Recognition method of sEMG gesture based on improved deep forest
-
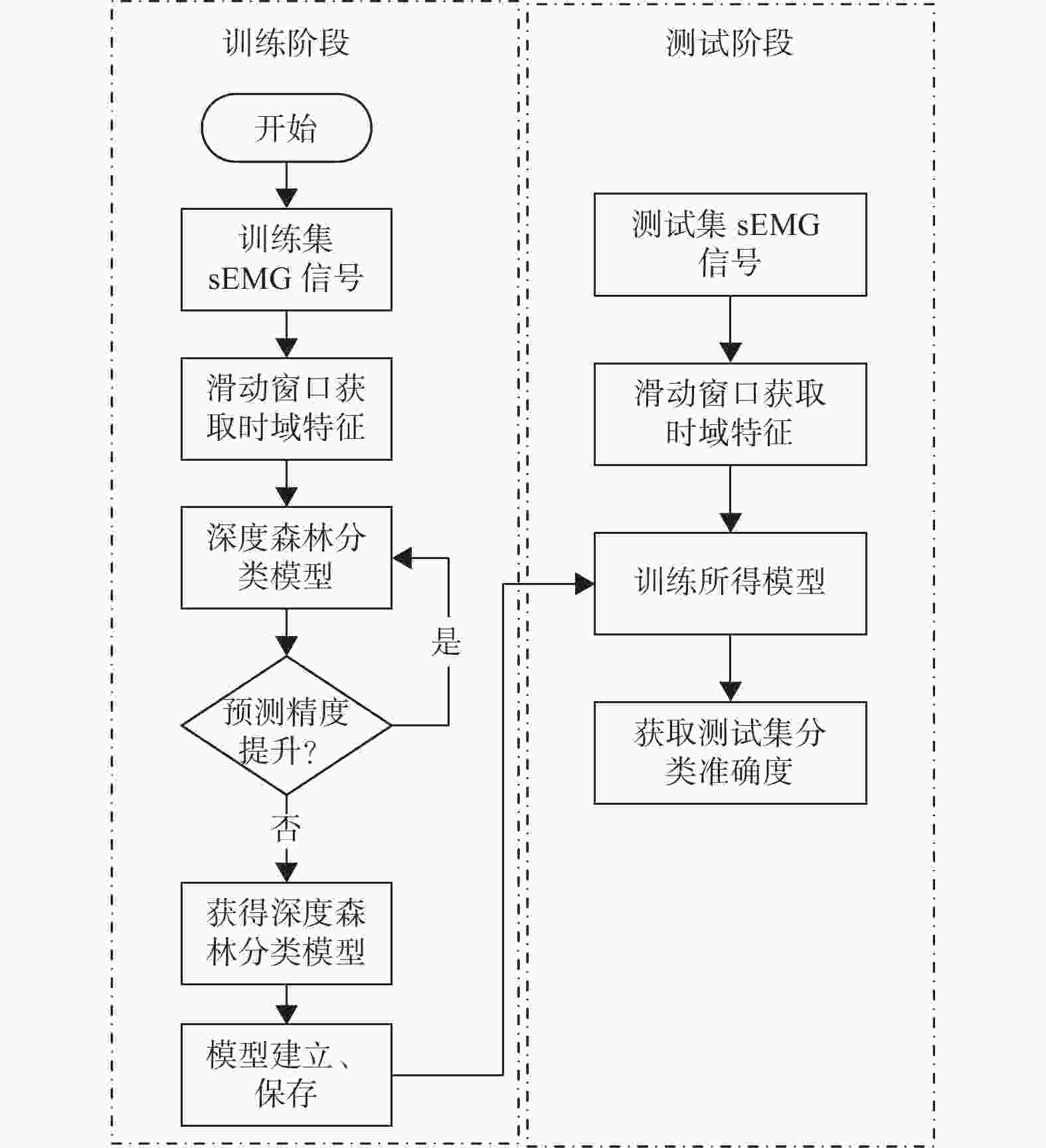
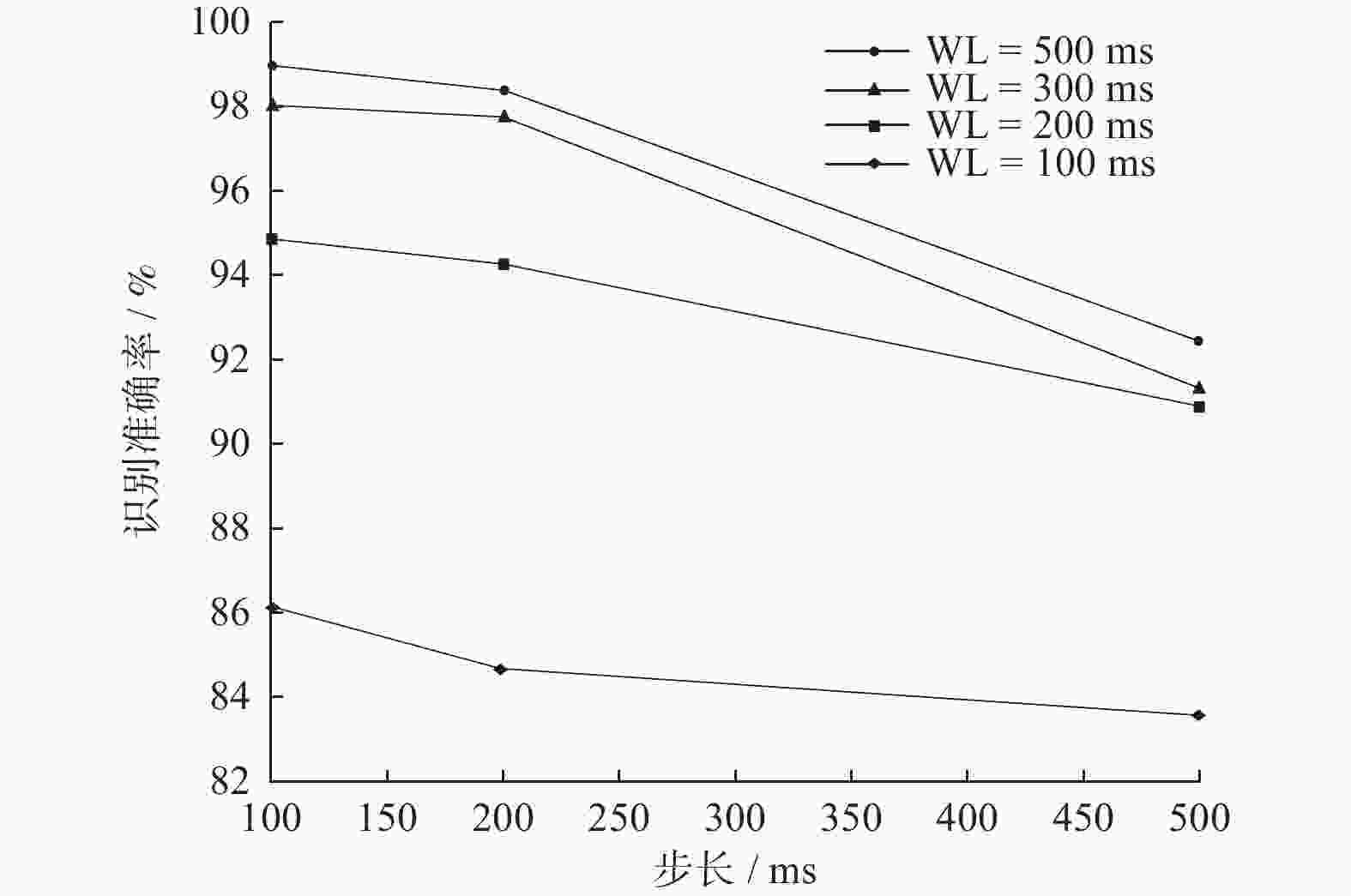
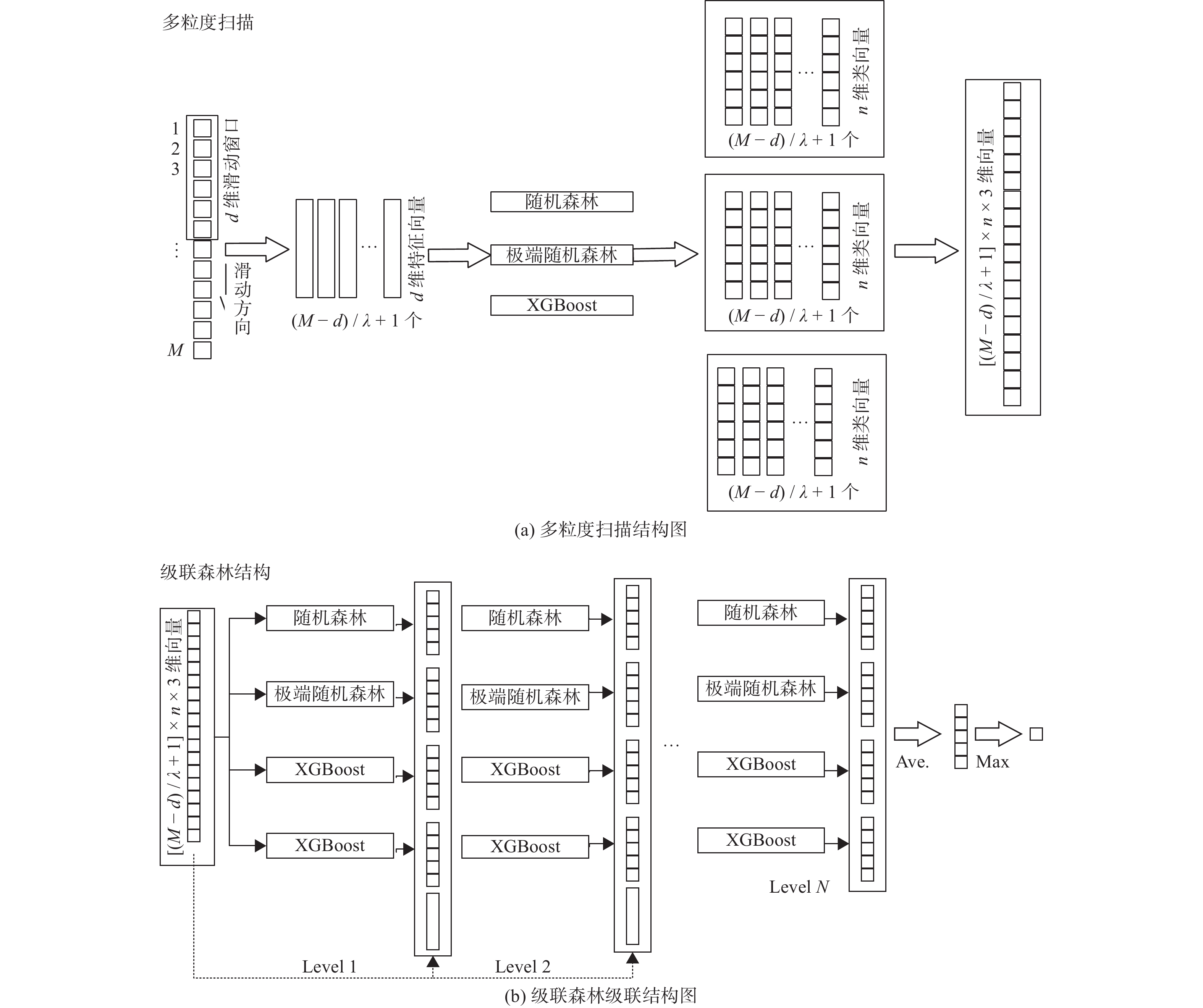
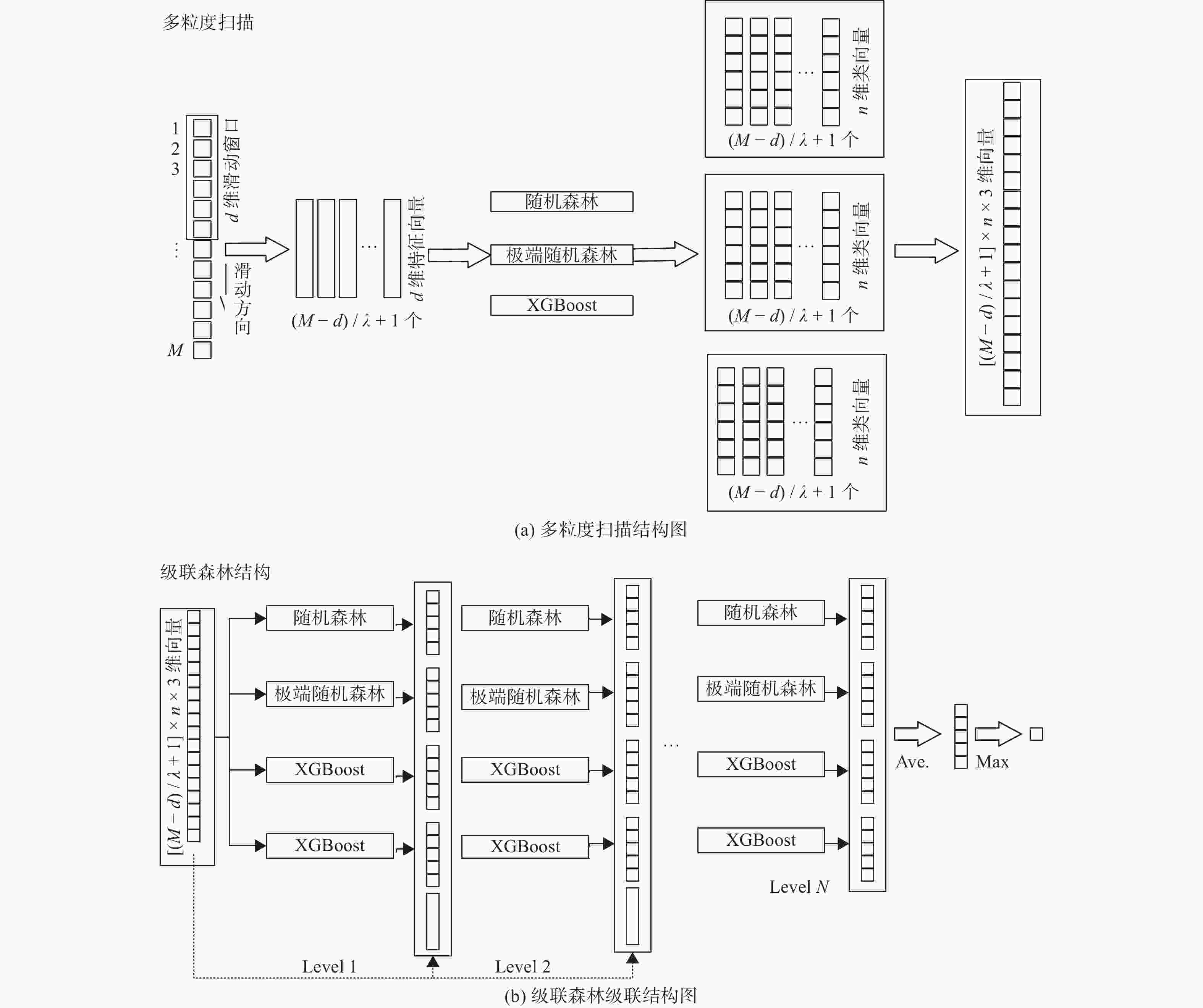
摘要: 为提高基于表面肌电图(surface Electromyo Graphy, sEMG)手势识别的准确率,提出一种改进深度森林相结合的手部运动识别方法. 将极致梯度提升(eXtreme Gradient Boosting, XGBoost)树引入深度森林模型,与随机森林和完全随机森林共同组成深度森林的级联结构. 深度森林模型在每个层次上集成3种不同的基于树的分类器,共4个决策森林,包括1个随机森林、1个极端随机森林和2个极致梯度提升树,利用不同学习算法之间的互补性来提高分类性能. 为评估该模型性能,采集4名健康受试者的表面肌电信号进行手部动作识别验证试验,并与随机森林、支持向量机、一维卷积神经网络及二维卷积神经网络等算法比较. 结果表明,提出方法对16种常用手部动作的平均识别精度为94.14%,对表面肌电信号实现了较高的分类准确率.Abstract: In order to improve the accuracy of gesture recognition based on surface electromyography (sEMG), an improved deep forest combined hand motion recognition method was proposed. The extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) tree was introduced into the deep forest model to form the cascade structure of deep forest together with the random forest and the complete random forest. The deep forest model integrates three different tree-based classifiers at each level, a total of four decision forests including a random forest, an extreme random forest and two extreme gradient boosting trees. The classification performance was improved by using the complementarity between different learning algorithms. In order to evaluate the performance of the model, the sEMG signals of 4 healthy subjects were collected for the verification experiment of hand action recognition, and compared with random forest, support vector machine, one-dimensional and two-dimensional convolutional neural networks algorithms. The result shows that the average recognition accuracy of the method for 16 commonly used hand actions is 94.14%, and the classification accuracy of sEMG signals is high.
-
表 1 本方法与其他方法识别准确率结果对比
Table 1. Recognition accuracy of this method compared with others
% 受试者编号 GC_Forest RF SVM 1D-CNN 2D-CNN TextCNN 1 97.47 91.44 89.17 87.46 90.43 90.38 2 95.39 92.69 93.31 88.29 93.41 90.70 3 91.61 89.14 87.89 85.78 88.50 87.77 4 93.08 87.68 86.84 84.01 88.92 88.81 Ave 94.14 90.54 89.30 86.39 90.32 89.42 -
[1] 王亮, 张安元, 李佳佳, 等. 基于时频组合特征的PSO-SVM手势识别方法[J] . 长春理大学学报(自然科学版),2021,44(4):104 − 110. [2] 胡少康, 张道辉, 赵新刚, 等. 基于特征工程与级联森林的中风患者手部运动肌电识别方法[J] . 机器人,2021,43(5):526 − 538. [3] 李自由, 赵新刚, 张弼, 等. 基于表面肌电的意图识别方法在非理想条件下的研究进展[J] . 自动化学报,2021,47(5):955 − 969. [4] OLBRICH M, PETERSEN E, HOFFMANN C, et al. Sparse estimation for the assessment of muscular activity based on sEMG measurements[J] . IFAC PapersOnLine,2018,51(15):305 − 310. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.09.152 [5] 刘光达, 董梦坤, 许蓝予, 等. 手臂疲劳时表面肌电信号特征[J] . 科学技术与工程,2021,21(25):10690 − 10696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.25.017 [6] MONIRI A, TERRACINA D, RODRIGUEZ-MANZANO J, et al. Real-time forecasting of sEMG features for trunk muscle fatigue using machine learning[J] . IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering,2021,68(2):718 − 727. [7] 曹梦琳, 陈宇豪, 王珏, 等. 基于表面肌电图的人体运动意图识别研究进展[J] . 中国康复理论与实践,2021,27(5):595 − 603. [8] HE J Y, JIANG N. Biometric from surface electromyogram (sEMG): Feasibility of user verification and identification based on gesture recognition[J] . Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology,2020,8:58. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00058 [9] 汤纬地. 基于表面肌电的上肢运动分析关健技术研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2021. [10] AI-TIMEMY A H, KHUSHABA R N, BUGMANN G, et al. Improving the performance against force variation of EMG controlled multifunctional upper-limb prostheses for transradial amputees[J] . IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering,2016,24(6):650 − 661. [11] DUAN F, DAI L L, CHANG W N, et al. sEMG-based identification of hand motion commands using wavelet neural network combined with discrete wavelet transform[J] . IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2016,63(3):1923 − 1934. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2497212 [12] WEI W T, DAI Q F, WONG Y K, et al. Surface-electromyography-based gesture recognition by multi-view deep learning[J] . IEEE Transactions on Bio-medical Engineering,2019,66(10):2964 − 2973. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2899222 [13] KHEZRI M, JAHED M. A neuro-fuzzy inference system for sEMG-based identification of hand motion commands[J] . IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2011,58(5):1952 − 1960. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2053334 [14] WEI W T, WONG Y K, DU Y, et al. A multi-stream convolutional neural network for sEMG-based gesture recognition in muscle computer interface[J] . Pattern Recognition Letters,2019,119:131 − 138. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2017.12.005 [15] TSINGANOS P, CORNELIS B, CORNELIS J, et al. Improved gesture recognition based on sEMG signals and TCN[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 1169 − 1173. [16] HEATHER D, KEVIN E, LEVI H, et al. High density electromyography data of normally limbed and trans radial amputee subjects for multifunction prosthetic control[J] . Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology,2012,22(3):478 − 484. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2011.12.012 [17] SAMUEL O W, ZHOU H, LI X X, et al. Pattern recognition of electromyography signals based on novel time domain features for amputees' limb motion classification[J] . Computers & Electrical Engineering,2018,67:646 − 655. [18] HUDGINS B, PARKER P, SCOTT R N. A new strategy for multifunction myoelectric control[J] . IEEE Transactions on Bio-medical Engineering,1993,40(1):82 − 94. doi: 10.1109/10.204774 [19] POWELL M A, THAKOR N V. A training strategy for learning pattern recognition control for myoelectric prostheses[J] . Journal of Prosthetics and Orthotics: JPO,2013,25(1):30 − 41. doi: 10.1097/JPO.0b013e31827af7c1 [20] LEE S W, WILSON K M, LOCK B A, et al. Subject-specific myoelectric pattern classification of functional hand movements for stroke survivors[J] . IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering,2011,19(5):558 − 566. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2010.2079334 [21] ZHOU Z H, FENG J. Deep forest: Towards an alternative to deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2017: 3553 − 3559. [22] 葛绍林, 叶剑, 何明祥. 基于深度森林的用户购买行为预测模型[J] . 计算机科学,2019,46(9):190 − 194. [23] LUO J L, ZHANG Z L, FU Y, et al. Time series prediction of COVID-19 transmission in America using LSTM and XGBoost algorithms[J] . Results in Physics,2021,27:104462. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2021.104462 [24] PALECZEK A, GROCHALA D, RYDOSZ A. Artificial breath classification using XGBoost algorithm for diabetes detection[J] . Sensors,2021,21(12):4187. doi: 10.3390/s21124187 [25] 李建平, 张小庆, 李莹. 基于XGBoost的低渗油田储层粒度预测[J] . 计算机系统应用,2022,31(2):241 − 245. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.008325 [26] 邹海洋, 李振华, 邓利平. 基于改进XGBoost和随机森林的VR三维手势识别[J] . 西华师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,42(4):426 − 431. -





 下载:
下载: