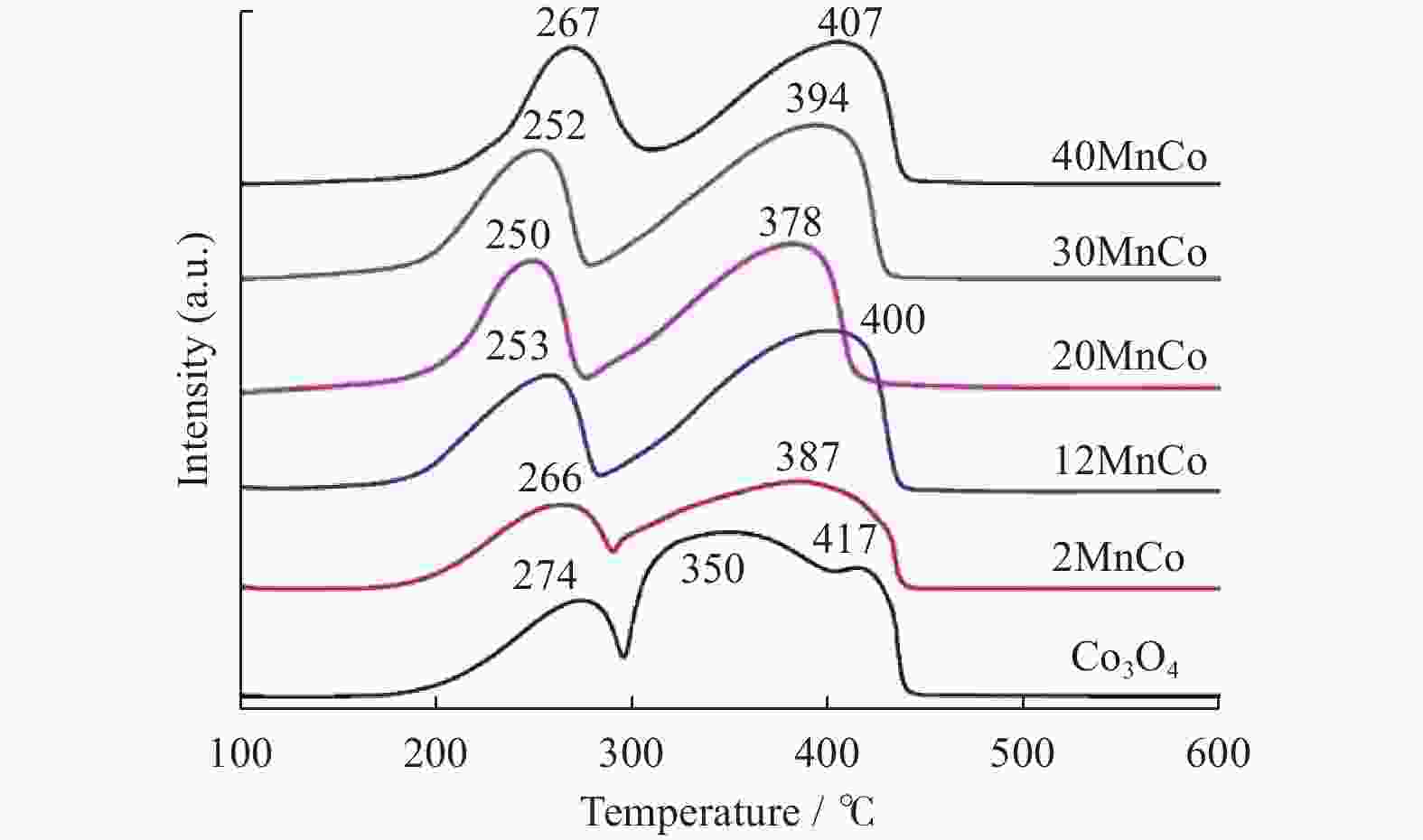
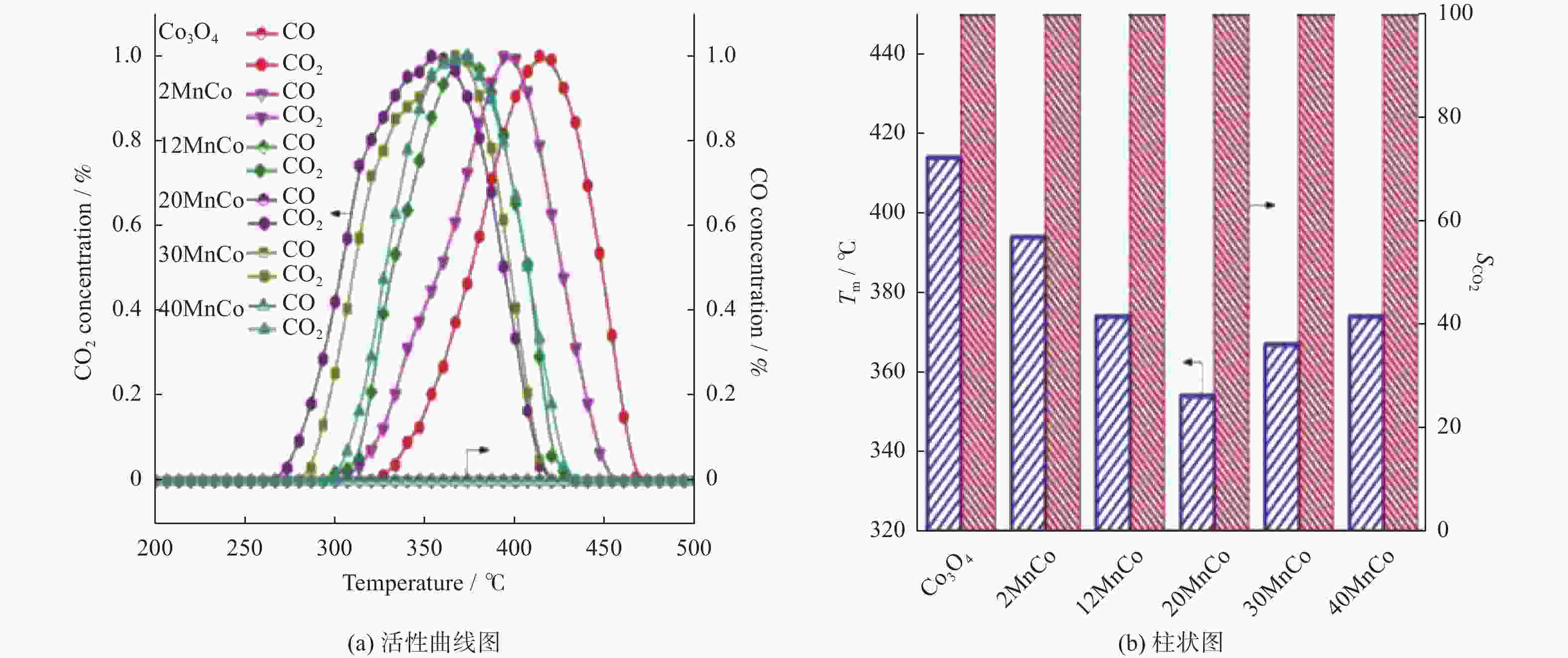
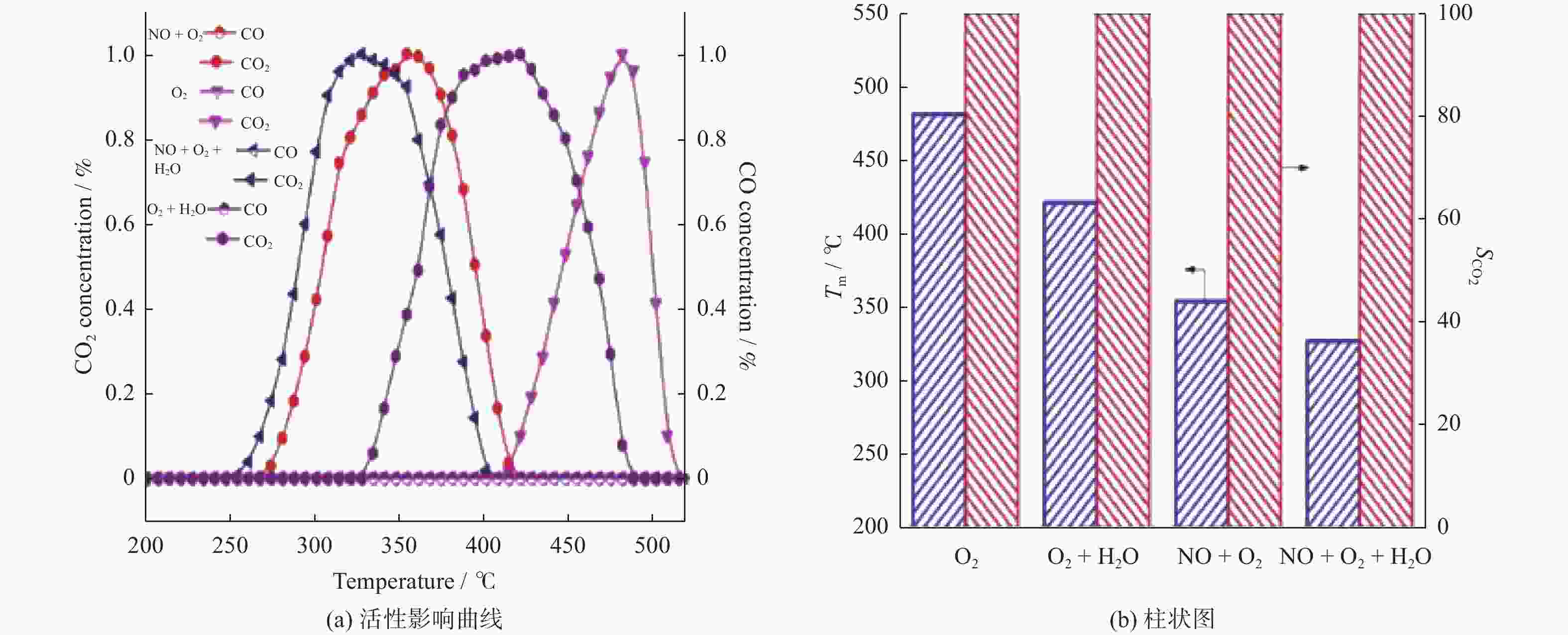
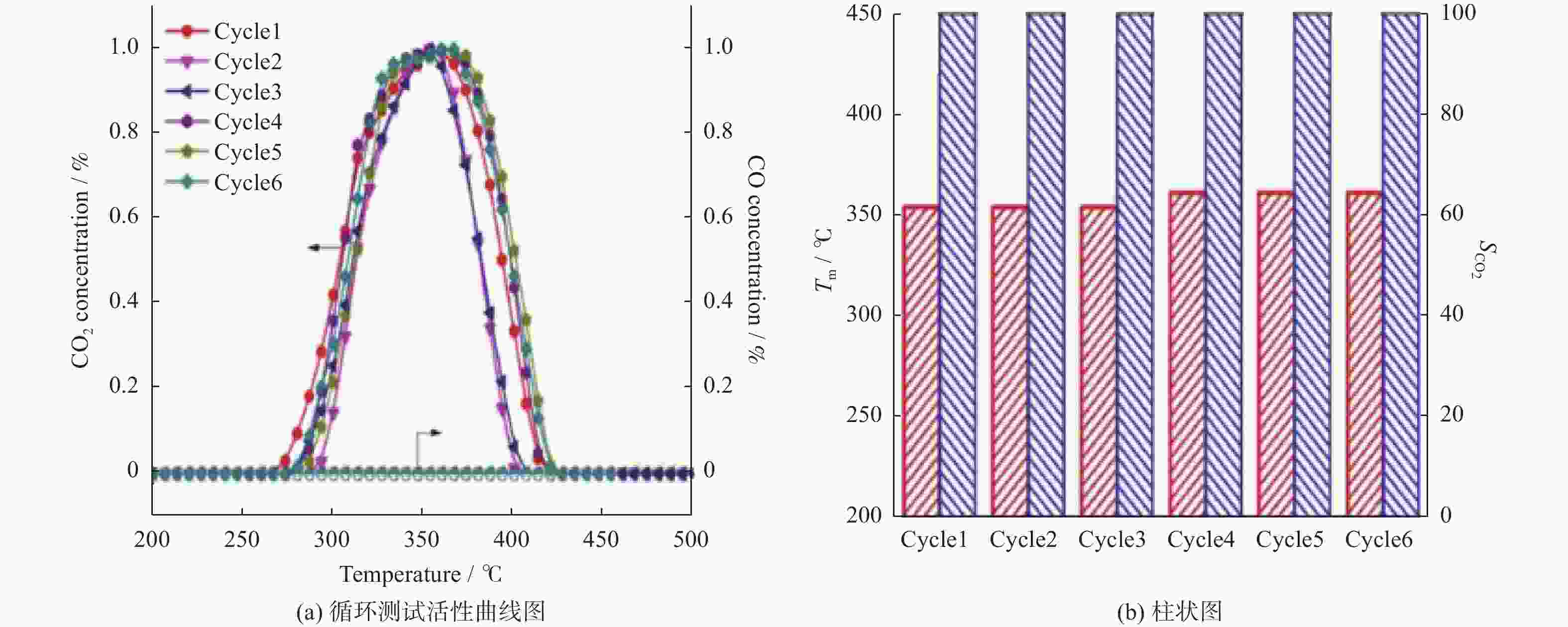
摘要: 催化燃烧是治理柴油机尾气排放碳烟的有效方法,但关键是如何构筑高效催化剂。通过水热结合等体积浸渍法合成系列MnOx/Co3O4片状复合物,并采用碳烟催化净化反应评价了其催化净化性能。结果显示,Mn/Co物质的量比为20%时,20MnCo片状复合物催化净化碳烟的性能最优,其CO2选择性为100%、Tm值为354 ℃,这主要源于三方面原因:1)片状复合物具有丰富孔结构和较高比表面积,增大了碳烟与复合物的接触面积,同时降低了气体反应物的传质阻力;2) 负载MnOx提高了复合物表面Co3+和Mn3+数量,促进了氧物种吸附活化形成更多活性氧物种参与催化净化碳烟;3) 负载MnOx提高了复合物氧化还原能力,增强了NO氧化生成NO2进而提升催化净化碳烟性能。同时,20MnCo片状复合物显示了优异的循环稳定性,说明其具有良好应用前景。
-
关键词:
- 碳烟颗粒 /
- 催化燃烧 /
- MnOx/Co3O4复合物 /
- 多孔纳米片 /
- 柴油机尾气
Abstract: Catalytic combustion is presently considered as one of the most effective methods to control soot particles from diesel exhaust, while its key issue is how to construct efficient catalysts. Herein, a series of MnOx/Co3O4 composites within nanosheets were prepared using the hydrothermal integrating with wet-impregnation approach, chiefly aiming to catalyze soot purification. Experimental results indicate that, 20MnCo nanosheet composites with Mn/Co molar ratio of 20% show the optimal soot purification performance with Tm of 354 ℃ and 100% CO2 selectivity, mainly attributing to the three aspects: 1) porous nanosheets with high surface area and rich pores not merely improved the contact area of composites and soot, but also benefited the decreased mass transfer resistance of gas reactants; 2) loading MnOx led to the increased ratio of Mn3+ and Co3+ on composite’s surface, which favored the activating the adsorbed oxygen species on composite’s surface to generate more reactive oxygen species; 3) loading MnOx resulted in the improved redox ability that facilitated NO oxidation to produce NO2. Meanwhile, 20MnCo nanosheet composites demonstrated the good recycling stability, showing a good application prospect.-
Key words:
- soot particles /
- catalytic combustion /
- MnOx/Co3O4 composites /
- porous nanosheets /
- diesel exhaust
-
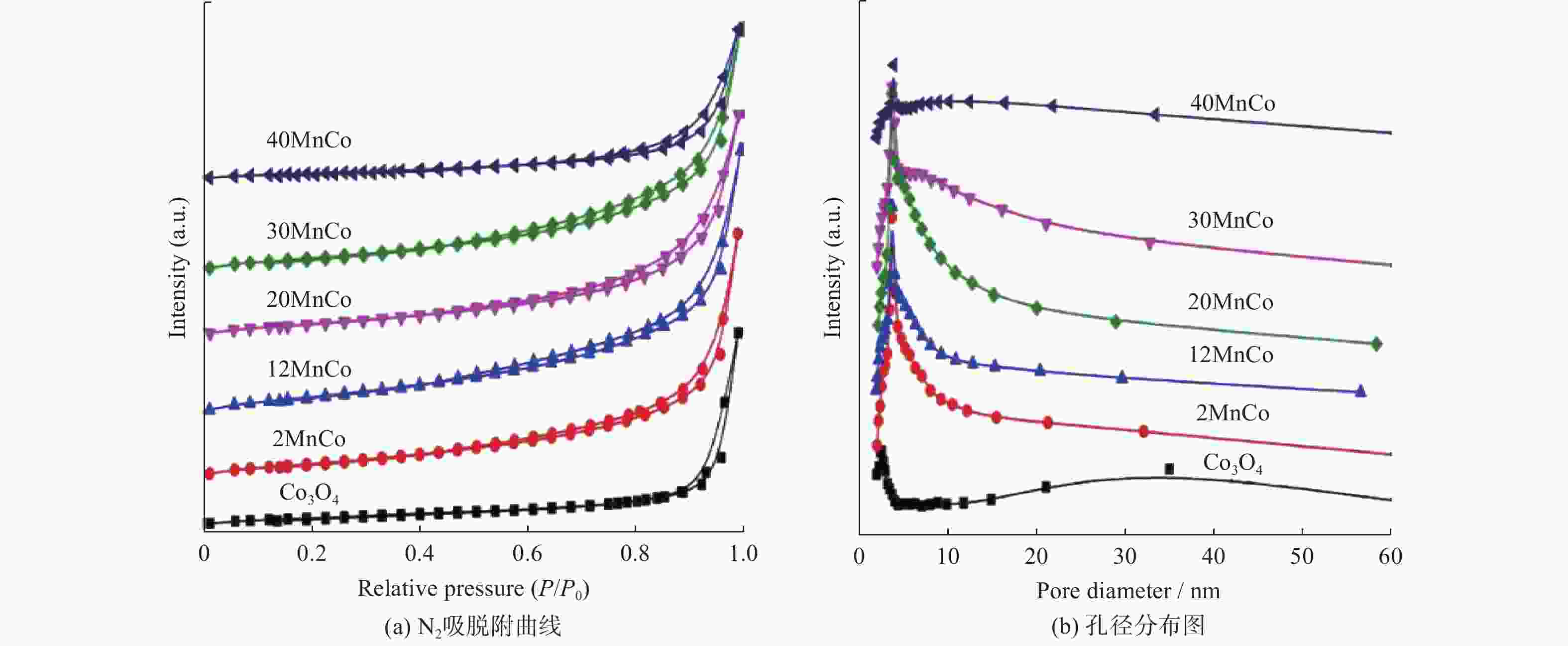
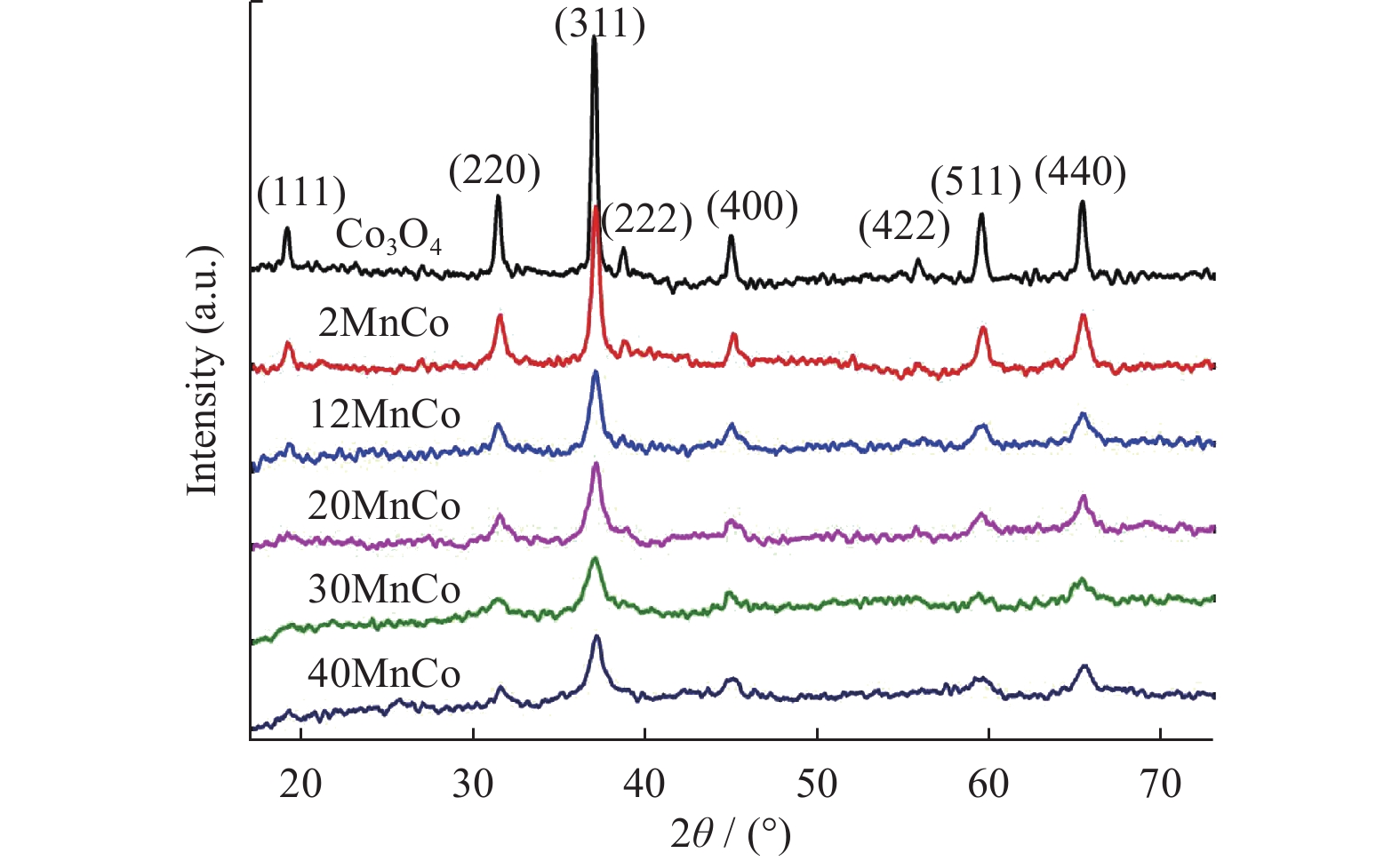
表 1 所制备复合物的物理结构参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of the prepared composites
Catalyst Mn/Co molar ratio
determined by
XRF/%SBET
(m2↔g−1)VP
(cm3↔g−1)DP
/nmCrystallite
size/nmCo3O4 0 20 0.09 24 29 2MnCo 1.95 33 0.12 14 17 12MnCo 11.98 35 0.13 13 13 20MnCo 19.96 38 0.15 12 13 30MnCo 29.92 31 0.11 14 12 40MnCo 39.43 15 0.07 13 11 表 2 所制备复合物的元素组成和价态参数
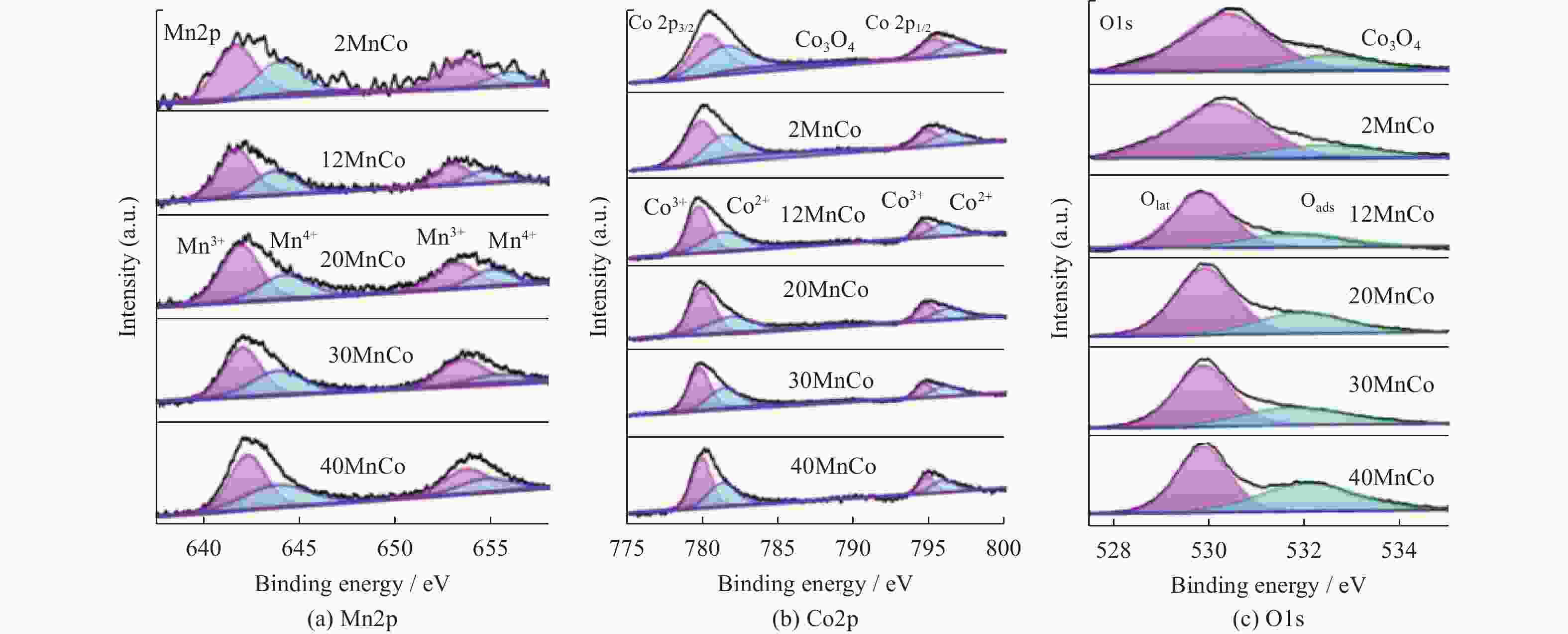
Table 2. Elemental composition and chemical valence states of prepared composites
Catalyst Mn2p Co2p O1s Mn3+/% Mn4+/% n(Mn3+)/n(Mn4+) Co3+/% Co2+/% n(Co3+)/n(Co2+) Oads /% Olatt /% n(Oads)/n(Olatt) Co3O4 — — — 53 47 1.13 21 79 0.27 2MnCo 62 38 1.63 57 43 1.33 23 77 0.30 12MnCo 63 37 1.70 58 42 1.38 30 70 0.43 20MnCo 64 36 1.78 60 40 1.50 32 68 0.47 30MnCo 62 38 1.38 57 43 1.33 34 66 0.52 40MnCo 60 40 1.50 56 44 1.27 39 61 0.64 -
[1] 贺泓, 翁端, 资新运. 柴油车尾气排放污染控制技术综述[J] . 环境科学, 2007, 28(6): 1169 − 1177. [2] 陈卫红, 曹丽敏, 刘跃伟, 等. 空气细颗粒物与呼吸系统的健康损害[J] . 公共卫生与预防医学, 2016, 27(3) : 1 − 4. [3] 李炳章, 张文军, 张园园, 等. 柴油车尾气净化技术研究进展[J] . 山东化工, 2019, 48(9) : 105 − 106. [4] FRANK B, SCHLÖGL R, SU D S. Diesel soot toxification[J] . Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(7) : 3026 − 3027. [5] YU X H, WANG L Y, CHEN M Z, et al. Enhanced activity and sulfur resistance for soot combustion on three-dimensionally ordered macroporous-mesoporous MnxCe1-xOδ/SiO2 catalysts[J] . Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2019, 254: 246 − 259. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.04.097 [6] ZHAI G J, WANG J G, CHEN Z M, et al. Boosting soot combustion efficiency of Co3O4 nanocrystals via tailoring crystal facets[J] . Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018, 337: 488 − 498. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.141 [7] CHENG Y, LIU J, ZHAO Z, et al. Highly efficient and simultaneously catalytic removal of PM and NOx from diesel engines with 3DOM Ce0.8M0.1Zr0.1O2 (M = Mn, Co, Ni) catalysts[J] . Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 167: 219 − 228. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2017.04.023 [8] REN W, DING T, YANG Y X, et al. Identifying oxygen activation/oxidation sites for efficient soot combustion over silver catalysts interacted with nanoflower-Like hydrotalcite-derived CoAlO metal oxides[J] . ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(9) : 8772 − 8784. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b01897 [9] WU Q Q, XIONG J, ZHANG Y L, et al. Interaction-induced self-assembly of Au@La2O3 core-shell nanoparticles on La2O2CO3 nanorods with enhanced catalytic activity and stability for soot oxidation[J] . ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(4) : 3700 − 3715. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b00107 [10] XIONG J, WU Q Q, MEI X L, et al. Fabrication of spinel-type PdxCo3-xO4 binary active sites on 3D ordered meso-macroporous Ce-Zr-O2 with enhanced activity for catalytic soot oxidation[J] . ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(9) : 7915 − 7930. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.8b01924 [11] ZHAI G J, WANG J G, CHEN Z M, et al. Highly enhanced soot oxidation activity over 3DOM Co3O4-CeO2 catalysts by synergistic promoting effect[J] . Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 363: 214 − 226. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.065 [12] WANG J G, YANG S F, SUN H H, et al. Highly improved soot combustion performance over synergetic MnxCe1-xO2 solid solutions within mesoporous nanosheets[J] . Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 577: 355 − 367. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.05.090 [13] YANG S F, WANG J G, CHAI W, et al. Enhanced soot oxidation activity over CuO/CeO2 mesoporous nanosheets[J] . Catalysis Science & Technology, 2019, 9(7) : 1699 − 1709. [14] PUSHKIN A N, GULISH O K, KOSHCHEEVA D A, et al. Catalytic activity of Cu-containing oxide systems with K2CO3 additives in the oxidation of diesel soot by oxygen[J] . Russian Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2013, 87(1) : 23 − 27. doi: 10.1134/S0036024413010196 [15] XU J N, LU G Z, GUO Y, et al. A highly effective catalyst of Co-CeO2 for the oxidation of diesel soot: the excellent NO oxidation activity and NOx storage capacity[J] . Applied Catalysis A: General, 2017, 535: 1 − 8. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2017.02.005 [16] WANG J G, CHENG L, AN W, et al. Boosting soot combustion efficiencies over CuO-CeO2 catalysts with a 3DOM structure[J] . Catalysis Science & Technology, 2016, 6(19) : 7342 − 7350. [17] JUNG J, LEE J H, SONG S, et al. Measurement of soot oxidation with NO2-O2-H2O in a flow reactor simulating diesel engine DPF[J] . International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2008, 9(4) : 423 − 428. doi: 10.1007/s12239-008-0051-4 [18] OI-UCHISAWA J, OBUCHI A, OGATA A, et al. Effect of feed gas composition on the rate of carbon oxidation with Pt/SiO2 and the oxidation mechanism[J] . Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 1999, 21(1) : 9 − 17. doi: 10.1016/S0926-3373(99)00002-8 [19] ZHOU X X, CHEN H R, ZHANG G B, et al. Cu/Mn co-loaded hierarchically porous zeolite beta: a highly efficient synergetic catalyst for soot oxidation[J] . Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(18) : 9745 − 9753. doi: 10.1039/C5TA00094G [20] FINO D, RUSSO N, SARACCO G, et al. Catalytic removal of NOx and diesel soot over nanostructured spinel-type oxides[J] . Journal of Catalysis, 2006, 242(1) : 38 − 47. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2006.05.023 [21] WANG J G, YANG G Y, CHENG L, et al. Three-dimensionally ordered macroporous spinel-type MCr2O4 (M = Co, Ni, Zn, Mn) catalysts with highly enhanced catalytic performance for soot combustion[J] . Catalysis Science & Technology, 2015, 5(9) : 4594 − 4601. -





 下载:
下载: