Effects of iron overload on duodenal iron metabolism and health in rats
-
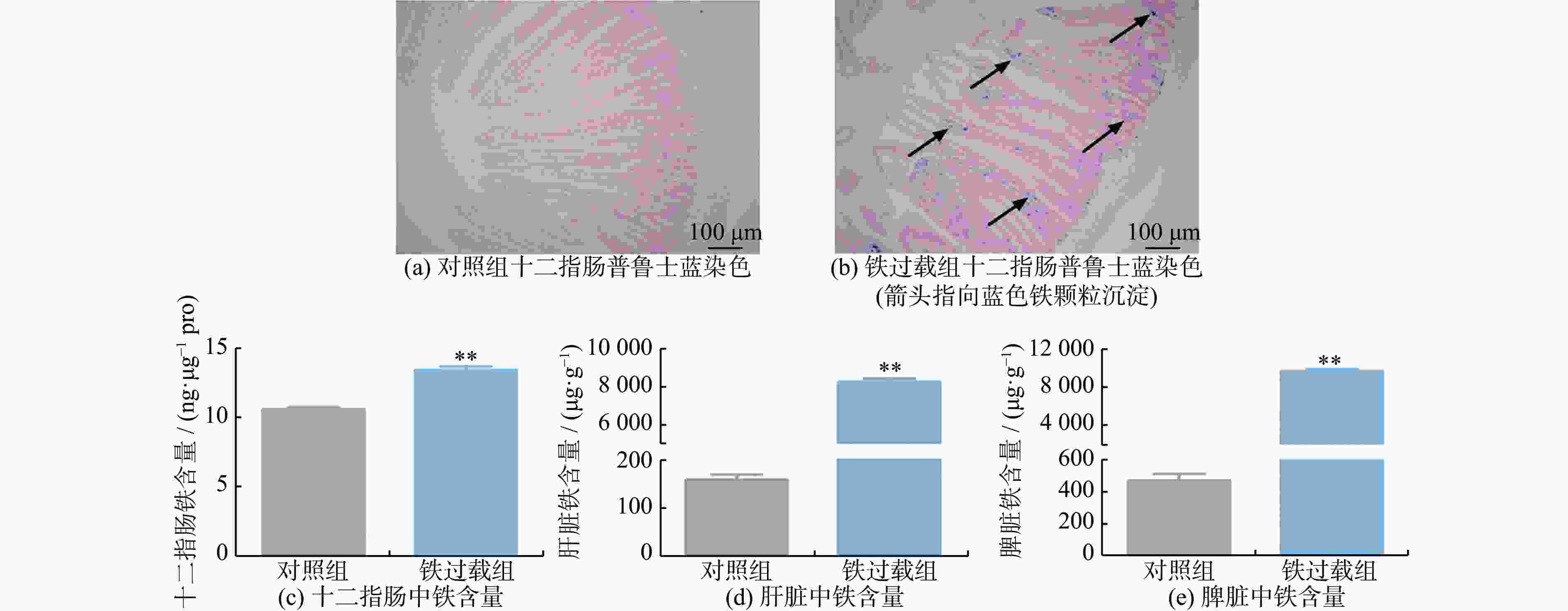
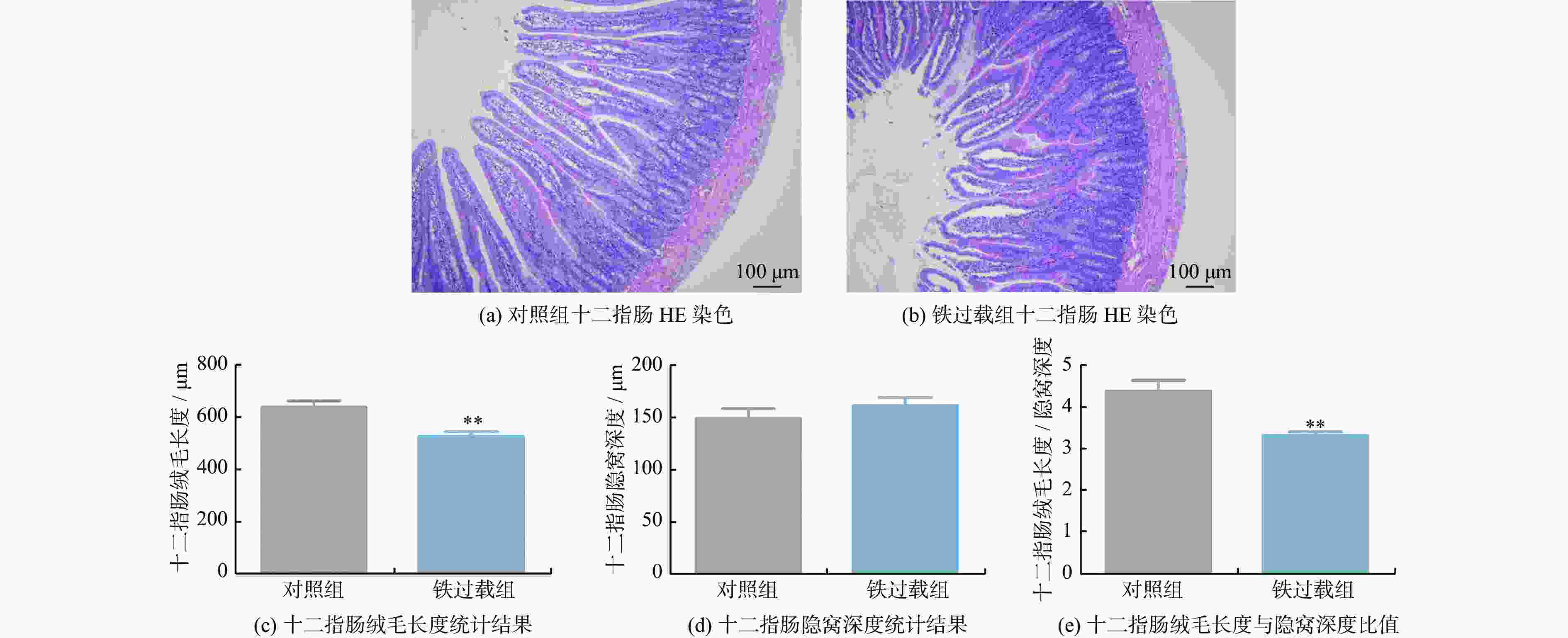
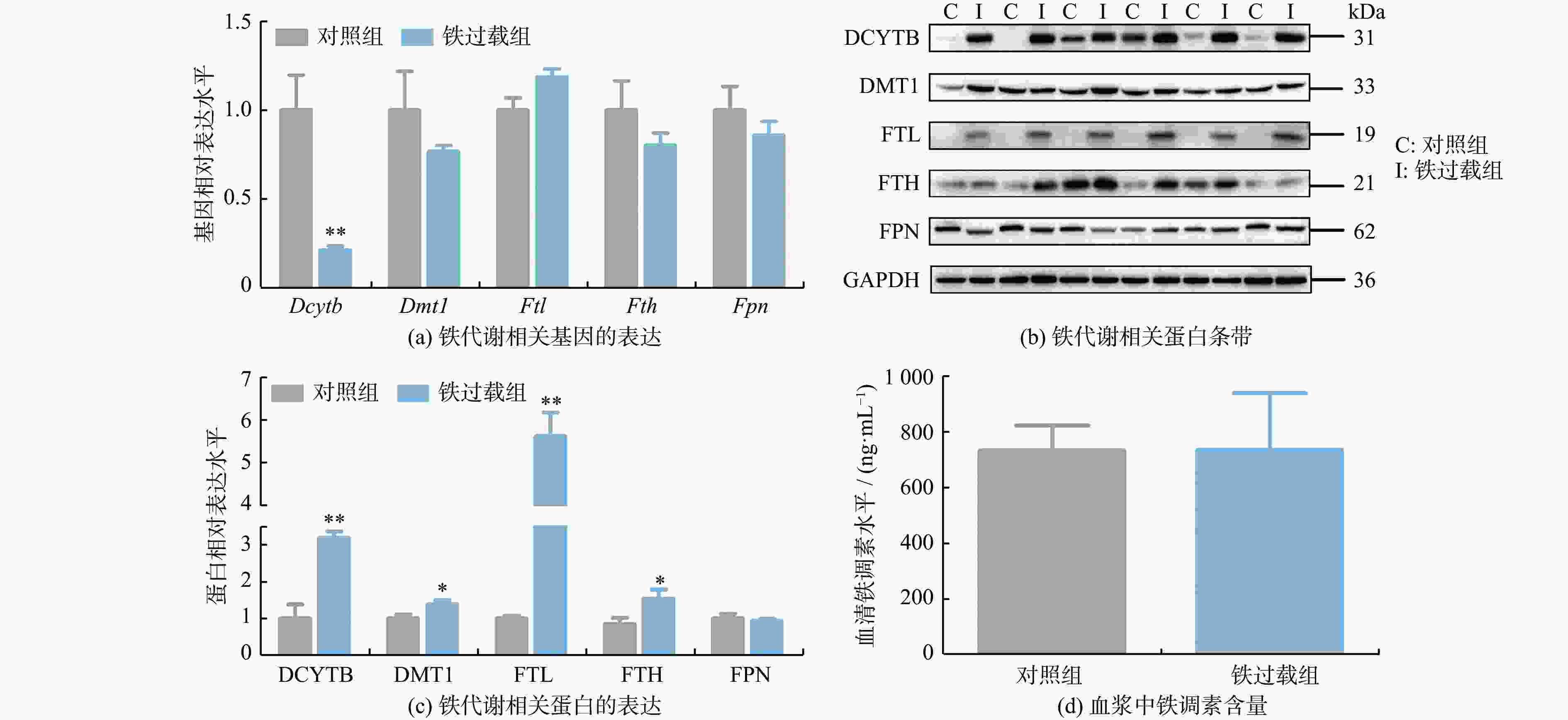
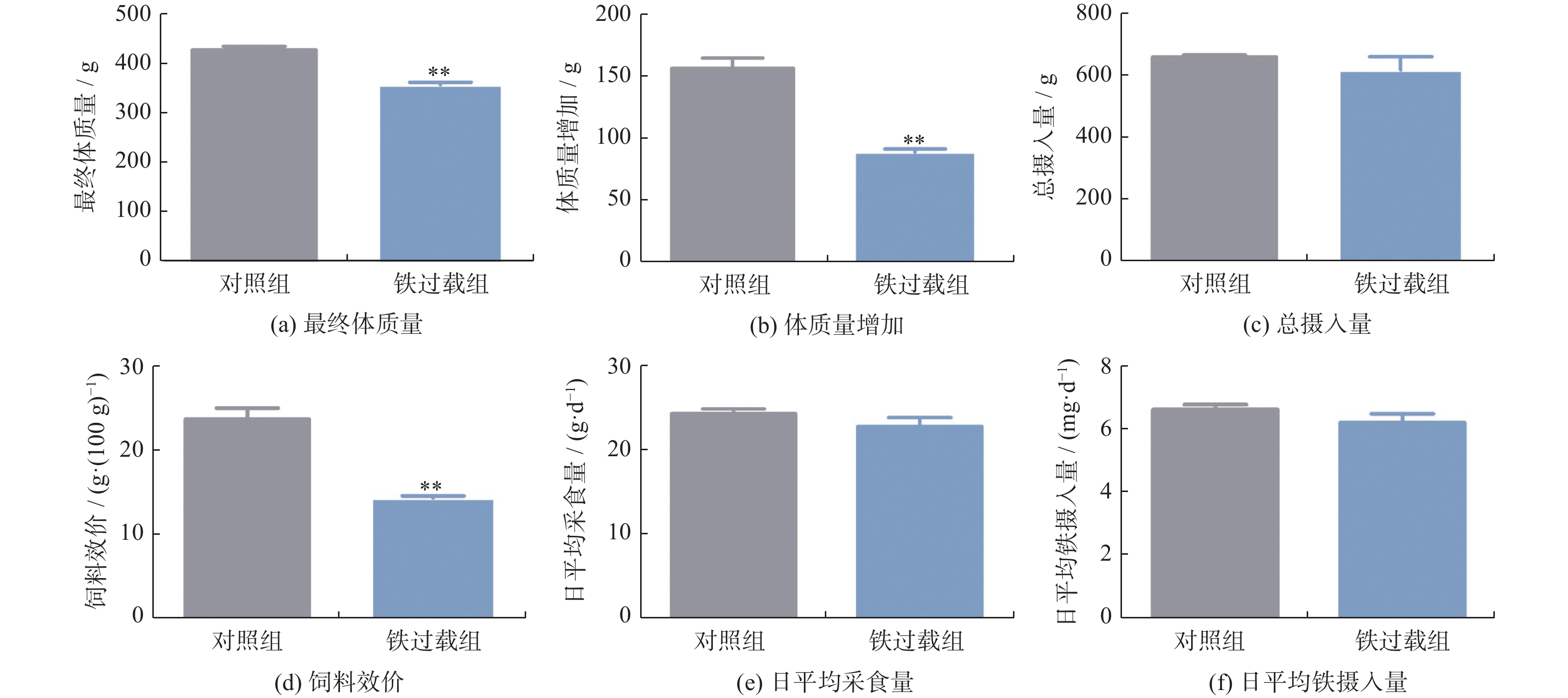
摘要: 铁是维持各种生理功能所必需的微量营养素,但过量的铁因其氧化还原活性具有高度毒性。将6 ~ 7周龄雄性SD大鼠随机分为对照组和铁过载组,分别给予生理盐水和150 mg/kg右旋糖酐铁连续处理4周。结果发现,铁过载显著降低大鼠体质量,增加血清铁、转铁蛋白结合铁、铁蛋白含量和转铁蛋白饱和度。铁过载组大鼠十二指肠、肝脏和脾脏铁含量显著增加,而十二指肠绒毛长度及其与隐窝深度的比值显著下降。此外,铁过载大鼠表现出与吸收和储存相关的DCYTB、DMT1、FTL和FTH的表达上调,但FPN和血清铁蛋白水平没有显著变化。以上结果表明,铁过载通过上调十二指肠铁吸收和储存蛋白表达,诱发十二指肠铁沉积和肠道损伤,为铁过载引起的十二指肠健康问题提供了理论证据。Abstract: Iron is an essential trace element for various physiological functions, yet excessive iron is highly toxic owing to its redox activity property. Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats, aged 6~7 weeks were randomly divided into a control group and an iron overload group. They were administered either saline or 150 mg/kg iron dextran for four consecutive weeks. The results show that iron overload significantly reduced body mass and increased serum iron, transferrin-bound iron, ferritin levels, and transferrin saturation. Elevated iron contents were observed in the duodenum, liver, and spleen of iron overloaded rats, whereas duodenal villus length and the villus-length-to-crypt-depth ratio were significantly decreased. Furthermore, an upregulation of DCYTB, DMT1, FTL, and FTH associated with absorption and storage, was observed in iron-overloaded rats, yet no significant changes were found in ferroportin (FPN) or serum ferritin levels. These findings indicate that iron overload induces duodenal iron deposition and intestinal damage by upregulating the expression of duodenal iron-absorption and storage proteins, thereby providing theoretical evidence for duodenal health issues caused by iron overload.
-
Key words:
- iron overload /
- duodenum /
- iron metabolism /
- intestinal damage /
- rats
-
表 1 RT-qPCR特异性引物序列
Table 1. Sequences of specific primers for RT-qPCR
目的基因 引物序列(5'→3') 基因序列号 Dcytb F: TTCTGGACTCCTCCTCTTTGG NM_001011954.1 R: TTCTGGTGGGAATGAATGGTA Dmt1 F: TTGTCGTCTCCGTCTTTGCT NM_013173.2 R: CCAGGGTAGAGTTGTCGTTAGG Ftl F: TCCAGGATGTGCAGAAGCC NM_022500.4 R: CCCTACGGAGGTTGGTCAG Fth F: GGAACTTCACAAACTGGCTAC NM_012848.2 R: TGGATTTCACCTGCTCATT Fpn F: AGTCATTGGCTGTGGTTTC NM_ 133315.2 R: TCAAGTTCACGGATGTTAGA Gapdh F: GGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTATGA NM_017008.4 R: AATGGGAGTTGCTGTTGAAGT 注:Dcytb为十二指肠细胞色素b;Dmt1为二价金属离子转运体;Ftl为铁储存基因铁蛋白轻链;Fth为铁蛋白重链;Fpn为膜铁转运蛋白基因;Gapdh为甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶。 表 2 铁过载对大鼠血液铁代谢指标的影响
Table 2. Effects of iron overload on blood iron metabolism parameters in rats
指标 对照组 铁过载组 血红蛋白含量/(g·L−1) 167.50 ± 2.5 176 ± 2.67 转铁蛋白结合铁含量/(μg·mL−1) 23.68 ± 1.2 74.05 ± 2.82** 总铁结合力/(μmol·L−1) 80.27 ± 2.58 77.65 ± 2.59 不饱和铁结合力/(μmol·L−1) 56.58 ± 2.71 3.60 ± 0.50** 转铁蛋白饱和度/% 29.62 ± 1.53 95.31 ± 0.71** 铁含量/(μg·mL−1) 6.83 ± 1.27 10.68 ± 1.18* 铁蛋白含量/(ng·mL−1) 29.14 ± 1.95 44.83 ± 2.48* 注:*和**分别为差异显著(P<0.05)和差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] CORRENTI M, GAMMELLA E, CAIRO G, et al. Iron absorption: molecular and pathophysiological aspects[J] . Metabolites, 2024, 14(4): 228. doi: 10.3390/metabo14040228 [2] CHEN Y, ZHANG J Q, TIAN Y, et al. Iron accumulation in ovarian microenvironment damages the local redox balance and oocyte quality in aging mice[J] . Redox Biology, 2024, 73: 103195. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103195 [3] CHARLEBOIS E, PANTOPOULOS K. Nutritional aspects of iron in health and disease[J] . Nutrients, 2023, 15(11): 2441. doi: 10.3390/nu15112441 [4] GONZÁLEZ-DOMÍNGUEZ Á, VISIEDO-GARCÍA F M, DOMÍNGUEZ-RISCART J, et al. Iron metabolism in obesity and metabolic syndrome[J] . International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2020, 21(15): 5529. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155529 [5] BAO H H, WANG Y, XIONG H L, et al. Mechanism of iron ion homeostasis in intestinal immunity and gut microbiota remodeling[J] . International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2024, 25(2): 727. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020727 [6] ZHANG Y, ZOU L Y, LI X D, et al. SLC40A1 in iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and disease: a review[J] . Wires Mechanisms of Disease, 2024, 16(4): e1644. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1644 [7] PARK W R, CHOI B, KIM Y J, et al. Melatonin regulates iron homeostasis by inducing hepcidin expression in hepatocytes[J] . International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(7): 3593. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073593 [8] 阎春生, 周源苑. 铁负荷对正常生长期大鼠营养代谢的影响[J] . 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 41(5): 52 − 55. [9] MA W, JIA L, XIONG Q Q, et al. Iron overload protects from obesity by ferroptosis[J] . Foods, 2021, 10(8): 1787. doi: 10.3390/foods10081787 [10] SHETE P A, GHATPANDE N S, VARMA M E, et al. Chronic dietary iron overload affects hepatic iron metabolism and cognitive behavior in Wistar rats[J] . Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2024, 84: 127422. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2024.127422 [11] MILINKOVIĆ N, ZEKOVIĆ M, DODEVSKA M, et al. Magnesium supplementation and iron status among female students: the intervention study[J] . Journal of Medical Biochemistry, 2022, 41(3): 316 − 326. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-33898 [12] NAVARRETE J E, AJIBOYE O, LEA J I. Biochemical markers of iron status and iron accumulation in peritoneal dialysis patients treated with ferric citrate[J] . Peritoneal Dialysis International: Journal of the International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis, 2024, 44(2): 133 − 140. doi: 10.1177/08968608231197361 [13] PISKIN E, CIANCIOSI D, GULEC S, et al. Iron absorption: factors, limitations, and improvement methods[J] . ACS Omega, 2022, 7(24): 20441 − 20456. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01833 [14] WANG M, YANG C, WANG Q Y, et al. The relationship between villous height and growth performance, small intestinal mucosal enzymes activities and nutrient transporters expression in weaned piglets[J] . Journal of Animal Physiology and Animal Nutrition, 2020, 104(2): 606 − 615. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13299 -





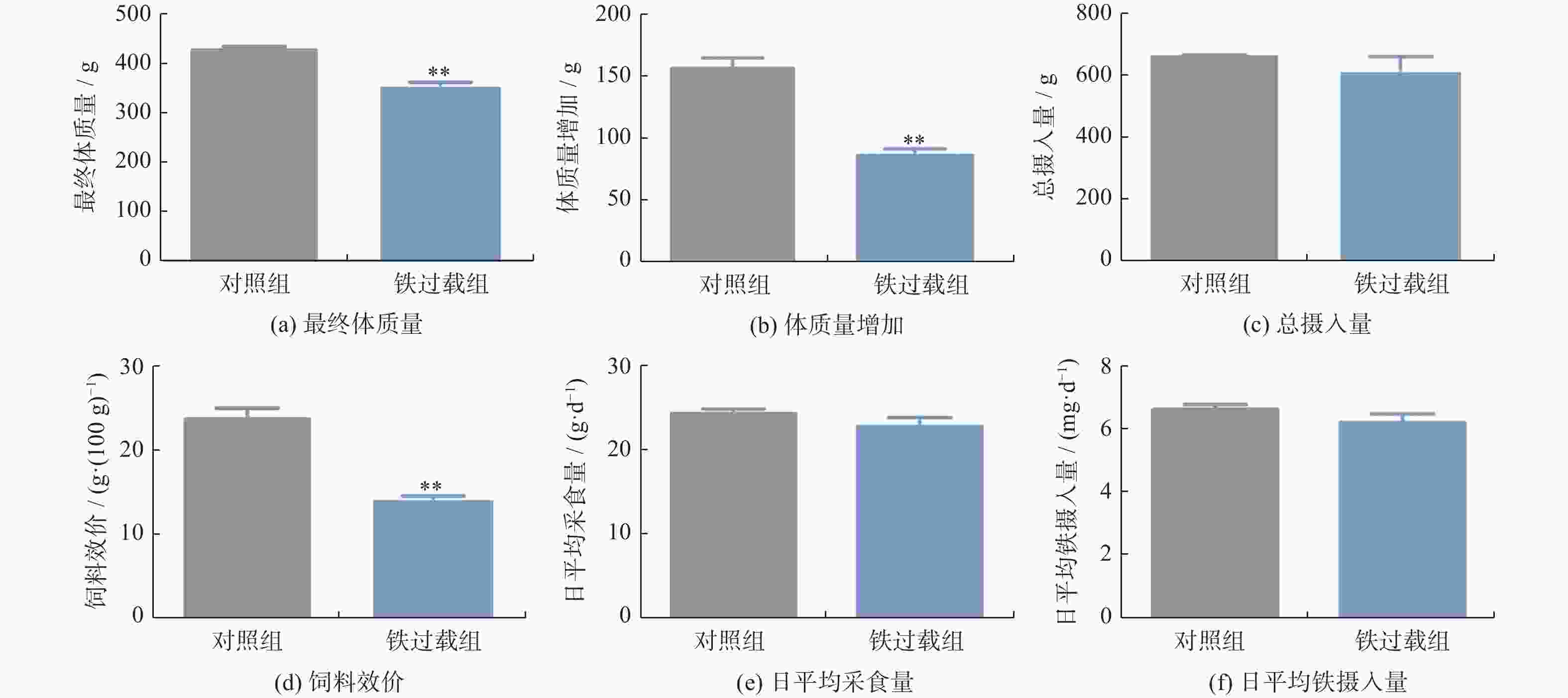
 下载:
下载: