Data driven health monitoring and fault diagnosis of mechanical equipment
-
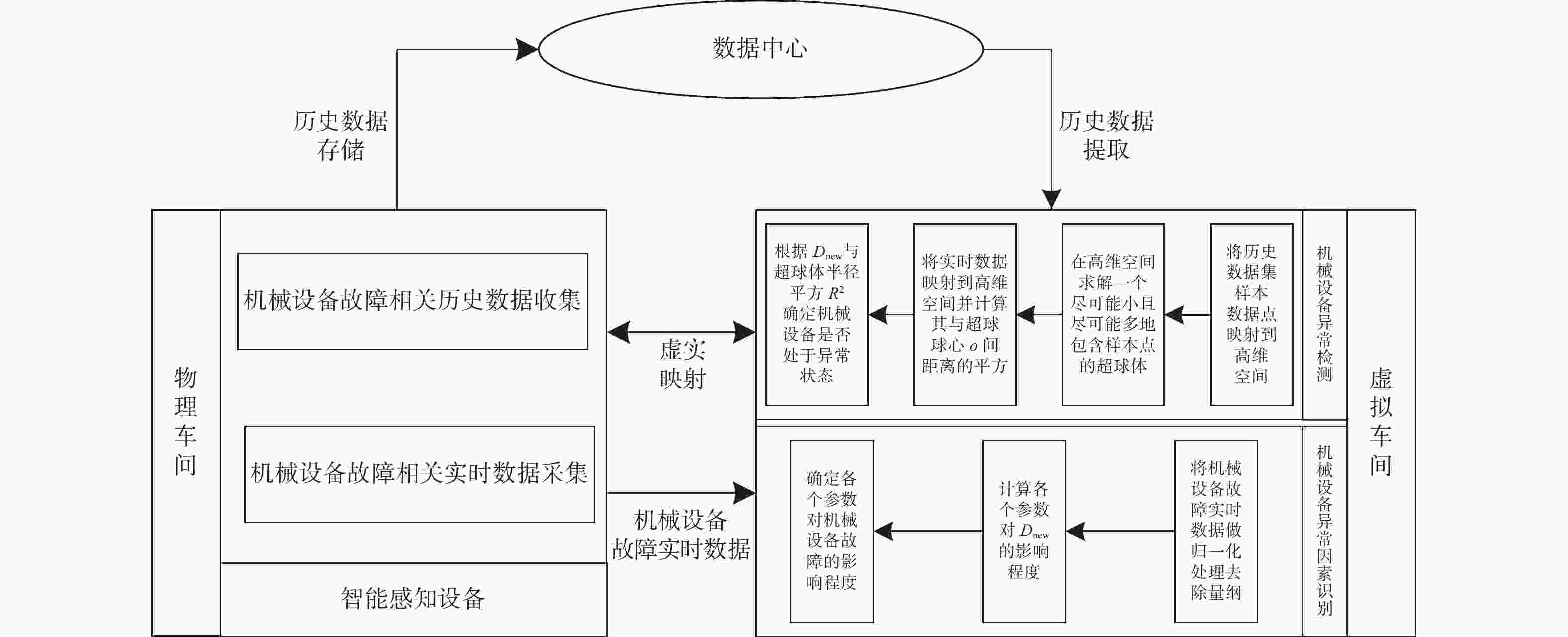
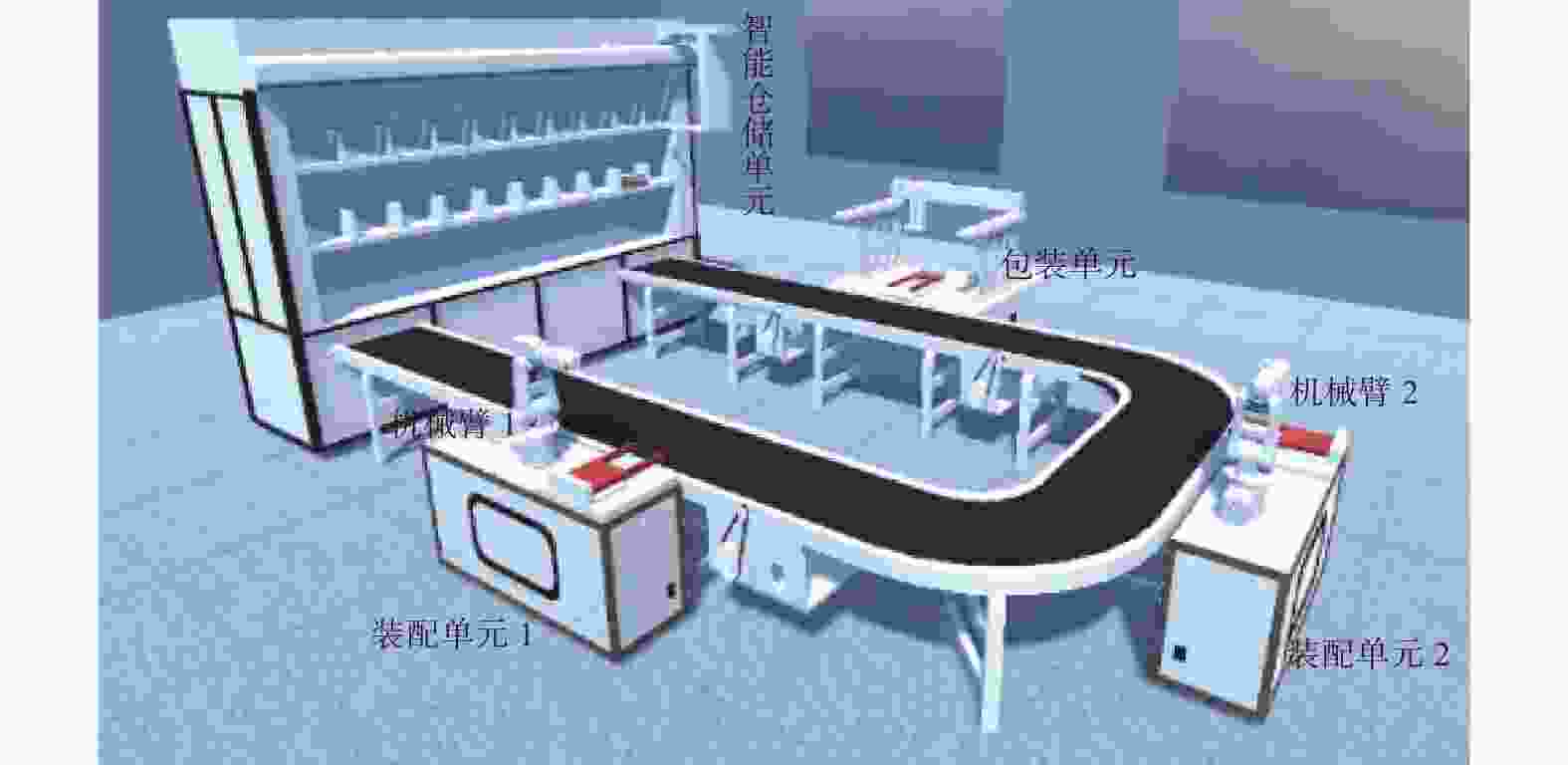
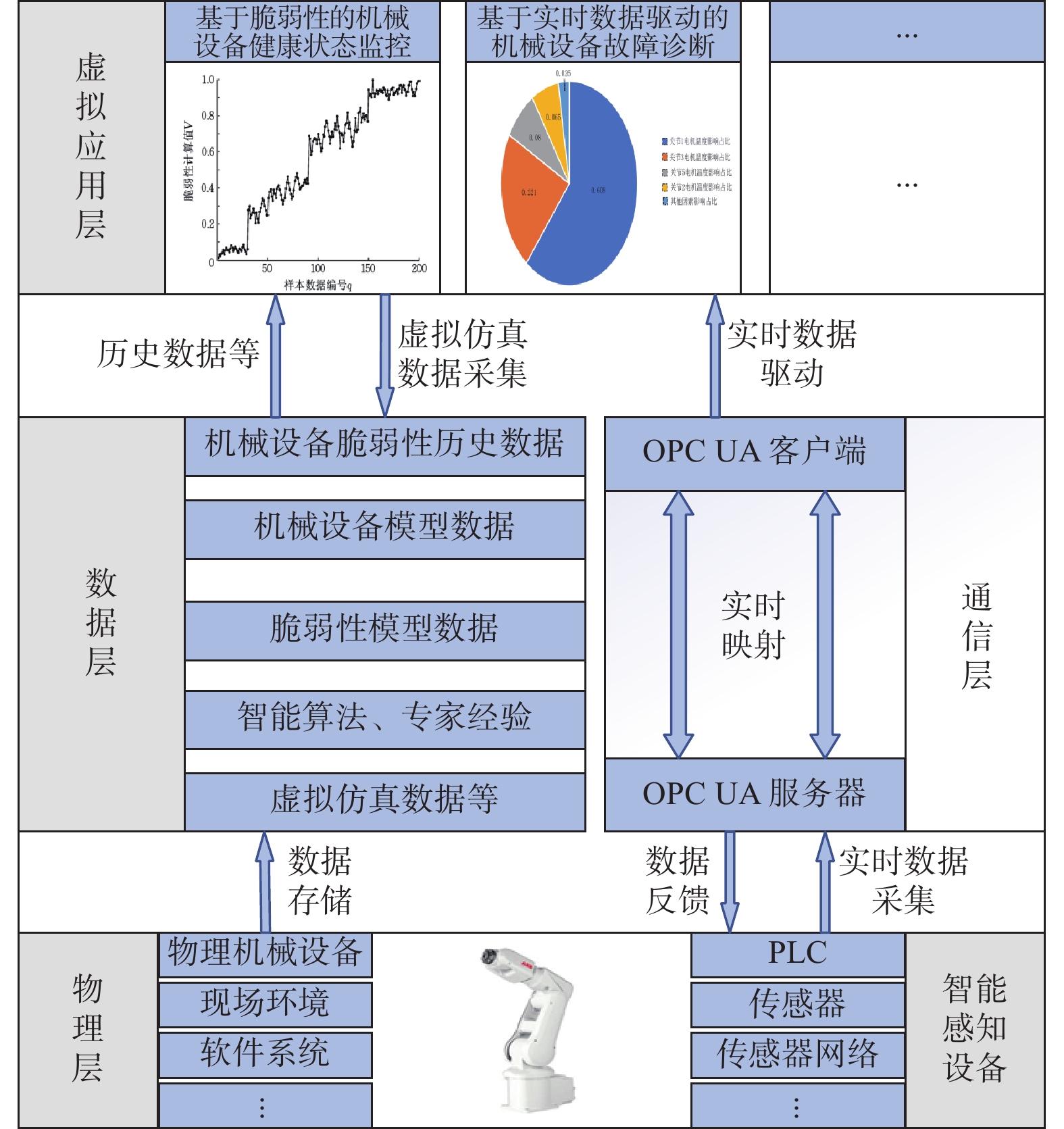
摘要: 针对机械设备故障数据利用不完全、传统健康状态监控及故障诊断方法存在局限的问题,构建一种数据驱动的设备健康状态监控及故障诊断系统架构。提出一种基于数字孪生的健康状态监控方法,结合机械设备脆弱性监控健康状态。研究一种数据驱动的故障诊断方法,运用非线性核映射算法分析故障的历史数据,确定设备异常边界,通过分析相关实时数据确定设备是否异常及导致异常的关键因素。最后以某装配生产线机械手臂为例进行实证分析,结果表明,所提方法可有效识别导致设备异常的性能参数,提高了车间对机器故障的动态响应能力。Abstract: To address the incomplete utilization of mechanical equipment fault data and overcome the limitations of traditional health status monitoring and fault diagnosis methods, a data-driven system architecture for health monitoring and fault diagnosis was constructed. A health status monitoring method based on digital twins was proposed, in which equipment vulnerability was incorporated to monitor the health status. Furthermore, a data-driven fault diagnosis method was studied. By utilizing a nonlinear kernel mapping algorithm, historical fault data were analyzed to determine the abnormal boundary of the equipment. Through the analysis of real-time data, equipment abnormalities and the key factors leading to these abnormalities were identified. Finally, an empirical analysis was conducted taking a robotic arm on an assembly line as a case study. The results indicate that the proposed method can effectively identify the performance parameters leading to equipment abnormalities and improve the dynamic response performance of the workshop to machine failures.
-
Key words:
- date-driven /
- mechanical equipment /
- health status /
- fault diagnosis /
- vulnerability
-
表 1 各性能参数指标统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of each performance parameter index
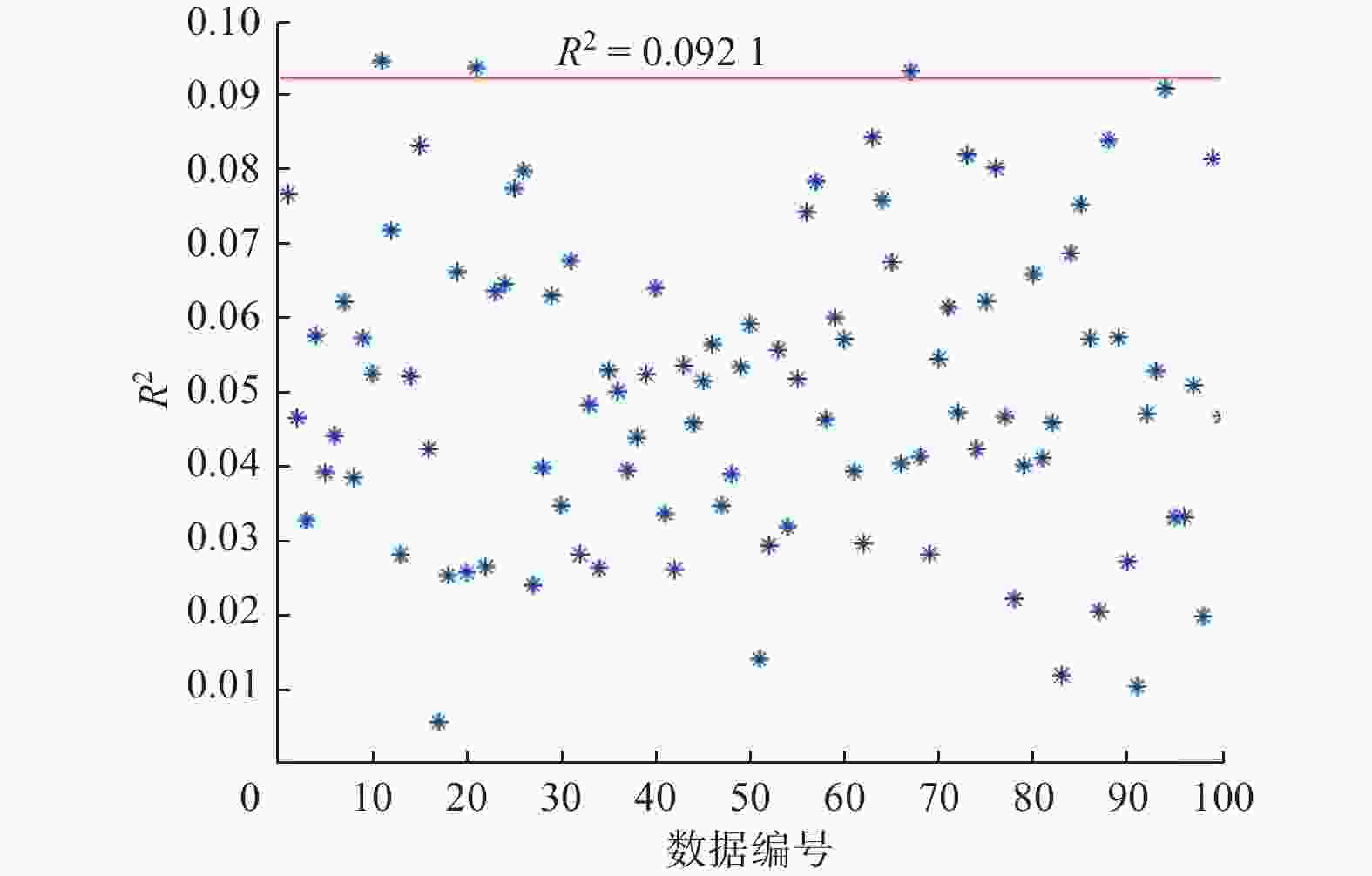
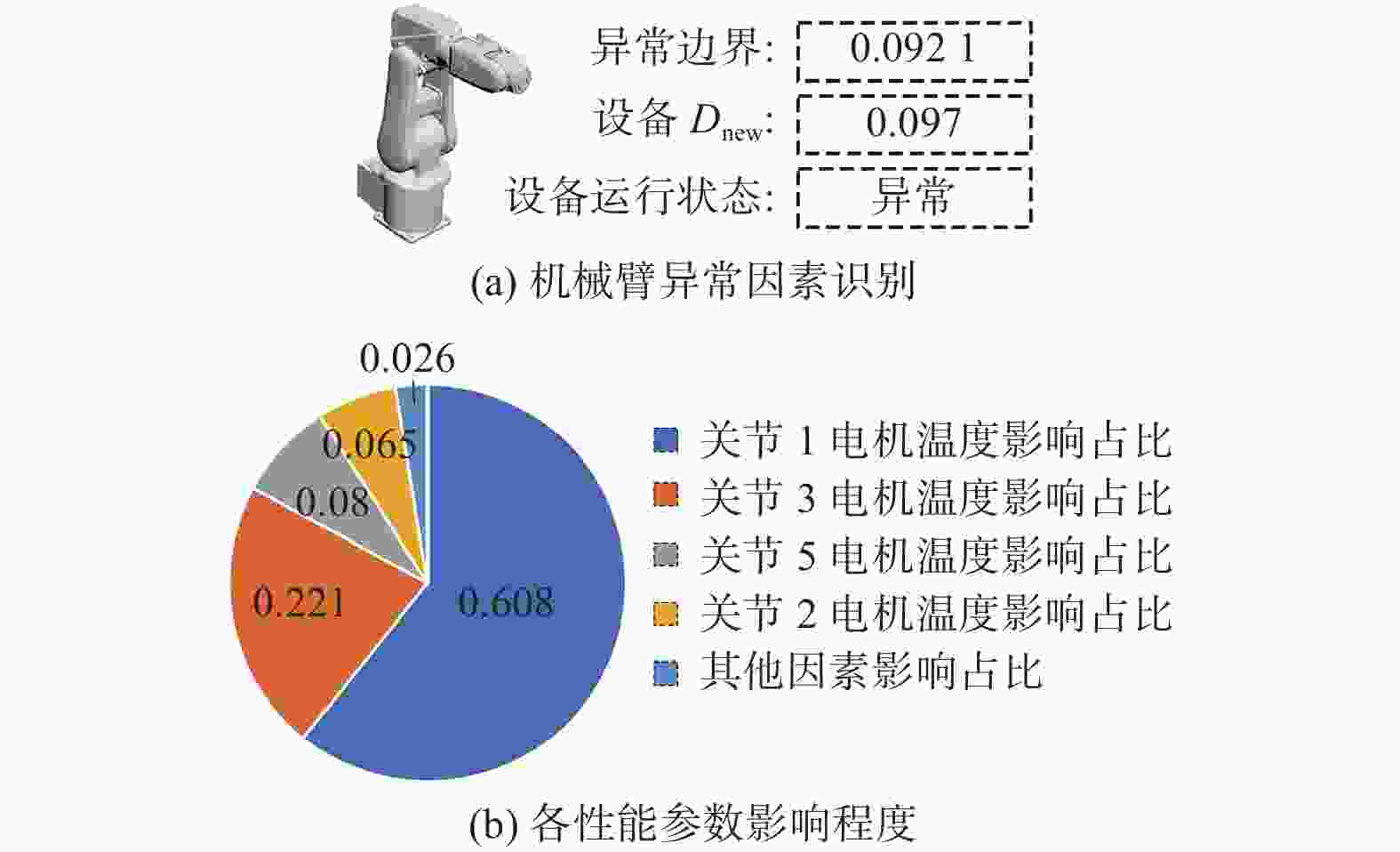
变量 最大值 最小值 平均值 伺服电机温度/℃ 79 16 49 电机响应时间/ms 20 6 10 表 2 增加扰动后实时采集到的机械臂性能参数
Table 2. Performance parameters of robotic arm collected in real time after addition of disturbance
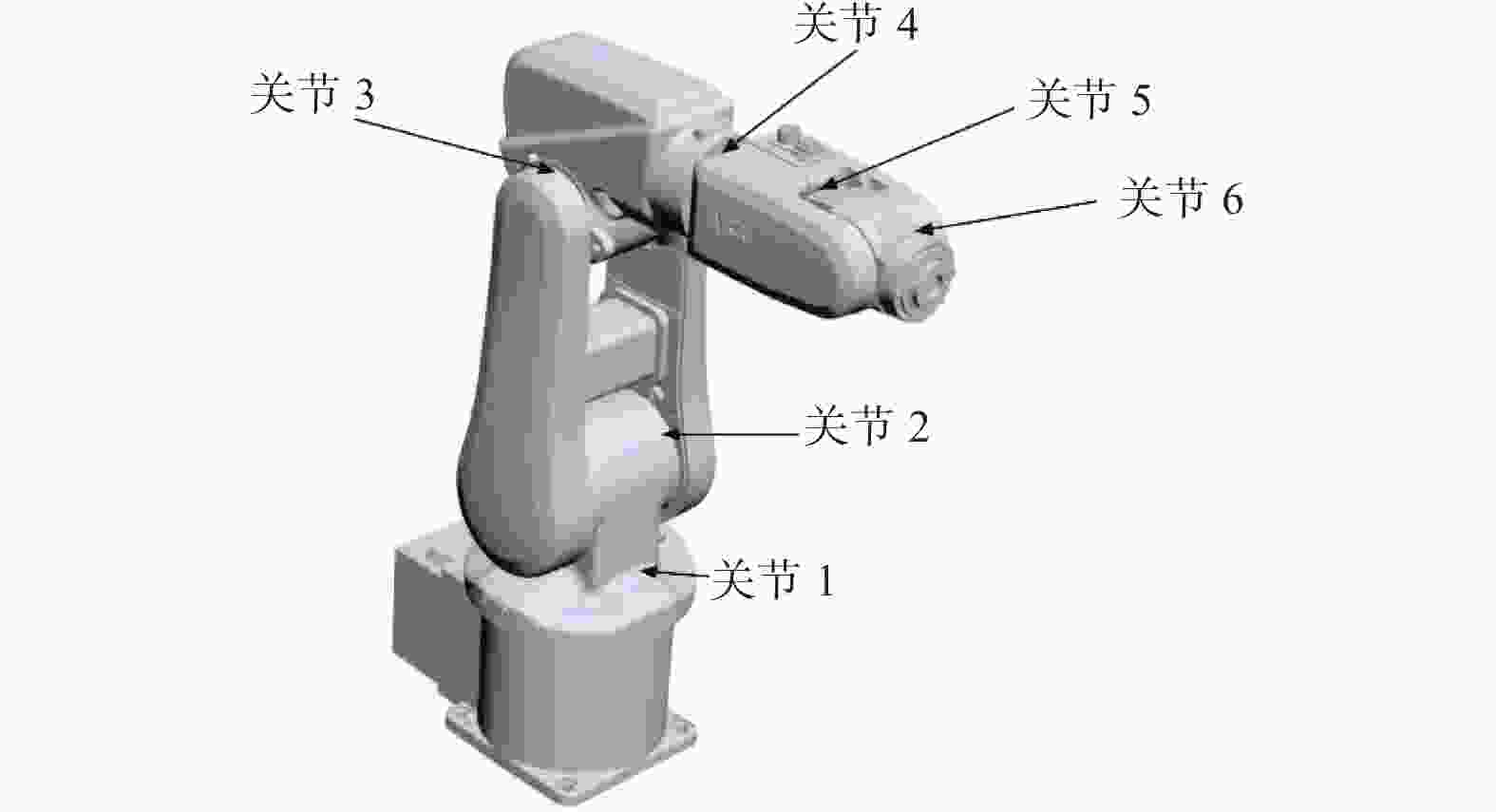
机械臂性能参数 参数值 关节1处伺服电机温度/℃ 80 关节1处伺服电机响应时间/ms 17 关节2处伺服电机温度/℃ 40 关节2处伺服电机响应时间/ms 19 关节3处伺服电机温度/℃ 30 关节3处伺服电机响应时间/ms 18 关节4处伺服电机温度/℃ 48 关节4处伺服电机响应时间/ms 16 关节5处伺服电机温度/℃ 36 关节5处伺服电机响应时间/ms 14 关节6处伺服电机温度/℃ 45 关节6处伺服电机响应时间/ms 17 -
[1] 雷亚国, 贾峰, 孔德同, 等. 大数据下机械智能故障诊断的机遇与挑战[J] . 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(5): 94 − 104. [2] GRIEVES M, VICKERS J. Digital twin: mitigating unpredictable, undesirable emergent behavior in complex systems[M] //KAHLEN F J, FLUMERFELT S, ALVES A. Transdisciplinary perspectives on complex systems. Cham: Springer, 2017: 85−113. [3] 陶飞, 刘蔚然, 张萌, 等. 数字孪生五维模型及十大领域应用[J] . 计算机集成制造系统, 2019, 25(1): 1 − 18. [4] 陶飞, 张贺, 戚庆林, 等. 数字孪生模型构建理论及应用[J] . 计算机集成制造系统, 2021, 27(1): 1 − 15. [5] SARACCO R. Digital twins: bridging physical space and cyberspace[J] . Computer, 2019, 52(12): 58 − 64. [6] COHEN Y, PILATI F, FACCIO M. Digitization of assembly line for complex products-the digital nursery of workpiece digital twins[J] . IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2021, 54(1): 158 − 162. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2021.08.018 [7] 杨俊峰, 王红军, 冯昊天, 等. 基于数字孪生模型的设备故障诊断技术[J] . 设备管理与维修, 2021(9): 128 − 130. [8] 孙元亮, 马文茂, 张超, 等. 面向数字孪生的智能生产线监控系统关键技术研究[J] . 航空制造技术, 2021, 64(8): 58 − 65. [9] 武颖, 姚丽亚, 熊辉, 等. 基于数字孪生技术的复杂产品装配过程质量管控方法[J] . 计算机集成制造系统, 2019, 25(6): 1568 − 1575. [10] SULEIMENOV B A, SUGUROVA L A, SULEIMENOV A B, et al. Synthesis of the equipment health management system of the turbine units' of thermal power stations[J] . Mechanics & Industry, 2018, 19(2): 209. [11] DINARDO G, FABBIANO L, VACCA G. A smart and intuitive machine condition monitoring in the Industry 4.0 scenario[J] . Measurement, 2018, 126: 1 − 12. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2018.05.041 [12] MANIKANDAN S, DURAIVELU K. Fault diagnosis of various rotating equipment using machine learning approaches-a review[J] . Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part E: Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 235(2): 629-642. [13] HONG G, SUH D. Supervised-learning-based intelligent fault diagnosis for mechanical equipment[J] . IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 116147 − 116162. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3104189 [14] 赖英旭, 刘静, 刘增辉, 等. 工业控制系统脆弱性分析及漏洞挖掘技术研究综述[J] . 北京工业大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 571 − 582. [15] UR-REHMAN A, GONDAL I, KAMRUZZAMAN J, et al. Vulnerability modeling for hybrid industrial control system networks[J] . Journal of Grid Computing, 2020, 18(4): 863 − 878. doi: 10.1007/s10723-020-09528-w [16] ALONSO M, TURANZAS J, AMARIS H, et al. Cyber-physical vulnerability assessment in smart grids based on multilayer complex networks[J] . Sensors, 2021, 21(17): 5826. doi: 10.3390/s21175826 [17] GAO G B, ZHOU D M, TANG H, et al. An intelligent health diagnosis and maintenance decision-making approach in smart manufacturing[J] . Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2021, 216: 107965. [18] 高贵兵, 王俊深, 岳文辉, 等. 基于脆弱性的制造设备故障智能诊断与维护[J] . 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(23): 141 − 149. -





 下载:
下载: