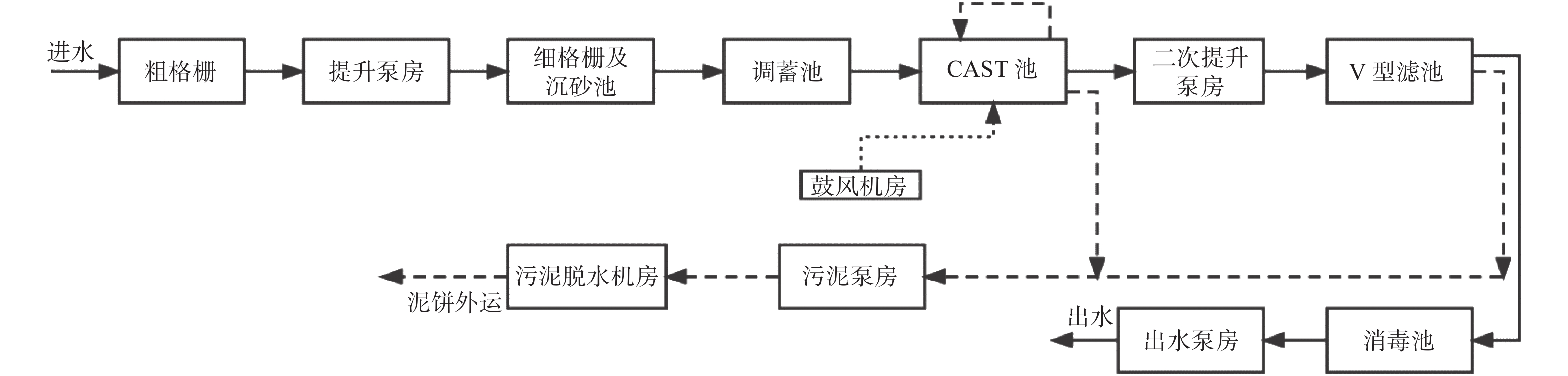
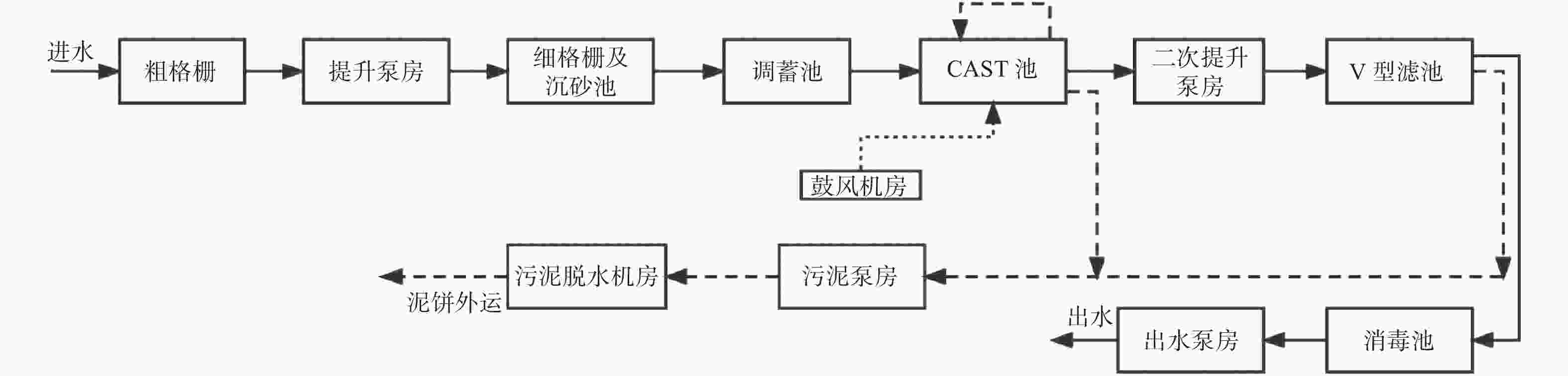
Modeling and simulation of CAST-MBBR process for wastewater treatment
-
摘要: 基于循环式活性污泥工艺(Cyclic Activated Sludge Technology,CAST)和移动床生物膜反应器(Moving-Bed Biofilm Reactor,MBBR),对浙江省某污水处理厂开展CAST-MBBR工艺的建模和模拟研究. 针对工艺机制,将半经验生物膜模型嵌入活性污泥1号模型,描述CAST-MBBR除碳脱氮的生化过程,再与描述颗粒沉降过程的双指数模型复合,形成完整的CAST-MBBR工艺模型,并建立进水、出水水质与模型组分的转换方法. 通过灵敏度分析筛选出对出水指标影响较大的关键性参数并进行调校. 利用污水处理厂全年的实测进水、出水数据对校正后的模型验证,结果显示出水指标的模拟值与实测值总体吻合良好,表明该模型方法可有效应用于CAST-MBBR工艺的模拟.Abstract: Based on cyclic activated sludge technology (CAST) and moving-bed biofilm reactor (MBBR), mathematical modeling and simulation of CAST-MBBR process for a real wastewater treatment plant in Zhejiang Province was carried out. Based on the process mechanism, a semi-empirical biofilm model was embedded into the activated sludge model No.1 to describe the biochemical process of carbon and nitrogen removal in CAST-MBBR. It is then combined with a double exponential model describing particle sedimentation to form a complete CAST-MBBR process model, and a conversion method between inlet and outlet water quality and model components was established. The key parameters that have a significant impact on effluent indicators were screened through sensitivity analysis and adjusted. The calibrated model was verified by using the influent and effluent water data of the wastewater treatment plant throughout the year. The result shows that the simulated effluent data can agree well with the measured data, indicating that the modeling method can be effectively applied to the simulation of CAST-MBBR process.
-
表 1 进水水质与模型组分的比例关系
Table 1. Proportional relationship between influent water quality and model components
进水水质 模型组分 比例关系/ % COD SI 4 Ss 19 XI 8 Xs 55 XBH 14 XBA 0 TN SNH 65 SNO 0 SND 7 XND 28 表 2 初次模拟出水水质
Table 2. Preliminary simulation results of effluent quality
项目 ρ(COD)/
(mg∙L−1)ρ(NH3-N)/
(mg∙L−1)ρ(TN)/
(mg∙L−1)ρ(TSS)/
(mg∙L−1)实际进水 354.80 16.61 18.52 302.77 实际出水 12.18 0.18 5.42 3.45 模拟出水 35.84 5.16 9.18 6.28 表 3 调校参数值
Table 3. Adjusted parameter values
参数 单位 校准值 v0 m/d 651 rp m3/(g SS) 0.01417 rh m3/(g SS) 0.002173 fns — 0.00157 YH g (cell) COD/g N 0.92 bH d−1 0.6 µA d−1 0.3 iXB g N/g COD 0.059 KNH,bf g NH3-N/m3 21 kh g COD/g (cell) COD·d 13 Kx g COD/g (cell) COD 0.09 -
[1] 邹宗森, 施汉昌, 陈向强, 等. 生物滤池工艺的数值模拟与运行优化[J] . 环境科学,2014,35(12):4627 − 4635. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.2014.12.028 [2] 彭玉, 王建辉, 齐高相, 等. 活性污泥模型(ASMs)研究进展及其发展前景[J] . 应用化工,2020,49(5):1288 − 1292. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.05.051 [3] 王文英, 黄勇, 顾晓丹, 等. 活性污泥数学模型在污水处理中的研究进展[J] . 工业水处理,2014,34(7):1 − 4. doi: 10.11894/1005-829x.2014.34(7).001 [4] 徐承志, 操家顺, 罗景阳, 等. 活性污泥数学模型在污水处理中的研究进展[J] . 应用化工,2021,50(5):1341 − 1354. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2021.05.039 [5] 周祯领, 吴迪, 韩文杰, 等. MBBR镶嵌氧化沟在某污水处理厂的提标效果分析[J] . 中国给水排水,2019,35(17):1 − 6. doi: 10.19853/j.zgjsps.1000-4602.2019.17.001 [6] 吴生余, 汤嵩瑜, 胡婷婷. CAST-MBBR工艺在污水处理厂提标改造中的应用[J] . 净水技术,2019,38(z2):43 − 46. [7] FOUAD M, BHARGAVA R. A simplified model for the steady-state biofilm-activated sludge reactor[J] . Journal of Environmental Management,2005,74(3):245 − 253. [8] SEN D, RANDALL C W. Improved computational model (AQUIFAS) for activated sludge, integrated fixed-film activated sludge, and moving-bed biofilm reactor systems, Part I: Semi-empirical model development[J] . Water Environment Research,2008,80(5):439 − 453. doi: 10.1002/j.1554-7531.2008.tb00350.x [9] SEN D, RANDALL C W. Improved computational model (AQUIFAS) for activated sludge, integrated fixed-film activated sludge, and moving-bed biofilm reactor systems, Part II: Multilayer biofilm diffusional model[J] . Water Environment Research,2008,80(7):624 − 632. doi: 10.2175/106143008X268434 [10] MANNINA G, TRAPANI D D. Modelling and dynamic simulation of hybrid moving bed biofilm reactors: Model concepts and application to a pilot plant[J] . Biochemical Engineering Journal,2011,56(1):23 − 36. [11] RAUCH W, VANHOOREN H, VANROLLEGHEM P, et al. A simplified mixed-culture biofilm model[J] . Water Research,1999,33(9):2148 − 2162. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00415-1 [12] 徐涛, 彭党聪, 徐天凯, 等. 活性污泥和生物膜复合模型的建立与模拟[J] . 环境工程学报,2017,11(11):5909 − 5916. doi: 10.12030/j.cjee.201607103 [13] 巩书涵. 基于 ASM2d 模型对 MBBR 工艺的模拟与优化 [D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2017. [14] JABRI K M, FIEDLER T, SAIDI A, et al. Steady-state modeling of the biodegradation performance of a multistage moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) used for on-site grey water treatment[J] . Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2019,26(19):19047 − 19062. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3984-9 [15] HENZE M, GUJER W, MINO T, et al. Activated sludge models ASM1, ASM2, ASM2d and ASM3 [M]. London: IWA Publishing, 2006. [16] ALEX J, BENEDETTI L, COPP J, et al. Benchmark Simulation Model no.1 (BSM1) [M]. Sweden: Lund University, 2008. [17] JEPPSSON U, DIEHI S. An evaluation of a dynamic model of the secondary clarifier[J] . Water Science Technology,1996,34:19 − 26. doi: 10.2166/wst.1996.0530 [18] 李振亮. 二沉池一维通量模型及其应用[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2006. [19] TAKÁCS L, PATRY G G, NOLASCO D. A dynamic model of the clarification-thickening process[J] . Water Research,1991,25(10):1263 − 1271. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(91)90066-Y [20] 袁良松, 谢长焕, 邓科, 等. 试论 ASM 水质特性参数测定方法[J] . 能源环境与保护,2007,21(5):1 − 4. [21] 陈莉荣, 肖作义, 彭党聪. 活性污泥 1 号模型含碳组分测定方法探讨[J] . 环境工程,2004,22(1):67 − 69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8942.2004.01.021 [22] 周振, 吴志超, 王志伟, 等. 基于活性污泥模型的污水COD 组分划分方案研究[J] . 环境科学,2010,31(6):1478 − 1482. [23] SEN D. COD removal, nitrification and denitrification kinetics and mathematical modeling of integrated fixed film activated sludge systems [D]. Blacksburg: Virginia Technology, 1995. [24] 鞠兴华, 彭党聪. ASM1模型动力学参数敏感度分析[J] . 环境科学与技术,2010,33(2):312 − 314,318. [25] MANNINA G, COSENZA A, VIVIANI G, et al. Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of an integrated ASM2d MBR model for wastewater treatment[J] . Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,351:579 − 588. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.06.126 -





 下载:
下载: