Ensemble model and empirical analysis of breast cancer diagnosis based on Stacking
-
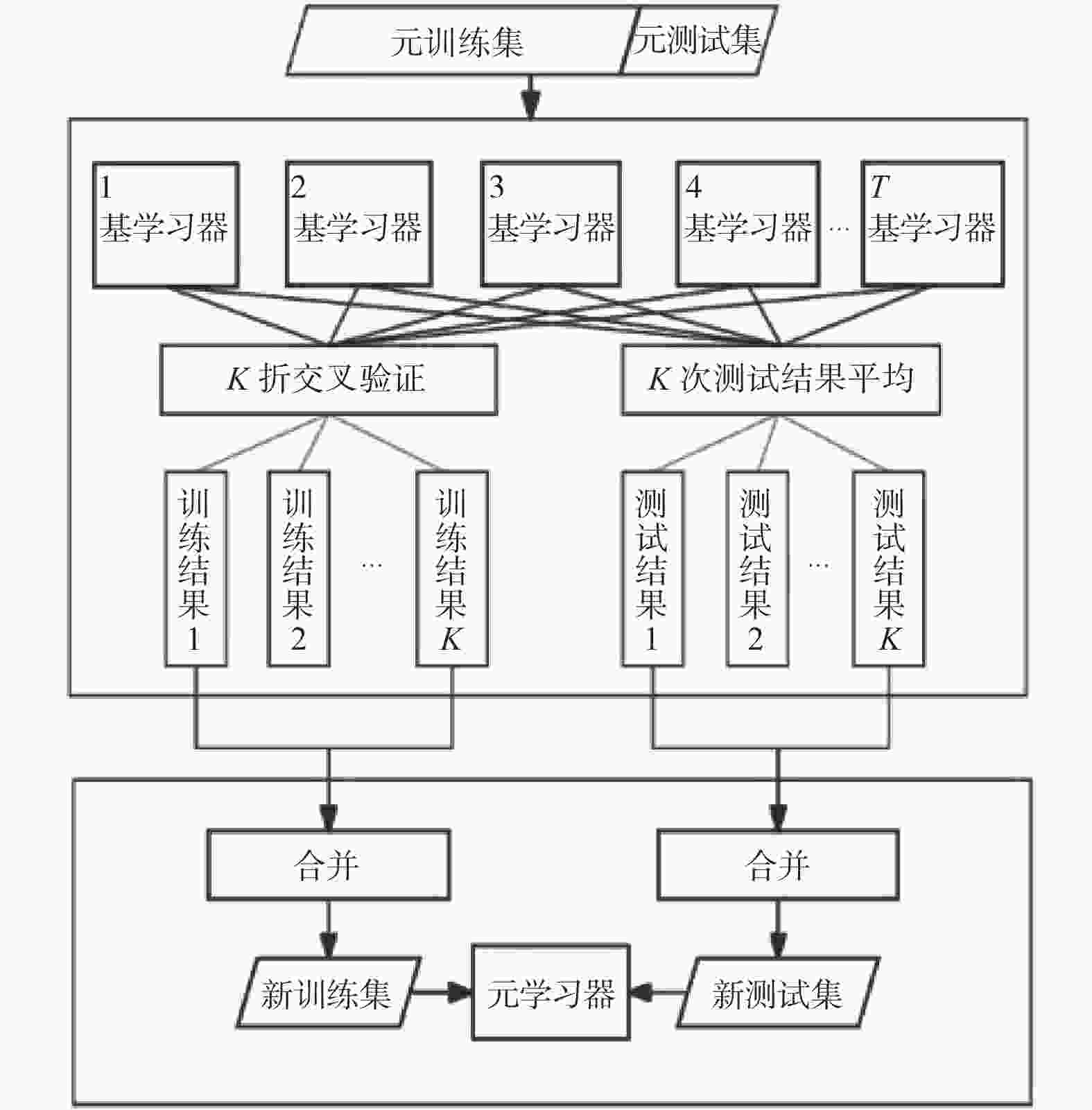
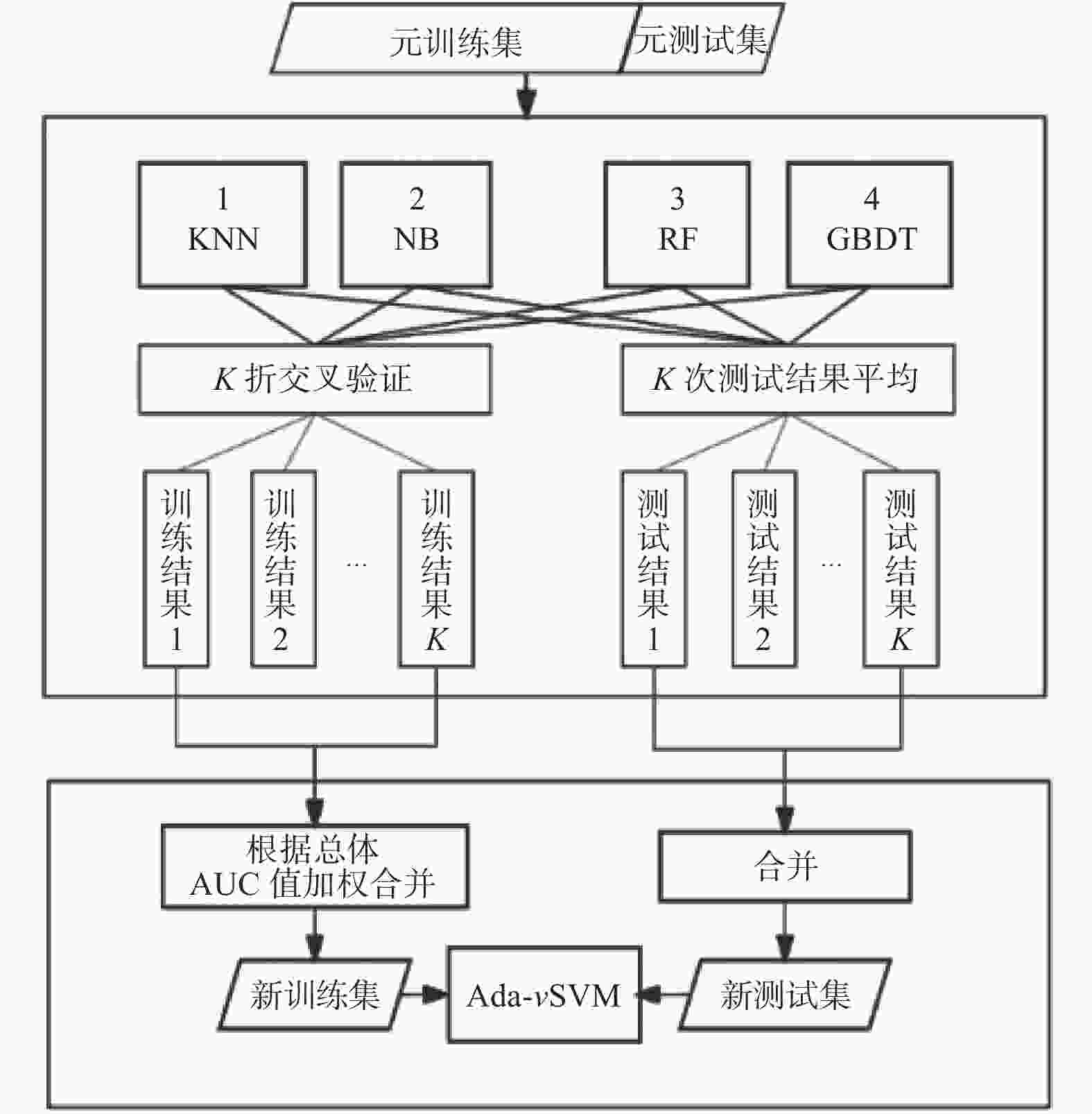
摘要: 乳腺癌的早期诊断可显著提高其治愈的可能性。近年来,大数据与人工智能技术的蓬勃兴起为乳腺癌在内的多种疾病早期诊断提供技术支持。为提升乳腺癌诊断的准确度,构建基于曲线下面积(area under curve, AUC)改进的Stacking集成模型。首先,构建基于
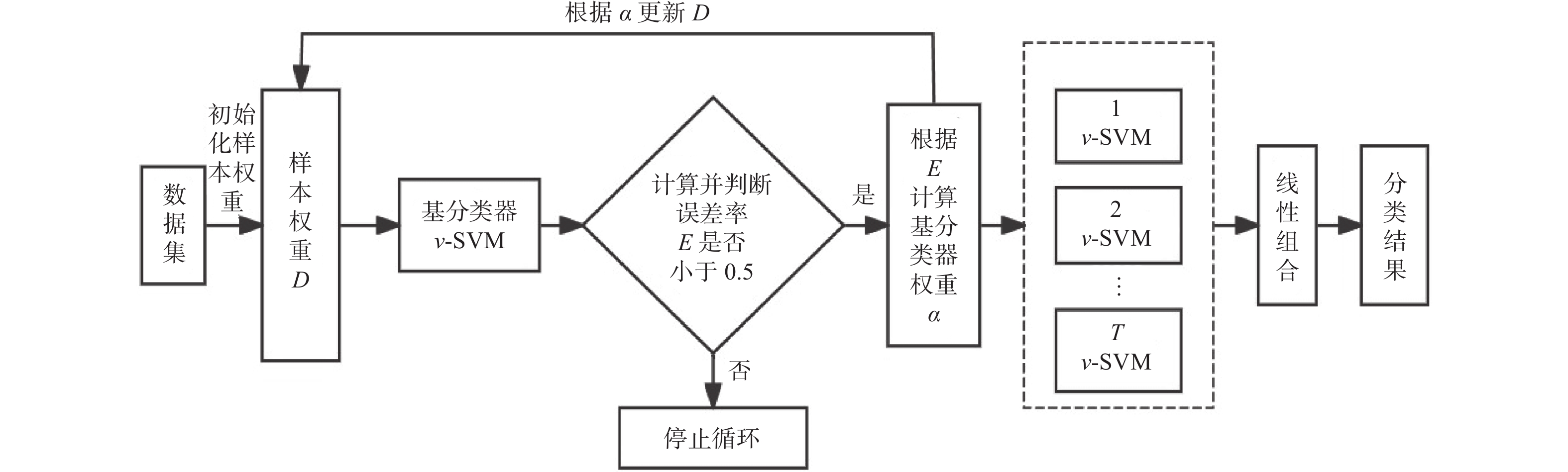
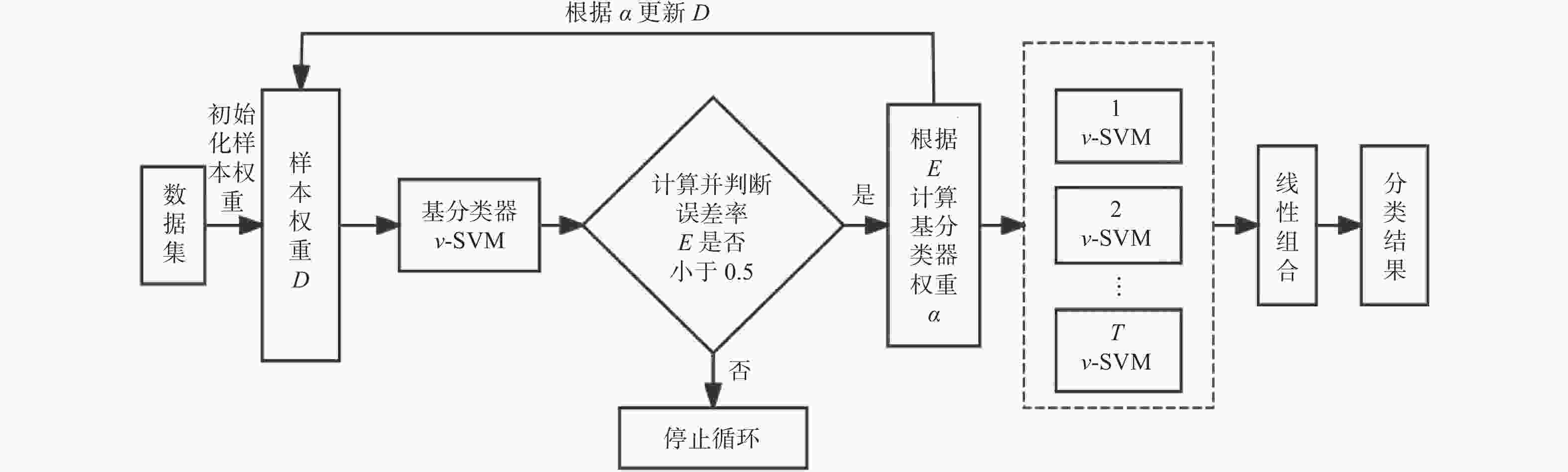
$v$ -SVM的AdaBoost集成模型,并将其作为Stacking的元学习器。其次,利用各基学习器的总体AUC值对各基学习器的训练结果进行加权,将加权后的结果作为元学习器的训练集对元学习器进行训练。最后,在WDBC和WBC数据集上进行实证分析。结果表明,基于AUC改进的Stacking集成模型在两个数据集上分别取得较高准确率,可为医生提供更为精细、个性化的诊断依据,进而实现更早介入、更高效治疗的目标。-
关键词:
- 乳腺癌诊断 /
- 曲线下面积 /
- Stacking集成模型 /
- 机器学习
Abstract: The early diagnosis of breast cancer can significantly improve the possibility of cure. In recent years, the boom of big data and artificial intelligence technology provides technical support for early diagnosis of many diseases, including breast cancer. In order to improve the accuracy of breast cancer diagnosis, an improved Stacking integration model based on area under curve (AUC) was constructed. Firstly, an AdaBoost ensemble model based on$v$ -SVM is constructed and used as a meta learner for Stacking. Secondly, the overall AUC values of each base learner were used to weight the training results of each base learner, and the weighted results were used as the training set of the meta learner for training. Finally, empirical analysis was conducted on the WDBC and WBC datasets. The experimental results show that the Stacking ensemble model based on AUC improvement can achieve high accuracy on two datasets, provide doctors with more refined and personalized diagnostic criteria, thereby achieving the goal of earlier intervention and more efficient treatment. -
表 1 改进Stacking集成模型与未改进模型对比结果
Table 1. Comparison results between improved Stacking ensemble model and unimproved model
模型 A /% AUC /% WDBC WBC WDBC WBC Stacking集成模型 95.61 97.08 94.68 97.27 改进Stacking集成模型 96.49 97.81 96.38 98.28 表 2 与基学习器的对比结果
Table 2. Comparison results with base learner
模型 A /% AUC /% WDBC WBC WDBC WBC 改进Stacking集成模型 96.49 97.81 96.38 98.28 KNN 95.61 94.89 94.68 95.98 GBDT 96.49 97.08 96.38 97.28 RF 96.49 95.62 96.70 95.28 NB 90.35 97.08 90.20 97.28 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J] . CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2021, 71(3): 209 − 249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [2] REZAEI Z. A review on image-based approaches for breast cancer detection, segmentation, and classification[J] . Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 182: 115204. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115204 [3] FATIMA N, LIU L, HONG S, et al. Prediction of breast cancer, comparative review of machine learning techniques, and their analysis[J] . IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 150360 − 150376. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3016715 [4] ASRI H, MOUSANNIF H, AL MOATASSIME H, et al. Using machine learning algorithms for breast cancer risk prediction and diagnosis[J] . Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 83: 1064 − 1069. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.04.224 [5] WOLBERG W, MANGASARIAN O, STREET N, et al. Breast cancer Wisconsin (diagnostic)[EB/OL] . (1995-11-01)[2024-06-05] . https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/17/breast+cancer+wisconsin+diagnostic. [6] 李勇, 陈思萱, 贾海, 等. 基于C-AdaBoost模型的乳腺癌预测研究[J] . 计算机工程与科学, 2020, 42(8): 1414 − 1422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2020.08.011 [7] WANG H F, ZHENG B C, YOON S W, et al. A support vector machine-based ensemble algorithm for breast cancer diagnosis[J] . European Journal of Operational Research, 2018, 267(2): 687 − 699. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2017.12.001 [8] PRIYA R S P, VADIVU P S. Bio-inspired ensemble feature selection (biefs) and ensemble multiple deep learning (emdl) classifier for breast cancer diagnosis[J] . Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results, 2022, 13(6): 483 − 499. [9] NANGLIA S, AHMAD M, KHAN F A, et al. An enhanced predictive heterogeneous ensemble model for breast cancer prediction[J] . Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 72: 103279. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103279 [10] ABDAR M, ZOMORODI-MOGHADAM M, ZHOU X J, et al. A new nested ensemble technique for automated diagnosis of breast cancer[J] . Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 132: 123 − 131. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2018.11.004 [11] SCHöLKOPF B, SMOLA A J, WILLIAMSON R C, et al. New support vector algorithms[J] . Neural Computation, 2000, 12(5): 1207 − 1245. doi: 10.1162/089976600300015565 [12] WOLPERT D H. Stacked generalization[J] . Neural Networks, 1992, 5(2): 241 − 259. doi: 10.1016/S0893-6080(05)80023-1 [13] 周星, 丁立新, 万润泽, 等. 分类器集成算法研究[J] . 武汉大学学报(理学版), 2015, 61(6): 503 − 508. [14] ZHANG X L, REN F. Improving svm learning accuracy with AdaBoost[C] //Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Natural Computation. Jinan: IEEE, 2008: 221 − 225. -









 下载:
下载: