|
[1]
|
PHILLIPS D R, RASBERY J M, BARTEL B, et al. Biosynthetic diversity in plant triterpene cyclization[J] . Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2006, 9(3): 305 − 314. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.03.004
|
|
[2]
|
BORELLA R, FORTI L, GIBELLINI L, et al. Synthesis and anticancer activity of CDDO and CDDO-Me, two derivatives of natural triterpenoids[J] . Molecules, 2019, 24(22): 4097. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224097
|
|
[3]
|
SUH N, WANG Y, HONDA T, et al. A novel synthetic oleanane triterpenoid, 2−cyano−3, 12−dioxoolean−1, 9−dien−28−oic acid, with potent differentiating, antiproliferative, and anti−inflammatory activity[J] . Cancer Research, 1999, 59(2): 336 − 341.
|
|
[4]
|
COUCH R D, BROWNING R G, HONDA T, et al. Studies on the reactivity of CDDO, a promising new chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agent: implications for a molecular mechanism of action[J] . Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 2005, 15(9): 2215 − 2219.
|
|
[5]
|
HONDA T, ROUNDS B V, GRIBBLE G W, et al. Design and synthesis of 2−cyano−3, 12−dioxoolean−1, 9−dien−28−oic acid, a novel and highly active inhibitor of nitric oxide production in mouse macrophages[J] . Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 1998, 8(19): 2711 − 2714.
|
|
[6]
|
FU L F, GRIBBLE G W. Efficient and scalable synthesis of bardoxolone methyl (CDDO-methyl ester)[J] . Organic Letters, 2013, 15(7): 1622 − 1625. doi: 10.1021/ol400399x
|
|
[7]
|
SPORN M B, LIBY K T, YORE M M, et al. New synthetic triterpenoids: potent agents for prevention and treatment of tissue injury caused by inflammatory and oxidative stress[J] . Journal of Natural Products, 2011, 74(3): 537 − 545. doi: 10.1021/np100826q
|
|
[8]
|
SHANMUGAM M K, DAI X Y, KUMAR A P, et al. Oleanolic acid and its synthetic derivatives for the prevention and therapy of cancer: preclinical and clinical evidence[J] . Cancer Letters, 2014, 346(2): 206 − 216. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.01.016
|
|
[9]
|
JOHNSON D E, O'KEEFE R A, GRANDIS J R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer[J] . Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology, 2018, 15(4): 234 − 248. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.8
|
|
[10]
|
GEE M S, KANG S B, KIM N, et al. Bardoxolone methyl suppresses hepatitis B virus large surface protein variant W4P-related carcinogenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation via the inhibition of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling[J] . Pharmacology, 2018, 102(1/2): 105 − 113.
|
|
[11]
|
TORRES G M, YANG H, PARK C, et al. T cells and CDDO-Me attenuate immunosuppressive activation of human melanoma-conditioned macrophages[J] . Frontiers in Immunology, 2022, 13: 768753. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.768753
|
|
[12]
|
HAYASHI M, KUGA A, SUZUKI M, et al. Microenvironmental activation of Nrf2 restricts the progression of Nrf2-activated malignant tumors[J] . Cancer Research, 2020, 80(16): 3331 − 3344. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-2888
|
|
[13]
|
YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization[J] . European Journal of Pharmacology, 2020, 877: 173090. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173090
|
|
[14]
|
XU F, WEI Y, TANG Z, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages in lung cancer: friend or foe? (Review)[J] . Molecular Medicine Reports, 2020, 22(5): 4107 − 4115.
|
|
[15]
|
MOERLAND J A, LEAL A S, LOCKWOOD B, et al. The triterpenoid CDDO-methyl ester redirects macrophage polarization and reduces lung tumor burden in a Nrf2-dependent manner[J] . Antioxidants, 2023, 12(1): 116. doi: 10.3390/antiox12010116
|
|
[16]
|
YU L, WEI J, LIU P D. Attacking the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment in human cancer[J] . Seminars in Cancer Biology, 2022, 85: 69 − 94. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.06.019
|
|
[17]
|
GAO X H, DEEB D, LIU Y B, et al. CDDO-Me inhibits tumor growth and prevents recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma[J] . International Journal of Oncology, 2015, 47(6): 2100 − 2106. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.3212
|
|
[18]
|
ZHANG Y, WANG X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer[J] . Journal of Hematology & Oncology, 2020, 13(1): 165.
|
|
[19]
|
ZHOU L, WANG Z Y, YU S B, et al. CDDO-Me elicits anti-breast cancer activity by targeting LRP6 and FZD7 receptor complex[J] . The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 2020, 373(1): 149 − 159. doi: 10.1124/jpet.119.263434
|
|
[20]
|
SHISHODIA S, SETHI G, KONOPLEVA M, et al. A synthetic triterpenoid, CDDO-Me, inhibits IκBαkinase and enhances apoptosis induced by TNF and chemotherapeutic agents through down-regulation of expression of nuclear factor κB-regulated gene products in human leukemic cells[J] . Clinical Cancer Research, 2006, 12(6): 1828 − 1838. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2044
|
|
[21]
|
ANSELMI A, ABBATE A, GIROLA F, et al. Myocardial ischemia, stunning, inflammation, and apoptosis during cardiac surgery: a review of evidence[J] . European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, 2004, 25(3): 304 − 311. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2003.12.003
|
|
[22]
|
BALK R A. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS): where did it come from and is it still relevant today?[J] . Virulence, 2014, 5(1): 20 − 26. doi: 10.4161/viru.27135
|
|
[23]
|
YANG Z H, WU X N, HE P, et al. A non-canonical PDK1-RSK signal diminishes pro-caspase-8-mediated necroptosis blockade[J] . Molecular Cell, 2020, 80(2): 296 − 310.
|
|
[24]
|
WU Z M, GENG Y, LU X J, et al. Chaperone-mediated autophagy is involved in the execution of ferroptosis[J] . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2019, 116(8): 2996 − 3005.
|
|
[25]
|
WANG Y Y, MA H, HUANG J X, et al. Discovery of bardoxolone derivatives as novel orally active necroptosis inhibitors[J] . European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2021, 212: 113030. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113030
|
|
[26]
|
CHEN X, KANG R, KROEMER G, et al. Ferroptosis in infection, inflammation, and immunity[J] . Journal of Experimental Medicine, 2021, 218(6): e20210518. doi: 10.1084/jem.20210518
|
|
[27]
|
MAYR L, GRABHERR F, SCHWÄRZLER J, et al. Dietary lipids fuel GPX4-restricted enteritis resembling Crohn's disease[J] . Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 1175. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15029-x
|
|
[28]
|
XU M Y, TAO J, YANG Y D, et al. Ferroptosis involves in intestinal epithelial cell death in ulcerative colitis[J] . Cell Death & Disease, 2020, 11(2): 86.
|
|
[29]
|
ANSARI M Y, AHMAD N, HAQQI T M. Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: role of polyphenols[J] . Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2020, 129: 110452.
|
|
[30]
|
CAI D W, YIN S S, YANG J, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibition activates Nrf2 and protects against osteoarthritis[J] . Arthritis Research & Therapy, 2015, 17(1): 269.
|
|
[31]
|
DONG J, ZHANG K J, LI G C, et al. CDDO-Im ameliorates osteoarthritis and inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in mice via enhancing Nrf2-dependent autophagy[J] . Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 2022, 43(7): 1793 − 1802. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00782-6
|
|
[32]
|
KIM J E, KANG T C. CDDO-Me attenuates astroglial autophagy via Nrf2-, ERK1/2-SP1- and Src-CK2-PTEN-PI3K/AKT-mediated signaling pathways in the hippocampus of chronic epilepsy rats[J] . Antioxidants, 2021, 10(5): 655. doi: 10.3390/antiox10050655
|
|
[33]
|
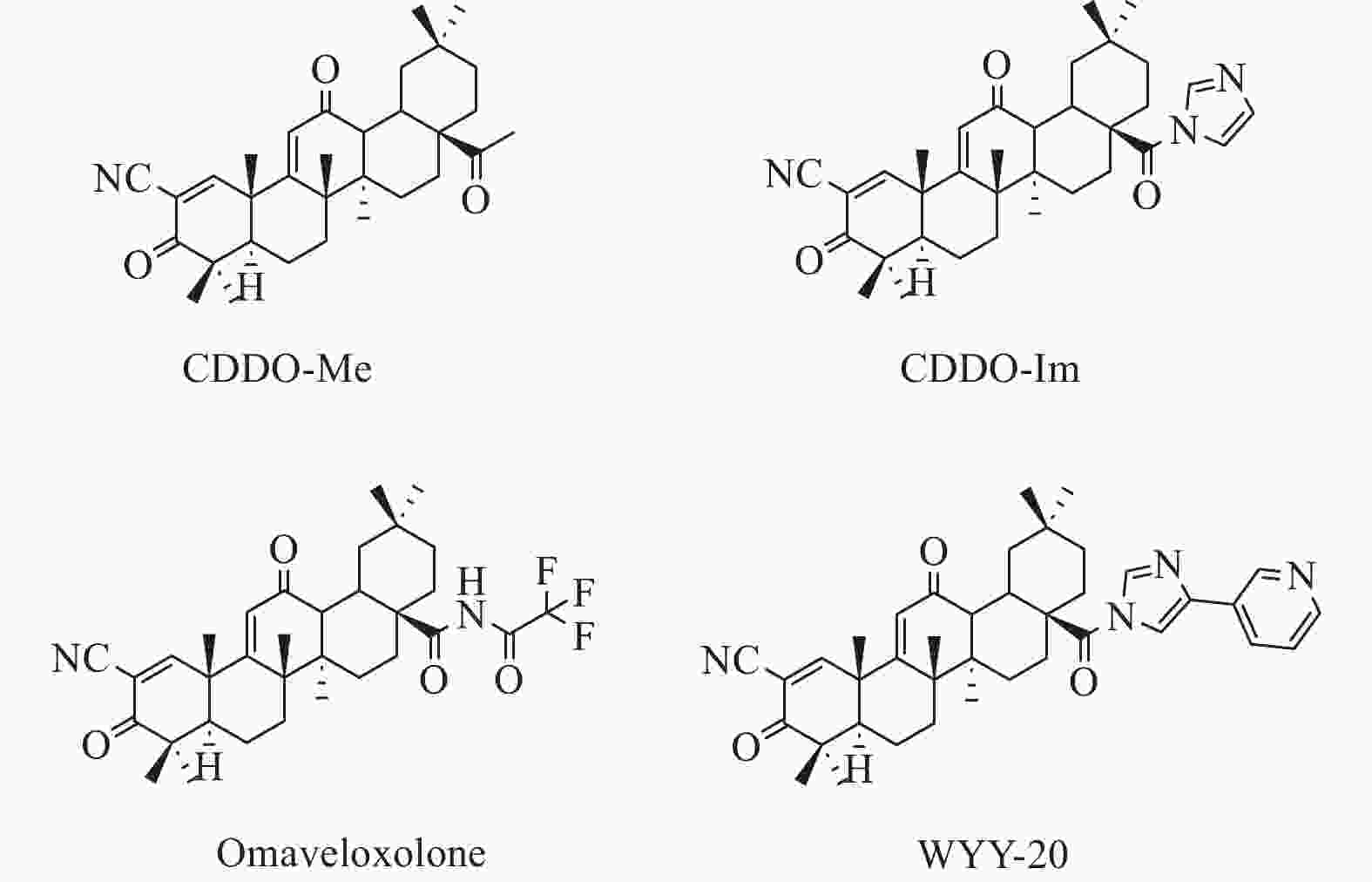
PILOTTO F, CHELLAPANDI D M, PUCCIO H. Omaveloxolone: a groundbreaking milestone as the first FDA-approved drug for Friedreich ataxia[J] . Trends in Molecular Medicine, 2024, 30(2): 117 − 125. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.12.002
|
|
[34]
|
GHANEKAR S D, MILLER W W, MEYER C J, et al. Orphan drugs in development for the treatment of friedreich's ataxia: focus on omaveloxolone[J] . Degenerative Neurological and Neuromuscular Disease, 2019, 9: 103 − 107. doi: 10.2147/DNND.S180027
|
|
[35]
|
LEE A. Omaveloxolone: first approval[J] . Drugs, 2023, 83(8): 725 − 729. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01874-9
|
|
[36]
|
ZHANG F, WANG S P, ZHANG M J, et al. Pharmacological induction of heme oxygenase-1 by a triterpenoid protects neurons against ischemic injury[J] . Stroke, 2012, 43(5): 1390 − 1397. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.647420
|
|
[37]
|
LU Y, SUN Y Z, LIU Z H, et al. Activation of NRF2 ameliorates oxidative stress and cystogenesis in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease[J] . Science Translational Medicine, 2020, 12(554): eaba3613. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aba3613
|
|
[38]
|
LIBY K, HOCK T, YORE M M, et al. The synthetic triterpenoids, CDDO and CDDO-imidazolide, are potent inducers of heme oxygenase-1 and Nrf2/ARE signaling[J] . Cancer Research, 2005, 65(11): 4789 − 4798. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4539
|
|
[39]
|
SHELTON L M, PARK B K, COPPLE I M. Role of Nrf2 in protection against acute kidney injury[J] . Kidney International, 2013, 84(6): 1090 − 1095. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.248
|
|
[40]
|
JIANG T, HUANG Z P, LIN Y F, et al. The protective role of Nrf2 in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy[J] . Diabetes, 2010, 59(4): 850 − 860. doi: 10.2337/db09-1342
|
|
[41]
|
LIU M C, REDDY N M, HIGBEE E M, et al. The Nrf2 triterpenoid activator, CDDO-imidazolide, protects kidneys from ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice[J] . Kidney International, 2014, 85(1): 134 − 141. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.357
|
|
[42]
|
CHIN M P, BAKRIS G L, BLOCK G A, et al. Bardoxolone methyl improves kidney function in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 4 and type 2 diabetes: post-hoc analyses from bardoxolone methyl evaluation in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes study[J] . American Journal of Nephrology, 2018, 47(1): 40 − 47. doi: 10.1159/000486398
|
|
[43]
|
ROTHAN H A, ZHONG Y W, SANBORN M A, et al. Small molecule grp94 inhibitors block dengue and Zika virus replication[J] . Antiviral Research, 2019, 171: 104590. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.104590
|
|
[44]
|
VÁZQUEZ N, GREENWELL-WILD T, MARINOS N J, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-induced macrophage gene expression includes the p21 gene, a target for viral regulation[J] . Journal of Virology, 2005, 79(7): 4479 − 4491. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.7.4479-4491.2005
|
|
[45]
|
SUN Q, YE F, LIANG H, et al. Bardoxolone and bardoxolone methyl, two Nrf2 activators in clinical trials, inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication and its 3C-like protease[J] . Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 2021, 6(1): 212. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00628-x
|





 下载:
下载: