Map construction for construction robot based on integrated improved algorithm
-
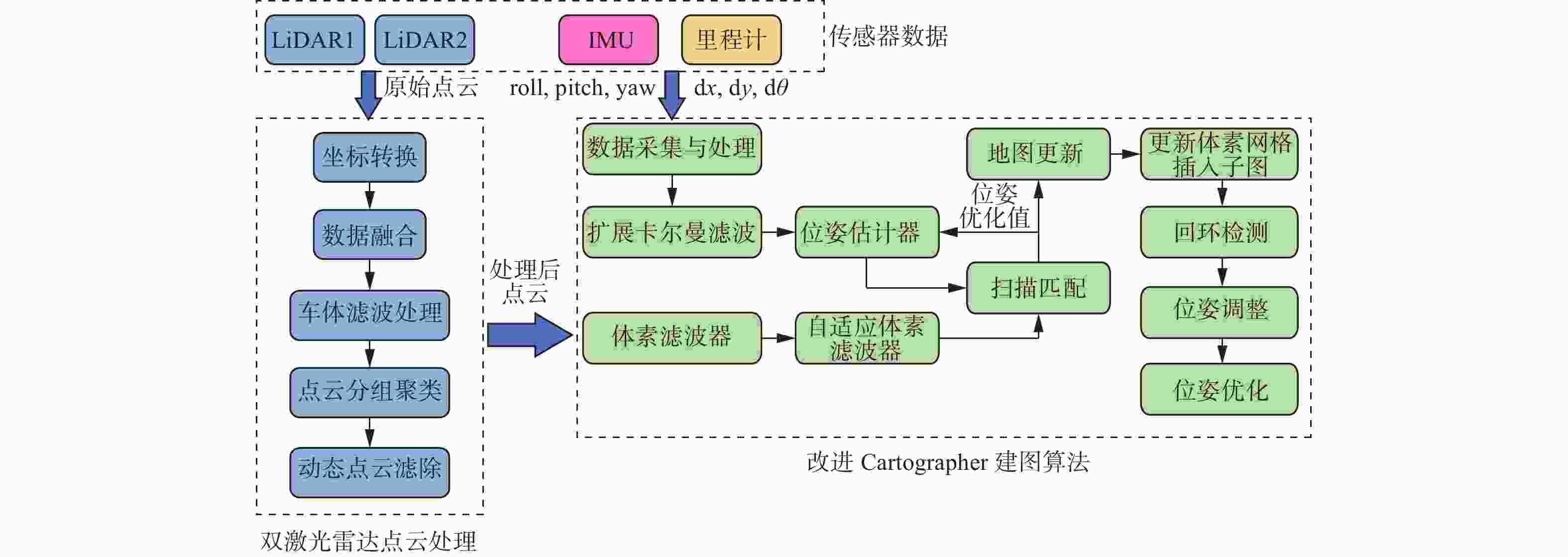
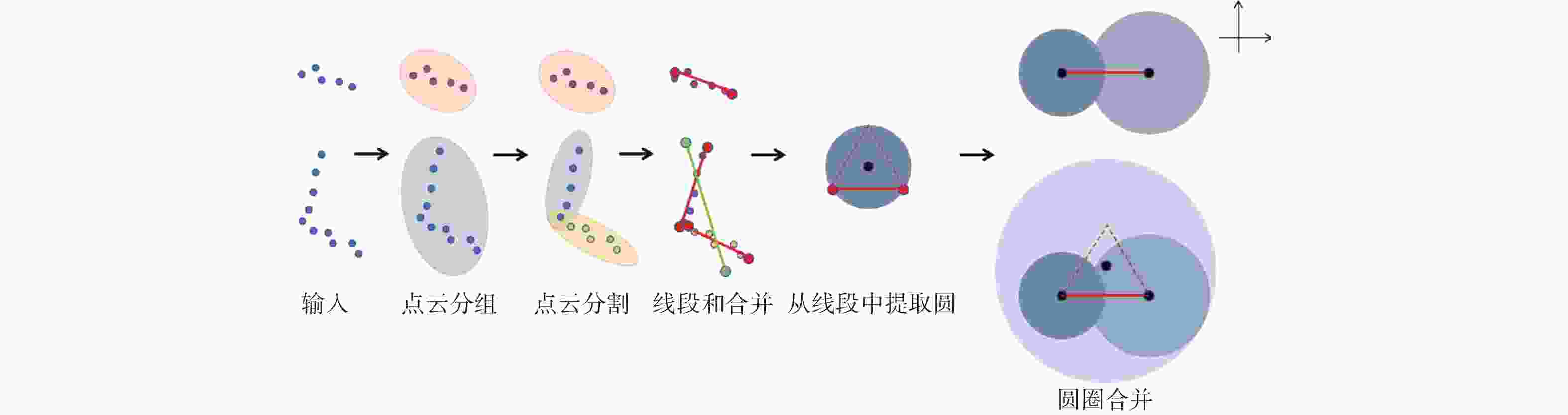
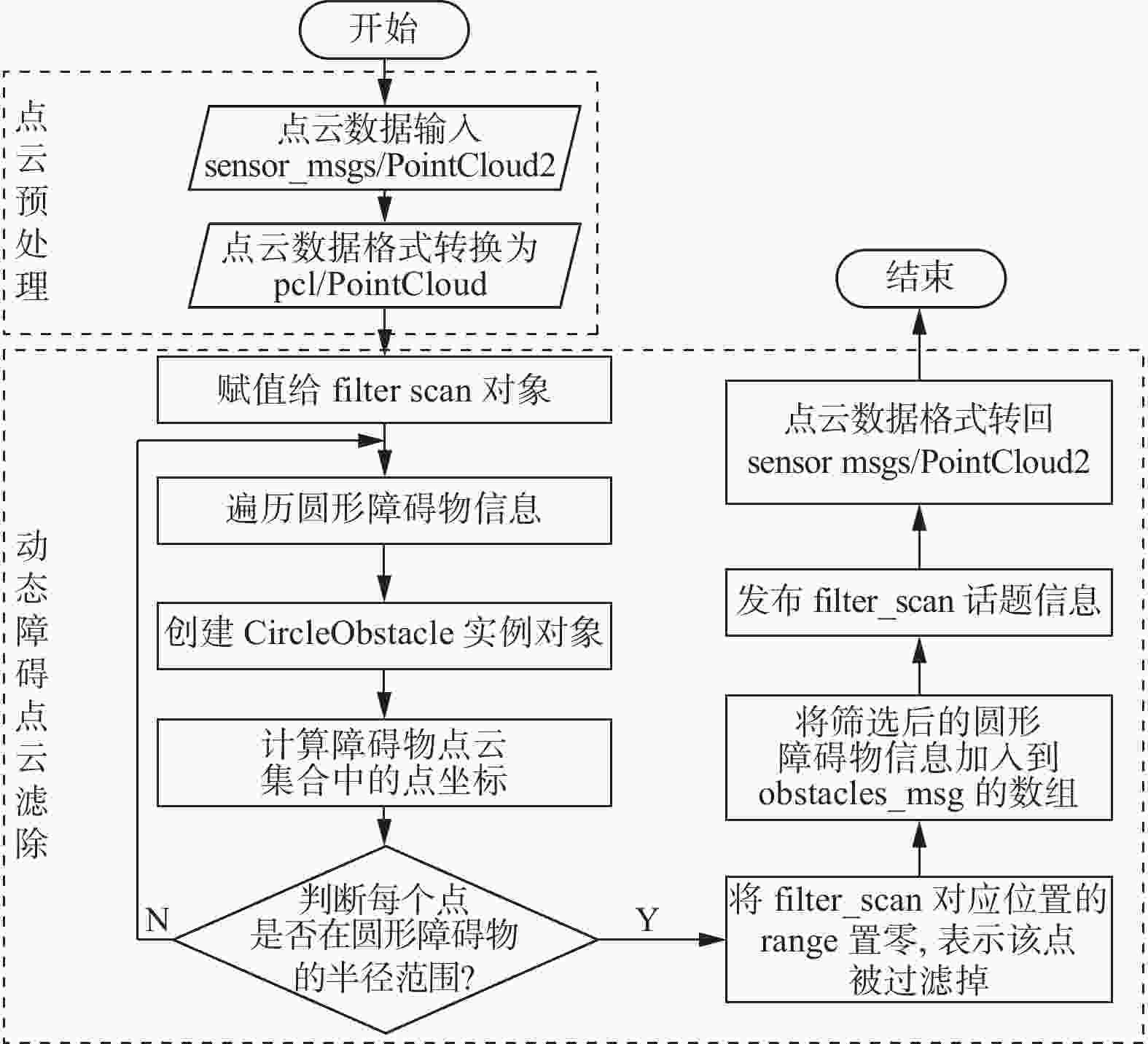
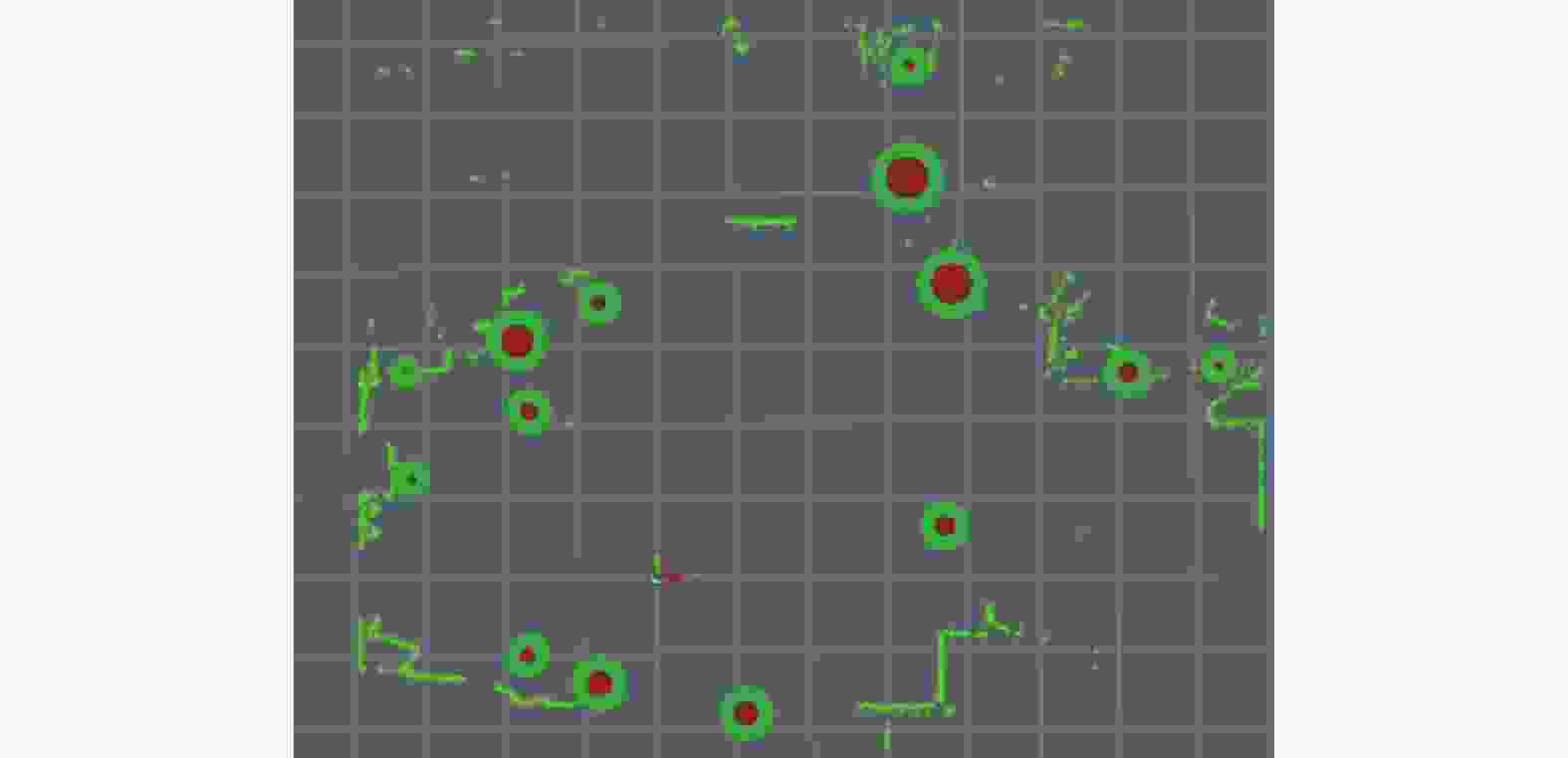
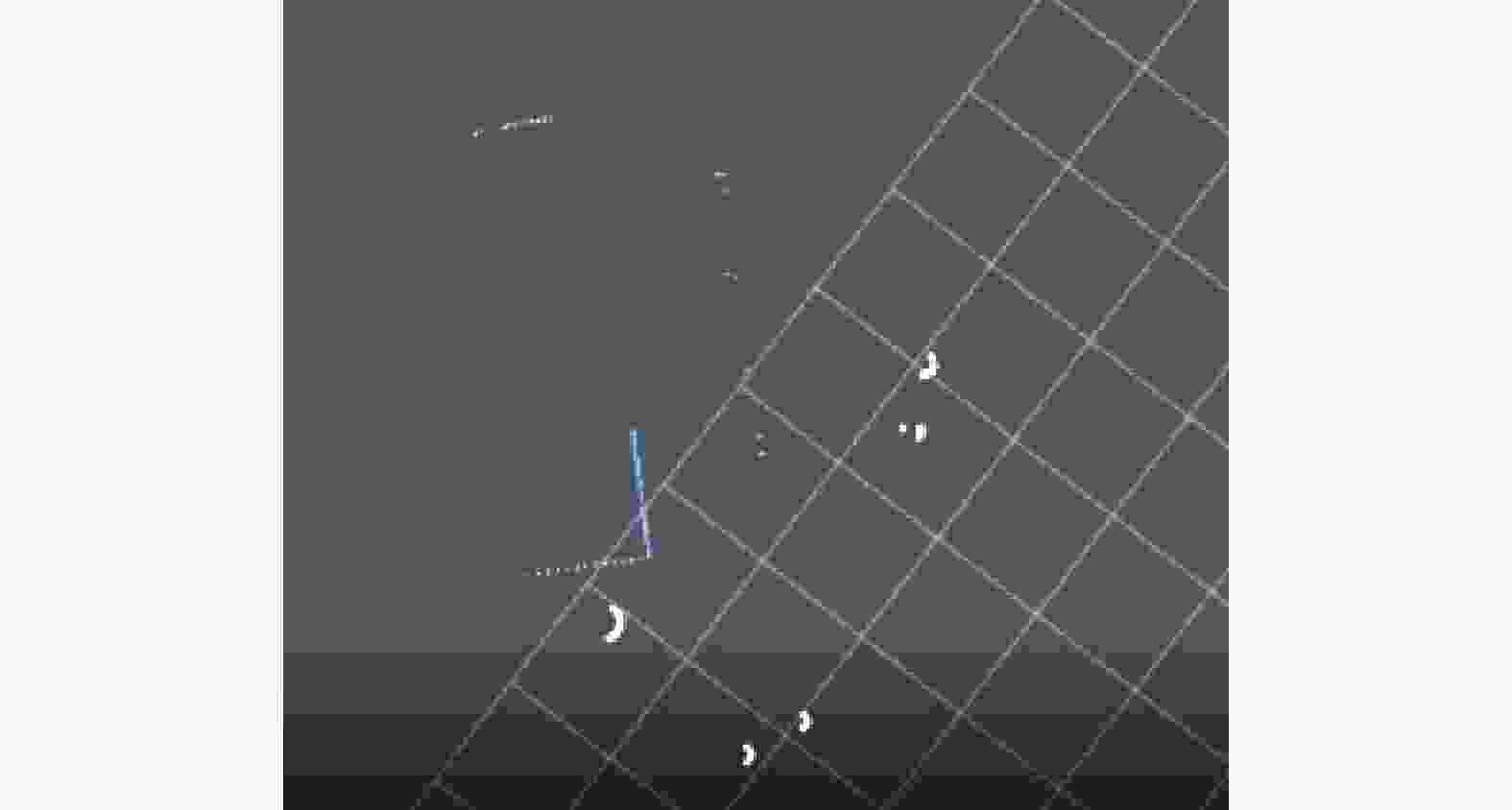
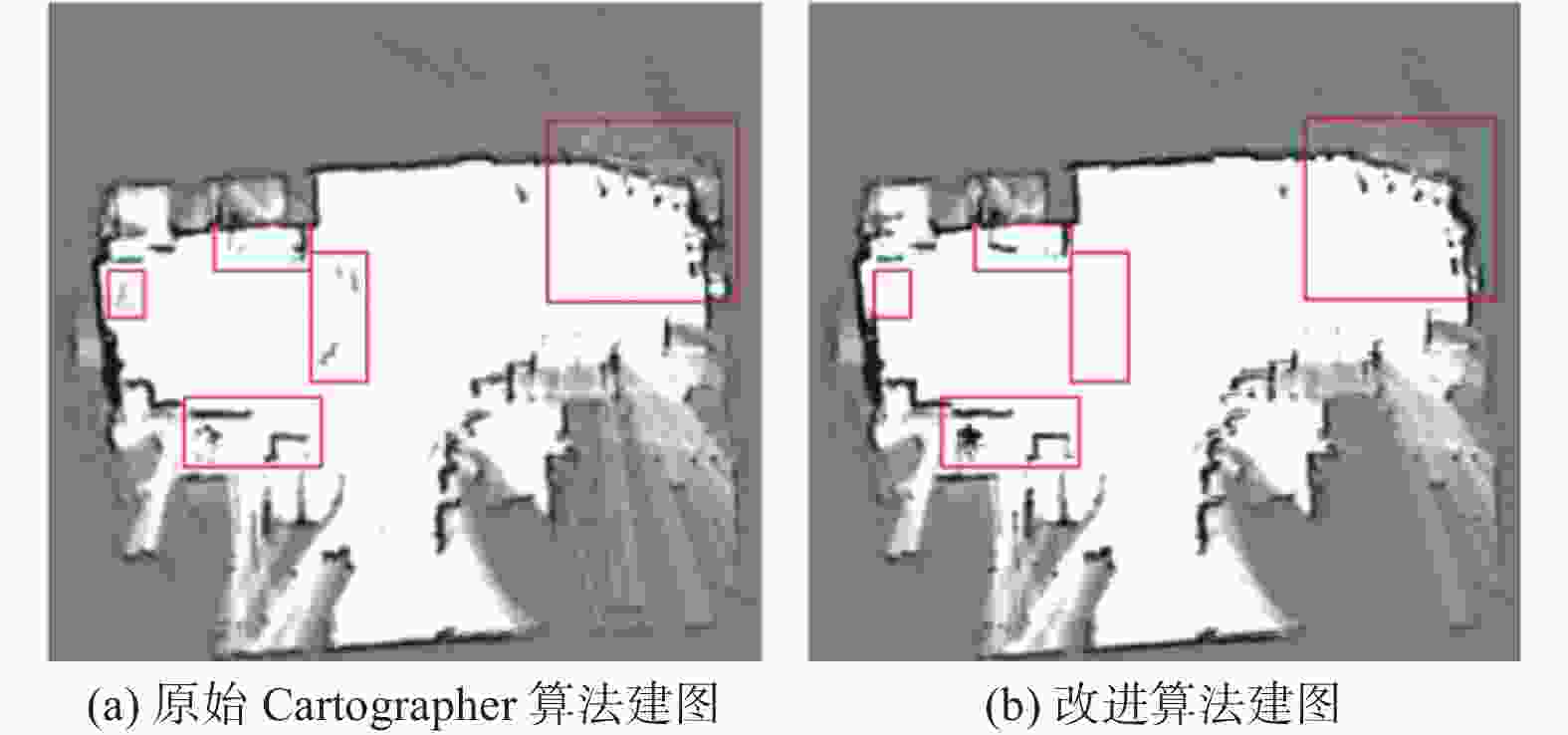
摘要: 建筑环境具有非结构化、大工作空间、施工工艺流程受现场环境影响明显等特点。针对建筑机器人定位和地图构建时,位姿估计不准确、地图显示不完整、高度动态场景下残影较多等问题,融合双激光雷达、惯性测量单元(IMU)和轮式里程计等多传感器,以Cartographer算法为基础框架,采用扩展卡尔曼滤波算法对多传感器融合优化,获得更准确的位姿估计;从原始激光点云数据中过滤剔除动态障碍物点云,提高地图构建的质量。实验结果表明,提出的数据融合Cartographer改进算法提高了地图质量和定位精度,可以满足建筑作业环境下地图构建需求。Abstract: The construction environment is characterized by unstructured, large workspace, and construction processes that are significantly influenced by on-site conditions. To address problems such as inaccurate pose estimation, incomplete map display, and more residual shadows in highly dynamic scenes during construction robot localization and mapping, multiple sensors including dual LiDAR, inertial measurement unit (IMU), and wheeled odometry were fused. Based on the Cartographer algorithm framework, an extended Kalman filter was employed to optimize the multi-sensor for more accurate pose estimation. Furthermore, dynamic obstacle point clouds were filtered and removed from the raw laser scan data to enhance mapping quality. Experimental results show that the proposed improved data fusion Cartographer algorithm can improve map quality and positioning accuracy, meeting the requirements for map construction in construction environment.
-
Key words:
- construction environment /
- multi-sensor /
- extended Kalman filter /
- dynamic barriers /
- map construction
-
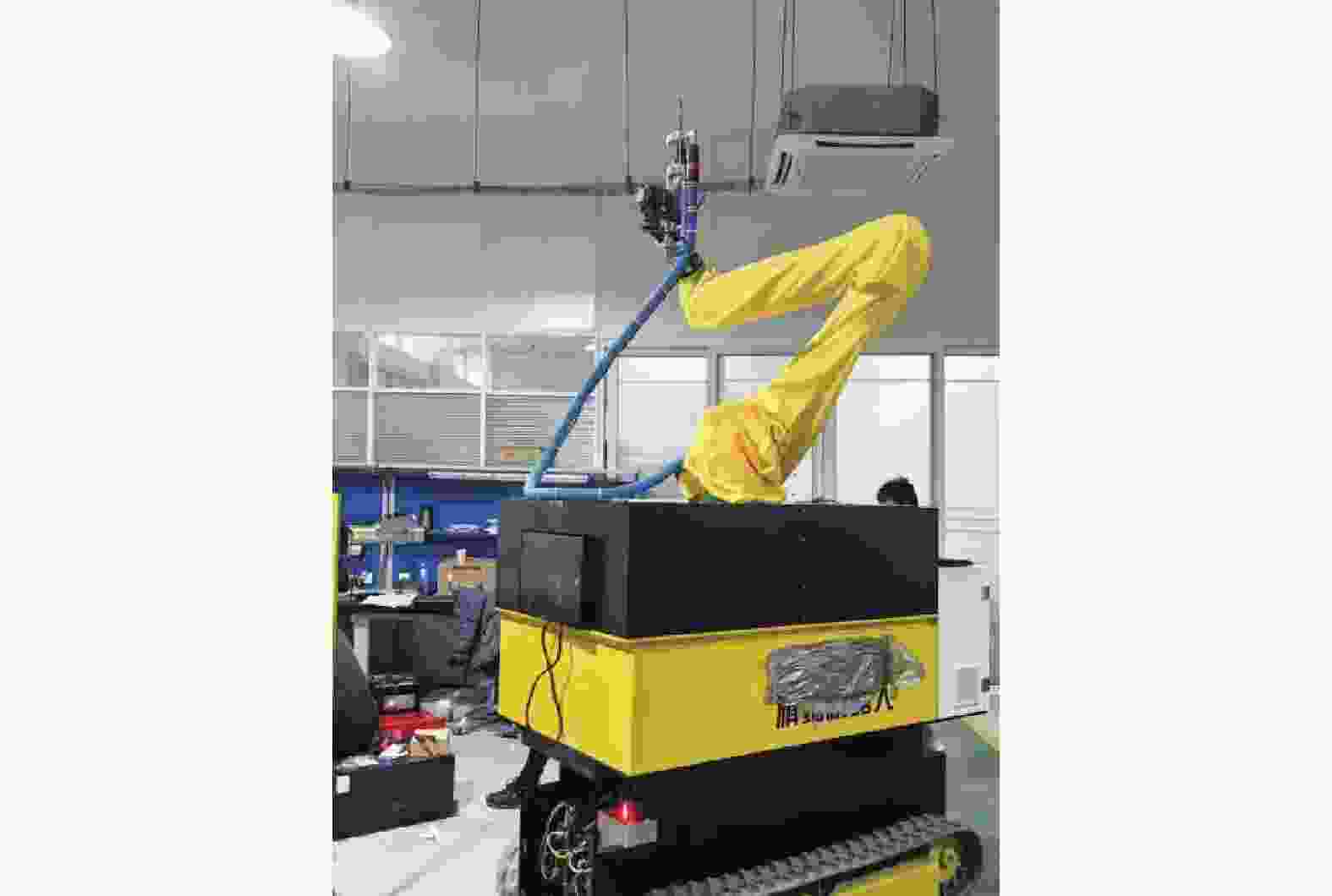
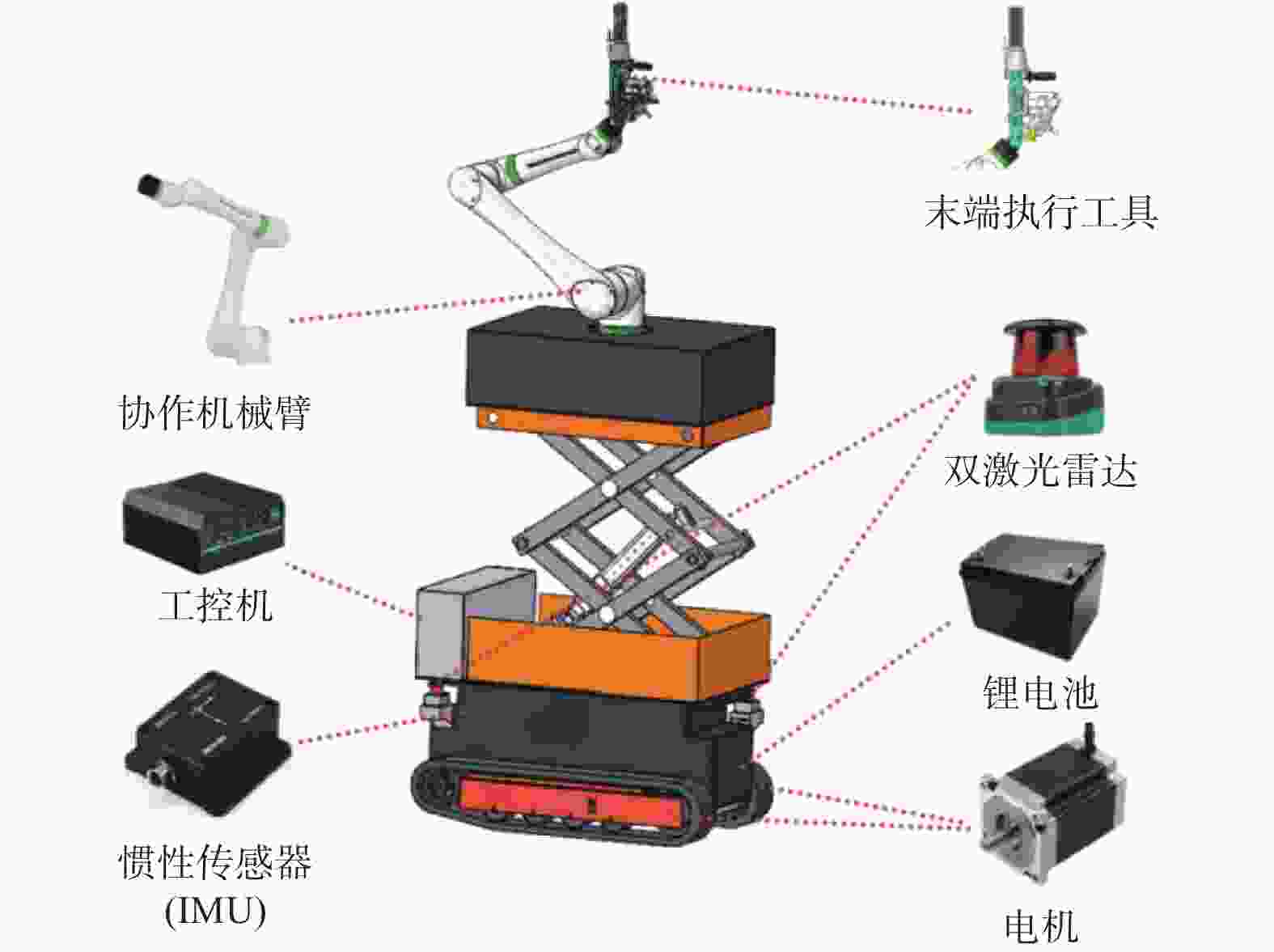
表 1 机器人硬件及主要传感器的关键参数
Table 1. Robot design index and key parameters
参数名称 参数大小 外形尺寸 1600 mm×1000 mm×2000 mm底盘质量 400 kg 举升平台高度 ≤1.5 m 机械臂工作空间 1300 mmIMU测量精度 0.5 (°)/s 激光雷达测距精度 ± 25 mm 表 2 不同算法误差分析结果
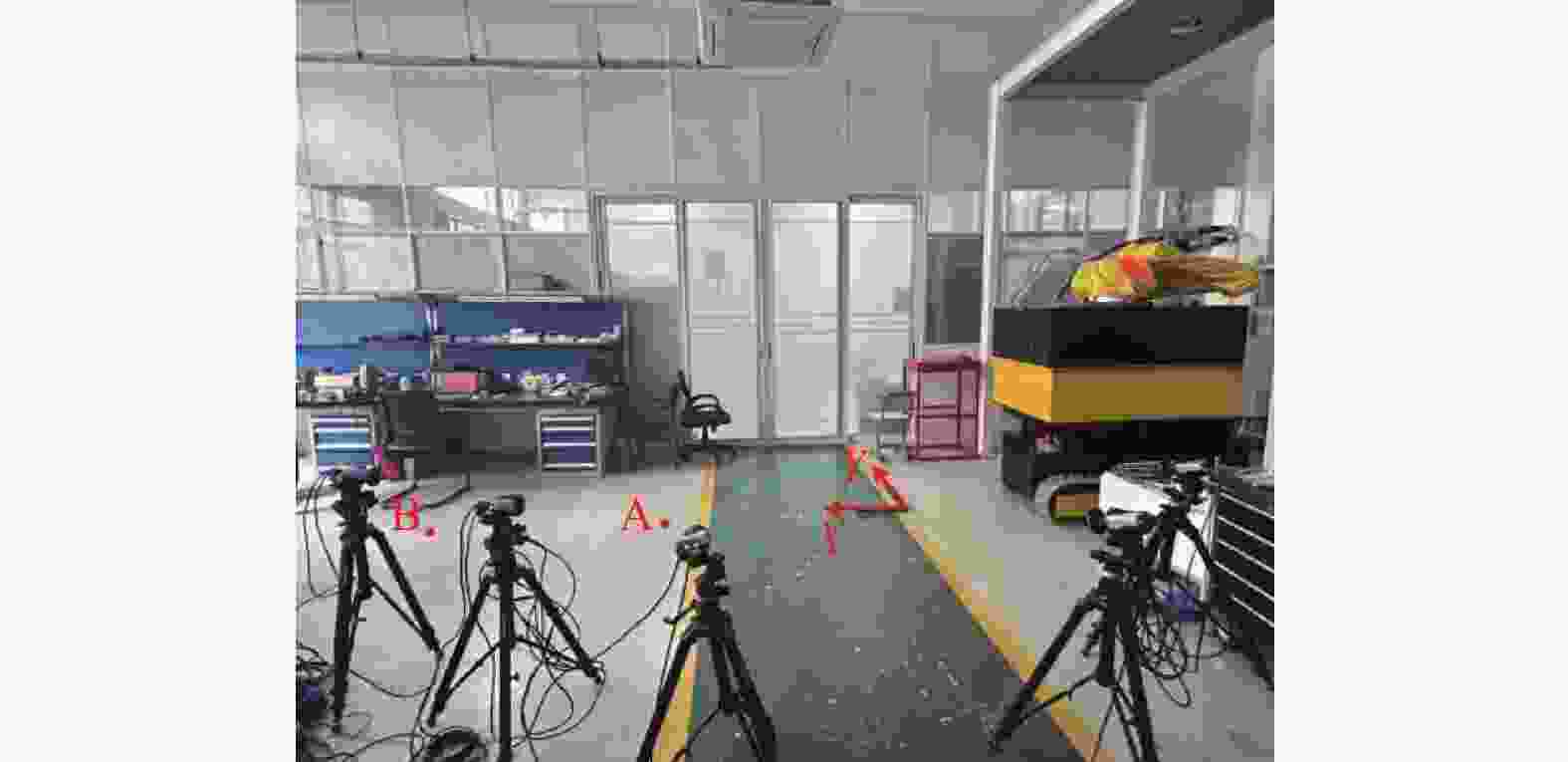
Table 2. Error analysis results of different algorithms
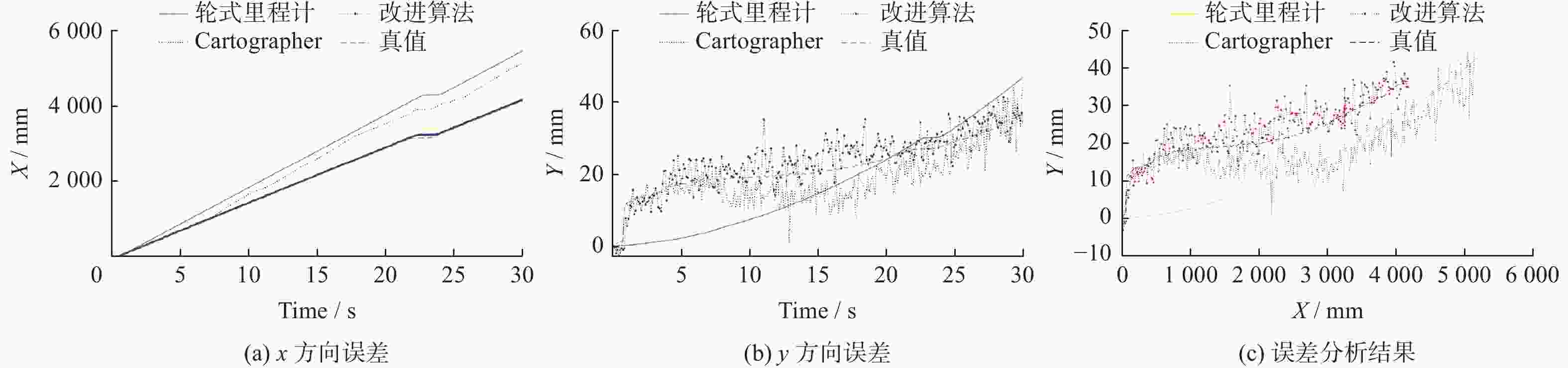
精度评估 轮式里程计 原始算法 改进算法 最大误差/m 0.984 0.153 0.090 最小误差/m 0.036 0.008 0.012 平均绝对误差/m 0.629 0.070 0.024 均方误差/m2 0.043 0.007 0.002 均方根误差/m 0.738 0.084 0.029 -
[1] DAVILA DELGADO J M, OYEDELE L, AJAYI A, et al. Robotics and automated systems in construction: understand ingindustry-specific challenges for adoption[J] . Journal of Building Engineering, 2019, 26: 100868. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100868 [2] WANG X, WANG S Q, MENASSA C C, et al. Automatic high-level motion sequencing methods for enabling multi-tasking construction robots[J] . Automation in Construction, 2023, 155: 105071. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2023.105071 [3] CAI J N, DU A, LIANG X Y, et al. Prediction-based path planning for safe and efficient human–robot collaboration in construction via deep reinforcement learning[J] . Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2023, 37(1): 04022046. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0001056 [4] FENG C, XIAO Y, WILLETTE A, et al. Vision guided autonomous robotic assembly and as-built scanning on unstructured construction sites[J] . Automation in Construction, 2015, 59: 128 − 138. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2015.06.002 [5] LUNDEEN K M, KAMAT V R, MENASSA C C, et al. Scene understanding for adaptive manipulation in robotized construction work[J] . Automation in Construction, 2017, 82: 16 − 30. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2017.06.022 [6] PAN M, LINNER T, PAN W, et al. Influencing factors of the future utilisation of construction robots for buildings: a Hong Kong perspective[J] . Journal of Building Engineering, 2020, 30: 101220. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101220 [7] LIANG C J, KAMAT V R, MENASSA C C. Teaching robots to perform quasi-repetitive construction tasks through human demonstration[J] . Automation in Construction, 2020, 120: 103370. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103370 [8] YAROVOI A, CHO Y K. Review of simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) for construction robotics applications[J] . Automation in Construction, 2024, 162: 105344. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105344 [9] 刘铭哲, 徐光辉, 唐堂, 等. 激光雷达SLAM算法综述[J] . 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(1): 1 − 14. [10] SHAN T X, ENGLOT B, MEYERS D, et al. LIO-SAM: tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping[C] //2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Las Vegas: IEEE, 2020: 5135 − 5142. [11] 帅子沛. 室内建筑抹灰机器人智能导航研究[D] . 成都: 电子科技大学, 2022: 18 − 30. [12] 周乐天. 建筑机器人移动定位技术研究[D] . 成都: 电子科技大学, 2019: 20 − 28. [13] 沈欣. 基于改进Cartographer的激光SLAM算法研究[D] . 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2021: 16 − 28. [14] 徐淑萍, 杨定哲, 熊小墩. 多传感器融合的室内机器人SLAM[J] . 西安工业大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 93 − 103. [15] LI L, SCHULZE L, KALAVADIA K. Promising SLAM methods for automated guided vehicles and autonomous mobile robots[J] . Procedia Computer Science, 2024, 232: 2867 − 2874. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2024.02.103 [16] 徐淑萍, 杨定哲, 房嘉翔, 等. 一种改进Cartographer算法的建图方法研究[J] . 激光杂志, 2024, 45(10): 86 − 93. [17] ALTINPINAR O V, SEZER V. A novel indoor localization algorithm based on a modified EKF using virtual dynamic point landmarks for 2D grid maps[J] . Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2023, 170: 104546. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2023.104546 [18] KUTI J, PIRICZ T, GALAMBOS P. Method for direction and orientation tracking using IMU sensor[J] . IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2023, 56(2): 10774 − 10780. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.744 [19] PRZYBYŁA M. Detection and tracking of 2D geometric obstacles from LRF data[C] //Proceedings of 2017 11th International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control (RoMoCo). Wasowo Palace: IEEE, 2017: 135 − 141. -






 下载:
下载: