Research on refrigeration cooling and temperature control of thermoelectric devices for cylindrical battery module
-
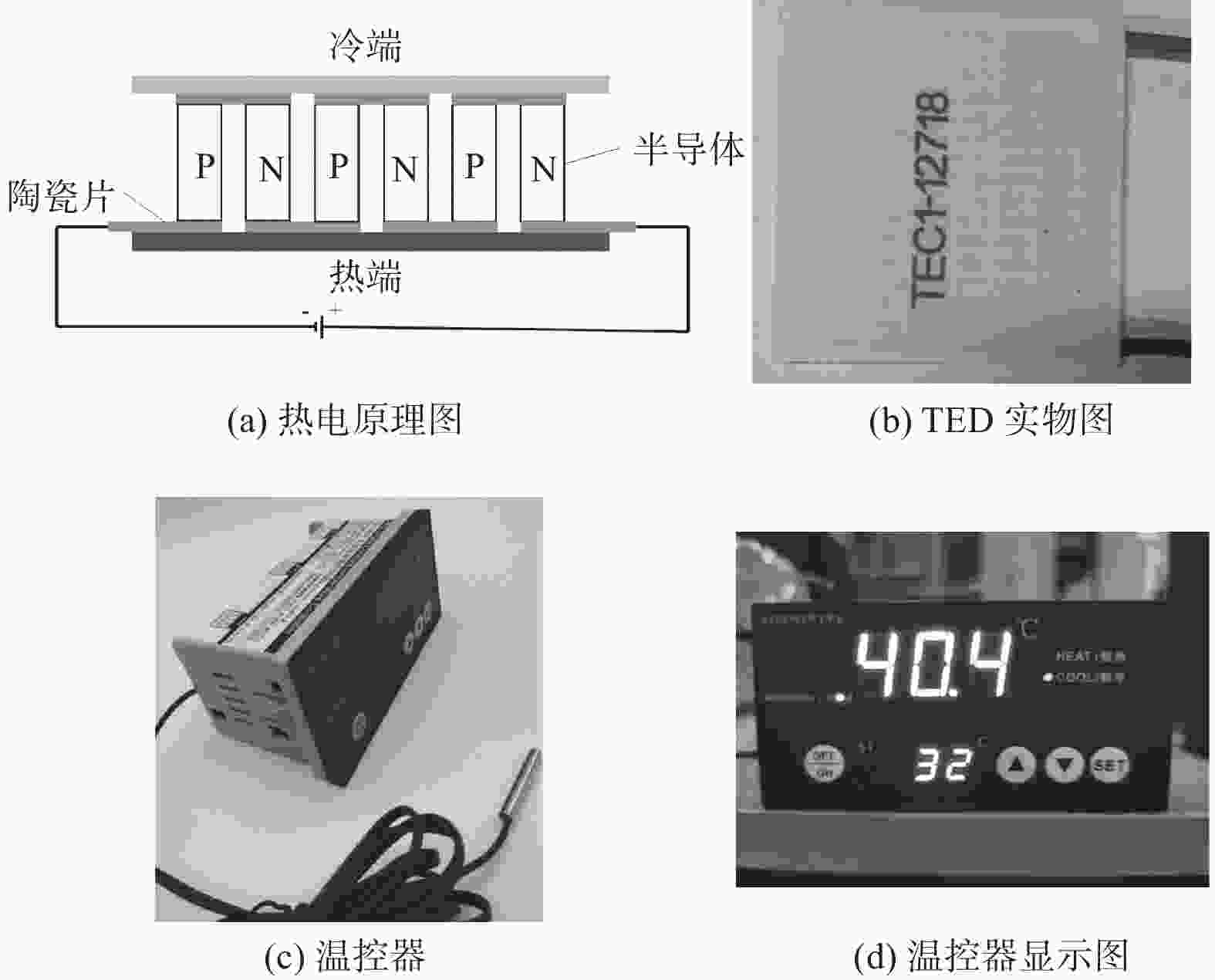
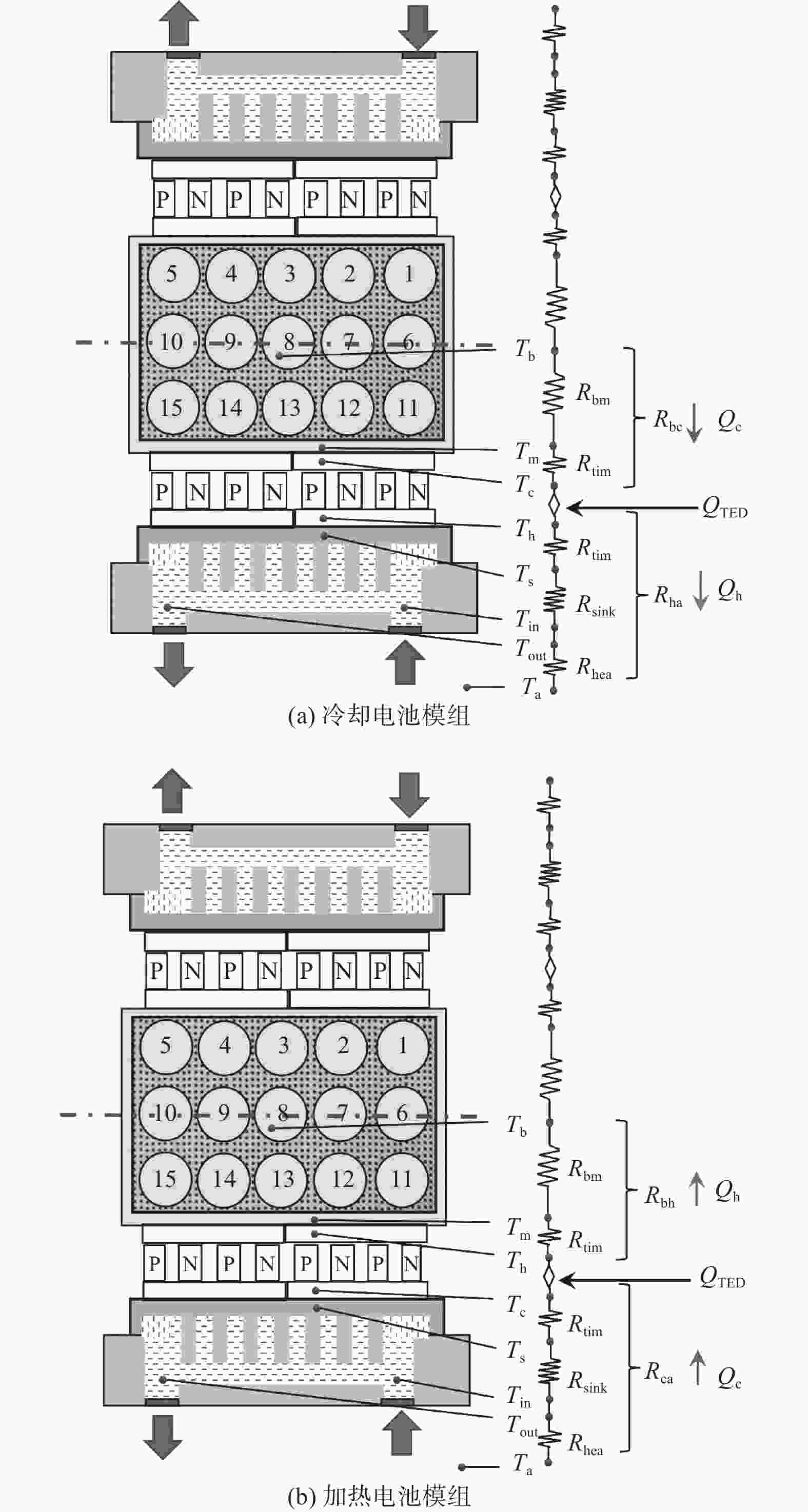
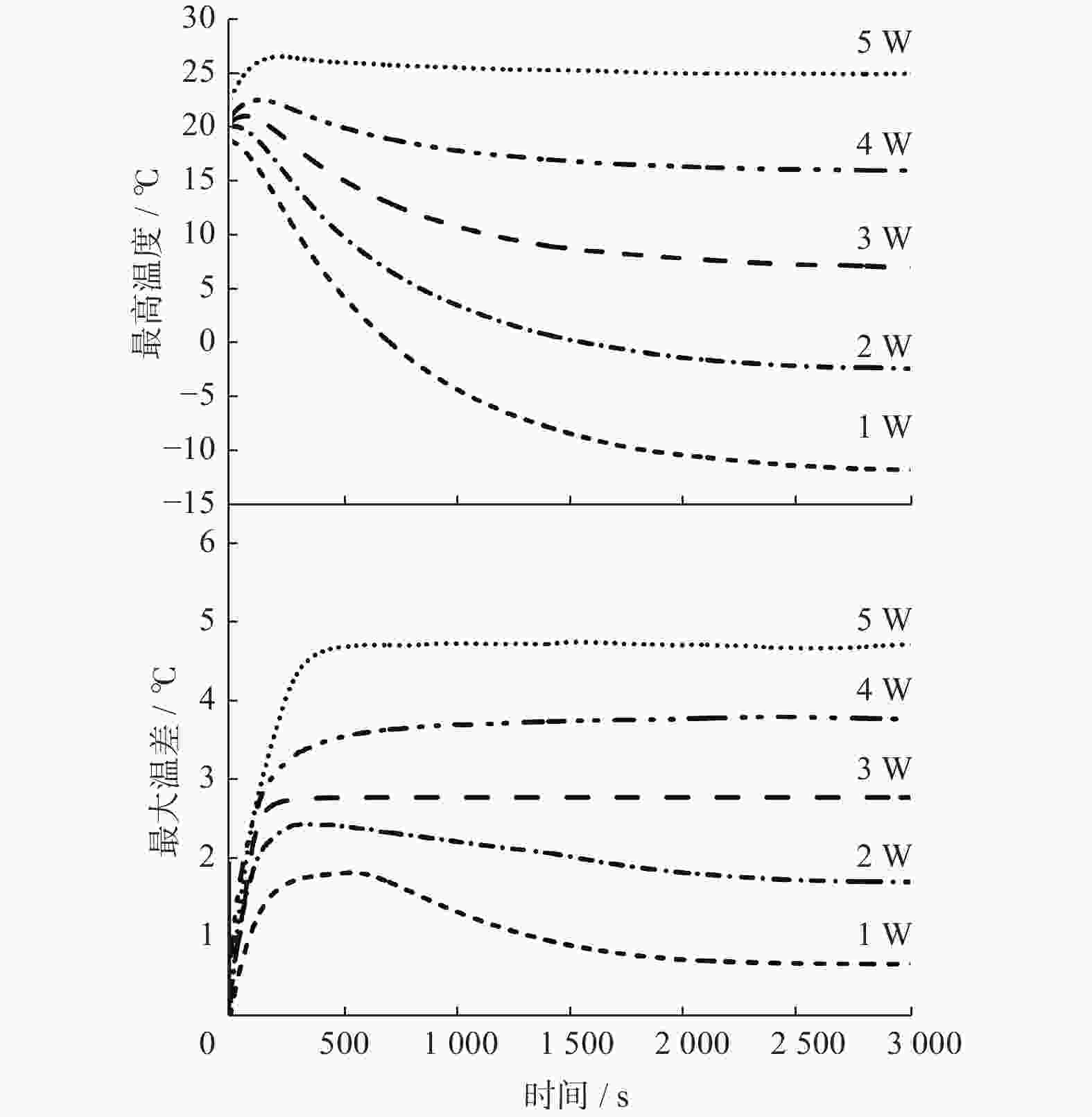
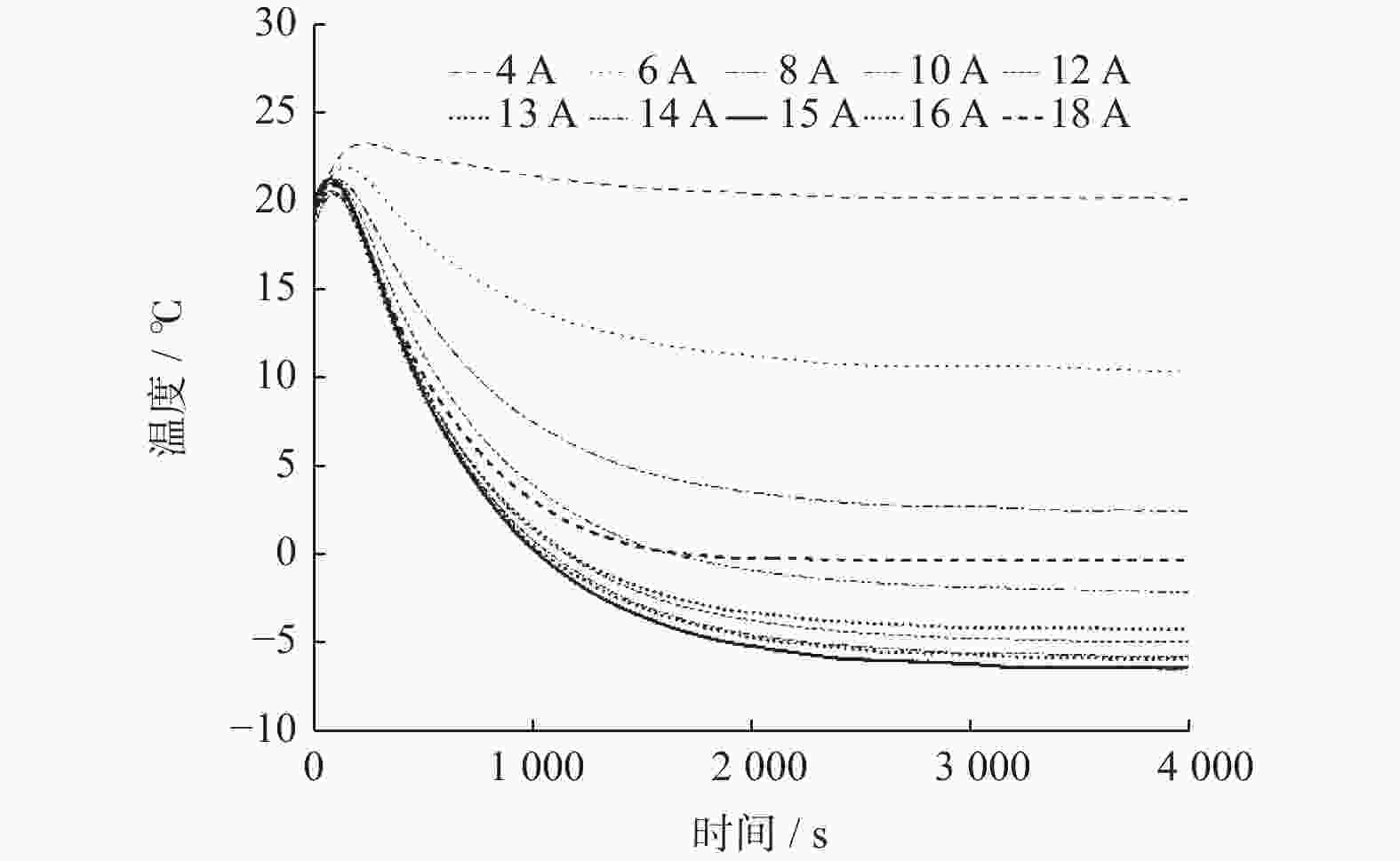
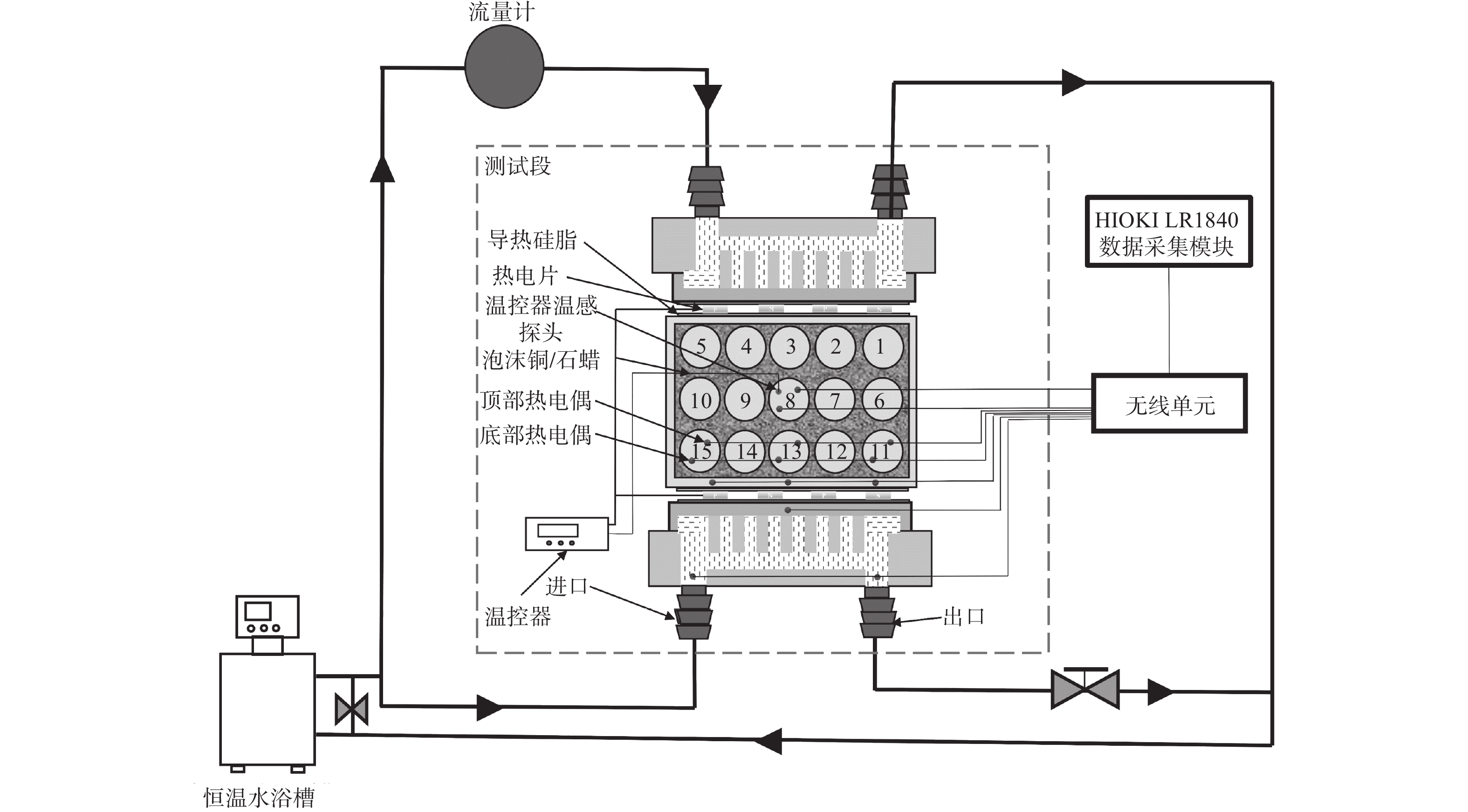
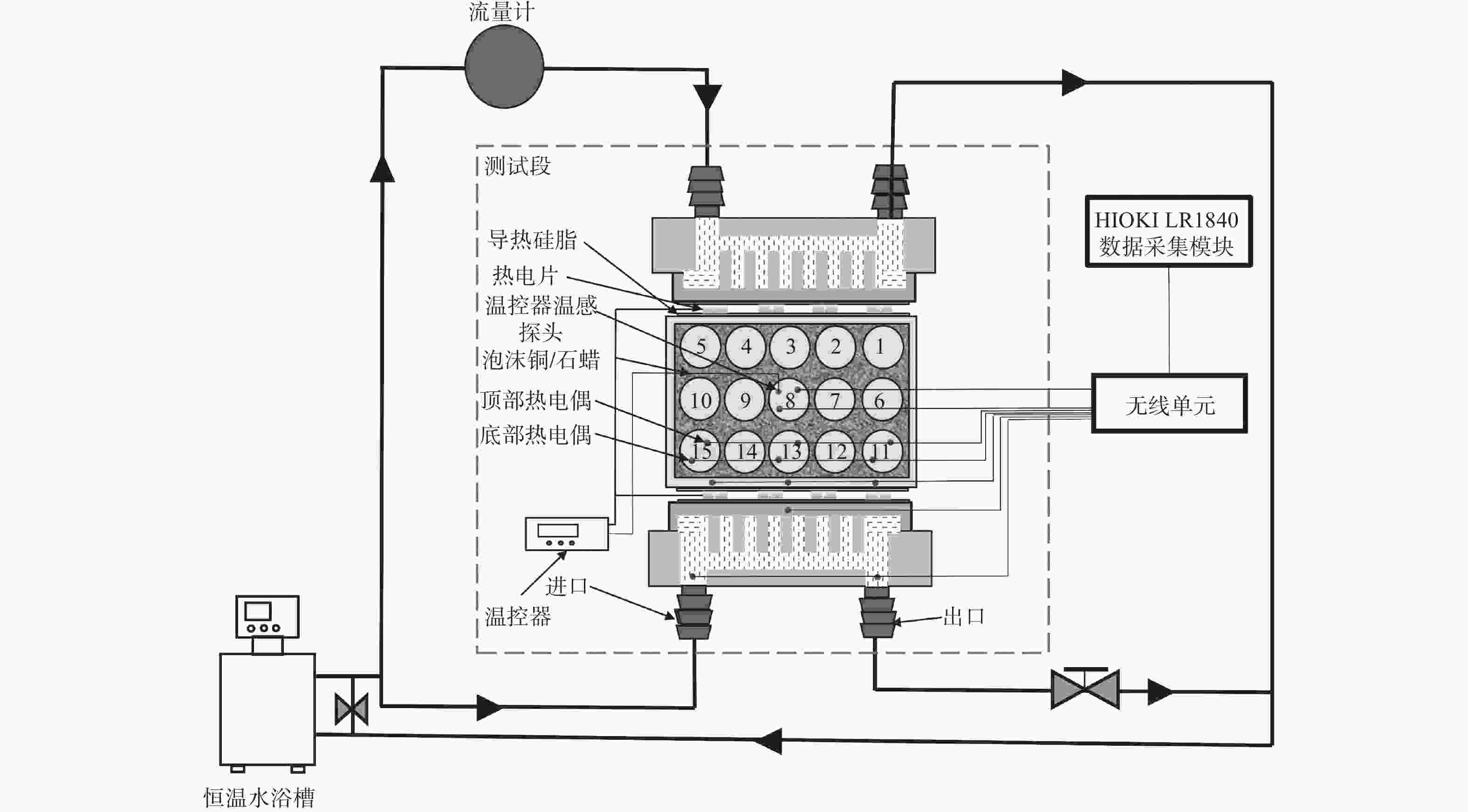
摘要: 基于帕尔贴效应提出一种通过热电装置(Thermoelectric Device,TED)实时控制电池温度的方法. 该方法集TED的制冷与加热功能于一体,控温效果良好,可以满足电池模组热管理需求. 电池模组由3×5排列的圆柱电池组成,填充泡沫金属复合相变材料,热电装置布置在电池模组外壳正对大面处. 与液冷试验相比,热电制冷可以在1~5 W单电池产热功率下显著降低电池模组的温度,将模组温差控制在5 ℃内. 温控试验进一步表明,采用温控器实时控制的TED可以有效稳定模组温度,将温度波动控制在2~3 ℃. 此外,建立一维热阻网络,基于稳态理论对TED热性能分析. 结果表明,在制冷工况下,TED的冷端温度随其电流的增大呈先减后增的趋势,热端温度与TED电流成正比.Abstract: Based on the Peltier effect, a method of real-time controlling battery temperature through thermoelectric device (TED) was proposed. It integrated the refrigeration and heating functions of TED, has a good temperature control effect, and can meet the thermal management needs of battery modules. The battery module consists of 3×5 rows of cylindrical batteries filled with foam metal composite phase change materials, and the thermoelectric device was arranged on the large face of the battery module shell. Compared with the liquid cooling experiment, thermoelectric refrigeration could significantly reduce the temperature of the battery module at 1~5 W of single cell heat generation power, and control the temperature difference of the module within 5 ℃. The temperature control experiment further shows that the TED controlled by the thermostat in real-time can effectively stabilize the module temperature and control the temperature fluctuation within 2~3 ℃. In addition, a one-dimensional thermal resistance network was established, and the thermal performance of TED was analyzed based on steady-state theory. The result shows that under the refrigeration condition, the cold junction temperature of TED is decreasing first and then increasing with increasing of its current, and the hot junction temperature is proportional to the TED current.
-
表 1 热电片1-12718参数
Table 1. Parameters of thermoelectric sheet 1-12718
TED参数 数值 热电臂个数2N 254 尺寸(长×宽×厚)/mm×mm×mm 50.0×50.0×3.6 Imax/A 18 Umax/V 15 ΔTmax/ ℃ 66 Qmax/W 150 Sm/(V·K−1) 0.0495 模块电阻Rm/ Ω 0.6519 模块热导率Km/(K·W−1) 1.6001 热电材料优值系数Z/ K−1 0.0023 表 2 石蜡的热物理性质
Table 2. Thermophysical properties of paraffin
名称 参数 石蜡熔化温度/ ℃ 41~44 比热容/(J·(kg·K)−1) 2000 潜热/(J·kg−1) 255000 密度/(kg·m−3) 880 热导率/(W·(m·K)−1) 0.2 表 3 热电装置各部分热阻
Table 3. Thermal resistances of TED system
各部分热阻 数值 /(K·W−1) 热界面材料热阻Rtim 0.055 #8电池到铝壳的热阻Rbm 0.064 散热器热阻Rsink 0.009 远程换热器热阻Rhea 0.070 冷却模组时TED冷端热阻Rbc 0.119 冷却模组时TED热端热阻Rha 0.091 加热模组时TED冷端热阻Rca 0.091 加热模组时TED热端热阻Rbh 0.119 -
[1] YI J, KIM U S, SHIN C B, et al. Modeling the temperature dependence of the discharge behavior of a lithium-ion battery in low environmental temperature[J] . Journal of Power Sources,2013,244:143 − 148. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.02.085 [2] PESARAN A A. Battery thermal models for hybrid vehicle simulations[J] . Journal of Power Sources,2002,110(2):377 − 382. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(02)00200-8 [3] WU M S, CHIANG P C J. High-rate capability of lithium-ion batteries after storing at elevated temperature[J] . Electrochimica Acta,2007,52(11):3719 − 3725. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2006.10.045 [4] RAMADASS P, HARAN B, WHITE R, et al. Capacity fade of Sony 18650 cells cycled at elevated temperatures: Part I. Cycling performance[J] . Journal of Power Sources,2002,112(2):606 − 613. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(02)00474-3 [5] MENALE C, D'ANNIBALE F, MAZZAROTTA B, et al. Thermal management of lithium-ion batteries: An experimental investigation[J] . Energy,2019,182:57 − 71. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2019.06.017 [6] BANDHAUER T M, GARIMELLA S, FULLER T F. A critical review of thermal issues in lithium-ion batteries[J] . Journal of The Electrochem Society,2011,158(3):21 − 25. doi: 10.1149/1.3515880 [7] RAO Z H, WANG S F. A review of power battery thermal energy management[J] . Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2011,15:4554 − 4571. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2011.07.096 [8] SONG H S, JEONG J B, LEE B H, et al. Experimental study on the effects of pre-heating a battery in a low-temperature environment[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference. Seoul: IEEE, 2012: 1198-1201. [9] ZHANG T S, GAO C, GAO Q, et al. Status and development of electric vehicle integrated thermal management from BTM to HVAC[J] . Applied Thermal Engineering,2015, 88: 398 − 409. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.02.001 [10] MATTHE R, TURNER L, METTLACH H. VOLTEC battery system for electric vehicle with extended range[J] . SAE International Journal of Engines,2011,4(1):1944 − 1962. doi: 10.4271/2011-01-1373 [11] WANG Z W, ZHANG H Y, XIA X. Experimental investigation on the thermal behavior of cylindrical battery with composite paraffin and fin structure[J] . International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2017,109:958 − 970. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.02.057 [12] YANG H, ZHANG H Y, SUI Y, et al. Numerical analysis and experimental visualization of phase change material melting process for thermal management of cylindrical power battery[J] . Applied Thermal Engineering,2018,128:489 − 499. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.09.022 [13] ZHAO D L, TAN G. A review of thermoelectric cooling: Materials, modeling and applications[J] . Applied Thermal Engineering,2014,66(1-2):15 − 24. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.01.074 [14] RIFFAT S B, MA X. Improving the coefficient of performance of thermoelectric cooling systems: A review[J] . International Journal of Energy Research,2004,28(8):753 − 768. [15] SUH I S, CHO H, LEE M. Feasibility study on thermoelectric device to energy storage system of an electric vehicle[J] . Energy,2014,76:436 − 444. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2014.08.040 [16] 王宇, 张国庆, 刘湘云. 半导体制冷技术在动力电池热管理中的应用研究[J] . 广东化工,2015,42(13):16 − 17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2015.13.008 [17] ALAOUI C, SALAMEH Z M. Solid state heater cooler: Design and evaluation[C]//Proceedings of 2001 Large Engineering Systems Conference on Power Engineering. Halifax: IEEE, 2001: 139-145. [18] ALAOUI C, SALAMEH Z M. A novel thermal management for electric and hybrid vehicles[J] . IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,2005,54(2):468 − 476. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2004.842444 [19] ZHANG H Y, MUI Y C, TARIN M. Analysis of thermoelectric cooler performance for high power electronic packages[J] . Applied Thermal Engineering,2010,30(6-7):561 − 568. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2009.10.020 [20] JIANG L, ZHANG H Y, LI J W, et al. Thermal performance of a cylindricalbattery module impregnated with PCM composite based on thermoelectric cooling[J] . Energy,2019,118:116048. -





 下载:
下载: